深度好文|钛及钛合金表面涂层制备方法研究现状 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 142mm钛膜 › 深度好文|钛及钛合金表面涂层制备方法研究现状 |
深度好文|钛及钛合金表面涂层制备方法研究现状
|
图1熔覆层的SEM形貌 [15]Fig.1SEM of cladding layer[15]
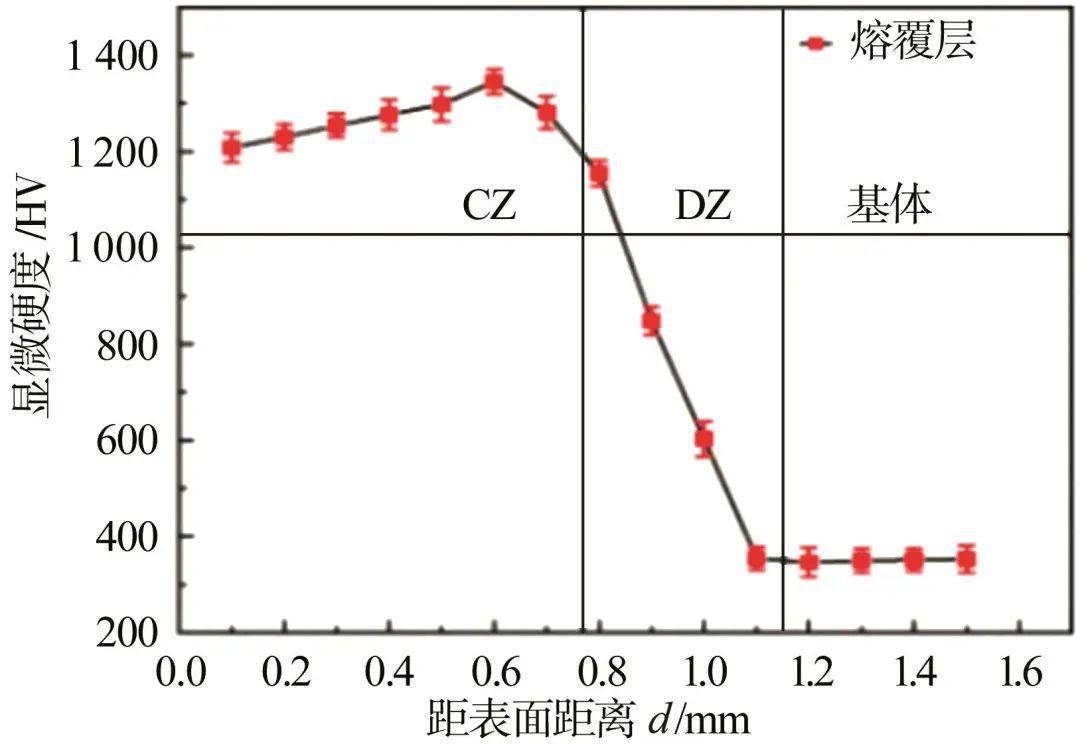
图2显微硬度分布曲线[15]Fig.2Microhardness distribution curves[15]
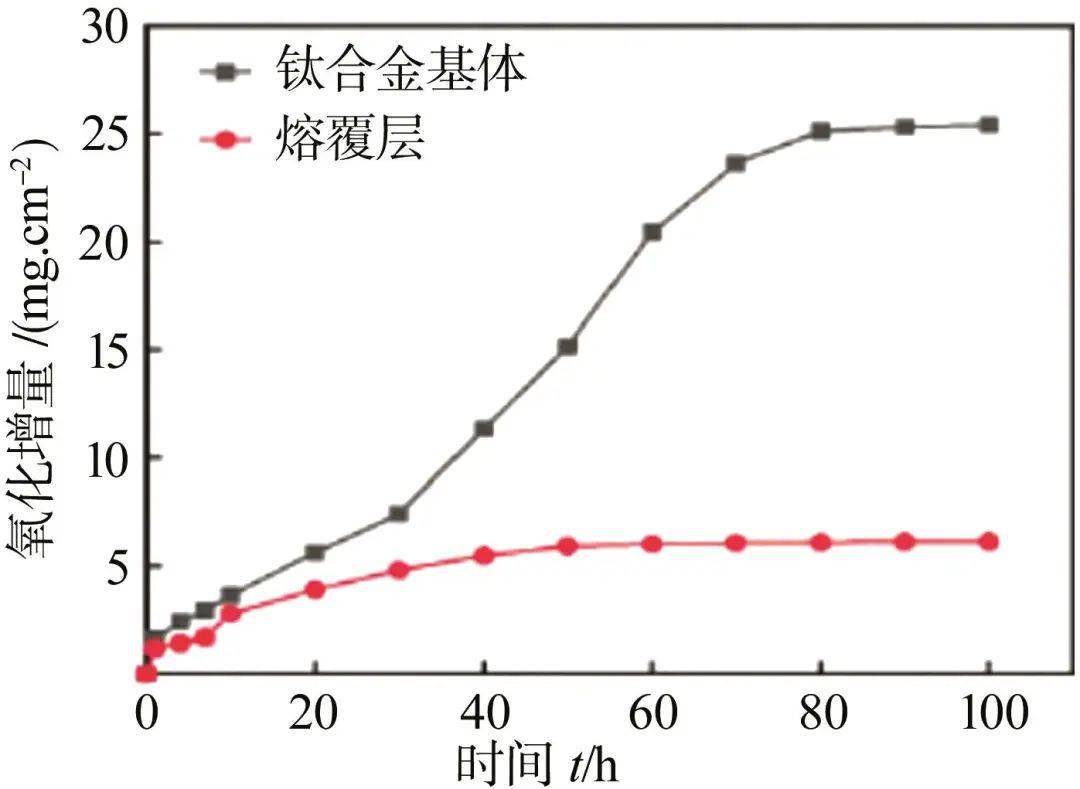
图3850 ℃的氧化动力学曲线[15]Fig.3Oxidation kinetics curves of 850 ℃[15] 在激光熔覆过程中外加法的陶瓷材料的涂层与钛合金基体结合力不高,容易开裂,产生孔洞等问题[18-19 ]。其主要原因首先是陶瓷颗粒与基体钛合金的热膨胀系数等物理性能相差较大,导致涂层存在较大的残余应力;其次从材料的键合方式角度分析,钛合金键合方式为金属键,而陶瓷材料的结合方式为共价键或离子键,钛合金和陶瓷材料的晶体结构也不相同,因此钛合金与陶瓷材料之间的相容性差。另外激光熔覆属于快热和快冷的过程,涂层内部会产生较大的拉应力,残余拉应力超过涂层材料的抗拉强度时即开裂。 安强[20]在TA15钛合金表面激光熔覆原位合成TiC增强钛基复合涂层。研究发现,整个涂层组织由平面晶、柱状晶、树枝晶和等轴晶组成;由XRD分析可知,涂层主要由β-Ti、Co3Ti、CrTi4和原位自生的TiC物相组成,涂层与基体形成了良好的冶金结合;涂层的显微硬度最高值为715 HV,约为TA15 基体显微硬度的2.1倍(见图4 );涂层具有较好的抗磨性能,磨损机制为磨粒磨损。利用原位合成陶瓷材料的方法即通过化学反应生成陶瓷涂层,增强相与基体结合界面干净,结合力较大,不容易脱落。但是化学反应过程无法控制,会有有害杂质的生成相[21]。所以原位自生法制备陶瓷涂层如何精确调控反应过程,是未来研究的重点。
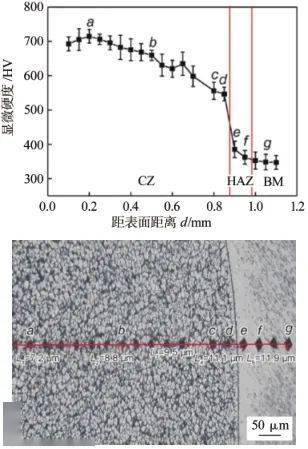
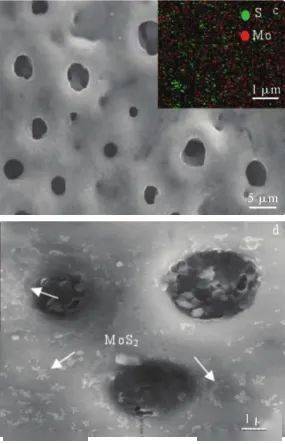
图4激光熔覆各微区的显微硬度分布和压痕的金相形貌[18] Fig.4Microhardness distribution curve of each zone in the coating and metallographic morphology of some coating indentation 激光熔覆技术经历了从单层熔覆层,到多层熔覆层、复合熔覆层以及梯度涂层研究的发展过程,随着技术的不断研究改进,出现了许多新型激光熔覆技术[22],例如环形激光熔覆技术。该技术是一项利用中空环形的聚焦高能激光束和光内输送的熔覆材料同轴耦合作用于基体表面的典型材料沉积加工技术,具有扫描方向不受限、熔覆材料种类多、材料利用率高和熔覆过程可干预性强等优点,与传统激光熔覆技术相比,其在激光能量利用率、熔覆材料沉积率、光料耦合精度、熔覆过程稳定性及熔覆层结合质量等方面均有大幅提升,在激光金属沉积领域有着巨大的发展潜力,因此备受关注[23]。在钛合金表面利用该方法制备熔覆层目前未见报道,学者可以开展此方面的研究工作。 激光熔覆在钛合金表面熔覆材料发展潜力较大,但是目前没有工业化生产,未来的发展主要在以下方面[10-11 ]:开发宽域的新型陶瓷熔覆材料体系;涂层的形成过程、形成机制的调控;熔覆涂层的裂纹和缺陷的控制。 2微弧氧化技术 微弧氧化技术是在阳极氧化基础上发展起来的表面改性技术。钛合金微弧氧化(MAO)[24]是一种在钛及钛合金表面原位生长成氧化物陶瓷膜,这种陶瓷膜与基体结合强度高,可以提升钛合金的抗磨损、耐腐蚀和绝缘性[25]。钛及钛合金微弧氧化是将Ti、Mg、Al等金属置于电解液中,在电源作用下基体表面产生放电出现高温、高压;在高温高压作用下基体表面熔化与游离离子相互作用,然后进行氧化、融合,最后在金属表面沉积成膜[26-30 ]。 李玉海[31]等通过微弧氧化方法分别向电解液中添加陶瓷颗粒SiC和SiO2在TC4钛合金表面制备复合陶瓷膜。氧化膜表面孔洞微小,膜层致密性较高,陶瓷膜组织主要有α-SiC和β-SiC相,SiO2颗粒的添加使得膜层摩擦系数波动平稳且波动范围仅在0.15~0.2。相同实验条件下添加SiC颗粒的陶瓷膜耐磨性比未添加陶瓷颗粒的耐磨性提高75%,而含有SiO2颗粒的膜层相对基体提高130%。在摩擦磨损实验过程中,添加SiC颗粒的陶瓷膜表面仅有轻微犁沟痕迹,含有SiO2的膜层表面磨损最轻微,只出现粘着磨损的痕迹,膜层耐磨性能均得到提升。 解念锁[32]等在Na2SiO3、Na3PO4电解液中对TC4表面进行微弧氧化制备抗氧化膜层。微弧氧化膜层的SEM形貌细小、均匀、多孔,主要由Al2SiO5和Al2TiO5组成,在750 ℃循环氧化100 h后,经300 V电压微弧氧化60 min的TC4钛合金的氧化增重为7.8 mg/cm2,而未经微弧氧化处理的TC4钛合金氧化增重为30.51 mg/cm2。并且随着微弧氧化时间的增加和电压的增大,微弧氧化TC4钛合金的高温抗氧化性能也有所增强。 杨泽慧[33]等人在TC4合金表面微弧氧化原位自生自润滑MoS2/TiO2膜层(见图5 ),讨论了原位反应中Na2S添加量对膜层微观结构及耐磨性能的影响。通过控制Na2S浓度可实现原位生成小尺寸MoS2颗粒,且其含量和形态可控,原位自生MoS2膜层的耐磨性较传统微弧氧化膜层或直接添加MoS2颗粒所得膜层分别提高了395.4%、129.4%;膜基结合力较传统微弧氧化提高了约87%,达到723.8 N,说明原位自生微弧氧化在保证良好的自润滑效果的同时改善了膜基结合力。
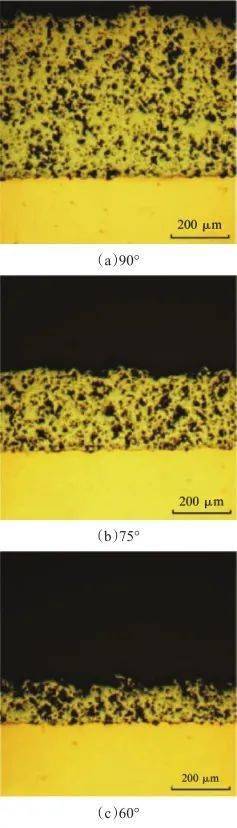
图5微弧氧化复合膜层表面形貌和能谱分析及MoS2在膜层表面存在的形态[33] Fig.5Surface morphology and EDS of micro-arc oxidation composite coating and morphology of MoS2 on the surface of coating[33] 微弧氧化技术的研究已经历了几十年的发展历程,从交流微弧氧化技术到现在较为热门的激光复合微弧氧化技术[34]。Wang等[35]将TC4钛合金进行激光表面重熔、微弧氧化处理,得到多孔生物陶瓷涂层。通过激光表面重熔预处理降低基材的表面粗糙度,提高微弧氧化涂层的均匀性和密度,同时减少厚度,与未处理的样品相比具有最佳的耐腐蚀性,表面粗糙度最低,孔隙率较低。 钛合金微弧氧化也存在急需解决的技术问题:(1)单位面积耗能较大;(2)氧化膜的膜基结合问题;(3)膜层多孔问题,影响基材的耐蚀性。 3喷涂 喷涂技术是在不改变基体其他性能的条件下,通过某种热源或者动力源将材料形成高速粒子流,喷向基体上不断沉积形成具有一定功能的涂层[36],其特点是工艺简便、应用范围较广[37-39 ]。近年来,研究人员在传统喷涂技术基础上发展出超音速火焰喷涂、超音速等离子喷涂、反应热喷涂和冷喷涂等工艺[40-42 ]。 钛合金的氧活性很高,传统的热喷涂技术不适合制备钛及钛合金涂层;冷喷涂作为新兴的喷涂技术由于制备温度低、涂层沉积率较高、孔隙率低和结合强度较高等特点,在钛合金表面制备涂层具有独特优势[43-50 ]。因为冷喷涂主要是高速飞行的粒子在撞击基体时发生严重的塑性变形,从而实现涂层沉积,对于金属材料来讲,面心立方金属的Al、Cu等滑移系较多,较易发生塑性变形,而对于密排六方金属的Ti、Co等,滑移系统较少、塑性较差[51]。李文亚等[52]以空气为喷涂气体,在气体温度520 ℃、压力2.8 MPa的条件下,制备了纯钛和钛合金涂层,发现两种涂层的孔隙率分别高达5.1%和22.4%,而孔隙往往存在于有限变形的粒子之间,所以影响了涂层性能。 近年来,国内外学者从喷涂参数、粉末状态、喷嘴及基体等不同方面对冷喷涂钛及钛合金涂层进行了组织调控。李海升[53]等在TC4钛合金表面冷喷涂制备CuNiIn涂层,研究其组织结构和微动磨损性能,涂层的孔隙率仅为2.8%,最高硬度可达到300 HV,磨损机理为粘着磨损和磨粒磨损。李长久等[54]分别采用N2和He两种气体作为喷涂气体制备了Ti涂层,结果表明,用惰性气体He制备的涂层其组织更加致密,主要原因是在He条件下粒子能获得更大的速度,从而发生更充分的变形。Pelletier J L等[55]研究发现喂料速度和粉末流动速度越高,涂层孔隙率越高,厚度越厚,其原因可能是低的喂料速度能够减小后面粒子与先沉积涂层的撞击角度,而粉末流动速度会对喷嘴中的气流产生影响。Zahiri S H等[56]研究了喷涂距离对Ti涂层质量的影响,发现喷涂距离主要影响粒子速度,喷涂距离增大,粒子速度减小,导致塑性变形小,随着喷涂距离的增大,涂层孔隙率上升。殷硕等[57]研究了喷涂角度对冷喷涂Ti粒子沉积行为的影响,认为喷射角度为非垂直角度时,粒子与基体的结合会减弱(见图6 )。综合来看,对于钛与钛合金涂层而言,尽可能采用高的气体温度和压力可以有效提高粒子速度,进而制备出高质量涂层。
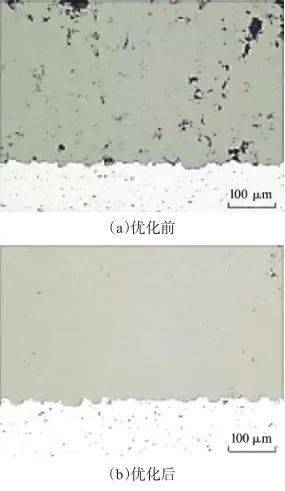
图6不同角度沉积在Cu基体上的Ti涂层的横截面金相组织[57] Fig.6Cross-sectional OM micrographs of the Ti coating deposited on the Cu substrate at different spray-angles[57] 除了粉末材质外,冷喷涂的粉末形状对喷涂质量也有影响。Wong W[58]等采用不规则形和球形两种不同形状的Ti粉制备冷喷涂涂层,研究结果表明,粒子的粉末不规则,制备的涂层致密性较好,主要是不规则粒子的拖曳常数较高,在喷嘴出口处可获得更高的粒子速度,所以与基体的结合力较好,而不规则粉末的流动性不如球形粉,喷涂过程中容易氧化[59-61]。Cinca N[62]等研究认为当粒子分布较窄时,涂层的孔隙、厚度和硬度更为均匀。 除粉末材料和形态外,喷嘴结构对冷喷涂涂层质量也有明显影响,图7 为喷嘴优化前后制备的Ti涂层,可以看出改善后涂层组织明显致密[63]。李文亚[64]等通过改善喷嘴内部形状实现了在低压下高的粒子温度。MACDONALD D[65]改变喷嘴材质,发现高热导率的喷嘴可以降低粒子的临界速度,从而实现更高的沉积效率。
图7喷嘴优化前后Ti涂层的横截面[61] Fig.7Cross-sections of Ti coatings pre-optimized nozzle optimized nozzle[61] 冷喷涂中涂层与基体以及涂层内部的机理主要是机械咬合和冶金结合,冶金结合的程度越高,结合强度越好,通过喷涂后热处理可以进一步提高其冶金结合程度。李文亚等[66]在850 ℃真空气氛下将Ti和Ti6A14V涂层进行退火4 h,发现退火过程中粒子之间的接触界面通过原子扩散和晶界迁移发生了冶金结合,但涂层的孔隙率统计结果表明,热处理后两种涂层的孔隙率均有所增加。 周红霞[51]研究了Ti6A14V涂层在后续热处理过程中孔隙的演变规律,结果表明,在局部热处理温度下涂层的孔隙率有所增加,原因是喷涂层热处理过程中残余应力得以释放,部分弱结合和未结合的粒子界面相互脱离引起的。 目前,喷涂对钛合金涂层研究相对较少,多数为喷涂Ti涂层。对喷涂工艺研究较多,对涂层形成过程、粒子内部显微结构研究较少。由于喷涂涂层与基体的结合力较弱,所以应用受到限制,喷涂后的热处理是提高其结合力的有效途径。对于冷喷涂技术与其他技术如激光熔覆、搅拌摩擦焊等的融合是未来的研究趋势。 4结论及展望 (1)激光表面改进技术在钛合金表面可以通过有限元软件和数学建模模拟熔覆过程,或者结合超声波辅助激光熔覆等方式,研发宽域的新型陶瓷熔覆材料体系、功能梯度涂层等以减少裂纹等缺陷。 (2)对于钛合金微弧氧化技术,能源消耗巨大、膜层易脱落和膜层多孔现象是急需解决的问题,需要通过进一步研究以提高钛合金微弧氧化膜层的性能。 (3)冷喷涂技术与其他技术如激光熔覆、搅拌摩擦焊等的融合是未来的研究方向。 在先进科学技术的高速发展背景下,钛及钛合金应用领域日益扩展,对钛合金表面性能的要求越来越高,随着这些使用条件的变化钛合金表面改性技术也必将日臻完善。 1.王欣, 罗学昆, 宇波, 等. 航空航天用钛合金表面工程技术研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2022, 65(04): 14-24. Wang Xin, Luo Xuekun, Yu Bo, et al. Research Progress on Surface Engineering Technology of Aerospace Titanium Alloys[J]. Aeronautical manufacturing technology, 2022, 65(04): 14-24. 2.李兴宇,李芳,牟刚,等. 钛及钛合金的焊接[J]. 电焊机,2017,47(04):67-70,107. LI Xingyu,LI Fang,MOU Gang,et al. Welding of titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Electric Welding Machine,2017,47(04):67-70,107. 3.李芳婷, 王恺婷, 李春波, 等. 钛及钛合金表面增强技术的研究进展[J]. 世界有色金属, 2021(16): 109-110. Li Fangting, Wang Kaiting, Li Chunbo, et al. Research Progress of Surface Strengthening Technology of Titanium and Titanium Alloys[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2021(16): 109-110. 4.陈钢. 钛及钛合金新工艺、新技术、新用途介绍[J]. 中国金属通报, 2018(01): 160-161. Chen Gang. Introduction of New Processes, New Technologies and New Uses of Titanium and Titanium Alloys[J]. China Metals Bulletin, 2018(01): 160-161. 5.高飞. 钛及钛合金材料的焊接技术[J]. 石油化工建设, 2006(04): 38-42. Gao Fei. Welding Technology for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Materials[J]. Petroleum and Chemical Construction, 2006(04): 38-42. 6.姜海涛, 邵忠财, 魏守强. 钛合金表面处理技术的研究进展[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2010, 32(10): 15-20. Jiang Haitao, Shao Zhongcai, Wei Shouqiang. Research Progress of Surface Treatment Techniques for Titanium Alloys[J]. Plating and Finishing,2010,32(10):15-20. 7.王迪, 林松盛, 刘灵云, 等. 表面处理技术对钛合金疲劳性能影响的研究进展[J]. 真空, 2019, 56(06): 36-42. Wang Di, Lin Songsheng, Liu Lingyun, et al. Research Progress of Surface Treatment Technology on Fatigue Properties of Titanium Alloy[J].Vacuum,2019,56(06): 36-42. 8.郭小汝, 陈百明, 贾金龙, 等. 处理方法对钛合金摩擦磨损性能影响的研究进展[J]. 粉末冶金工业,2021,31(02): 97-103. Guo Xiaoru, Chen Baiming, Jia Jinlong, et al. Research Progress on Friction and Wear Properties of Titanium Alloys by Treatment Methods[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2021, 31(02): 97-103. 9.Alexander Donchev, Michael Schütze, Andreas Kolit-sch. Economic Surface Treatment of Ti-Alloys to Improve their Resistance against Environmental High Te-mperature Attack[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2013,2362:551. 10.林基辉,温亚辉,范文博, 等. 钛合金表面激光改性技术研究进展[J]. 金属热处理, 2022,47(3):215-221. Lin Jihui, Wen Yahui, Fan Wenbo, et al. Research Progress of Laser Modification Technology for Titanium Alloy Surface[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(3): 215-221. 11.路世盛,周健松,王凌倩,等.钛合金表面激光熔覆陶瓷涂层的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2019, 48(11):82-91. Lu Shisheng, Zhou Jiansong, Wang Lingqian, et al. Development of Laser Cladding Ceramic Coatings on Titanium Alloy Surface[J]. Surface Technology, 2019,48(11): 82-91. 12.武万良, 李学伟. 钛合金激光熔覆技术研究进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006(06): 850-854. Wu Wanliang, Li Xuewei. Research Progresses on Laser Cladding of Titanium Alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2006(06): 850-854. 13.王超, 赵铁栓, 韩高阳, 等. 激光熔敷技术应用于新品制造的研究[J]. 建设机械技术与管理, 2017, 30(08): 79-82. Wang Chao, Zhao Tiezhu, Gaoyang Han, et al. Apply the Laser Cladding Technology to the New Product Manufacturing[J]. Construction Machinery Technology & Management, 2017, 30(08): 79-82. 14.吴影,刘艳,陈文静,等.超高速激光熔覆技术研究现状及其发展方向[J]. 电焊机,2020,50(03):1-10. WU Ying,LIU Yan,CHEN Wenjing,et al. Research status and development direction of extreme high-speed laser material deposition[J]. Electric Welding Machine,2020, 50(03):1-10. 16.SHAKTI K,AMITAVA M, DAS A K,et al. Parametric study and characterization of A1N-Ni-Ti6A14V composite cladding on titanium a11oy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2018,349: 37-49. 17.覃鑫, 祁文军, 左小刚. TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2复合涂层的摩擦和高温抗氧化性能[J]. 材料工程, 2021, 49(12): 107-114. Qin Xin, Qi Wenjun, Zuo Xiaogang. Friction and High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Laser Cladding NiCrCoAIY-Cr3C2 Composite Coating on TC4 Titanium Alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2021, 49(12): 107-114. 18.YANG C, CHENG X, TANG H B, et al. Influence of microstructures and wear behaviors of the microalloyed coatings on TC11 alloy surface using laser cladding technique[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2017,337(4):97-103. 19.ZHAO G L, ZOU Y, ZOU Z D, et al. Research on in situ synthesised (Ti,V)C/Fe composite coating by laser cladding[J].Materials Science & Technology,2014,31(11):1329-1334. 20.安强, 祁文军, 左小刚. TA15钛合金表面原位合成TiC增强钛基激光熔覆层的组织与耐磨性[J]. 材料工程,2022,55(4):139-146. An Qiang, Qi Wenjun, Zuo Xiaogang. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of In- situ TiC reinforced Ti- based Coating by Laser Cladding on TA15 Titanium Alloy Surface[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2022,55(4):139-146. 21.刘丹. TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆复合涂层及耐磨性能研究[D]. 湖南:南华大学,2015. Liu Dan. The Resea Rch of Laser Cladding Composite Coaying and Wear-resistance on TC4 alloy[D]. Hunan: University of South China, 2015. 22.苏猛. 环形件激光熔覆再制造研究[D]. 河北:燕山大学, 2016. Su Meng. Research on High-power Semiconductor Laser Cladding Circular Workpieces Remanufa Cturing[D]. Hebei:Yanshan University, 2016. 24.牛宗伟,李明哲. 钛合金微弧氧化技术的研究进展[J]. 电镀与环保, 2015(1): 1-4. Niu Zongwei, Li Mingzhe. Research Progress of Micro-arc Oxidation Technology for Titanium Alloy[J]. Electroplating & Pollution Control,2015(1):1-4. 25.Yang W, Xu D P, Wang J L, et al. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of micro arc oxidation plus electrostatic powder spraying composite coating on magnesium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2018,136:174-179. 27.董凯辉,宋影伟,韩恩厚. 钛合金内膜微弧氧化制备技术的研究进展[J]. 表面技术,2021, 50(7):57-66. Dong Kaihui, Song Yingwei, Han Enhou. Research Progress on the Preparation of Wear-resistant Micro-arc Oxidation Coatings on Titanium Alloys[J]. Surface Technology,2021, 50(7):57-66. 28.陈宏,丁健,陈永楠,等. 钛合金微弧氧化生物膜制备与性能研究[J]. 表面技术, 2021(50):45-51. Chen Hong, Ding Jian, Chen Yongnan, et al. Study on Preparation and Properties of Micro-arc Oxidation Biofilm on Titanium Alloy[J]. Surface Technology, 2021(50): 45-51. 29.Shuo-Jen L, Le H, Toan D. Effects of copper additive on microarc oxidation coating of LZ91 magnesium-lithium alloy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2016, 307: 781-789. 30.Chen Q Z, Jiang Z Q, Tang S G, et al. Influence of graphene particles on the micro-arc oxidation behaviors of 6063 aluminum alloy and the coating properties[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 423: 939-950. 32.解念锁, 武立志. 微弧氧化对TC4钛合金高温抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 铸造技术, 2012, 33(04): 416-418. Xie Niansuo, Wu Lizhi. Effects of Micro-arc Oxidation on High-temperature Oxidation Resistance of TC4 Titanium Alloy[J]. Foundry Technology, 2012, 33(04):416-418. 36.Kamal S, Jayaganthan R, Prakash S. Evaluation of cyclic hot corrosion behaviour of detonation gun sprayed Cr3C2-25%NiCr coatings on nickel- and iron-based superalloys[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2009, 203(8): 1004-1013. 37.Hsiung J C, Tzeng J, Kung K. A Study of Thermal Spray Coating on Artificial Knee Joints[J]. Life Science Journal, 2013, 10(2): 457-463. 38.Huang J, Liu Y, Yuan J H. Al/Al2O3Composite Coating Deposited by Flame Spraying for Marine Applications:Alumina Skeleton Enhances Anti-Corrosion and Wear Performances[J]. Journal of thermal spray technology, 2014, 23(4): 676-683. 39.Wu Y Z, Zhang D. Electrochemical corrosion behaviors and microhardness of laser thermal sprayed amorphous AlCrNi coating on S275JR steel[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2019, 118: 115-120. 40.李长久. 热喷涂技术应用及研究进展与挑战[J]. 热喷涂技术, 2018,10(04): 1-22. Li Changjiu. Applications,Research Progresses and Future Challenges of Thermal Spray Technology[J]. Thermal Spray Technology, 2018, 10(04): 1-22. 41.Huang J, Liu Y, Yuan J H. Al/Al2O3Composite Coating Deposited by Flame Spraying for Marine Applications:Alumina Skeleton Enhances Anti-Corrosion and Wear Performances[J]. Journal of thermal spray technology, 2014, 23(4): 676-683. 42.Bonabi S F, Ashrafizadeh F, Sanati A N, et al. Structure and Corrosion Behavior of Arc-Sprayed Zn-Al Coatings on Ductile Iron Substrate[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2018, 27(3): 524-537. 43.李长久. 中国冷喷涂研究进展[J]. 中国表面工程,2009, 22(4):5-14. Li Changjiu. The State-of-art of Research and Development on Cold Spraying in China[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2009, 22(4):5-14. 44.HASSANI-GANGATAJ S M,MORlDl A, GGAGLIA-NO M. Critical review of corrosion protection by cold spray coatings[J]. Surface Engineering, 2015,31(11):803-815. 46.MENG X,ZHANG J,ZHAO J,et al. In fluence of gas temperature on microstructure and properties of cold spray 304SS coating[J]. Joumal of Materials Science & Technology, 2011, 27(9): 809-815. 47.KARTHIKEYAN, YAN J. The advantages and disadvantages of the cold spray coating process[J]. Cold Spray Materials Deposition Process, 2007: 62-71. 48.HGSSAIN T, MCCAARTNEY D G, SHIPWAY P H, et al. Corrosion behavior of cold sprayed titanium coatings and free standing deposits[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray feclmology, 2010, 20(1-2):260-274. 49.KHUN W, TAN A W Y, BI K U W,et al. Effects of working gas on wear and corrosion resistances of cold sprayed Ti-6A1-4V coatings[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2016,302:1-12. 50.GHELICHI R, GUAGLIANO M. Coating by the cole sparay process:A state of the art[J]. Frattura ed Integrita Sturtturale, 2009, 3(8): 30-44. 51.周红霞,李成新,李长久. 冷喷涂制备钛及钛合金涂层研究进展[J]. 中国表面工程, 2020, 33(2): 1-14. Zhou Hongxia, Li Chengxin, Li Changjiu. Research Progress of Cold Sprayed Ti and Ti Alloy Coatings[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2020, 33(2):1-14. 53.李海升, 刘坤, 李文亚, 等. TC4钛合金表面冷喷涂制备CuNiIn涂层组织及其微动磨损性能研究[J]. 材料保护, 2022, 55(1): 22-27. LI Hai-sheng, LIU Kun, LI Wen-ya, et al.Microstructure and Fretting Wear Properties of CuNiIn Coating Prepared by Cold Spraying on Surface of TC4 Titanium Alloy[J]. Material Protection, 2022, 55(1): 22-27. 54.Ll C J,Ll W Y. Deposition characteristics of titanium coating in cold spraying[J]. Surface&Coatings Technology, 2003, 167(2-3): 278-283. 55.PELLETIER J L. Development of Ti-6Al-4V Coaring ontoTi-6Al-4V substrate using low pressure cold spray and pulse gas dynamic spray[M]. Gniversity of Ottawa, 2013. 56.YIN S, SUO X, SU J,et al. Effects of substrate hardness and spray angle on the deposition behavior of cold-sprayed T'i particles[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Teclmology, 2013, 23(1-2): 76-83. 57.ZAHIRI S H, ANTONIO C I, JAHEDI M. Elimination of porosity in directly fabricated titanium via cold gas dynamic spraying[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(2): 922-929. 58.WONG W,REZAELAN A, lRISSOG L, et al. Cold spray characteristics of commercially pure Ti and Ti6-A14-V[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 89-91: 639-644. 59.MGNAGALA V NV,IMBRIGLIO S I, CHROMIK R R. Significant influences of metal reactibity and oxide films at particle surgaces on coating microstructure in cold spraying Ti6A14V single splats[J]. Materials Letters, 2019, 244: 58-61. Research Status of Preparation Methods for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Surface Coatings WANG Yongdong1CHANG Mengyang1WANG Jinyu1ZHENG Yongjie2REN Yuanda1 Abstract: The application range of titanium alloys has been expanding, and higher requirements have been put forward for their properties. Therefore, the surface modification of titanium alloys has become a research hotspot. This paper reviews the application of laser cladding, micro-arc oxidation and spraying technology in the surface modification of titanium alloys, analyzes the research progress of various methods, factors affecting the quality and performance of coatings, and their existing problems and development trends are summed up. The application of laser cladding technology in titanium alloy coating mainly adopts autogenous preparation of ceramic coating. This method has a clean bonding interface between the reinforced phase and the substrate, and the bonding force is large, and it is not easy to fall off; the most popular micro-arc oxidation of titanium alloy is laser composite Micro-arc oxidation technology, but the application of micro-arc oxidation technology on the surface of titanium alloys also has problems of film-base bonding and film porosity of the oxide film, which affect the corrosion resistance of the substrate; cold spraying technology has the characteristics of low preparation temperature, high coating deposition rate and low porosity. The control means of cold spraying titanium alloy coating are mainly in the aspects of spraying parameters, powder state, matrix state and nozzle. The future research trend is the integration of cold spraying technology and other technologies such as laser cladding and friction stir welding. Keywords: titanium alloy; laser cladding; micro-arc oxidation; spray 引用本文:王永东,常萌阳,王金宇,等.钛及钛合金表面涂层制备方法研究现状[J].电焊机,2022,52(6):46-54.( WANG Yongdong, CHANG Mengyang, WANG Jinyu, et al.Research Status of Preparation Methods for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Surface Coatings[J].Electric Welding Machine, 2022, 52(6): 46-54.) 作者简介:王永东(1979—),男,教授,博士,主要从事材料表面改性及连接技术的研究。E-mail:[email protected]。 中图分类号:TG174 文献标识码:A 本文编辑:唐凰 “焊割在线”微信粉丝群正式全面开放。 ❤ 【进群方法】 第一步:请先加小编微信:touming188 (加微信时请备注:“焊割在线真爱粉”+所在城市+行业+专长) 第二步: 关注公众号“焊割在线”, 将关注界面截图发给小编, 第三步: 烦请帮忙点点文末的广告 小编将手动拉你入群。 ❤ 不定期开放,限时限量 我们期待与您 360°无死角全方位互动 ❤ 别忘记了我们的 三部曲, 点赞、留言加转发!互动连接你我他! 好文,这里点赞 返回搜狐,查看更多 |
【本文地址】