Shiro 登录认证源码详解 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 6realm › Shiro 登录认证源码详解 |
Shiro 登录认证源码详解
|
Shiro 登录认证源码详解
https://blog.csdn.net/w1196726224/article/details/53560385 Apache Shiro 是一个强大且灵活的 Java 开源安全框架,拥有登录认证、授权管理、企业级会话管理和加密等功能,相比 Spring Security 来说要更加的简单。 本文主要介绍 Shiro 的登录认证(Authentication)功能,主要从 Shiro 设计的角度去看这个登录认证的过程。 一、Shiro 总览首先,我们思考整个认证过程的业务逻辑: 获取用户输入的用户名,密码; 从服务器数据源中获取相应的用户名和密码; 判断密码是否匹配,决定是否登录成功。我们现在来看看 Shiro 是如何设计这个过程的:
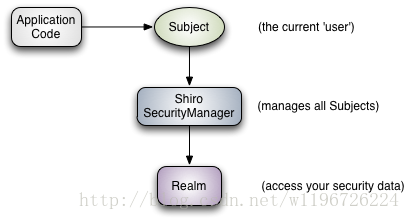
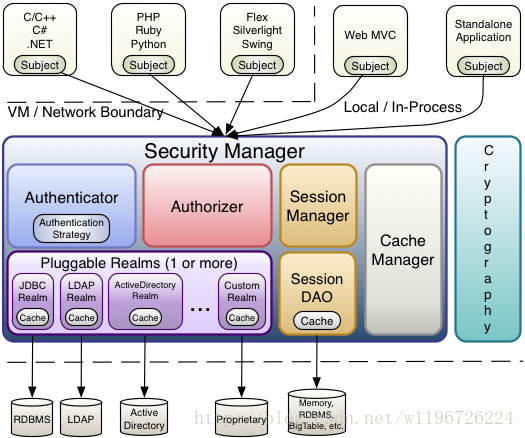
图中包含三个重要的 Shiro 概念:Subject、SecurityManager、Realm。接下来,分别介绍这三者有何用: Subject:表示“用户”,表示当前执行的用户。Subject 实例全部都绑定到了一个 SecurityManager 上,当和 Subject 交互时,它是委托给 SecurityManager 去执行的。 SecurityManager:Shiro 结构的心脏,协调它内部的安全组件(如登录,授权,数据源等)。当整个应用配置好了以后,大多数时候都是直接和 Subject 的 API 打交道。 Realm:数据源,也就是抽象意义上的 DAO 层。它负责和安全数据交互(比如存储在数据库的账号、密码,权限等信息),包括获取和验证。Shiro 支持多个 Realm,但是至少也要有一个。Shiro 自带了很多开箱即用的 Reams,比如支持 LDAP、关系数据库(JDBC)、INI 和 properties 文件等。但是很多时候我们都需要实现自己的 Ream 去完成获取数据和判断的功能。登录验证的过程就是:Subject 执行 login 方法,传入登录的「用户名」和「密码」,然后 SecurityManager 将这个 login 操作委托给内部的登录模块,登录模块就调用 Realm 去获取安全的「用户名」和「密码」,然后对比,一致则登录,不一致则登录失败。 Shiro 详细结构:
二、Shiro 登录示例 代码来自 Shiro 官网教程。Shiro 配置 INI 文件: # ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Users and their (optional) assigned roles # username = password, role1, role2, ..., roleN # ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- [users] wang=123 1 2 3 4 5 6测试 main 方法: public static void main(String[] args) { log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application"); //1.从 Ini 配置文件中获取 SecurityManager 工厂 Factory factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); //2.获取 SecurityManager 实例 SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); //3.将 SecurityManager 实例绑定给 SecurityUtils SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //4.获取当前登录用户 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //5.判断是否登录,如果未登录,则登录 if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) { //6.创建用户名/密码验证Token(Web 应用中即为前台获取的用户名/密码) UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("wang", "123"); try { //7.执行登录,如果登录未成功,则捕获相应的异常 currentUser.login(token); } catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal()); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) { log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!"); } catch (LockedAccountException lae) { log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " + "Please contact your administrator to unlock it."); } // ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application? catch (AuthenticationException ae) { //unexpected condition? error? } } } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 三、登录逻辑详解Shiro 登录过程主要涉及到 Subject.login 方法,接下来我们将通过查看源码来分析整个登录过程。 创建 AuthenticationToken 接口的实例 token,比如例子中的 UsernamePasswordToken,包含了登录的用户名和密码; 获取当前用户 Subject,然后调用 Subject.login(AuthenticationToken) 方法; Subject 将 login 代理给 SecurityManager 的 login() 3.1 创建AuthenticationToken第一步是创建 AuthenticationToken 接口的身份 token,比如例子中的 UsernamePasswordToken。 package org.apache.shiro.authc; public interface AuthenticationToken extends Serializable { // 获取“用户名” Object getPrincipal(); // 获取“密码” Object getCredentials(); } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 3.2 获取当前用户并执行登录获取的 Subject 当前用户是我们平时打交道最多的接口,有很多方法,但是这里我们只分析 login 方法。 package org.apache.shiro.subject; public interface Subject { void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException; } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7login 方法接受一个 AuthenticationToken 参数,如果登录失败则抛出 AuthenticationException 异常,可通过判断异常类型来知悉具体的错误类型。 接下来,分析 Subject 接口的实现类 DelegatingSubject 是如何实现 login 方法的: public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); // 代理给SecurityManager Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token); ... } 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.3 SecurityManager 接口前面说过,整个 Shiro 安全框架的心脏就是 SecurityManager,我们看这个接口都有哪些方法: package org.apache.shiro.mgt; public interface SecurityManager extends Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager { Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException; void logout(Subject subject); Subject createSubject(SubjectContext context); } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10SecurityManager 包含很多内置的模块来完成功能,比如登录(Authenticator),权限验证(Authorizer)等。这里我们看到 SecurityManager 接口继承了 Authenticator 登录认证的接口: package org.apache.shiro.authc; public interface Authenticator { public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException; } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7那么,SecurityManager 的实现都是怎样来实现 Authenticator 接口的呢?答案是:使用了组合。SecurityManager 都拥有一个 Authenticator 的属性,这样调用 SecurityManager.authenticate 的时候,是委托给内部的 Authenticator 属性去执行的。
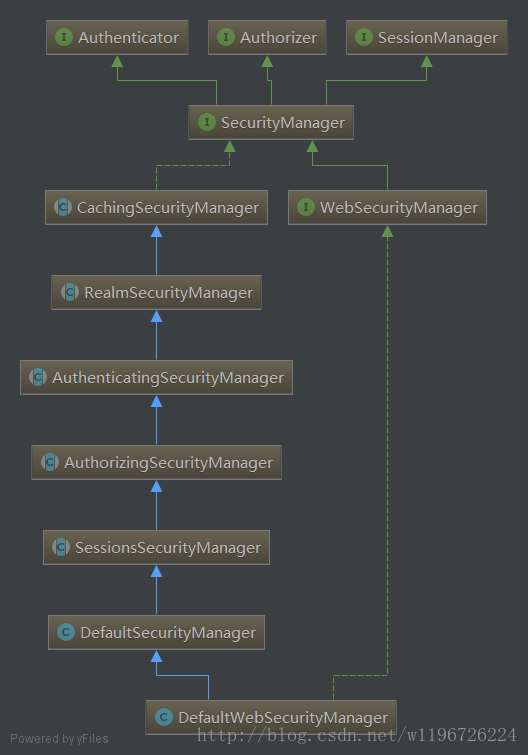
3.4 SecurityManager.login 的实现 // DefaultSecurityManager.java public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try { info = authenticate(token); } catch (AuthenticationException ae) { try { onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " + "exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e); } } throw ae; //propagate } Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject); onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); return loggedIn; } // AuthenticatingSecurityManager.java /** * Delegates to the wrapped {@link org.apache.shiro.authc.Authenticator Authenticator} for authentication. */ public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { return this.authenticator.authenticate(token); } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 调用自己的 authenticate 方法执行登录; 在 authenticate 方法中代理给 Authenticator 接口类型的属性去真正执行 authenticate(token) 方法。 3.5 Authenticator 登录模块 Authenticator 接口如下: package org.apache.shiro.authc; public interface Authenticator { public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException; } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7其实现类有 AbstractAuthenticator 和 ModularRealmAuthenticator:
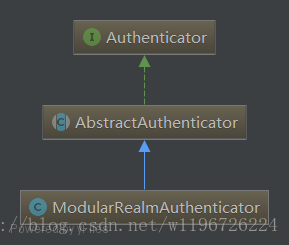
下面来看看如何实现的 authenticate 方法: // AbstractAuthenticator.java public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { AuthenticationInfo info; try { // 调用doAuthenticate方法 info = doAuthenticate(token); if (info == null) { ... } } catch (Throwable t) { ... } ... } // ModularRealmAuthenticator.java protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { assertRealmsConfigured(); Collection realms = getRealms(); if (realms.size() == 1) { // Realm唯一时 return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken); } else { return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken); } } protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) { if (!realm.supports(token)) { ... } // 调用Realm的getAuthenticationInfo方法获取AuthenticationInfo信息 AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token); if (info == null) { ... } return info; } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38从源码中可以看出,最后会调用 Realm 的 getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken) 方法。 3.6 Realm 接口Realm 相当于数据源,功能是通过 AuthenticationToken 获取数据源中的安全数据,这个过程中可以抛出异常,告诉 shiro 登录失败。 package org.apache.shiro.realm; public interface Realm { // 获取 shiro 唯一的 realm 名称 String getName(); // 是否支持给定的 AuthenticationToken 类型 boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token); // 获取 AuthenticationInfo AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException; } 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13Shiro 自带了很多开箱即用的 Realm 实现,具体的类图如下:
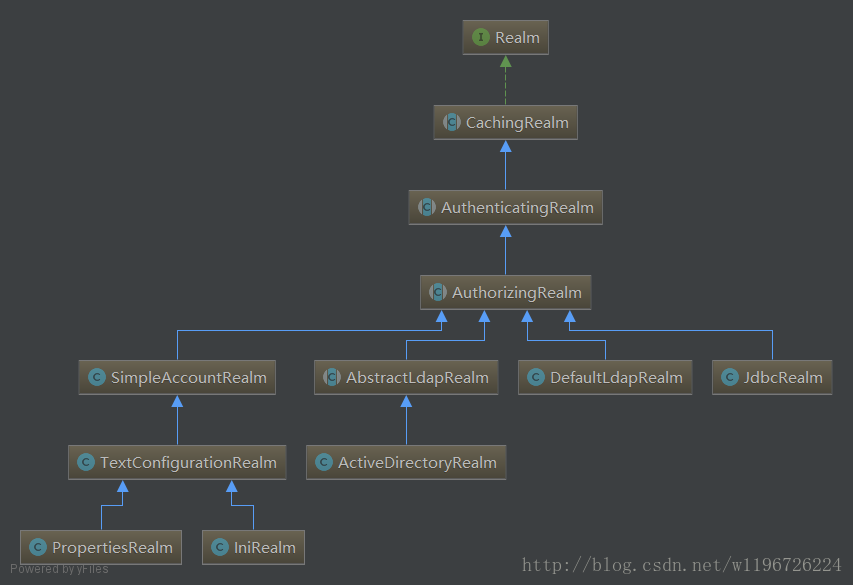
3.7 总结 到此,我们把整个 Shiro 的登录认证流程分析了一遍。 创建 AuthenticationToken,然后调用 Subject.login 方法进行登录认证; Subject 委托给 SecurityManager; SecurityManager 委托给 Authenticator 接口; Authenticator 接口调用 Realm 获取登录信息。整个过程中,如果登录失败,就抛出异常,是使用异常来进行逻辑控制的。 四、登录密码的存储 页面使用 Https 协议; 页面传送密码时要先加密后再传输,最好是不可逆的加密算法(MD5,SHA2); 后端存储时要结合盐(随机数)一起加密存储; 使用不可逆的加密算法,而且可以加密多次; 把加密后的密码和盐一起存储到数据库; 五、学习 Shiro 源码感悟 从整体去思考框架的实现,带着业务逻辑去看实现逻辑; 不要抠细节,要看抽象,学习其实现方法; 首先看官方文档,官方文档一般会从整体设计方面去说明,遇到具体的接口再去看Javadoc文档; 结合类图等工具方便理解; 六、参考 Apache Shiro 跟我学Shiro目录贴 |
【本文地址】