C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › mel频率倒谱系数的语言录音能鉴别真伪吗 › C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc |
C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc
|
C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc
目录 C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc 1.项目结构 2.依赖环境 3.C++ librosa音频处理库实现 (1) 对齐读取音频文件 (2) 对齐melspectrogram (3) 对齐MFCC 4.Demo运行 5.librosa库C++源码下载 深度学习语音处理中,经常要用到音频处理库librosa,奈何librosa目前仅有python版本;而语音识别算法开发中,经常要用到melspectrogram(Mel-spectrogram梅尔语谱图)和MFCC(梅尔频率倒谱系数)这些音频信息,因此需要实现C/C++版本melspectrogram和MFCC;网上已经存在很多版本的C/C++的melspectrogram和MFCC,但测试发现跟Python的librosa的处理结果存在很大差异;经过多次优化测试,本项目实现了C/C++版本的音频处理库librosa中load、melspectrogram和mfcc的功能,项目基本完整对齐Pyhon音频处理库librosa三个功能: librosa.load:实现语音读取librosa.feature.melspectrogram:实现计算梅尔语谱图melspectrogramlibrosa.feature.mfcc:实现计算梅尔频率倒谱系数MFCC
【尊重原创,转载请注明出处】https://blog.csdn.net/guyuealian/article/details/132077896 1.项目结构
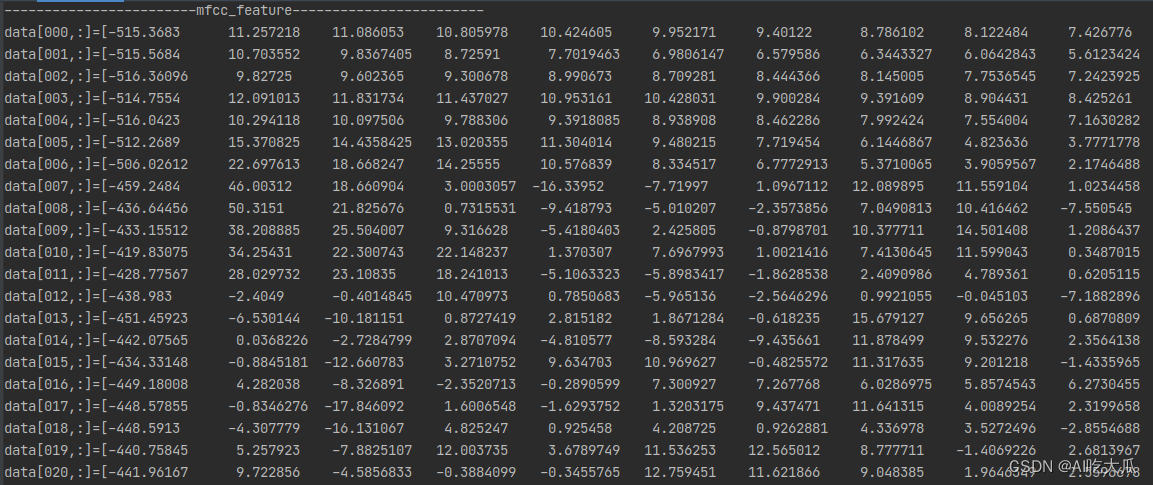
项目需要安装Python和C/C++相关的依赖包 Python依赖库,使用pip install即可 numpy==1.16.3 matplotlib==3.1.0 Pillow==6.0.0 easydict==1.9 opencv-contrib-python==4.5.2.52 opencv-python==4.5.1.48 pandas==1.1.5 PyYAML==5.3.1 scikit-image==0.17.2 scikit-learn==0.24.0 scipy==1.5.4 seaborn==0.11.2 tqdm==4.55.1 xmltodict==0.12.0 pybaseutils==0.7.6 librosa==0.8.1 pyaudio==0.2.11 pydub==0.23.1C++依赖库,主要用到Eigen3和OpenCV Eigen3:用于矩阵计算,项目已经支持Eigen3,无须安装OpenCV: 用于显示图像,安装方法请参考Ubuntu18.04安装opencv和opencv_contrib 3.C++ librosa音频处理库实现语音处理中常用的特征值: Mel频谱图(Mel Spectrogram)和Mel频率倒谱系数(Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficient, MFCC),参考文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/Ge-ronimo/p/17281385.html (1) 对齐读取音频文件Python中可使用librosa.load读取音频文件 data, sr = librosa.load(path, sr, mono)Python实现读取音频文件: # -*-coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import librosa def read_audio(audio_file, sr=16000, mono=True): """ 默认将多声道音频文件转换为单声道,并返回一维数组; 如果你需要处理多声道音频文件,可以使用 mono=False,参数来保留所有声道,并返回二维数组。 :param audio_file: :param sr: sampling rate :param mono: 设置为true是单通道,否则是双通道 :return: """ audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_file, sr=sr, mono=mono) audio_data = audio_data.T.reshape(-1) return audio_data, sr def print_vector(name, data): np.set_printoptions(precision=7, suppress=False) print("------------------------%s------------------------\n" % name) print("{}".format(data.tolist())) if __name__ == '__main__': sr = None audio_file = "data/data_s1.wav" data, sr = read_audio(audio_file, sr=sr, mono=False) print("sr = %d, data size=%d" % (sr, len(data))) print_vector("audio data", data)C/C++读取音频文件:需要根据音频的数据格式进行解码,参考:C语言解析wav文件格式 ,本项目已经实现C/C++版本的读取音频数据,可支持单声道和双声道音频数据(mono) /** * 读取音频文件,目前仅支持wav格式文件 * @param filename wav格式文件 * @param out 输出音频数据 * @param sr 输出音频采样率 * @param mono 设置为true是单通道,否则是双通道 * @return */ int read_audio(const char *filename, vector &out, int *sr, bool mono = true); #include #include #include #include "librosa/audio_utils.h" #include "librosa/librosa.h" using namespace std; int main() { int sr = -1; string audio_file = "../data/data_s1.wav"; vector data; int res = read_audio(audio_file.c_str(), data, &sr, false); if (res < 0) { printf("read wav file error: %s\n", audio_file.c_str()); return -1; } printf("sr = %d, data size=%d\n", sr, data.size()); print_vector("audio data", data); return 0; }测试和对比Python和C++版本读取音频文件数据,经过多轮测试,二者的读取的音频数值差异已经很小,基本已经对齐python librosa库的librosa.load()函数 数值对比C++版本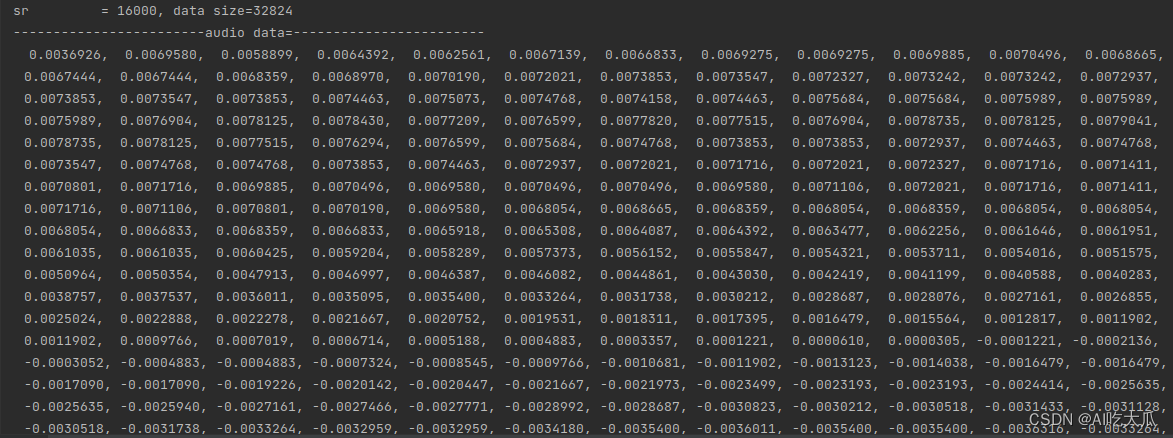 Python版本 Python版本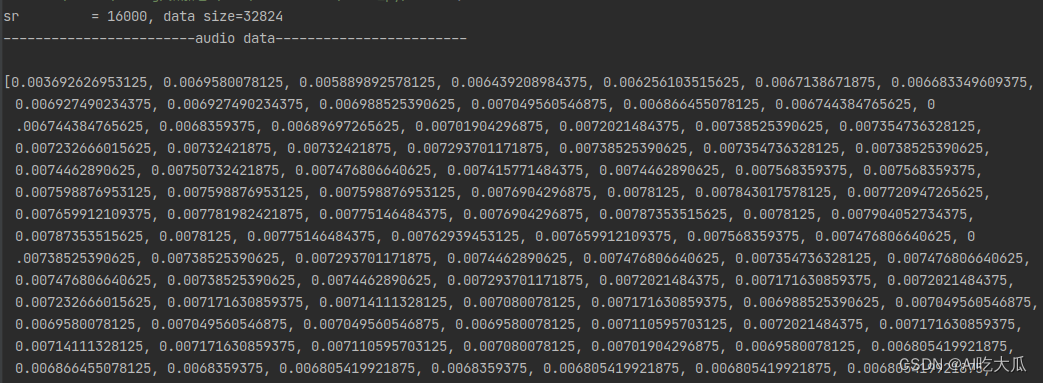 (2) 对齐Mel频谱图melspectrogram
(2) 对齐Mel频谱图melspectrogram
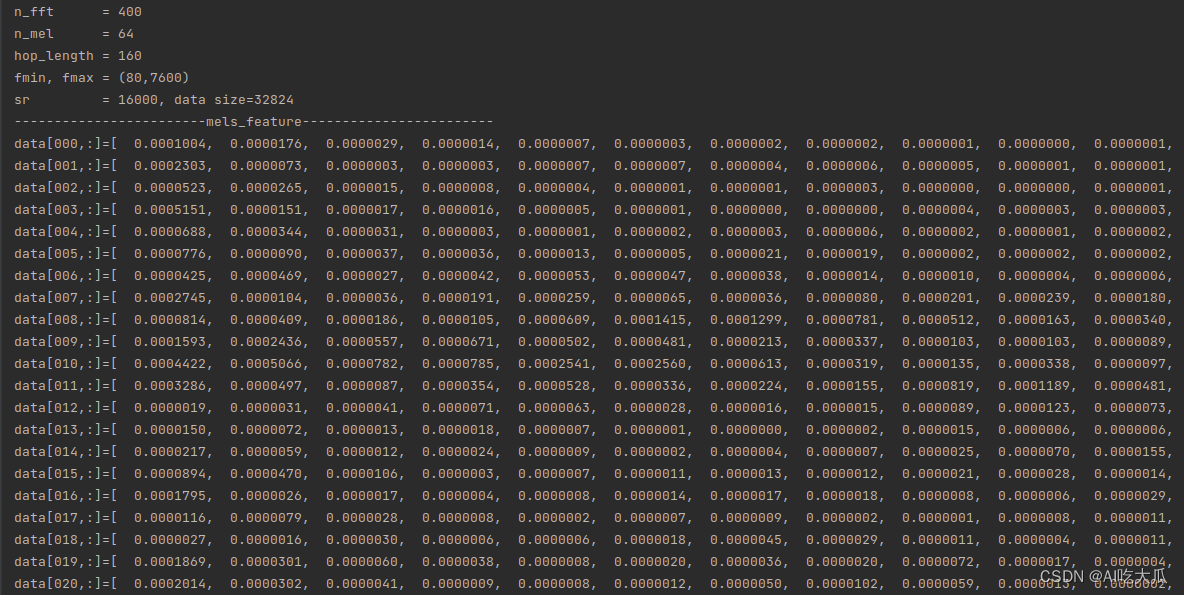
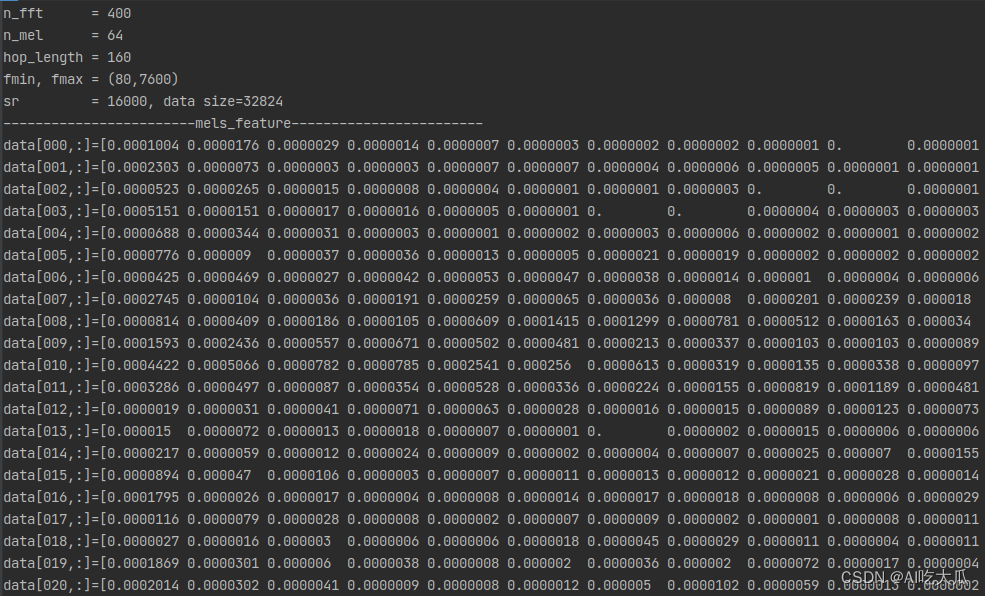
关于melspectrogram梅尔频谱的相关原理,请参考基于梅尔频谱的音频信号分类识别(Pytorch) Python的librosa库的提供了librosa.feature.melspectrogram()函数,返回一个二维数组,可以使用OpenCV显示该图像 def librosa_feature_melspectrogram(y, sr=16000, n_mels=128, n_fft=2048, hop_length=256, win_length=None, window="hann", center=True, pad_mode="reflect", power=2.0, fmin=0.0, fmax=None, **kwargs): """ 计算音频梅尔频谱图(Mel Spectrogram) :param y: 音频时间序列 :param sr: 采样率 :param n_mels: number of Mel bands to generate产生的梅尔带数 :param n_fft: length of the FFT window FFT窗口的长度 :param hop_length: number of samples between successive frames 帧移(相邻窗之间的距离) :param win_length: 窗口的长度为win_length,默认win_length = n_fft :param window: :param center: 如果为True,则填充信号y,以使帧 t以y [t * hop_length]为中心。 如果为False,则帧t从y [t * hop_length]开始 :param pad_mode: :param power: 幅度谱的指数。例如1代表能量,2代表功率,等等 :param fmin: 最低频率(Hz) :param fmax: 最高频率(以Hz为单位),如果为None,则使用fmax = sr / 2.0 :param kwargs: :return: 返回Mel频谱shape=(n_mels,n_frames),n_mels是Mel频率的维度(频域),n_frames为时间帧长度(时域) """ mel = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=y, sr=sr, S=None, n_mels=n_mels, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, **kwargs) return mel根据Python版本的librosa.feature.melspectrogram(),项目实现了C++版本melspectrogram /*** * compute mel spectrogram similar with librosa.feature.melspectrogram * @param x input audio signal * @param sr sample rate of 'x' * @param n_fft length of the FFT size * @param n_hop number of samples between successive frames * @param win window function. currently only supports 'hann' * @param center same as librosa * @param mode pad mode. support "reflect","symmetric","edge" * @param power exponent for the magnitude melspectrogram * @param n_mels number of mel bands * @param fmin lowest frequency (in Hz) * @param fmax highest frequency (in Hz) * @return mel spectrogram matrix */ static std::vector melspectrogram(std::vector &x, int sr, int n_fft, int n_hop, const std::string &win, bool center, const std::string &mode, float power, int n_mels, int fmin, int fmax)测试和对比Python和C++版本melspectrogram,二者的返回数值差异已经很小,其可视化的梅尔频谱图基本一致。 版本数值对比C++版本
Python版本
Python版可使用librosa库的librosa.feature.mfcc实现MFCC(Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients) def librosa_feature_mfcc(y, sr=16000, n_mfcc=128, n_mels=128, n_fft=2048, hop_length=256, win_length=None, window="hann", center=True, pad_mode="reflect", power=2.0, fmin=0.0, fmax=None, dct_type=2, **kwargs): """ 计算音频MFCC :param y: 音频时间序列 :param sr: 采样率 :param n_mfcc: number of MFCCs to return :param n_mels: number of Mel bands to generate产生的梅尔带数 :param n_fft: length of the FFT window FFT窗口的长度 :param hop_length: number of samples between successive frames 帧移(相邻窗之间的距离) :param win_length: 窗口的长度为win_length,默认win_length = n_fft :param window: :param center: 如果为True,则填充信号y,以使帧 t以y [t * hop_length]为中心。 如果为False,则帧t从y [t * hop_length]开始 :param pad_mode: :param power: 幅度谱的指数。例如1代表能量,2代表功率,等等 :param fmin: 最低频率(Hz) :param fmax: 最高频率(以Hz为单位),如果为None,则使用fmax = sr / 2.0 :param kwargs: :return: 返回MFCC shape=(n_mfcc,n_frames) """ # MFCC 梅尔频率倒谱系数 mfcc = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, S=None, n_mfcc=n_mfcc, n_mels=n_mels, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, dct_type=dct_type, **kwargs) return mfcc根据Python版本的librosa.feature.mfcc(),项目实现了C++版本MFCC /*** * compute mfcc similar with librosa.feature.mfcc * @param x input audio signal * @param sr sample rate of 'x' * @param n_fft length of the FFT size * @param n_hop number of samples between successive frames * @param win window function. currently only supports 'hann' * @param center same as librosa * @param mode pad mode. support "reflect","symmetric","edge" * @param power exponent for the magnitude melspectrogram * @param n_mels number of mel bands * @param fmin lowest frequency (in Hz) * @param fmax highest frequency (in Hz) * @param n_mfcc number of mfccs * @param norm ortho-normal dct basis * @param type dct type. currently only supports 'type-II' * @return mfcc matrix */ static std::vector mfcc(std::vector &x, int sr, int n_fft, int n_hop, const std::string &win, bool center, const std::string &mode, float power, int n_mels, int fmin, int fmax, int n_mfcc, bool norm, int type)测试和对比Python和C++版本MFCC,二者的返回数值差异已经很小,其可视化的MFCC图基本一致。 版本数值对比C++版本
main函数 /**** * @Author : [email protected] * @E-mail : * @Date : * @Brief : C/C++实现Melspectrogram和MFCC */ #include #include #include #include "librosa/audio_utils.h" #include "librosa/librosa.h" #include "librosa/cv_utils.h" using namespace std; int main() { int sr = -1; int n_fft = 400; int hop_length = 160; int n_mel = 64; int fmin = 80; int fmax = 7600; int n_mfcc = 64; int dct_type = 2; float power = 2.f; bool center = false; bool norm = true; string window = "hann"; string pad_mode = "reflect"; //string audio_file = "../data/data_d2.wav"; string audio_file = "../data/data_s1.wav"; vector data; int res = read_audio(audio_file.c_str(), data, &sr, false); if (res < 0) { printf("read wav file error: %s\n", audio_file.c_str()); return -1; } printf("n_fft = %d\n", n_fft); printf("n_mel = %d\n", n_mel); printf("hop_length = %d\n", hop_length); printf("fmin, fmax = (%d,%d)\n", fmin, fmax); printf("sr = %d, data size=%d\n", sr, data.size()); //print_vector("audio data", data); // compute mel Melspectrogram vector mels_feature = librosa::Feature::melspectrogram(data, sr, n_fft, hop_length, window, center, pad_mode, power, n_mel, fmin, fmax); int mels_w = (int) mels_feature.size(); int mels_h = (int) mels_feature[0].size(); cv::Mat mels_image = vector2mat(get_vector(mels_feature), 1, mels_h); print_feature("mels_feature", mels_feature); printf("mels_feature size(n_frames,n_mels)=(%d,%d)\n", mels_w, mels_h); image_show("mels_feature(C++)", mels_image, 10); // compute MFCC vector mfcc_feature = librosa::Feature::mfcc(data, sr, n_fft, hop_length, window, center, pad_mode, power, n_mel, fmin, fmax, n_mfcc, norm, dct_type); int mfcc_w = (int) mfcc_feature.size(); int mfcc_h = (int) mfcc_feature[0].size(); cv::Mat mfcc_image = vector2mat(get_vector(mfcc_feature), 1, mfcc_h); print_feature("mfcc_feature", mfcc_feature); printf("mfcc_feature size(n_frames,n_mfcc)=(%d,%d)\n", mfcc_w, mfcc_h); image_show("mfcc_feature(C++)", mfcc_image, 10); cv::waitKey(0); printf("finish..."); return 0; } Python版本,可在项目根目录,终端输入:python main.py ,即可运行测试demo # -*-coding: utf-8 -*- """ @Author : @E-mail : @Date : 2023-08-01 22:27:56 @Brief : """ import cv2 import numpy as np import librosa def cv_show_image(title, image, use_rgb=False, delay=0): """ 调用OpenCV显示图片 :param title: 图像标题 :param image: 输入是否是RGB图像 :param use_rgb: True:输入image是RGB的图像, False:返输入image是BGR格式的图像 :param delay: delay=0表示暂停,delay>0表示延时delay毫米 :return: """ img = image.copy() if img.shape[-1] == 3 and use_rgb: img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) # 将BGR转为RGB # cv2.namedWindow(title, flags=cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) cv2.namedWindow(title, flags=cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL) cv2.imshow(title, img) cv2.waitKey(delay) return img def librosa_feature_melspectrogram(y, sr=16000, n_mels=128, n_fft=2048, hop_length=256, win_length=None, window="hann", center=True, pad_mode="reflect", power=2.0, fmin=0.0, fmax=None, **kwargs): """ 计算音频梅尔频谱图(Mel Spectrogram) :param y: 音频时间序列 :param sr: 采样率 :param n_mels: number of Mel bands to generate产生的梅尔带数 :param n_fft: length of the FFT window FFT窗口的长度 :param hop_length: number of samples between successive frames 帧移(相邻窗之间的距离) :param win_length: 窗口的长度为win_length,默认win_length = n_fft :param window: :param center: 如果为True,则填充信号y,以使帧 t以y [t * hop_length]为中心。 如果为False,则帧t从y [t * hop_length]开始 :param pad_mode: :param power: 幅度谱的指数。例如1代表能量,2代表功率,等等 :param fmin: 最低频率(Hz) :param fmax: 最高频率(以Hz为单位),如果为None,则使用fmax = sr / 2.0 :param kwargs: :return: 返回Mel频谱shape=(n_mels,n_frames),n_mels是Mel频率的维度(频域),n_frames为时间帧长度(时域) """ mel = librosa.feature.melspectrogram(y=y, sr=sr, S=None, n_mels=n_mels, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, **kwargs) return mel def librosa_feature_mfcc(y, sr=16000, n_mfcc=128, n_mels=128, n_fft=2048, hop_length=256, win_length=None, window="hann", center=True, pad_mode="reflect", power=2.0, fmin=0.0, fmax=None, dct_type=2, **kwargs): """ 计算音频MFCC :param y: 音频时间序列 :param sr: 采样率 :param n_mfcc: number of MFCCs to return :param n_mels: number of Mel bands to generate产生的梅尔带数 :param n_fft: length of the FFT window FFT窗口的长度 :param hop_length: number of samples between successive frames 帧移(相邻窗之间的距离) :param win_length: 窗口的长度为win_length,默认win_length = n_fft :param window: :param center: 如果为True,则填充信号y,以使帧 t以y [t * hop_length]为中心。 如果为False,则帧t从y [t * hop_length]开始 :param pad_mode: :param power: 幅度谱的指数。例如1代表能量,2代表功率,等等 :param fmin: 最低频率(Hz) :param fmax: 最高频率(以Hz为单位),如果为None,则使用fmax = sr / 2.0 :param kwargs: :return: 返回MFCC shape=(n_mfcc,n_frames) """ # MFCC 梅尔频率倒谱系数 mfcc = librosa.feature.mfcc(y=y, sr=sr, S=None, n_mfcc=n_mfcc, n_mels=n_mels, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, dct_type=dct_type, **kwargs) return mfcc def read_audio(audio_file, sr=16000, mono=True): """ 默认将多声道音频文件转换为单声道,并返回一维数组; 如果你需要处理多声道音频文件,可以使用 mono=False,参数来保留所有声道,并返回二维数组。 :param audio_file: :param sr: sampling rate :param mono: 设置为true是单通道,否则是双通道 :return: """ audio_data, sr = librosa.load(audio_file, sr=sr, mono=mono) audio_data = audio_data.T.reshape(-1) return audio_data, sr def print_feature(name, feature): h, w = feature.shape[:2] np.set_printoptions(precision=7, suppress=True, linewidth=(11 + 3) * w) print("------------------------{}------------------------".format(name)) for i in range(w): v = feature[:, i].reshape(-1) print("data[{:0=3d},:]={}".format(i, v)) def print_vector(name, data): np.set_printoptions(precision=7, suppress=False) print("------------------------%s------------------------\n" % name) print("{}".format(data.tolist())) if __name__ == '__main__': sr = None n_fft = 400 hop_length = 160 n_mel = 64 fmin = 80 fmax = 7600 n_mfcc = 64 dct_type = 2 power = 2.0 center = False norm = True window = "hann" pad_mode = "reflect" audio_file = "data/data_s1.wav" data, sr = read_audio(audio_file, sr=sr, mono=False) print("n_fft = %d" % n_fft) print("n_mel = %d" % n_mel) print("hop_length = %d" % hop_length) print("fmin, fmax = (%d,%d)" % (fmin, fmax)) print("sr = %d, data size=%d" % (sr, len(data))) # print_vector("audio data", data) mels_feature = librosa_feature_melspectrogram(y=data, sr=sr, n_mels=n_mel, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=None, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power) print_feature("mels_feature", mels_feature) print("mels_feature size(n_frames,n_mels)=({},{})".format(mels_feature.shape[1], mels_feature.shape[0])) cv_show_image("mels_feature(Python)", mels_feature, delay=10) mfcc_feature = librosa_feature_mfcc(y=data, sr=sr, n_mfcc=n_mfcc, n_mels=n_mel, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=None, fmin=fmin, fmax=fmax, window=window, center=center, pad_mode=pad_mode, power=power, dct_type=dct_type) print_feature("mfcc_feature", mfcc_feature) print("mfcc_feature size(n_frames,n_mfcc)=({},{})".format(mfcc_feature.shape[1], mfcc_feature.shape[0])) cv_show_image("mfcc_feature(Python)", mfcc_feature, delay=10) cv2.waitKey(0) 5.librosa库C++源码下载C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc项目代码下载地址:C/C++实现librosa音频处理库melspectrogram和mfcc 项目源码内容包含: 提供C++版的read_audio()函数读取音频文件,目前仅支持wav格式文件,支持单/双声道音频读取提供C++版的librosa::Feature::melspectrogram(),实现melspectrogram功能提供C++版的librosa::Feature::mfcc(),实现MFCC功能提供OpenCV图谱显示方式项目demo自带测试数据,编译build完成后,即可运行 |
【本文地址】