python数据可视化 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › bob的英文名叫什么 › python数据可视化 |
python数据可视化
腾讯云实验平台开春福利,100+门实验限免体验,精品实验享8折优惠! >>>
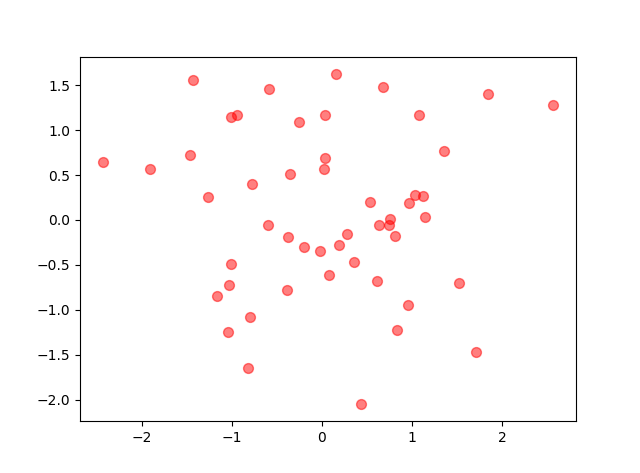
1.环境 系统:windows10 python版本:python3.6.1 使用的库:matplotlib,numpy 2.numpy库产生随机数几种方法 import numpy as np numpy.random rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)In [2]: x=np.random.rand(2,5) In [3]: x Out[3]: array([[ 0.84286554, 0.50007593, 0.66500549, 0.97387807, 0.03993009], [ 0.46391661, 0.50717355, 0.21527461, 0.92692517, 0.2567891 ]]) randn(d0, d1, ..., dn)查询结果为标准正态分布 In [4]: x=np.random.randn(2,5) In [5]: x Out[5]: array([[-0.77195196, 0.26651203, -0.35045793, -0.0210377 , 0.89749635], [-0.20229338, 1.44852833, -0.10858996, -1.65034606, -0.39793635]]) randint(low,high,size)生成low到high之间(半开区间 [low, high)),size个数据 In [6]: x=np.random.randint(1,8,4) In [7]: x Out[7]: array([4, 4, 2, 7]) random_integers(low,high,size)生成low到high之间(闭区间 [low, high)),size个数据 In [10]: x=np.random.random_integers(2,10,5) In [11]: x Out[11]: array([7, 4, 5, 4, 2]) 3.散点图 x x轴 y y轴 s 圆点面积 c 颜色 marker 圆点形状 alpha 圆点透明度 #其他图也类似这种配置 N=50 # height=np.random.randint(150,180,20) # weight=np.random.randint(80,150,20) x=np.random.randn(N) y=np.random.randn(N) plt.scatter(x,y,s=50,c='r',marker='o',alpha=0.5) plt.show()
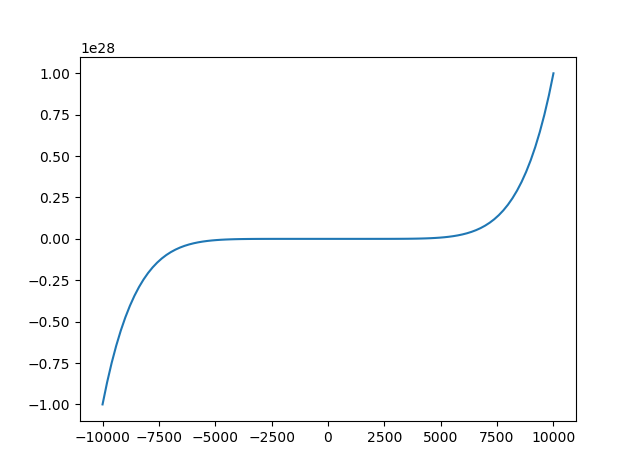
4.折线图 x=np.linspace(-10000,10000,100) #将-10到10等区间分成100份 y=x**2+x**3+x**7 plt.plot(x,y) plt.show()折线图使用plot函数
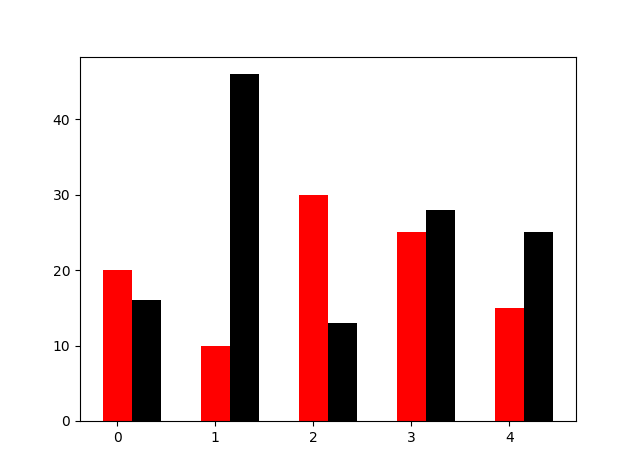
5.条形图 N=5 y=[20,10,30,25,15] y1=np.random.randint(10,50,5) x=np.random.randint(10,1000,N) index=np.arange(N) plt.bar(left=index,height=y,color='red',width=0.3) plt.bar(left=index+0.3,height=y1,color='black',width=0.3) plt.show()
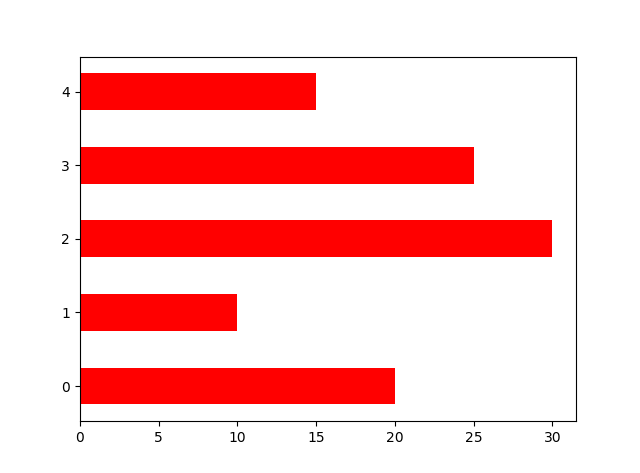
orientation设置横向条形图 N=5 y=[20,10,30,25,15] y1=np.random.randint(10,50,5) x=np.random.randint(10,1000,N) index=np.arange(N) # plt.bar(left=index,height=y,color='red',width=0.3) # plt.bar(left=index+0.3,height=y1,color='black',width=0.3) #plt.barh() 加了h就是横向的条形图,不用设置orientation plt.bar(left=0,bottom=index,width=y,color='red',height=0.5,orientation='horizontal') plt.show()
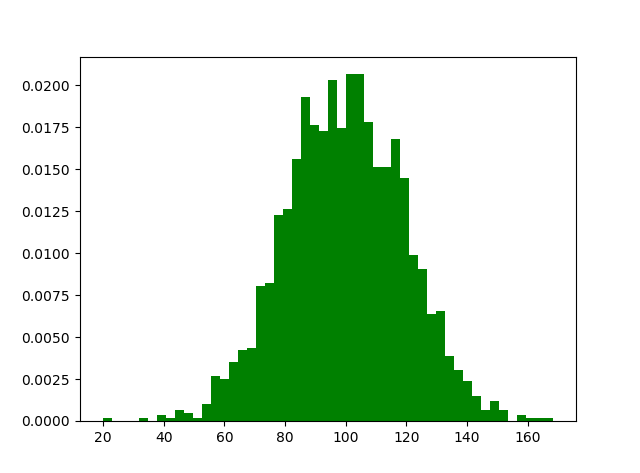
6.直方图 m1=100 sigma=20 x=m1+sigma*np.random.randn(2000) plt.hist(x,bins=50,color="green",normed=True) plt.show()
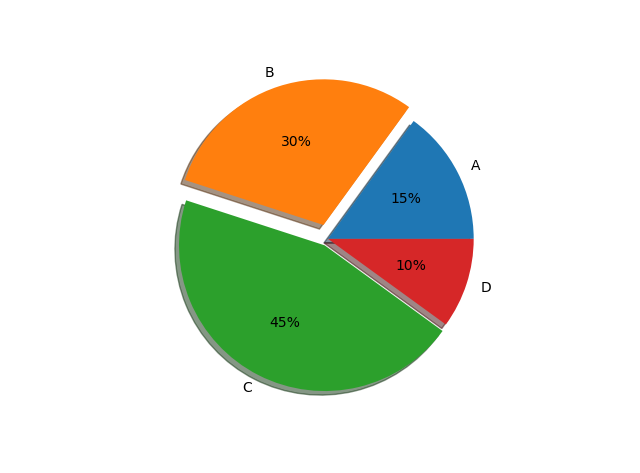
7.饼状图 #设置x,y轴比例为1:1,从而达到一个正的圆 #labels标签参数,x是对应的数据列表,autopct显示每一个区域占的比例,explode突出显示某一块,shadow阴影 labes=['A','B','C','D'] fracs=[15,30,45,10] explode=[0,0.1,0.05,0] #设置x,y轴比例为1:1,从而达到一个正的圆 plt.axes(aspect=1) #labels标签参数,x是对应的数据列表,autopct显示每一个区域占的比例,explode突出显示某一块,shadow阴影 plt.pie(x=fracs,labels=labes,autopct="%.0f%%",explode=explode,shadow=True) plt.show()
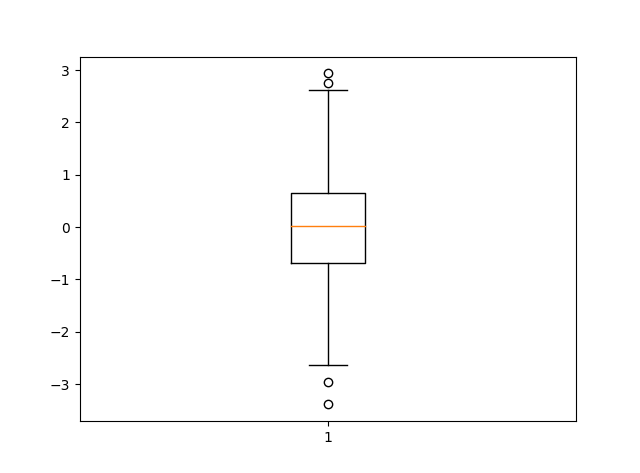
8.箱型图 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np data=np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=1000) #sym 点的形状,whis虚线的长度 plt.boxplot(data,sym="o",whis=1.5) plt.show() #sym 点的形状,whis虚线的长度
github地址:https://github.com/nanxung/python-.git 码云地址:https://git.oschina.net/nanxun/pythonshujukeshihuajiantu.git |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |