Python爬取天气数据及可视化分析!(含源码) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 天气统计分析报告范文 › Python爬取天气数据及可视化分析!(含源码) |
Python爬取天气数据及可视化分析!(含源码)
|
天气预报我们每天都会关注,我们可以根据未来的天气增减衣物、安排出行,每天的气温、风速风向、相对湿度、空气质量等成为关注的焦点。本次使用python中requests和BeautifulSoup库对中国天气网当天和未来14天的数据进行爬取,保存为csv文件,之后用matplotlib、numpy、pandas对数据进行可视化处理和分析,得到温湿度度变化曲线、空气质量图、风向雷达图等结果,为获得未来天气信息提供了有效方法。
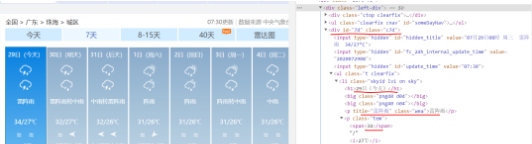
1、数据获取 请求网站链接 首先查看中国天气网的网址:http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101280701.shtml这里就访问本地的天气网址,如果想爬取不同的地区只需修改最后的101280701地区编号即可,前面的weather代表是7天的网页,weather1d代表当天,weather15d代表未来14天。这里就主要访问7天和14天的中国天气网。采用requests.get()方法,请求网页,如果成功访问,则得到的是网页的所有字符串文本。这就是请求过程。 def getHTMLtext(url): """请求获得网页内容""" try: r = requests.get(url, timeout = 30) r.raise_for_status() r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding print("成功访问") return r.text except: print("访问错误") return" "提取有用信息 这里采用BeautifulSoup库对刚刚获取的字符串进行数据提取,首先对网页进行检查,找到需要获取数据的标签:
可以发现7天的数据信息在div标签中并且id=“7d”,并且日期、天气、温度、风级等信息都在ul和li标签中,所以我们可以使用BeautifulSoup对获取的网页文本进行查找div标签id=“7d”,找出他包含的所有的ul和li标签,之后提取标签中相应的数据值,保存到对应列表中。 这里要注意一个细节就是有时日期没有最高气温,对于没有数据的情况要进行判断和处理。另外对于一些数据保存的格式也要提前进行处理,比如温度后面的摄氏度符号,日期数字的提取,和风级文字的提取,这需要用到字符查找及字符串切片处理。 def get_content(html): """处理得到有用信息保存数据文件""" final = [] # 初始化一个列表保存数据 bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser") # 创建BeautifulSoup对象 body = bs.body data = body.find('div', {'id': '7d'}) # 找到div标签且id = 7d下面爬取当天的数据 data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'}) text = data2[2].find('script').string text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据 jd = json.loads(text) dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据 final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据 count = 0 for i in dayone: temp = [] if count 'id': '7d'}) # 找到div标签且id = 7d # 下面爬取当天的数据 data2 = body.find_all('div',{'class':'left-div'}) text = data2[2].find('script').string text = text[text.index('=')+1 :-2] # 移除改var data=将其变为json数据 jd = json.loads(text) dayone = jd['od']['od2'] # 找到当天的数据 final_day = [] # 存放当天的数据 count = 0 for i in dayone: temp = [] if count ;=23: temp.append(i['od21']) # 添加时间 temp.append(i['od22']) # 添加当前时刻温度 temp.append(i['od24']) # 添加当前时刻风力方向 temp.append(i['od25']) # 添加当前时刻风级 temp.append(i['od26']) # 添加当前时刻降水量 temp.append(i['od27']) # 添加当前时刻相对湿度 temp.append(i['od28']) # 添加当前时刻控制质量 #print(temp) final_day.append(temp) count = count +1 # 下面爬取7天的数据 ul = data.find('ul') # 找到所有的ul标签 li = ul.find_all('li') # 找到左右的li标签 i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数 for day in li: # 遍历找到的每一个li if i ; 7 and i ; 0: temp = [] # 临时存放每天的数据 date = day.find('h1').string # 得到日期 date = date[0:date.index('日')] # 取出日期号 temp.append(date) inf = day.find_all('p') # 找出li下面的p标签,提取第一个p标签的值,即天气 temp.append(inf[0].string) tem_low = inf[1].find('i').string # 找到最低气温 if inf[1].find('span') is None: # 天气预报可能没有最高气温 tem_high = None else: tem_high = inf[1].find('span').string # 找到最高气温 temp.append(tem_low[:-1]) if tem_high[-1] == '℃': temp.append(tem_high[:-1]) else: temp.append(tem_high) wind = inf[2].find_all('span') # 找到风向 for j in wind: temp.append(j['title']) wind_scale = inf[2].find('i').string # 找到风级 index1 = wind_scale.index('级') temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1])) final.append(temp) i = i + 1 return final_day,final #print(final) def get_content2(html): """处理得到有用信息保存数据文件""" final = [] # 初始化一个列表保存数据 bs = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser") # 创建BeautifulSoup对象 body = bs.body data = body.find('div', {'id': '15d'}) # 找到div标签且id = 15d ul = data.find('ul') # 找到所有的ul标签 li = ul.find_all('li') # 找到左右的li标签 final = [] i = 0 # 控制爬取的天数 for day in li: # 遍历找到的每一个li if i ; 8: temp = [] # 临时存放每天的数据 date = day.find('span',{'class':'time'}).string # 得到日期 date = date[date.index('(')+1:-2] # 取出日期号 temp.append(date) weather = day.find('span',{'class':'wea'}).string # 找到天气 temp.append(weather) tem = day.find('span',{'class':'tem'}).text # 找到温度 temp.append(tem[tem.index('/')+1:-1]) # 找到最低气温 temp.append(tem[:tem.index('/')-1]) # 找到最高气温 wind = day.find('span',{'class':'wind'}).string # 找到风向 if '转' in wind: # 如果有风向变化 temp.append(wind[:wind.index('转')]) temp.append(wind[wind.index('转')+1:]) else: # 如果没有风向变化,前后风向一致 temp.append(wind) temp.append(wind) wind_scale = day.find('span',{'class':'wind1'}).string # 找到风级 index1 = wind_scale.index('级') temp.append(int(wind_scale[index1-1:index1])) final.append(temp) return final def write_to_csv(file_name, data, day=14): """保存为csv文件""" with open(file_name, 'a', errors='ignore', newline='') as f: if day == 14: header = ['日期','天气','最低气温','最高气温','风向1','风向2','风级'] else: header = ['小时','温度','风力方向','风级','降水量','相对湿度','空气质量'] f_csv = csv.writer(f) f_csv.writerow(header) f_csv.writerows(data) def main(): """主函数""" print("Weather test") # 珠海 url1 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101280701.shtml' # 7天天气中国天气网 url2 = 'http://www.weather.com.cn/weather15d/101280701.shtml' # 8-15天天气中国天气网 html1 = getHTMLtext(url1) data1, data1_7 = get_content(html1) # 获得1-7天和当天的数据 html2 = getHTMLtext(url2) data8_14 = get_content2(html2) # 获得8-14天数据 data14 = data1_7 + data8_14 #print(data) write_to_csv('weather14.csv',data14,14) # 保存为csv文件 write_to_csv('weather1.csv',data1,1) if __name__ == '__main__': main() 'size':'10','color':'red'}) plt.show() print("相关系数为:"+str(calc_corr(tem,hum))) def main(): plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题 data1 = pd.read_csv('weather1.csv',encoding='gb2312') print(data1) tem_curve(data1) hum_curve(data1) air_curve(data1) wind_radar(data1) corr_tem_hum(data1) if __name__ == '__main__': main() } for i in range(0,14): if weather[i] in dic_wea.keys(): dic_wea[weather[i]] += 1 else: dic_wea[weather[i]] = 1 print(dic_wea) explode=[0.01]*len(dic_wea.keys()) color = ['lightskyblue','silver','yellow','salmon','grey','lime','gold','red','green','pink'] plt.pie(dic_wea.values(),explode=explode,labels=dic_wea.keys(),autopct='%1.1f%%',colors=color) plt.title('未来14天气候分布饼图') plt.show() def main(): plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 解决中文显示问题 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题 data14 = pd.read_csv('weather14.csv',encoding='gb2312') print(data14) tem_curve(data14) wind_radar(data14) weather_pie(data14) if __name__ == '__main__': main() |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |