Python Statements |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › pythonmulti › Python Statements |
Python Statements
|
Python statements are the code instructions that are executed by the Python interpreter. Python executes statements one by one as they appear in the code. Python Statements ExamplesLet’s look at some simple statement examples. count = 10 # statement 1 class Foo: # statement 2 pass # statement 3 Python Multi-line StatementsPython statements are usually written in a single line. The newline character marks the end of the statement. If the statement is very long, we can explicitly divide it into multiple lines with the line continuation character (\). Let’s look at some examples of multi-line statements. message = "Hello There.\nYou have come to the right place to learn Python Programming.\n" \ "Follow the tutorials to become expert in Python. " \ "Don't forget to share it with your friends too." math_result = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + \ 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + \ 9 + 10 print(message) print(math_result)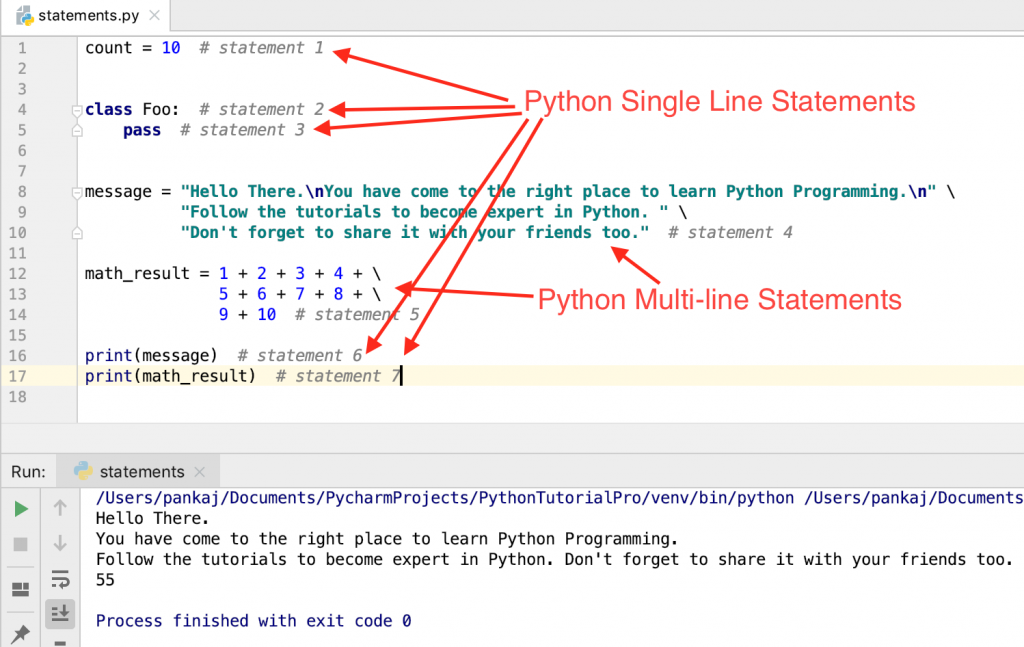 Python Statements Python StatementsPython supports multi-line continuation inside parentheses ( ), brackets [ ], and braces { }. The brackets are used by List and the braces are used by dictionary objects. We can use parentheses for expressions, tuples, and strings. message = ("Hello\n" "Hi\n" "Namaste") math_result = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10) prime_numbers_tuple = (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17) list_fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Orange", "Mango"] dict_countries = {"USA": "United States of America", "IN": "India", "UK": "United Kingdom", "FR": "France"} Can we have multiple statements in a single line?We can use a semicolon (;) to have multiple statements in a single line. x = 1; y = 2; z = 3 Python Simple StatementsPython simple statement is comprised of a single line. The multiline statements created above are also simple statements because they can be written in a single line. Let’s look at some important types of simple statements in Python. 1. Python Expression Statement i = int("10") # expression is evaluated and the result is assigned to the variable. sum = 1 + 2 + 3 # statement contains an expression to be evaluated first. 2. Python Assignment Statement count = 10 # value is assigned to the variable, no expression is evaluated message = "Hi" 3. Python Assert Statement assert 5 < 10 assert (True or False)Read more at Python assertions. 4. Python pass Statement def foo(): pass # pass statementRead more at pass statement in Python. 5. Python del Statement name = "Python" del name # del statement 6. Python return Statement def foo(): return 10 # return statementRecommended Read: return statement in Python. 7. Python yield Statement def yield_statement(): yield 'Statement 1' # yield statementRead more at yield in Python. 8. Python raise Statement def raise_example(): raise TypeError('Exception Example') # raise statementRead more about exception handling in Python. 9. Python break Statement numbers = [1, 2, 3] for num in numbers: if num > 2: break # break statementRead more at Python break statement. 10. Python continue Statement numbers = [1, 2, 3] for num in numbers: if num > 2: continue # continue statement print(num)Further Reading: Python continue statement 11. Python import Statement import collections import calendar as cal from csv import DictReaderRecommended Read: import in Python. 12. Python global Statement name = "Python" def global_example(): global name # global statement name = "Flask" print(name) # prints Python global_example() print(name) # prints Flask 13. Python nonlocal Statement def outer_function(): scope = "local" def inner_function(): nonlocal scope # nonlocal statement scope = "nonlocal" print(scope) inner_function() print(scope) outer_function() Python Compound StatementsPython compound statements contain a group of other statements and affect their execution. The compound statement generally spans multiple lines. Let’s briefly look into a few compound statements. 1. Python if Statement if 5 < 10: print("This will always print") else: print("Unreachable Code")Recommended Read: Python if-else statement 2. Python for Statement for n in (1, 2, 3): print(n)Further Reading: Python for loop 3. Python while Statement count = 5 while count > 0: print(count) count -= 1Read more at Python while loop. 4. Python try Statement try: print("try") except ValueError as ve: print(ve) 5. Python with Statement with open('data.csv') as file: file.read() 6. Python Function Definition StatementA python function definition is an executable statement. Its execution binds the function name in the current local namespace to a function object. The function is executed only when it’s called. def useless(): pass 7. Python Class Definition StatementIt’s an executable statement. Python class definition defines the class object. class Data: id = 0 8. Python Coroutines Function Definition Statement import asyncio async def ping(url): print(f'Ping Started for {url}') await asyncio.sleep(1) print(f'Ping Finished for {url}') SummaryPython statements are used by the Python interpreter to run the code. It’s good to know about the different types of statements in Python. References:Simple StatementsCompound Statements |
【本文地址】