【开源】轻松实现车牌检测与识别:yolov8+paddleocr【python源码+数据集】 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › yolov5识别车牌项目详解 › 【开源】轻松实现车牌检测与识别:yolov8+paddleocr【python源码+数据集】 |
【开源】轻松实现车牌检测与识别:yolov8+paddleocr【python源码+数据集】
|
《博主简介》 小伙伴们好,我是阿旭。专注于人工智能、AIGC、python、计算机视觉相关分享研究。 ✌更多学习资源,可关注公-仲-hao:【阿旭算法与机器学习】,共同学习交流~ 👍感谢小伙伴们点赞、关注! 《------往期经典推荐------》 一、AI应用软件开发实战专栏【链接】 项目名称项目名称1.【人脸识别与管理系统开发】2.【车牌识别与自动收费管理系统开发】3.【手势识别系统开发】4.【人脸面部活体检测系统开发】5.【图片风格快速迁移软件开发】6.【人脸表表情识别系统】7.【YOLOv8多目标识别与自动标注软件开发】8.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的行人跌倒检测系统】9.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的PCB板缺陷检测系统】10.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的生活垃圾分类目标检测系统】11.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的安全帽目标检测系统】12.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的120种犬类检测与识别系统】13.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的路面坑洞检测系统】14.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的火焰烟雾检测系统】15.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的钢材表面缺陷检测系统】16.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的舰船目标分类检测系统】17.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的西红柿成熟度检测系统】18.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的血细胞检测与计数系统】19.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的吸烟/抽烟行为检测系统】20.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的水稻害虫检测与识别系统】21.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的高精度车辆行人检测与计数系统】22.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的路面标志线检测与识别系统】22.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的智能小麦害虫检测识别系统】23.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的智能玉米害虫检测识别系统】24.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的200种鸟类智能检测与识别系统】25.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的45种交通标志智能检测与识别系统】26.【基于YOLOv8深度学习的人脸面部表情识别系统】二、机器学习实战专栏【链接】,已更新31期,欢迎关注,持续更新中~~ 三、深度学习【Pytorch】专栏【链接】 四、【Stable Diffusion绘画系列】专栏【链接】 《------正文------》 实现效果
点击跳转至文末《完整相关文件及源码》免费获取 前言车牌识别在我们实际生活中十分常见,本文主要介绍一种基于YOLOv8目标检测与PaddleOcr进行车牌识别的实现方法。本文提供了完整的数据集和代码,完全免费,供小伙伴们学习参考。感兴趣的小伙伴们学习参考。 要进行车牌识别,主要分为两步。 第一步:进行车辆车牌位置的检测,本文是使用yolov8训练一个车牌检测模型来进行车牌检测,精度为0.99; 第二步:对第一步检测出的车牌进行识别,直接使用的是PaddleOCR对于车牌进行识别。 下面对这些内容进行详细介绍 1.第一步:车牌检测本文主要基于yolov8训练了一个车牌检测模型,用于进行车牌位置的检测,主要步骤如下: 1.1 yolov8环境配置pip install ultralytics -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple yolov8源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics 1.2 数据集准备与处理本文训练模型使用的数据集为CPDD2020数据集。 数据集下载地址:https://github.com/detectRecog/CCPD CCPD是一个大型的、多样化的、经过仔细标注的中国城市车牌开源数据集。CCPD数据集主要分为CCPD2019数据集和CCPD2020(CCPD-Green)数据集。CCPD2019数据集车牌类型仅有普通车牌(蓝色车牌),CCPD2020数据集车牌类型仅有新能源车牌(绿色车牌)。 在CCPD数据集中,每张图片仅包含一张车牌,车牌的车牌省份主要为皖。CCPD中的每幅图像都包含大量的标注信息,但是CCPD数据集没有专门的标注文件,每张图像的文件名就是该图像对应的数据标注。 标注最困难的部分是注释四个顶点的位置。为了完成这项任务,数据发布者首先在10k图像上手动标记四个顶点的位置。然后设计了一个基于深度学习的检测模型,在对该网络进行良好训练后,对每幅图像的四个顶点位置进行自动标注。最后,数据发布者雇用了7名兼职工人在两周内纠正这些标注。CCPD提供了超过250k个独特的车牌图像和详细的注释。每张图像的分辨率为720(宽度)× 1160(高)× 3(通道)。实际上,这种分辨率足以保证每张图像中的车牌清晰可辨,但是该数据有些图片标注可能不准。不过总的来说CCPD数据集非常推荐研究车牌识别算法的人员学习使用。 CPDD2020数据集一共包含11774张新能源汽车的车牌数据。部分图片如下: 数据集中图片的命名规则如下: 图片命名:“025-95_113-154&383_386&473-386&473_177&454_154&383_363&402-0_0_22_27_27_33_16-37-15.jpg” 解释: 1. 025:车牌区域占整个画面的比例; 2. 95_113: 车牌水平和垂直角度, 水平95°, 竖直113° 3. 154&383_386&473:标注框左上、右下坐标,左上(154, 383), 右下(386, 473) 4. 86&473_177&454_154&383_363&402:标注框四个角点坐标,顺序为右下、左下、左上、右上 5. 0_0_22_27_27_33_16:车牌号码映射关系如下: 第一个0为省份 对应省份字典provinces中的’皖’,;第二个0是该车所在地的地市一级代码,对应地市一级代码字典alphabets的’A’;后5位为字母和文字, 查看车牌号ads字典,如22为Y,27为3,33为9,16为S,最终车牌号码为皖AY339S省份:[“皖”, “沪”, “津”, “渝”, “冀”, “晋”, “蒙”, “辽”, “吉”, “黑”, “苏”, “浙”, “京”, “闽”, “赣”, “鲁”, “豫”, “鄂”, “湘”, “粤”, “桂”, “琼”, “川”, “贵”, “云”, “藏”, “陕”, “甘”, “青”, “宁”, “新”] 地市:[‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’, ‘E’, ‘F’, ‘G’, ‘H’, ‘J’, ‘K’, ‘L’, ‘M’, ‘N’, ‘P’, ‘Q’, ‘R’, ‘S’, ‘T’, ‘U’, ‘V’, ‘W’,‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’] 车牌字典:[‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’, ‘E’, ‘F’, ‘G’, ‘H’, ‘J’, ‘K’, ‘L’, ‘M’, ‘N’, ‘P’, ‘Q’, ‘R’, ‘S’, ‘T’, ‘U’, ‘V’, ‘W’, ‘X’,‘Y’, ‘Z’, ‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’] 制作车牌检测数据集: 这个数据集的检测和识别标签都在图片名中,可以直接通过上述图片的命名规则,从图片读取出来,再写入txt文件中即可。代码如下: import shutil import cv2 import os def txt_translate(path, txt_path): print(path) print(txt_path) for filename in os.listdir(path): # print(filename) list1 = filename.split("-", 3) # 第一次分割,以减号'-'做分割 subname = list1[2] list2 = filename.split(".", 1) subname1 = list2[1] if subname1 == 'txt': continue lt, rb = subname.split("_", 1) # 第二次分割,以下划线'_'做分割 lx, ly = lt.split("&", 1) rx, ry = rb.split("&", 1) width = int(rx) - int(lx) height = int(ry) - int(ly) # bounding box的宽和高 cx = float(lx) + width / 2 cy = float(ly) + height / 2 # bounding box中心点 img = cv2.imread(path + filename) if img is None: # 自动删除失效图片(下载过程有的图片会存在无法读取的情况) print(path + filename) os.remove(path + filename) continue width = width / img.shape[1] height = height / img.shape[0] cx = cx / img.shape[1] cy = cy / img.shape[0] txtname = filename.split(".", 1) txtfile = txt_path + txtname[0] + ".txt" # 绿牌是第0类,蓝牌是第1类 with open(txtfile, "w") as f: f.write(str(0) + " " + str(cx) + " " + str(cy) + " " + str(width) + " " + str(height)) if __name__ == '__main__': # det图片存储地址 trainDir = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/train/" validDir = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/val/" testDir = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test/" # det txt存储地址 train_txt_path = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/train_labels/" val_txt_path = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/val_labels/" test_txt_path = r"G:/datasets/CarPlateData/CCPD2020/ccpd_green/test_labels/" txt_translate(trainDir, train_txt_path) txt_translate(validDir, val_txt_path) txt_translate(testDir, test_txt_path)
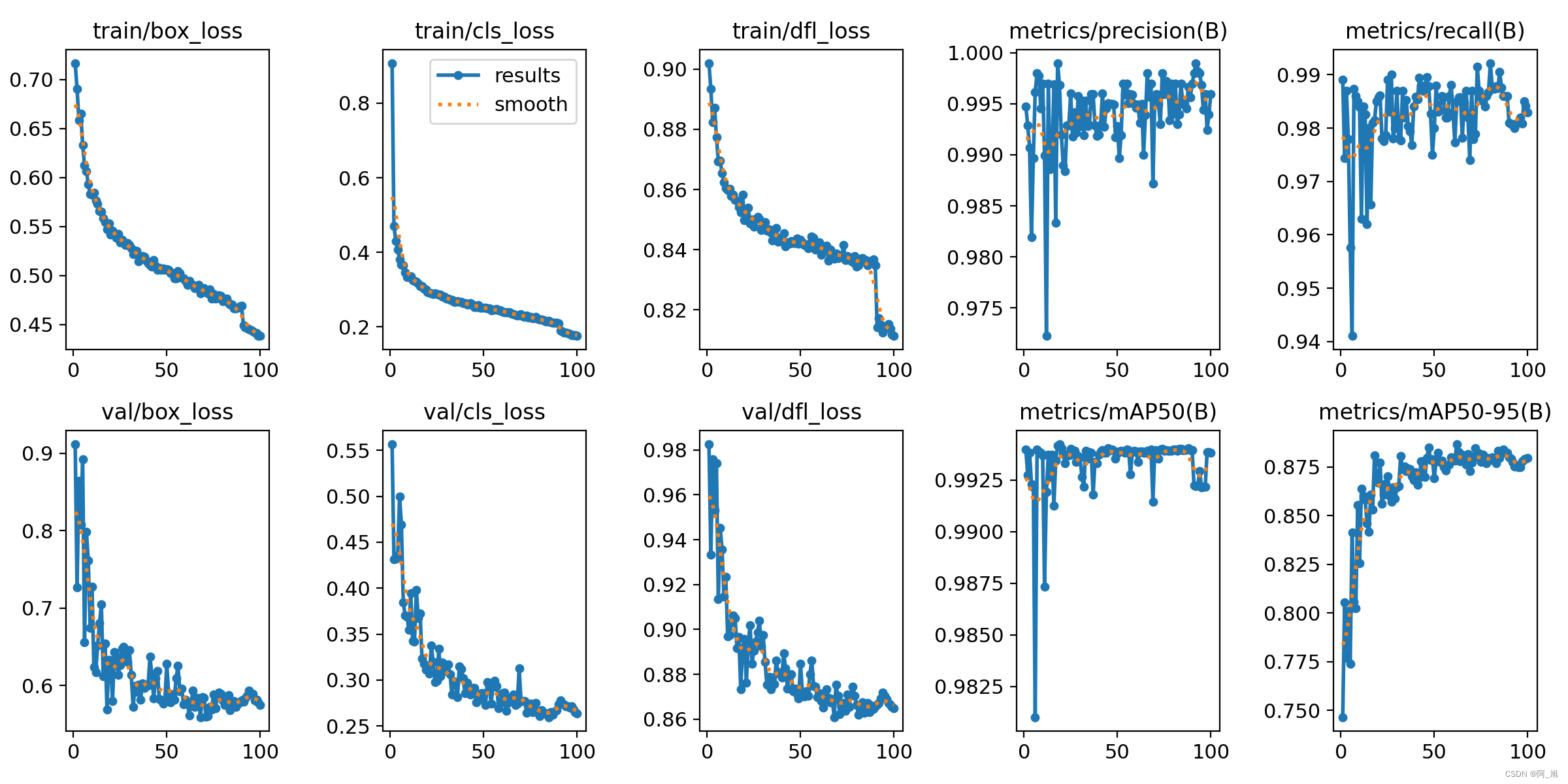
图片数据集的存放格式如下,在项目目录中新建datasets目录,同时将分类的图片分为训练集、验证集与测试集放入PlateData目录下。 数据准备完成后,通过调用train.py文件进行模型训练,epochs参数用于调整训练的轮数,batch参数用于调整训练的批次大小【根据内存大小调整,最小为1】,代码如下: #coding:utf-8 from ultralytics import YOLO # 加载预训练模型 model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # Use the model if __name__ == '__main__': # Use the model results = model.train(data='datasets/PlateData/data.yaml', epochs=300, batch=4) # 训练模型 # 将模型转为onnx格式 # success = model.export(format='onnx') 训练结果评估在深度学习中,我们通常用损失函数下降的曲线来观察模型训练的情况。YOLOv8在训练时主要包含三个方面的损失:定位损失(box_loss)、分类损失(cls_loss)和动态特征损失(dfl_loss),在训练结束后,可以在runs/目录下找到训练过程及结果文件,如下所示:
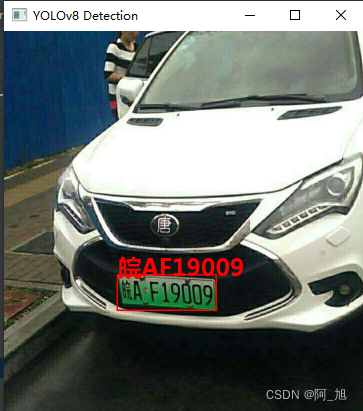
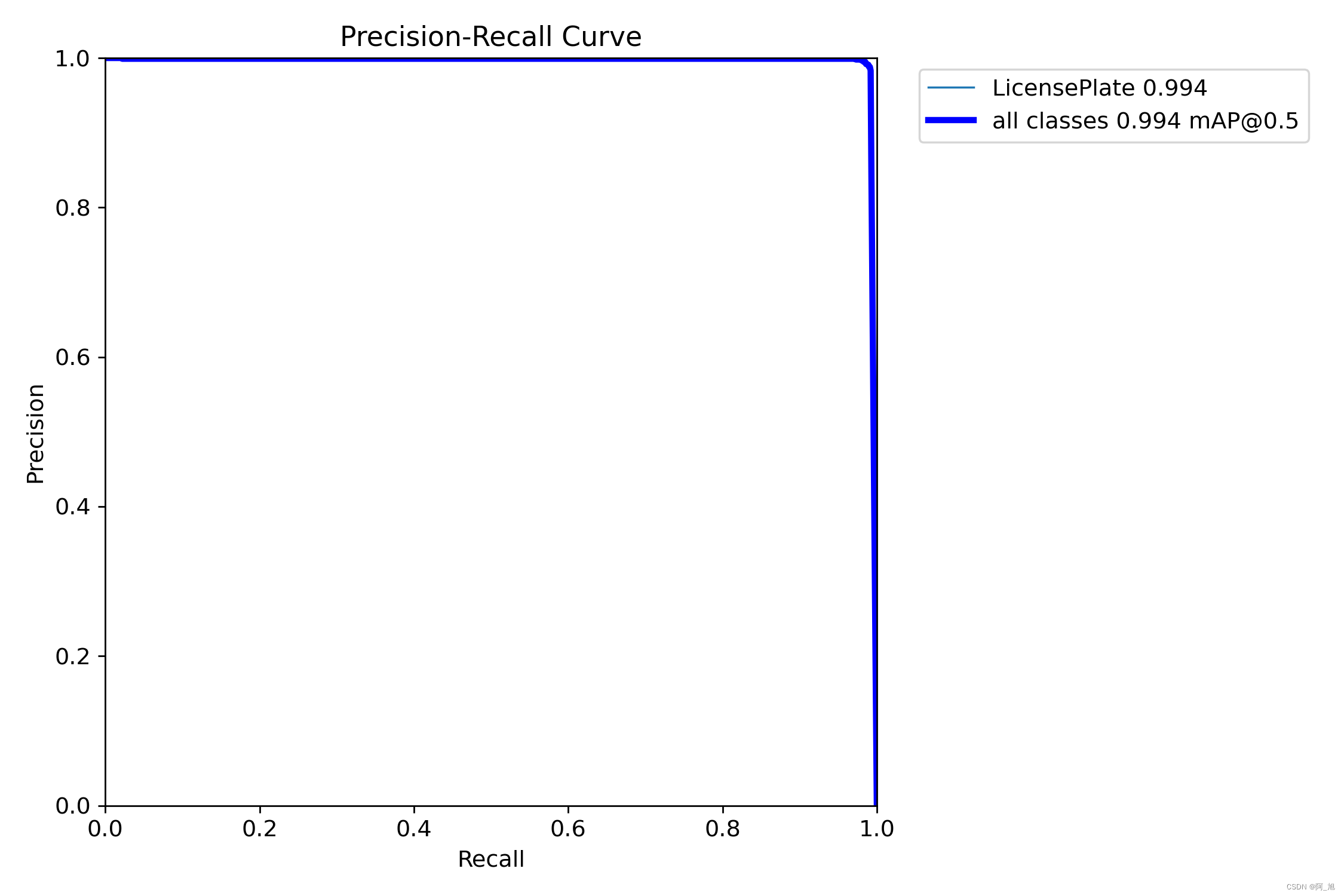
各损失函数作用说明: 定位损失box_loss:预测框与标定框之间的误差(GIoU),越小定位得越准; 分类损失cls_loss:计算锚框与对应的标定分类是否正确,越小分类得越准; 动态特征损失(dfl_loss):DFLLoss是一种用于回归预测框与目标框之间距离的损失函数。在计算损失时,目标框需要缩放到特征图尺度,即除以相应的stride,并与预测的边界框计算Ciou Loss,同时与预测的anchors中心点到各边的距离计算回归DFLLoss。这个过程是YOLOv8训练流程中的一部分,通过计算DFLLoss可以更准确地调整预测框的位置,提高目标检测的准确性。 本文训练结果如下: 我们通常用PR曲线来体现精确率和召回率的关系,本文训练结果的PR曲线如下。mAP表示Precision和Recall作为两轴作图后围成的面积,m表示平均,@后面的数表示判定iou为正负样本的阈值。[email protected]:表示阈值大于0.5的平均mAP,可以看到本文模型目标检测的[email protected]平均值为0.994,结果相当不错。 模型训练完成后,我们可以得到一个最佳的训练结果模型best.pt文件,在runs/trian/weights目录下。我们可以使用该文件进行后续的推理检测。 图片检测代码如下: #coding:utf-8 from ultralytics import YOLO import cv2 # 所需加载的模型目录 path = 'models/best.pt' # 需要检测的图片地址 img_path = "TestFiles/013671875-93_102-226&489_426&558-426&558_234&546_226&489_417&494-0_0_5_25_33_24_24_33-86-80.jpg" # 加载预训练模型 # conf 0.25 object confidence threshold for detection # iou 0.7 intersection over union (IoU) threshold for NMS model = YOLO(path, task='detect') # model = YOLO(path, task='detect',conf=0.5) # 检测图片 results = model(img_path) res = results[0].plot() # res = cv2.resize(res,dsize=None,fx=0.3,fy=0.3,interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Detection", res) cv2.waitKey(0)执行上述代码后,会将执行的结果直接标注在图片上,结果如下: 本文的车牌识别直接使用的是开源的PaddleOCR检测模型。地址:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR 环境配置pip install paddlepaddle2.5.2 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pip install paddleocr2.7.0.3 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pip install shapely -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple 模型使用demo
以上便是关于车牌检测与识别的原理与代码介绍。感兴趣的小伙伴可以自行尝试。 【免费获取方式】关注下方名片G-Z-H:【阿旭算法与机器学习】,回复【开源】即可获取下载方式 本文涉及到的完整全部程序文件:包括python源码、数据集、训练代码、测试图片视频等(见下图),获取方式见文末: 关注下方名片GZH:【阿旭算法与机器学习】,回复【开源】即可获取下载方式 关于本篇文章大家有任何建议或意见,欢迎在评论区留言交流! 觉得不错的小伙伴,感谢点赞、关注加收藏哦! |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |

 制作完成后,如上图所示。
制作完成后,如上图所示。
 可以发现,该模型能够很好的检测出车牌区域。下面我们需要对检测出的车牌进行识别。
可以发现,该模型能够很好的检测出车牌区域。下面我们需要对检测出的车牌进行识别。