Kotlin基础 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 高阶基本变量 › Kotlin基础 |
Kotlin基础
|
高阶函数
高阶函数以另一个函数作为参数或者返回值,其可用Lambda或函数引用表示 函数类型下面将Lambda存储在sum变量中,其是函数类型 val sum = { x: Int, y: Int -> x + y }完整的函数类型为(para1,prar2…) -> returnValue,下面常量sum的类型是函数类型((Int, Int) -> Int) val a: Int = 0 val sum: (Int, Int) -> Int = { x, y -> x + y } val sum2: ((Int, Int) -> Int) = { x, y -> x + y } //感觉这样可读性更高若返回类型可空则为 val canReturnNull: (Int) -> Int? = { null }若变量类型本身为空,而不是函数类型返回值可空,则为 val funOrNull: ((Int) -> Int?)? = null 调用作为参数的函数如下,参数为函数类型,并在内部调用,通过不同函数类型的参数,实现不同的操作 fun twoAndThree(operation: (Int, Int) -> Int) { val result = operation(2, 3) println("result = $result") } twoAndThree { a, b -> a + b } twoAndThree { a, b -> a * b }如下对String实现filter,遍历字符串,若符合条件则添加到StringBuilder fun String.filter(predicate: (Char) -> Boolean): String { val sb = StringBuilder() for (index in 0 until length) { val element = get(index) if (predicate(element)) sb.append(element) } return sb.toString() } println("1abc".filter { it in 'a'..'z' }) Java中使用函数类型一个函数类型的变量是FunctionN接口的一个实现,其内部的invoke方法调用Lambda函数体 fun process(f: (Int) -> Int){ println(f(1)) }上面Kotlin函数接收一个函数类型,并调用该函数传入1,打印返回值,在Java中可直接传递Lambda public class Test { public static void run() { JoinKt.process(number -> number + 1); } }而在Java8之前可显式创建Function1,通过invoke代替Lambda public class Test { public static void run() { JoinKt.process(new Function1() { @Override public Integer invoke(Integer integer) { integer = integer + 1; return integer; } }); } }若使用带Lamba的扩展函数,需要将调用者作为第一个参数传递,且不能用void代替Unit作为返回值 public class Test { public static void run() { List strings = new ArrayList(); strings.add("1"); CollectionsKt.forEach(strings, s -> { System.out.println(s); return Unit.INSTANCE; }); } } 函数类型的参数设置默认值 fun joinToString( collection: Collection, separator: String = "", prefix: String = "", postfix: String = "" ): String { val result = StringBuilder(prefix) for ((index, element) in collection.withIndex()) { if (index > 0) result.append(separator) result.append(element) } result.append(postfix) return result.toString() }对于上面代码,添加一个函数类型的参数,并指定默认行为为拼接字符串 fun joinToString( collection: Collection, separator: String = "", prefix: String = "", postfix: String = "", transform: (T) -> String = { it.toString() } ): String { val result = StringBuilder(prefix) for ((index, element) in collection.withIndex()) { if (index > 0) result.append(separator) result.append(transform(element)) } result.append(postfix) return result.toString() }在实际调用时,可传入Lambda修改默认行为 val letters = listOf("a", "b") println(joinToString(letters)) println(joinToString(letters, transform = { it.toUpperCase() })) 函数类型的参数设置null值将函数类型的参数设置为可空,并在调用时检查 fun foo(callback: (() -> Unit)?) { if (callback != null) { callback() } }或者显式非空调用invoke fun foo(callback: (() -> Unit)?) { callback?.invoke() } 返回函数的函数如下函数根据运输方式返回不同的计算方式,getCost()根据不同的Delivery返回一个参数为Order,返回值为Double的函数 enum class Delivery { STANDARD, EXPEDITED } class Order(val itemCount: Int) fun getCost(delivery: Delivery): (Order) -> Double { if (delivery == Delivery.EXPEDITED) { return { order -> 2.0 * order.itemCount } } return { order -> 1.0 * order.itemCount } }在调用时,使用val变量接收该函数 val cost = getCost(Delivery.EXPEDITED) println("cost = " + cost(Order(3))) 内联函数使用 inline 修饰的函数被使用时编译器不会生成函数调用的代码,而是使用真实代码替换每一次的函数调用 inline fun synchronized(lock: Lock, action: () -> T): T { lock.lock() try { return action() } finally { lock.unlock() } } fun foo(l: Lock) { println("Before lock") synchronized(l) { println("Action") } println("After lock") }对于内联函数synchronized的调用,会被转化为如下,传入的Lambda和synchronized()函数都被内联 fun foo(l: Lock) { println("Before lock") l.lock() try { println("Action") } finally { l.unlock() } println("After lock") } 内联函数的限制函数类型的变量作为内联函数的参数,不能被内联,因为只有当外层的内联展开后,其中的Lambda才会被正常调用 inline fun synchronized(lock: Lock, action: () -> T): T { lock.lock() try { return action() } finally { lock.unlock() } } class LockOwner(val lock: Lock) { fun runUnderLock(body: () -> Unit) { synchronized(lock, body) } }如上,runUnderLock()将函数类型的变量作为参数body,传递给synchronized(),只能内联synchronized(),而不能一并内联body(),因为调用的时候还没有Lambda class LockOwner(val lock: Lock) { fun runUnderLock(body: () -> Unit) { lock.lock() try { body() } finally { lock.unlock() } } }如果参数为Lambda且在某个地方被保存,不能被内联,如Sequence中操作集合的方法 class Man(val name: String, val sex: String) fun Man.toWoman(transform: (String) -> String): WoMan { return WoMan(this, transform) } class WoMan(val man: Man, val change: (String) -> String) { override fun toString(): String { return "name=${man.name},sex=" + change(man.sex) } }如上,Lambda传递给Woman的构造函数并保存到change属性,toWoman()不能声明为内联函数
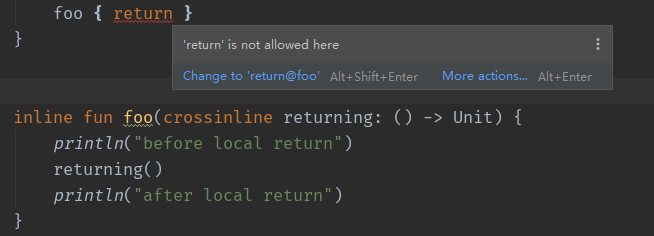
在Java中操作文件通常使用try-with-resource static String readFirstLineFromFile(String path) throws IOException { try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path))) { return br.readLine(); } }而在Kotlin中可以使用use代替,其会自动关闭流 fun readFirstLineFromFile(path: String): String { BufferedReader(FileReader(path)).use { br -> return br.readLine() } } 高阶函数中的控制流 使用标签返回内联Lambda中的return语句默认返回到外层函数,如下不会打印 not Fount class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) fun find() { val list = listOf(Person("A", 18), Person("A", 18)) list.forEach { if (it.name == "A") { println("Found") return } } println("not Found") }若使用标签,可实现Lambda的局部返回,如下使用@label表示标签,会打印 not Found class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) fun find() { val list = listOf(Person("A", 18), Person("A", 18)) list.forEach label@{ if (it.name == "A") { println("Found") return@label } } println("not Found") }使用Lambda作为参数的函数名可以作为标签,如下使用foreach作为标签,但如果显示指定了Lambda的标签,再使用函数名作为标签会失效 class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) fun find() { val list = listOf(Person("A", 18), Person("A", 18)) list.forEach { if (it.name == "A") { println("Found") return@forEach } } println("not Found") } crossinline在实际开发中接收的Lambda可能来自于其他地方,不能保证其内部没有return造成非局部返回 inline fun foo(returning: () -> Unit) { println("before local return") returning() println("after local return") } foo { return }对于上述代码,传递return造成后面的println未打印,添加crossinline修饰参数避免问题
如果一个Lambda包含多个局部返回语句会变得笨重,此时可以使用匿名函数替代 class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) val list = listOf() list.filter(fun(person): Boolean { return person.age < 30 }) list.filter(fun(person) = person.age < 30) |
【本文地址】
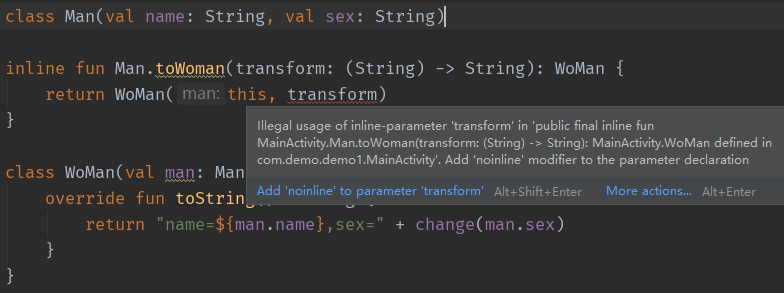 用noinline修饰的参数,不能被内联
用noinline修饰的参数,不能被内联