|
1. 介绍
1.1 Deep NLP
自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing,NLP)是计算机科学、人工智能和语言学领域交叉的分支学科,主要让计算机处理或理解自然语言,如机器翻译,问答系统等。但是因其在表示、学习、使用语言的复杂性,通常认为 NLP 是困难的。近几年,随着深度学习(Deep Learning, DL)兴起,人们不断尝试将 DL 应用在 NLP 上,被称为 Deep NLP,并取得了很多突破。其中就有 Seq2Seq 模型。
1.2 来由
Seq2Seq Model是序列到序列( Sequence to Sequence )模型的简称,也被称为一种编码器-解码器(Encoder-Decoder)模型,分别基于2014发布的两篇论文:
Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks by Sutskever et al.,Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation by Cho et al.,
作者 Sutskever 分析了 Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) 因限制输入和输出序列的长度,无法处理未知长度和不定长的序列;并且很多重要的问题都使用未知长度的序列表示的。从而论证在处理未知长度的序列问题上有必要提出新解决方式。于是,创新性的提出了 Seq2Seq 模型。下面让我们一起看看这个模型到底是什么。
2. Seq2Seq Model 之不断探索
为什么说是创新性提出呢? 因为作者 Sutskever 经过了三次建模论证,最终才确定下来 Seq2Seq 模型。而且模型的设计非常巧妙。让我们先回顾一下作者的探索经历。语言模型(Language Model, LM)是使用条件概率通过给定的词去计算下一个词。这是 Seq2Seq 模型的预测基础。由于序列之间是有上下文联系的,类似句子的承上启下作用,加上语言模型的特点(条件概率),作者首先选用了 RNN-LM(Recurrent Neural Network Language Model, 循环神经网络语言模型)。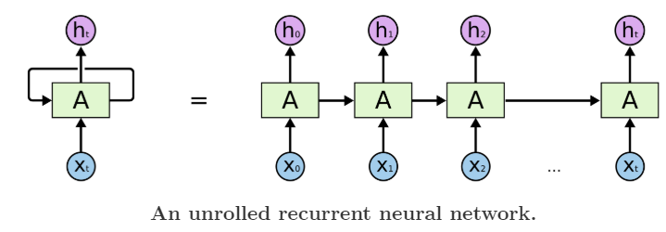 上图,是一个简单的 RNN 单元。RNN 循环往复地把前一步的计算结果作为条件,放进当前的输入中。适合在任意长度的序列中对上下文依赖性进行建模。但是有个问题,那就是我们需要提前把输入和输出序列对齐,而且目前尚不清楚如何将 RNN 应用在不同长度有复杂非单一关系的序列中。为了解决对齐问题,作者提出了一个理论上可行的办法:使用两个 RNN。 一个 RNN 把输入映射为一个固定长度的向量,另一个 RNN 从这个向量中预测输出序列。 上图,是一个简单的 RNN 单元。RNN 循环往复地把前一步的计算结果作为条件,放进当前的输入中。适合在任意长度的序列中对上下文依赖性进行建模。但是有个问题,那就是我们需要提前把输入和输出序列对齐,而且目前尚不清楚如何将 RNN 应用在不同长度有复杂非单一关系的序列中。为了解决对齐问题,作者提出了一个理论上可行的办法:使用两个 RNN。 一个 RNN 把输入映射为一个固定长度的向量,另一个 RNN 从这个向量中预测输出序列。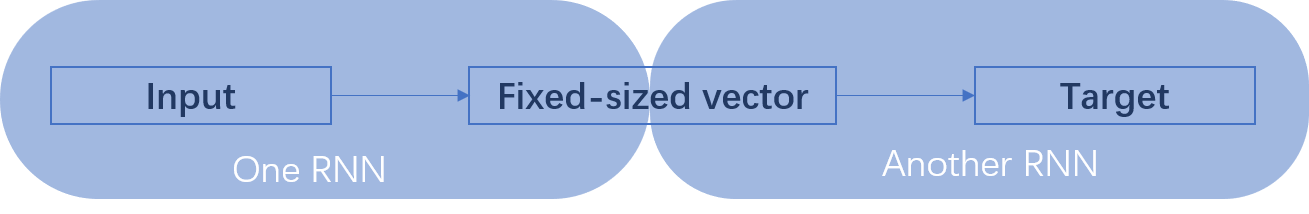 为什么说是理论可行的呢?作者 Sutskever 的博士论文 TRAINING RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS (训练循环神经网络)提出训练 RNN 是很困难的。因为由于 RNN 自身的网络结构,其当前时刻的输出需要考虑前面所有时刻的输入,那么在使用反向传播训练时,一旦输入的序列很长,就极易出现梯度消失(Gradients Vanish)问题。为了解决 RNN 难训练问题,作者使用 LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory,长短期记忆)网络。 为什么说是理论可行的呢?作者 Sutskever 的博士论文 TRAINING RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS (训练循环神经网络)提出训练 RNN 是很困难的。因为由于 RNN 自身的网络结构,其当前时刻的输出需要考虑前面所有时刻的输入,那么在使用反向传播训练时,一旦输入的序列很长,就极易出现梯度消失(Gradients Vanish)问题。为了解决 RNN 难训练问题,作者使用 LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory,长短期记忆)网络。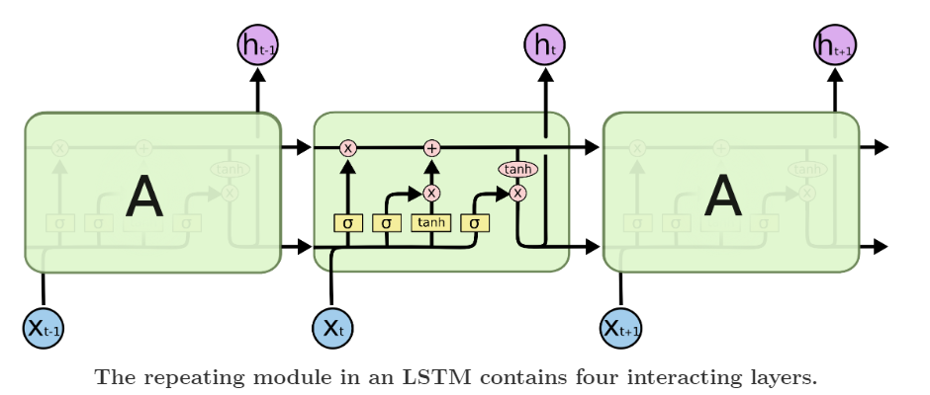 上图,是一个 LSTM 单元内部结构。LSTM 提出就是为了解决 RNN 梯度消失问题,其创新性的加入了遗忘门,让 LSTM 可以选择遗忘前面输入无关序列,不用考虑全部输入序列。经过3次尝试,最终加入 LSTM 后,一个简单的 Seq2Seq 模型就建立了。 上图,是一个 LSTM 单元内部结构。LSTM 提出就是为了解决 RNN 梯度消失问题,其创新性的加入了遗忘门,让 LSTM 可以选择遗忘前面输入无关序列,不用考虑全部输入序列。经过3次尝试,最终加入 LSTM 后,一个简单的 Seq2Seq 模型就建立了。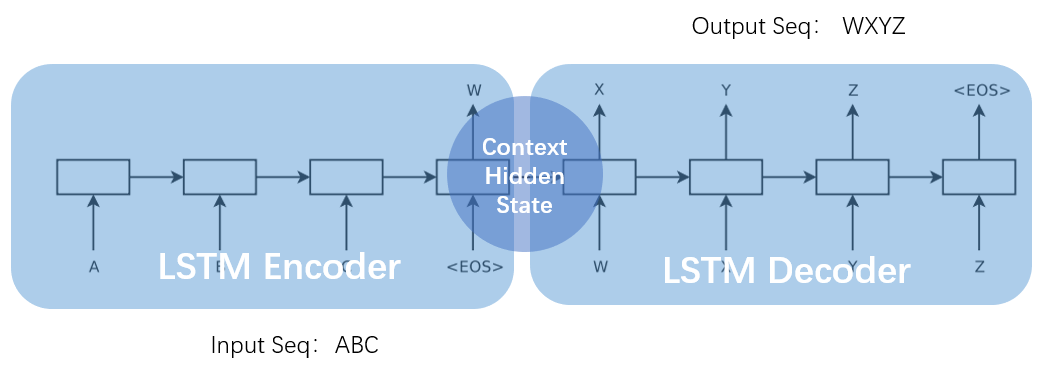 上图,一个简单的 Seq2Seq 模型包括3个部分,Encoder-LSTM,Decoder-LSTM,Context。输入序列是ABC,Encoder-LSTM 将处理输入序列并在最后一个神经元返回整个输入序列的隐藏状态(hidden state),也被称为上下文(Context,C)。然后 Decoder-LSTM 根据隐藏状态,一步一步的预测目标序列的下一个字符。最终输出序列wxyz。值得一提的是作者 Sutskever 根据其特定的任务具体设计特定的 Seq2Seq 模型。并对输入序列作逆序处理,使模型能处理长句子,也提高了准确率。 上图,一个简单的 Seq2Seq 模型包括3个部分,Encoder-LSTM,Decoder-LSTM,Context。输入序列是ABC,Encoder-LSTM 将处理输入序列并在最后一个神经元返回整个输入序列的隐藏状态(hidden state),也被称为上下文(Context,C)。然后 Decoder-LSTM 根据隐藏状态,一步一步的预测目标序列的下一个字符。最终输出序列wxyz。值得一提的是作者 Sutskever 根据其特定的任务具体设计特定的 Seq2Seq 模型。并对输入序列作逆序处理,使模型能处理长句子,也提高了准确率。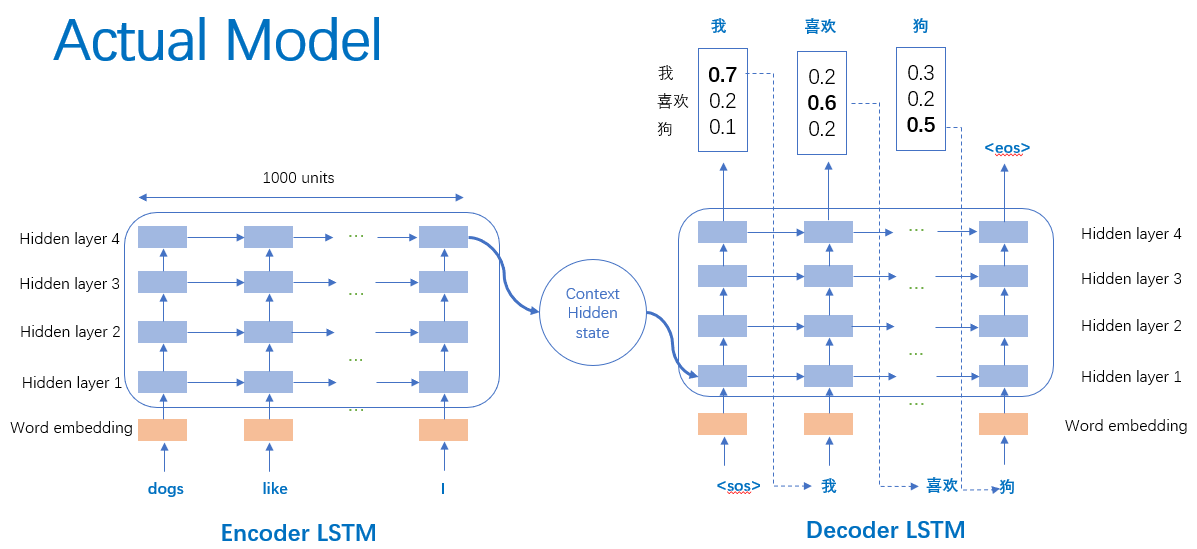 上图,是作者 Sutskever 设计的真实模型,并引以为傲一下三点。第一使用了两个 LSTM ,一个用于编码,一个用于解码。这也是作者探索并论证的结果。第二使用了深层的 LSTM (4层),相比于浅层的网络,每加一层模型困难程度就降低10% 。第三对输入序列使用了逆序操作,提高了 LSTM 处理长序列能力。 上图,是作者 Sutskever 设计的真实模型,并引以为傲一下三点。第一使用了两个 LSTM ,一个用于编码,一个用于解码。这也是作者探索并论证的结果。第二使用了深层的 LSTM (4层),相比于浅层的网络,每加一层模型困难程度就降低10% 。第三对输入序列使用了逆序操作,提高了 LSTM 处理长序列能力。
3. 中英文翻译
到了我们动手的时刻了,理解了上面 Seq2Seq 模型,让我们搭建一个简单的中英文翻译模型。
3.1 数据集
我们使用 manythings 网站的一个中英文数据集,现已经上传到 Mo 平台了,点击查看。该数据集格式为英文+tab+中文。
3.2 处理数据
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers import Input, LSTM, Dense
import numpy as np
batch_size = 64 # Batch size for training.
epochs = 100 # Number of epochs to train for.
latent_dim = 256 # Latent dimensionality of the encoding space.
num_samples = 10000 # Number of samples to train on.
# Path to the data txt file on disk.
data_path = 'cmn.txt'
# Vectorize the data.
input_texts = []
target_texts = []
input_characters = set()
target_characters = set()
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
lines = f.read().split('\n')
for line in lines[: min(num_samples, len(lines) - 1)]:
input_text, target_text = line.split('\t')
# We use "tab" as the "start sequence" character
# for the targets, and "\n" as "end sequence" character.
target_text = '\t' + target_text + '\n'
input_texts.append(input_text)
target_texts.append(target_text)
for char in input_text:
if char not in input_characters:
input_characters.add(char)
for char in target_text:
if char not in target_characters:
target_characters.add(char)
input_characters = sorted(list(input_characters))
target_characters = sorted(list(target_characters))
num_encoder_tokens = len(input_characters)
num_decoder_tokens = len(target_characters)
max_encoder_seq_length = max([len(txt) for txt in input_texts])
max_decoder_seq_length = max([len(txt) for txt in target_texts])
print('Number of samples:', len(input_texts))
print('Number of unique input tokens:', num_encoder_tokens)
print('Number of unique output tokens:', num_decoder_tokens)
print('Max sequence length for inputs:', max_encoder_seq_length)
print('Max sequence length for outputs:', max_decoder_seq_length)
3.3 Encoder-LSTM
# mapping token to index, easily to vectors
input_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(input_characters)])
target_token_index = dict([(char, i) for i, char in enumerate(target_characters)])
# np.zeros(shape, dtype, order)
# shape is an tuple, in here 3D
encoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_encoder_seq_length, num_encoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
decoder_input_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_decoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
decoder_target_data = np.zeros(
(len(input_texts), max_decoder_seq_length, num_decoder_tokens),
dtype='float32')
# input_texts contain all english sentences
# output_texts contain all chinese sentences
# zip('ABC','xyz') ==> Ax By Cz, looks like that
# the aim is: vectorilize text, 3D
for i, (input_text, target_text) in enumerate(zip(input_texts, target_texts)):
for t, char in enumerate(input_text):
# 3D vector only z-index has char its value equals 1.0
encoder_input_data[i, t, input_token_index[char]] = 1.
for t, char in enumerate(target_text):
# decoder_target_data is ahead of decoder_input_data by one timestep
decoder_input_data[i, t, target_token_index[char]] = 1.
if t > 0:
# decoder_target_data will be ahead by one timestep
# and will not include the start character.
# igone t=0 and start t=1, means
decoder_target_data[i, t - 1, target_token_index[char]] = 1.
3.4 Context(hidden state)
# Define an input sequence and process it.
# input prodocts keras tensor, to fit keras model!
# 1x73 vector
# encoder_inputs is a 1x73 tensor!
encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None, num_encoder_tokens))
# units=256, return the last state in addition to the output
encoder_lstm = LSTM((latent_dim), return_state=True)
# LSTM(tensor) return output, state-history, state-current
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = encoder_lstm(encoder_inputs)
# We discard `encoder_outputs` and only keep the states.
encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
3.5 Decoder-LSTM
# Set up the decoder, using `encoder_states` as initial state.
decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None, num_decoder_tokens))
# We set up our decoder to return full output sequences,
# and to return internal states as well. We don't use the
# return states in the training model, but we will use them in inference.
decoder_lstm = LSTM((latent_dim), return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
# obtain output
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_inputs,initial_state=encoder_states)
# dense 2580x1 units full connented layer
decoder_dense = Dense(num_decoder_tokens, activation='softmax')
# why let decoder_outputs go through dense ?
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
# Define the model that will turn, groups layers into an object
# with training and inference features
# `encoder_input_data` & `decoder_input_data` into `decoder_target_data`
# model(input, output)
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs)
# Run training
# compile -> configure model for training
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
# model optimizsm
model.fit([encoder_input_data, decoder_input_data],
decoder_target_data,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_split=0.2)
# Save model
model.save('seq2seq.h5')
3.6 解码序列
# Define sampling models
encoder_model = Model(encoder_inputs, encoder_states)
decoder_state_input_h = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_state_input_c = Input(shape=(latent_dim,))
decoder_states_inputs = [decoder_state_input_h, decoder_state_input_c]
decoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = decoder_lstm(decoder_inputs, initial_state=decoder_states_inputs)
decoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)
decoder_model = Model(
[decoder_inputs] + decoder_states_inputs,
[decoder_outputs] + decoder_states)
# Reverse-lookup token index to decode sequences back to
# something readable.
reverse_input_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in input_token_index.items())
reverse_target_char_index = dict(
(i, char) for char, i in target_token_index.items())
def decode_sequence(input_seq):
# Encode the input as state vectors.
states_value = encoder_model.predict(input_seq)
# Generate empty target sequence of length 1.
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
# Populate the first character of target sequence with the start character.
target_seq[0, 0, target_token_index['\t']] = 1.
# this target_seq you can treat as initial state
# Sampling loop for a batch of sequences
# (to simplify, here we assume a batch of size 1).
stop_condition = False
decoded_sentence = ''
while not stop_condition:
output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + states_value)
# Sample a token
# argmax: Returns the indices of the maximum values along an axis
# just like find the most possible char
sampled_token_index = np.argmax(output_tokens[0, -1, :])
# find char using index
sampled_char = reverse_target_char_index[sampled_token_index]
# and append sentence
decoded_sentence += sampled_char
# Exit condition: either hit max length
# or find stop character.
if (sampled_char == '\n' or len(decoded_sentence) > max_decoder_seq_length):
stop_condition = True
# Update the target sequence (of length 1).
# append then ?
# creating another new target_seq
# and this time assume sampled_token_index to 1.0
target_seq = np.zeros((1, 1, num_decoder_tokens))
target_seq[0, 0, sampled_token_index] = 1.
# Update states
# update states, frome the front parts
states_value = [h, c]
return decoded_sentence
3.7 预测
for seq_index in range(100,200):
# Take one sequence (part of the training set)
# for trying out decoding.
input_seq = encoder_input_data[seq_index: seq_index + 1]
decoded_sentence = decode_sequence(input_seq)
print('Input sentence:', input_texts[seq_index])
print('Decoded sentence:', decoded_sentence)
该项目已公开在 Mo 平台上,Seq2Seq之中英文翻译,建议使用GPU训练。介绍 Mo 平台一个非常贴心实用的功能: API Doc,(在开发界面的右侧栏,第二个)。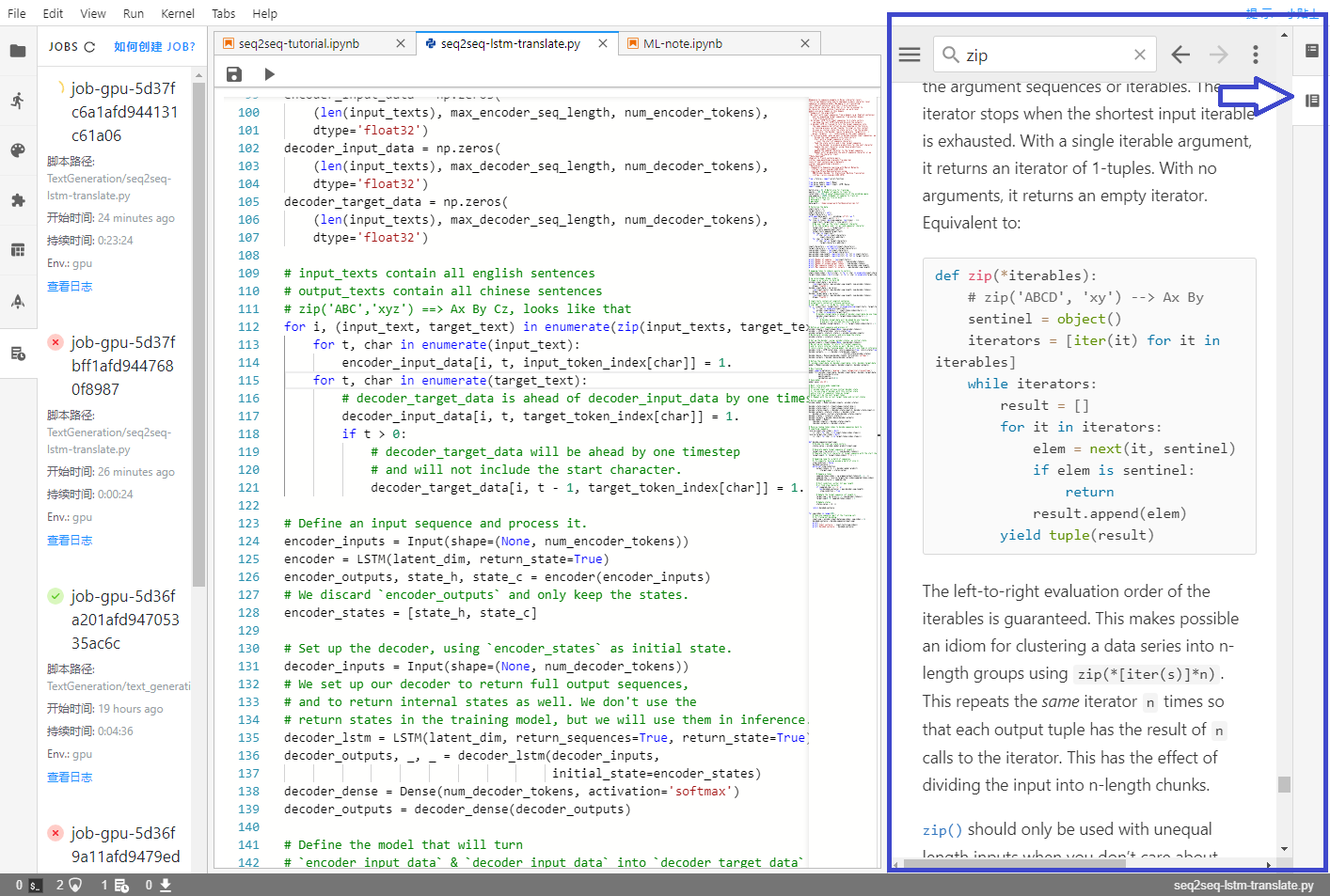 在 Mo 平台写代码可以很方便的实现多窗口显示,只要拖动窗口的标题栏就可实现分栏。 在 Mo 平台写代码可以很方便的实现多窗口显示,只要拖动窗口的标题栏就可实现分栏。
4. 总结与展望
提出经典的 Seq2Seq 模型是一件了不起的事情,该模型在机器翻译和语音识别等领域中解决了很多重要问题和 NLP 无法解决的难题。也是深度学习应用于 NLP 一件里程碑的事件。后续,又基于该模型提出了很多改进和优化,如 Attention 机制等。相信在不远的未来,会有崭新的重大发现,让我们拭目以待。项目源码地址(欢迎电脑端打开进行fork):https://momodel.cn/explore/5d38500a1afd94479891643a?type=app
5. 引用
论文:Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks博客:Understanding LSTM Networks代码:A ten-minute introduction to sequence-to-sequence learning in Keras
欢迎关注我们的微信公众号:MomodelAI
同时,欢迎使用 「Mo AI编程」 微信小程序
以及登录官网,了解更多信息:Mo 平台
Mo,发现意外,创造可能
|