Python: Pandas的DataFrame如何按指定list排序 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › excel按规定顺序排列 › Python: Pandas的DataFrame如何按指定list排序 |
Python: Pandas的DataFrame如何按指定list排序
|
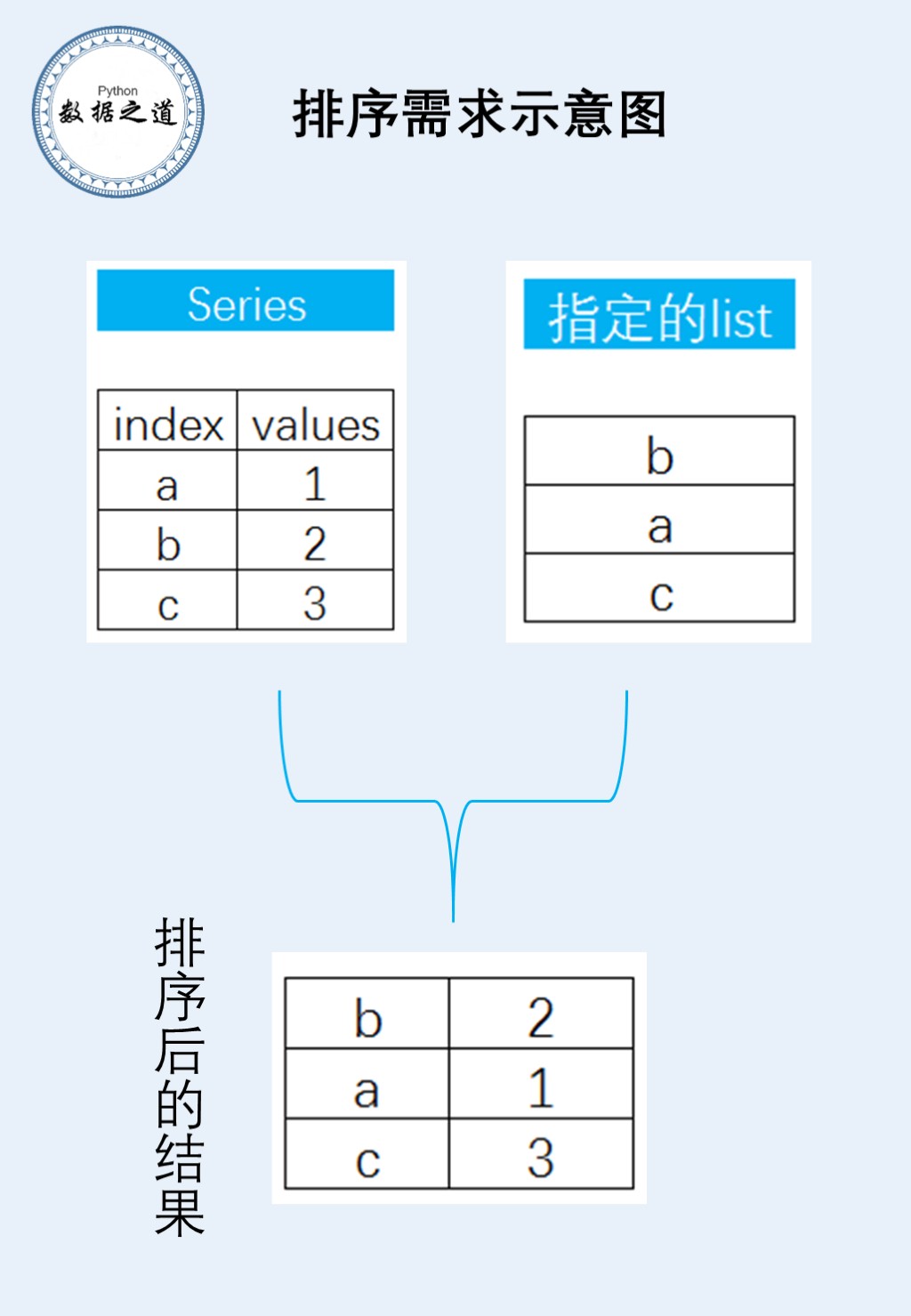
本文首发于微信公众号“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad) 前言写这篇文章的起由是有一天微信上一位朋友问到一个问题,问题大体意思概述如下: 现在有一个pandas的Series和一个python的list,想让Series按指定的list进行排序,如何实现? 这个问题的需求用流程图描述如下:
我思考了一下,这个问题解决的核心是引入pandas的数据类型“category”,从而进行排序。 在具体的分析过程中,先将pandas的Series转换成为DataFrame,然后设置数据类型,再进行排序。思路用流程图表示如下:
设置成“category”数据类型 # 设置成“category”数据类型 df['words'] = df['words'].astype('category') # inplace = True,使 recorder_categories生效 df['words'].cat.reorder_categories(list_custom, inplace=True) # inplace = True,使 df生效 df.sort_values('words', inplace=True) df wordsnumber 1 b 2 0 a 1 2 c 3 指定list元素多的情况:若指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素多,怎么办? reorder_catgories()方法不能继续使用,因为该方法使用时要求新的categories和dataframe中的categories的元素个数和内容必须一致,只是顺序不同。 这种情况下,可以使用 set_categories()方法来实现。新的list可以比dataframe中元素多。 list_custom_new = ['d', 'c', 'b','a','e'] dict_new = {'e':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} df_new = pd.DataFrame(list(dict_new.items()), columns=['words', 'value']) print(list_custom_new) df_new.sort_values('words', inplace=True) df_new ['d', 'c', 'b', 'a', 'e'] wordsvalue 0 b 2 1 c 3 2 e 1 df_new['words'] = df_new['words'].astype('category') # inplace = True,使 set_categories生效 df_new['words'].cat.set_categories(list_custom_new, inplace=True) df_new.sort_values('words', ascending=True) wordsvalue 1 c 3 0 b 2 2 e 1 指定list元素少的情况:若指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素少,怎么办? 这种情况下,set_categories()方法还是可以使用的,只是没有的元素会以NaN表示注意下面的list中没有元素“b” list_custom_new = ['d', 'c','a','e'] dict_new = {'e':1, 'b':2, 'c':3} df_new = pd.DataFrame(list(dict_new.items()), columns=['words', 'value']) print(list_custom_new) df_new.sort_values('words', inplace=True) df_new ['d', 'c', 'a', 'e'] wordsvalue 0 b 2 1 c 3 2 e 1 df_new['words'] = df_new['words'].astype('category') # inplace = True,使 set_categories生效 df_new['words'].cat.set_categories(list_custom_new, inplace=True) df_new.sort_values('words', ascending=True) wordsvalue 0 NaN 2 1 c 3 2 e 1 总结根据指定的list所包含元素比Dataframe中需要排序的列的元素的多或少,可以分为三种情况: 相等的情况下,可以使用 reorder_categories和 set_categories方法; list的元素比较多的情况下, 可以使用set_categories方法; list的元素比较少的情况下, 也可以使用set_categories方法,但list中没有的元素会在DataFrame中以NaN表示。源代码 需要的童鞋可在微信公众号“Python数据之道”(ID:PyDataRoad)后台回复关键字获取视频,关键字如下: “2017-025”(不含引号) |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |