Heat Capacity |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › j/(mol*k) › Heat Capacity |
Heat Capacity
|
Heat Capacity - C - is a characteristic of an object - the amount of heat required to change its temperature by one degree. Heat Capacity has the units of energy per degree.The amount of heat supplied to heat an object can be expressed as: Q = C dt (1) where Q = amount of heat supplied (J, Btu) C = heat capacity of system or object (J/K, Btu/ oF) dt = temperature change (K, C°, oF) The SI unit for heat capacity is J/K (joule per kelvin). In the English system, the units are British thermal units per pound per degree Fahrenheit (Btu/oF). In some contexts kJ or cal and kcal are used instead of J. Never use tabulated values of heat capacity without checking the unit of actual values!Specific Heat Capacity (c) is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree. Specific heat is a more common term for the same. The heat supplied to a mass can be expressed as dQ = m c dt (1) where dQ = heat supplied (J, kJ Btu) m = unit mass (g, kg, lb) c = specific heat (J/g K, kJ/kg oC, kJ/kg K, Btu/lb oF) dt = temperature change (K, C°, oF) (1) can be transferred to express Specific Heat as: c = dQ / m dt (1b) Example: The specific heat of iron is 0.45 J/(g K), which means that it takes 0.45 Joules of heat to raise one gram of iron by one degree Kelvin.
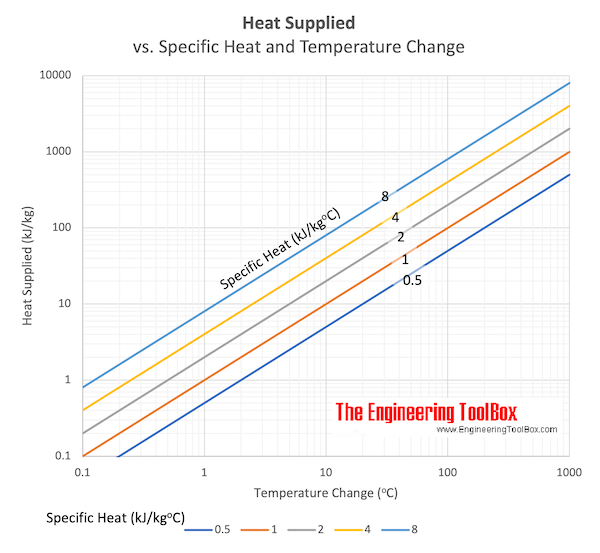
Download and print Heat supplied vs. Specfic heat and change in Temperature chart Specific Heat Gases There are two definitions of Specific Heat for vapors and gases: cp = (δh / δT)p - Specific Heat at constant pressure (J/gK) cv = ( δh / δT)v - Specific Heat at constant volume (J/gK) For solids and liquids, cp = cv Use the links to see tabulated values of specific heat of gases, common liquids and fluids, food and foodstuff, metals and semimetals, common solids and other common substances.Gas Constant The individual individual gas constant, R, can be expressed as R = cp - cv (2) Ratio of Specific Heat The Ratio of Specific Heat is expressed as k = cp / cv (3) Molar Heat Capacity (Cp) is the amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of one mol of a substance by one degree at constant pressure.It is expressed in joules per moles per degrees Kelvin (or Celsius), J/(mol K). Example: The molar heat capacity of iron is 25.10 J/(mol K), which means that it takes 25.10 Joules of heat to raise 1 mol of iron by 1 degree Kelvin. Tabulated values of molar heat capacity, Cp, of a lot of organic and inorganic substances can be found in Standard enthalpy of formation, Gibbs free energy of formation, entropy and molar heat capacity of organic substances and Standard state and enthalpy of formation, Gibbs free energy of formation, entropy and heat capacity, together with ΔH°f, ΔG°f and S° for the same substances at 25°C. Converting between Specific heat and Molar heat capacityThe specific heat capacity can be calculated from the molar heat capacity, and vise versa: cp = Cp / M and Cp = cp . M where cp = specific heat capacity Cp = molar heat capacity M = molar weight of the actual substance (g/mol). Example: Methanol (with molecular formula CH3OH) has a molar heat capacity, Cp, of 81.1 J/(mol K). What is the specific heat capacity, cp? First, we calculate (or find) the molar weight of methanol: 1*12.01g/mol C + 4*1.008g/mol H + 1*16.00g/mol O = 32.04 g/mol CH3OH Then, the specific heat capacity of methanol is: cp = 81.8 J/(molK) / 32.04 g/mol = 2.53 J/(g K) Converting between commonly used Units 1 Btu/lbmoF = 4186.8 J/kg K = 1 kcal/kgoC Online Specific heat capacity unit converter Example - Heating Aluminum2 kg of aluminum is heated from 20 oC to 100 oC. Specific heat of aluminum is 0.91 kJ/kg0C and the heat required can be calculated as dQ = (2 kg) (0.91 kJ/kg0C) ((100 oC) - (20 oC)) = 145.6 (kJ) Example - Heating WaterOne liter of water is heated from 0 oC to boiling 100 oC. Specific heat of water is 4.19 kJ/kg0C and the heat required can be calculated as dQ = (1 litre) (1 kg/litre) (4.19 kJ/kg0C) ((100 oC) - (0 oC)) = 419 (kJ) = 419 (kWs) (1/3600 h/s) = 0.12 kWh Energy Storage in Heated Water - kWh |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |