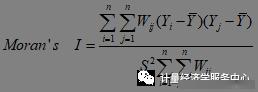空间计量经济学:从横截面数据到空间面板(附空间计量必读好文50余篇) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 面板数据的要求 › 空间计量经济学:从横截面数据到空间面板(附空间计量必读好文50余篇) |
空间计量经济学:从横截面数据到空间面板(附空间计量必读好文50余篇)
|
3、全局空间相关性检验与分析 全局空间自相关(Global Spatial Autocorrelation)是从区域空间的整体上刻画区域创新活动空间分布的集群情况。 在实际的空间相关分析应用研究中,由于Moran’s I指数和Geary’s C比率的作用基本相同,其不同之处是Moran’s I主要针对于全域空间相关性分析,而Geary’s C指数则适用于局域空间关联分析。 在许多实证研究中,Moran’s I 和Geary’s C是常用方法,已在大量文献中出现,尤其是前者。因此,以下介绍常用的Moran’s I指数的计算及检验过程。
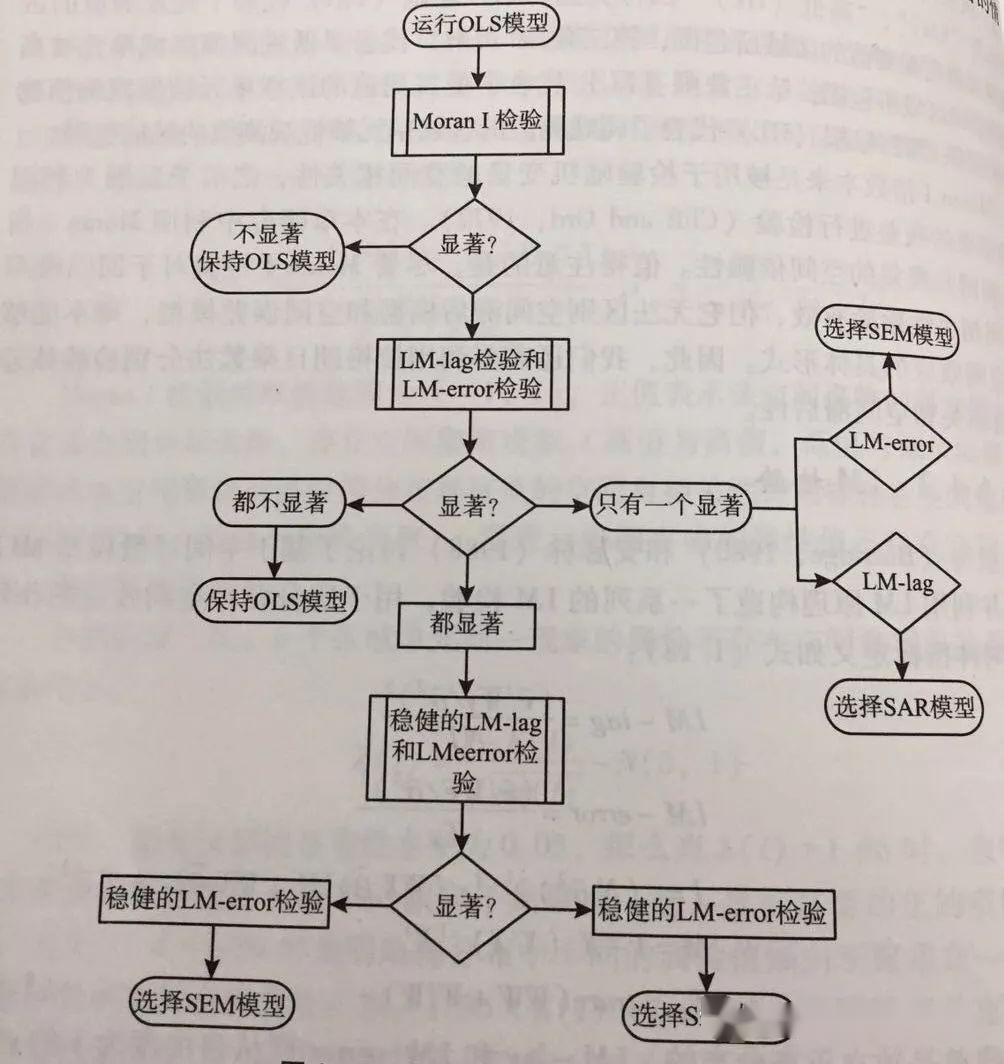
如果Moran’s I的正态统计量的Z值均大于正态分布函数在0.05(0.01)水平下的临界值1.65(1.96),表明区域创新在空间分布上具有明显的正向相关关系, 正的空间相关代表相邻地区的类似特征值出现集群(Clustering)趋势。 4、目前计量研究方法及其局限性 目前有关研究的计量方法主要是传统的回归分析方法(如多元统计分析、回归分析、数据包络分析DEA等方法),其实质上都是线性的变量之间相互关系的一种测量方法,适合于企业或产业部门时间序列层面的经验研究,未考虑区域(或截面单元)之间的空间关联,局限性比较明显。 区域之间的经济行为会相互影响,这使其存在显著的外部效应,导致地区之间的经济行为存在溢出效应。 经济产出不仅受到本地投资的强度、而且还会受到周边其他地区的投资活动产生的溢出效应及政策的影响。经济集群行为可以通过检验一个代表地区间考虑交互作用的生产函数,即该地区的经济活动及其自身的特征与其他地区的经济活动的关系,来考察区域经济行为的集群行为。 可通过纳入空间效应(空间相关和空间差异)的空间计量经济模型——空间回归模型,包括常系数的空间滞后模型(Spatial Lag Model,SLM)与空间误差模型两种(Spatial Error Model,SEM)(Anselin,1988;Anselin,Florax,1995;吴玉鸣,2005)和变系数的地理加权回归模型(Geographical Weighted Regression,GWR)来实现。 5、空间计量经济模型及估计技术 空间计量经济学是计量经济学的一个分支,研究的是在横截面数据(Cross-sectional Data)和面板数据(Panel Data)的回归模型中如何处理空间交互作用(空间自相关)和空间结构(空间非均匀性)(Anselin,1988)。 最近发展起来的空间统计学和空间计量经济学不仅解决了标准统计方法在处理空间数据时的失误问题,更重要的是为测量这种空间联系及其性质、并在建模时明确地引入空间联系变量以估算与检验其贡献提供了全新的手段(应龙根,宁越敏,2005)。 实际上,早在1970年代欧洲就展开了空间计量经济学研究,并将它作为一个确定的领域。Paelinck & Klaassen(1979)定义了这个领域,包括:空间相互依赖在空间模型中的任务;空间关系不对称性;位于其他空间的解释因素的重要性;过去的和将来的相互作用之间的区别;明确的空间模拟。 Anselin(1988)将空间计量经济学定义为:处理由区域科学模型统计分析中的空间所引起的特殊性的技术总称。换句话说,空间计量经济学研究的是明确考虑空间影响(空间自相关和空间不均匀性)的方法。 目前,空间计量经济学研究包括以下四个感兴趣的领域: 计量经济模型中空间效应的确定; 合并了空间影响的模型的估计;空间效应存在的说明、检验和诊断;空间预测。 空间计量经济学模型有多种类型(Anselin,et al. 2004)。 首先介绍纳入了空间效应(空间相关和空间差异)、适用于截面数据的空间常系数回归模型,包括空间滞后模型(Spatial Lag Model,SLM)与空间误差模型(Spatial Error Model,SEM)两种,以及空间变系数回归模型——地理加权回归模型(Geographical Weighted Regression,GWR)。适用于时间序列和截面数据合成的空间面板数据计量经济学模型将在以后予以介绍。 6、空间计量经济学模型 空间滞后模型(Spatial Lag Model,SLM)主要是探讨各变量在一地区是否有扩散现象(溢出效应)。其模型表达式为:参数 反映了自变量对因变量的影响,空间滞后因变量 是一内生变量,反映了空间距离对区域行为的作用。区域行为受到文化环境及与空间距离有关的迁移成本的影响,具有很强的地域性(Anselin et al.,1996)。由于SLM模型与时间序列中自回归模型相类似,因此SLM也被称作空间自回归模型(Spatial Autoregressive Model,SAR)。 空间误差模型(Spatial Error Model,SEM)存在于扰动误差项之中的空间依赖作用,度量了邻近地区关于因变量的误差冲击对本地区观察值的影响程度。由于SEM模型与时间序列中的序列相关问题类似,也被称为空间自相关模型(Spatial Autocorrelation Model,SAC)。 估计技术:鉴于空间回归模型由于自变量的内生性,对于上述两种模型的估计如果仍采用OLS,系数估计值会有偏或者无效,需要通过IV、ML或GLS、GMM等其他方法来进行估计。Anselin(1988)建议采用极大似然法估计空间滞后模型(SLM)和空间误差模型(SEM)的参数。 空间自相关检验与SLM、SEM的选择:判断地区间创新产出行为的空间相关性是否存在,以及SLM和SEM那个模型更恰当,一般可通过包括Moran’s I检验、两个拉格朗日乘数(Lagrange Multiplier)形式LMERR、LMLAG及其稳健(Robust)的R-LMERR、R-LMLAG)等形式来实现。由于事先无法根据先验经验推断在SLM和SEM模型中是否存在空间依赖性,有必要构建一种判别准则,以决定哪种空间模型更加符合客观实际。Anselin和Florax(1995)提出了如下判别准则:如果在空间依赖性的检验中发现LMLAG较之LMERR在统计上更加显著,且R-LMLAG显著而R-LMERR不显著,则可以断定适合的模型是空间滞后模型;相反,如果LMERR比LMLAG在统计上更加显著,且R-LMERR显著而R-LMLAG不显著,则可以断定空间误差模型是恰当的模型。
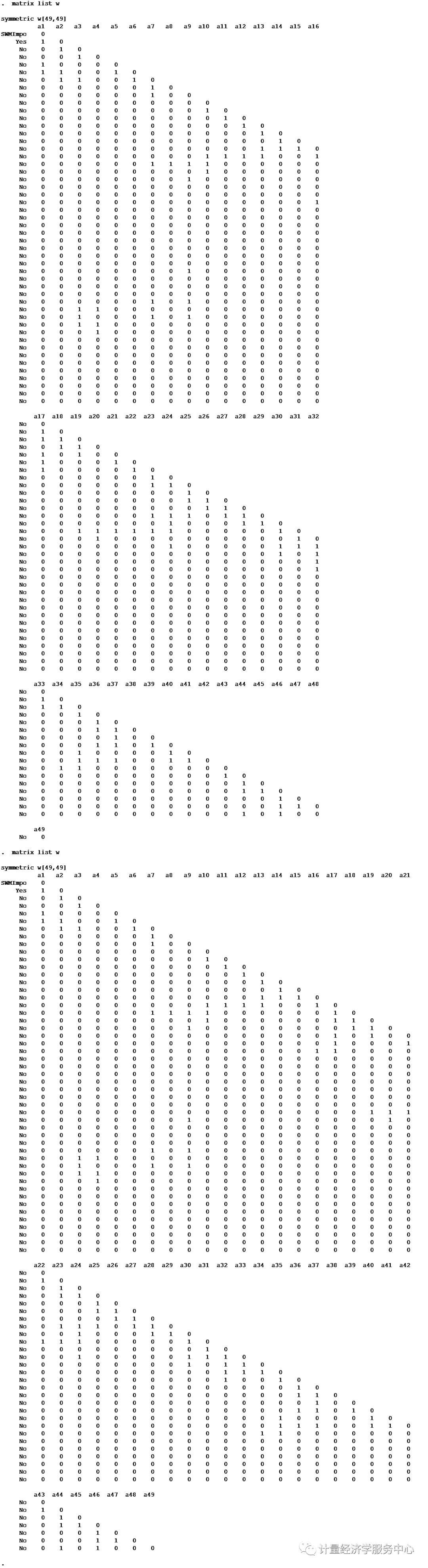
空间计量建模流程图 除了拟合优度R2检验以外,常用的检验准则还有:自然对数似然函数值(Log likelihood,LogL)、似然比率(Likelihood Ratio,LR)、赤池信息准则(Akaike information criterion,AIC)、施瓦茨准则(Schwartz criterion,SC)。对数似然值越大,AIC和SC值越小,模型拟合效果越好。这几个指标也用来比较OLS估计的经典线性回归模型和SLM、SEM,似然值的自然对数最大的模型最好。 空间变系数回归模型及估计:就目前国内外的研究来看,大多直接假定横截面单元是同质的,即地区或企业之间没有差异。传统的OLS只是对参数进行“平均”或“全域”估计,不能反映参数在不同空间的空间非稳定性(吴玉鸣,李建霞,2006;苏方林,2007)。 当用横截面数据建立计量经济学模型时,由于这种数据在空间上表现出的复杂性、自相关性和变异性,使得解释变量对被解释变量的影响在不同区域之间可能是不同的,假定区域之间的经济行为在空间上具有异质性的差异可能更加符合现实。空间变系数回归模型(Spatial Varying-Coefficient Regression Model)中的地理加权回归模型(Geographical Weighted Regression,GWR)是一种解决这种问题的有效方法。 7、空间计量主要命令 spmat 生成空间权重矩阵 spatwmat 用于定义空间权重矩阵 spatgsa 用于全局空间自相关检验 gsa表示global spatial autocorrelation spatlsa 进行局部空间自相关检验 lsa表示local spatial autocorrelation spatcorr 考察空间自相关指标对距离临界值d的依赖性 spatdiag 针对ols回归结果,考察是否存在空间效应 spatreg 估计空间滞后与空间误差模型 空间面板主要命令为:help xsmle Spatial Autoregressive (SAR) model xsmle depvar [indepvars] [if] [in] [weight] , wmat(name) model(sar) [SAR_options] Spatial Durbin (SDM) model xsmle depvar [indepvars] [if] [in] [weight] , wmat(name) model(sdm) [SDM_options] Spatial Autocorrelation (SAC) model xsmle depvar [indepvars] [if] [in] [weight] , wmat(name) emat(name) model(sac) [SAC_options] Spatial Error (SEM) model xsmle depvar [indepvars] [if] [in] [weight] , emat(name) model(sem) [SEM_options] Generalized Spatial Panel Random Effects (GSPRE) model xsmle depvar [indepvars] [if] [in] [weight] , wmat(name) model(gspre) [emat(name) GSPRE_options] 8、空间计量应用介绍 案例1、生成空间权重矩阵 案例1、生成空间权重矩阵 首先根据数据集生成的空间权重矩阵命令,需要用到的命令为:spatwmat,spatwmat的语法格式为: spatwmat [ using filename ] , name(weights_matrix) [ drop(numlist) xcoord(varname) ycoord(varname) band(numlist) friction(#) binary standardize eigenval(eigen_matrix) ] 具体应用案例介绍为: spatwmat using ColumbusSWM.dta, name(W) spatwmat using ColumbusSWM.dta, name(W) drop(11/49) standardize spatwmat, name(W) xcoord(x) ycoord(y) band(0 3) binary spatwmat using ColumbusSWM.dta, name(W) standardize eigenval(E) 本文首先应用 ColumbusSWM.dta数据生成空间权重矩阵W,结果为:
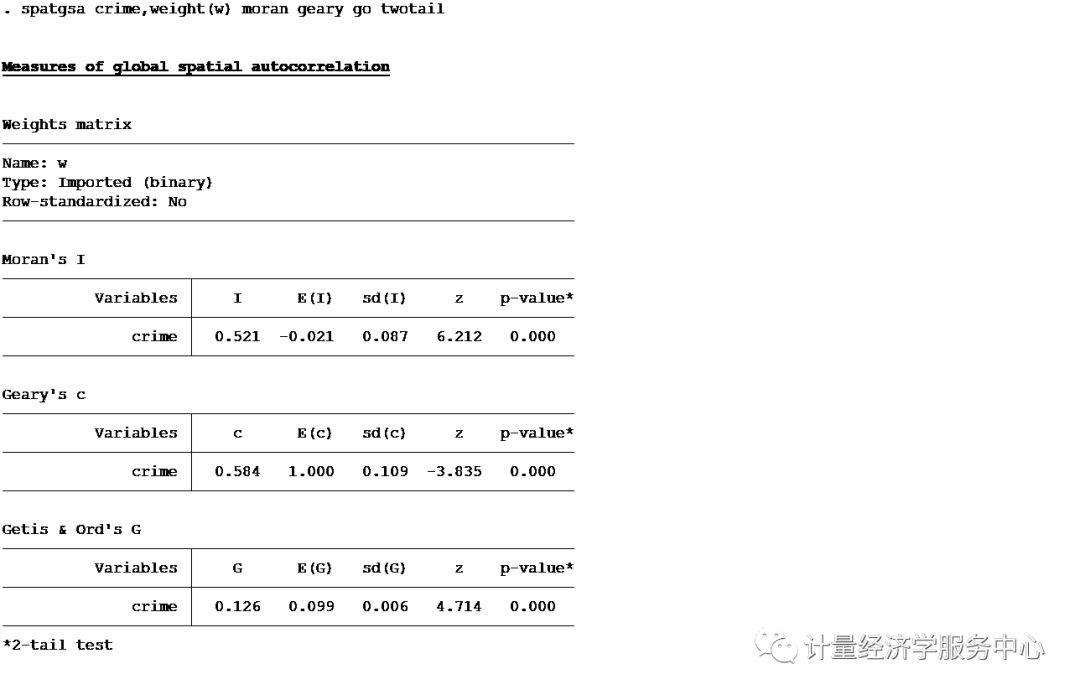
案例2、空间自相关检验 案例2、空间自相关检验 全局自相关检验用到的命令为spatgsa,语法格式为:spatgsa varlist , weights(matrix) [ moran geary go twotail ] 其中: weights(matrix) is always required. It specifies the name of the spatial weights matrix to be used in the computation of the requested global spatial autocorrelation statistics. This matrix must have been generated by spatwmat. moran requests that Moran's I and the related quantities of interest be computed and displayed. geary requests that Geary's c and the related quantities of interest be computed and displayed. go requests that Getis and Ord's G and the related quantities of interest be computed and displayed. This option requires that the spatial weights matrix specified by option weights(matrix) be a non-standardized symmetric binary weights matrix. twotail requests that 2-tail p-values be computed and displayed instead of the default 1-tail p-values. To run spatgsa it is necessary to specify at least one of the following options: moran, geary, and go. 相关案例介绍为: spatgsa hoval income crime, weights(W) moran geary go spatgsa hoval income crime, weights(W) moran geary twotail
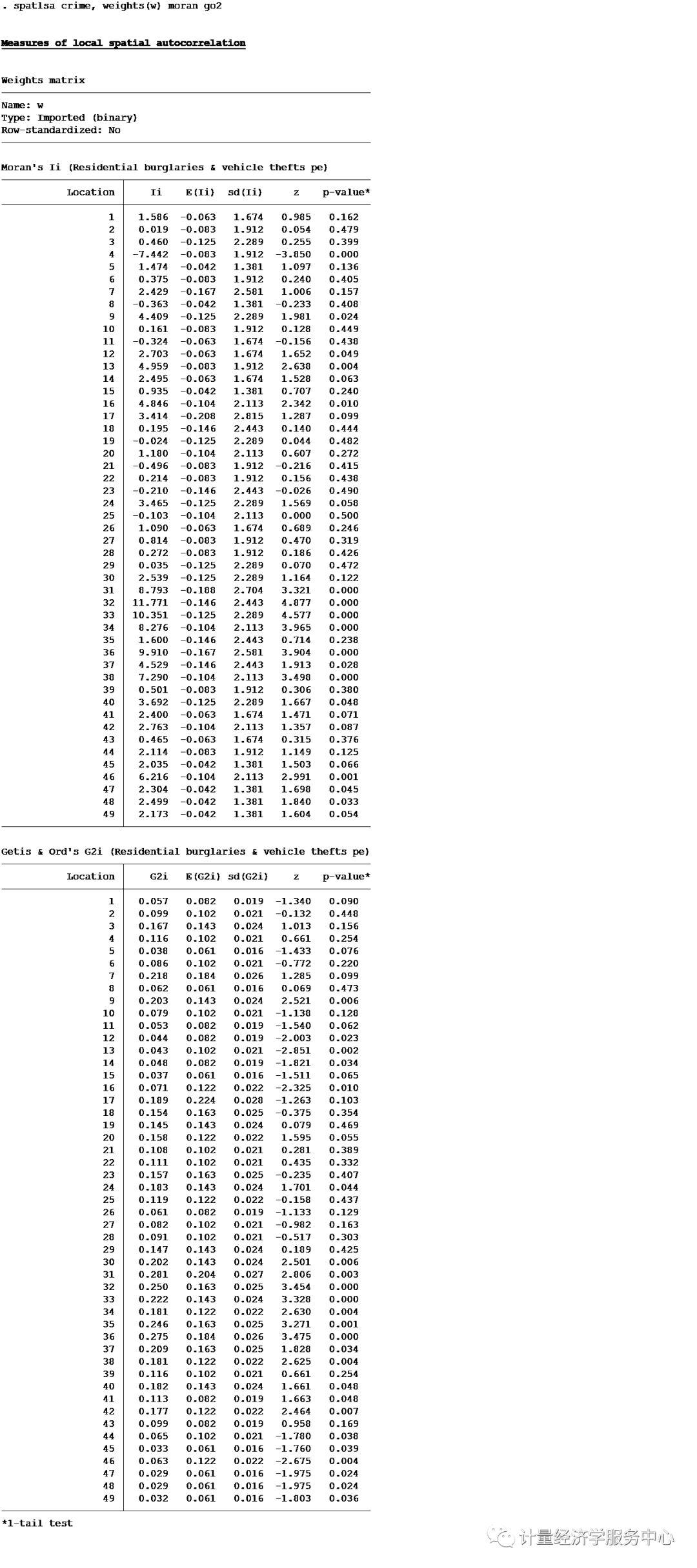
局部自相关检验用到的命令为spatlsa,语法格式为:spatlsa varname , weights(matrix) [ moran geary go1 go2 id(varname) twotail sort graph(moran|go1|go1) symbol(id|n) map(filename) xcoord(varname) ycoord(varname) savegraph(filename [, replace]) ] Examples spatlsa crime, weights(W) moran go2 spatlsa crime, weights(WS) moran graph(moran) symbol(n) spatlsa crime, w(W) go2 graph(go2) map(ColumbusBoundary.dta) x(x) y(y)
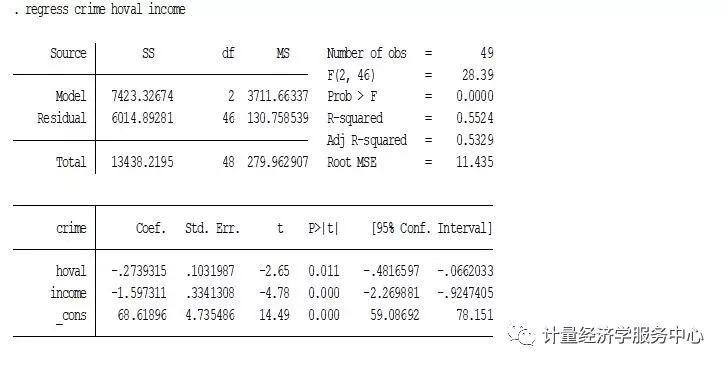
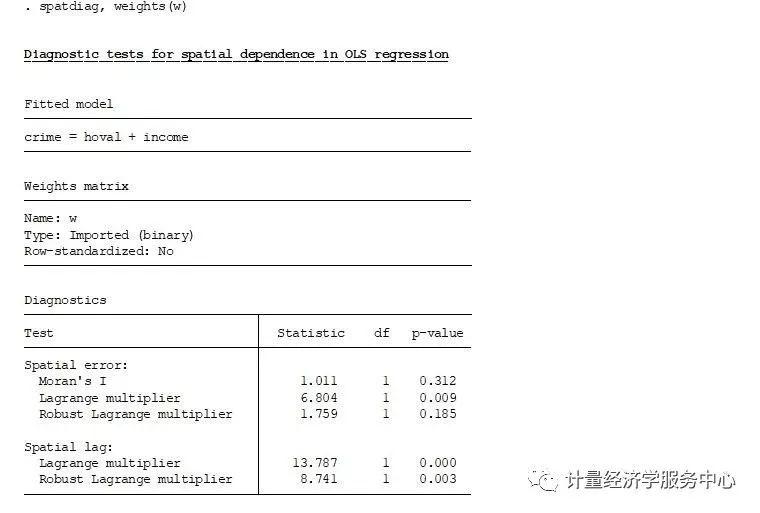
案例3、空间效应检验 案例3、空间效应检验 空间效应诊断spatdiag, spatdiag语法格式为spatdiag , weights(matrix),应用介绍为: regress crime hoval income spatdiag, weights(W)
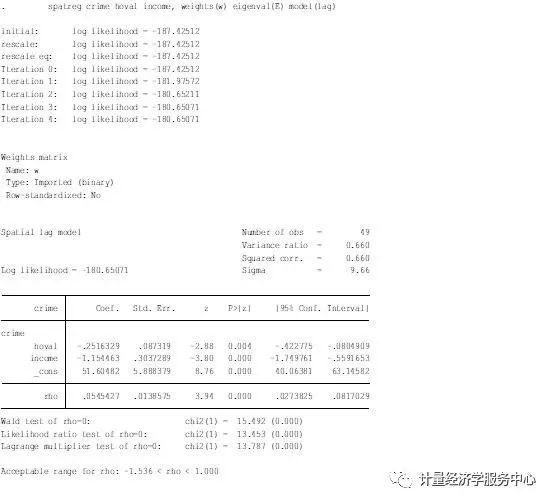
案例4、SAR与SEM模型估计 案例4、SAR与SEM模型估计 SAR与SEM模型估计用到的命令均为spatreg,spatreg语法格式为:spatreg varlist , weights(weights_matrix) eigenval(eigen_matrix) model(lag|error) [ nolog robust level(#) ] 其中,weights(weights_matrix) is always required. It specifies the name of the spatial weights matrix to be used in the estimation of the requested spatial regression model. This matrix must have been generated by spatwmat. eigenval(eigen_matrix) is always required. It specifies the name of the eigenvalues matrix to be used in the estimation of the requested spatial regression model. This matrix must have been generated by spatwmat. model(lag|error) is always required. It specifies the type of spatial regression model to be estimated. model(lag) requests that the spatial lag model be estimated. model(error) requests that the spatial error model be estimated. nolog requests that reporting of the iteration log be suppressed. robust requests that the Huber/White/sandwich estimator of variance be used instead of the traditional calculation. level(#) specifies the confidence level, in percent, for confidence intervals. The default is level(95) or as set by set level. 空间滞后(空间自回归模型SAR) spatreg crime hoval income, weights(W) eigenval(E) model(lag)
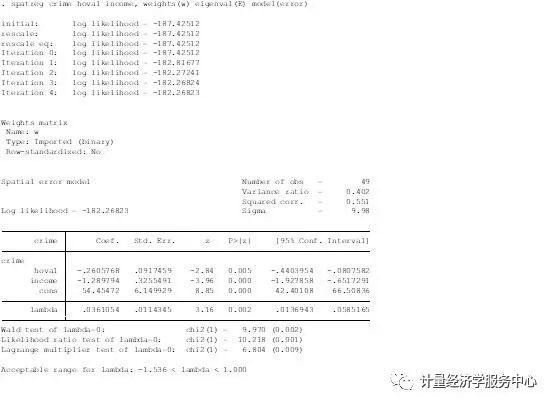
空间误差模型。model(error)表示进行估计空间误差模型SEM spatreg crime hoval income, weights(W) eigenval(E) model(error)
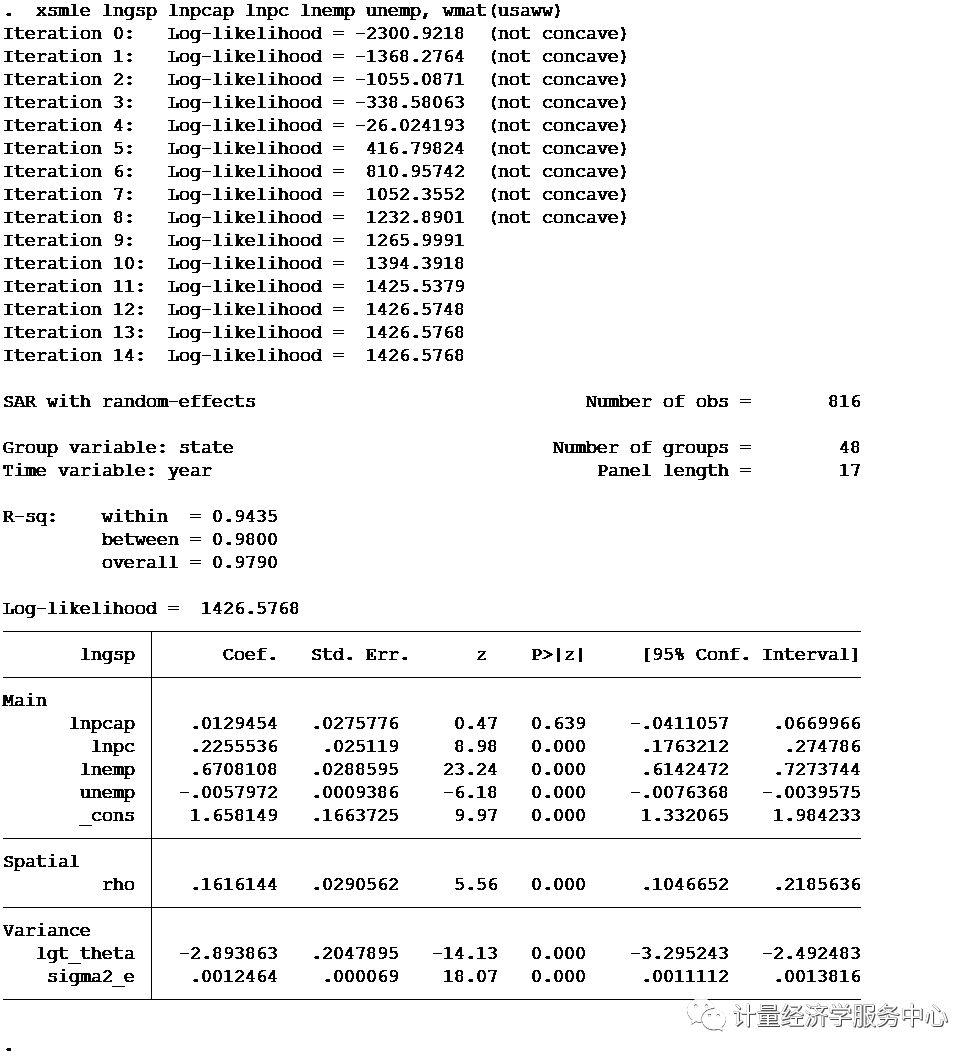
案例5、空间面板应用 案例5、空间面板应用 SAR model use http://www.econometrics.it/stata/data/xsmle/product.dta, clear spmat use usaww using http://www.econometrics.it/stata/data/xsmle/usaww.spmat gen lngsp = log(gsp) gen lnpcap = log(pcap) gen lnpc = log(pc) gen lnemp = log(emp) xsmle lngsp lnpcap lnpc lnemp unemp, wmat(usaww)
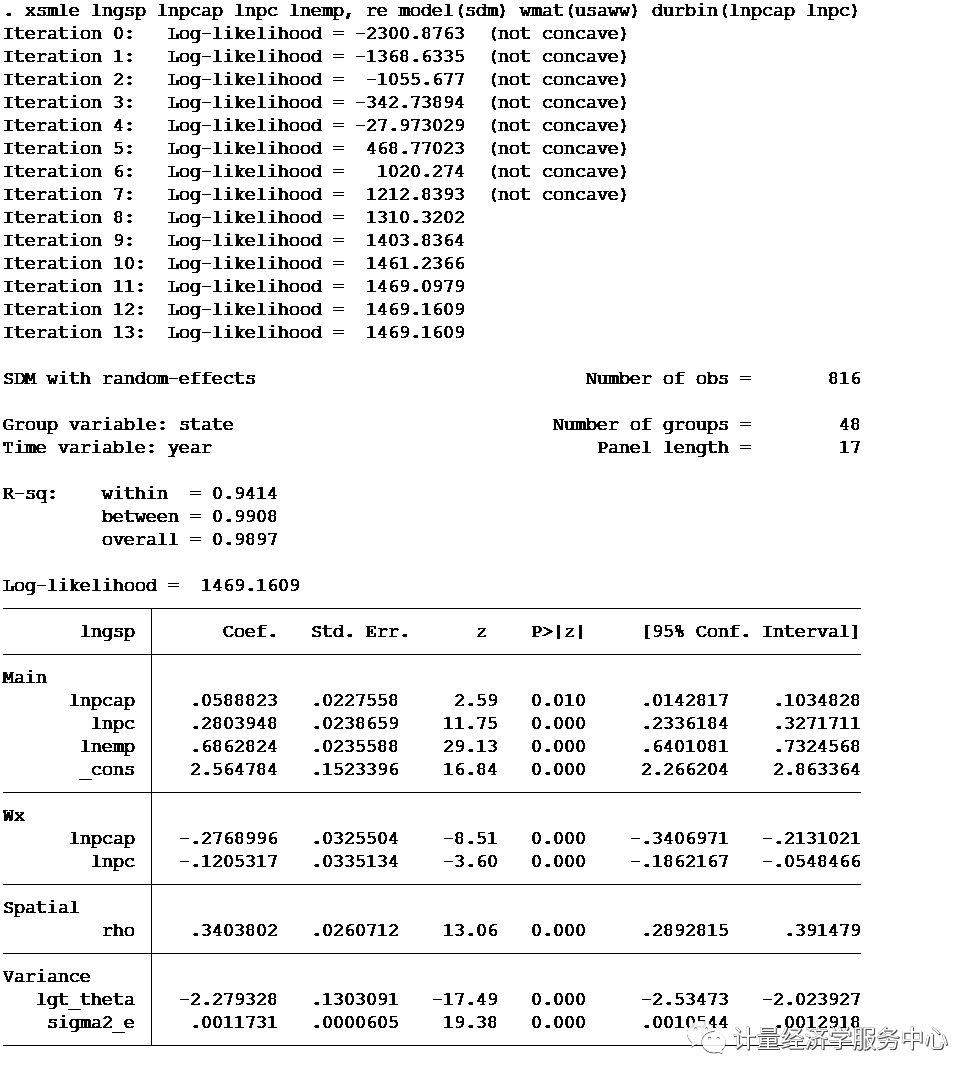
SDM model with selected spatially lagged regressors and direct+indirect effect xsmle lngsp lnpcap lnpc lnemp, re model(sdm) wmat(usaww) durbin(lnpcap lnpc)
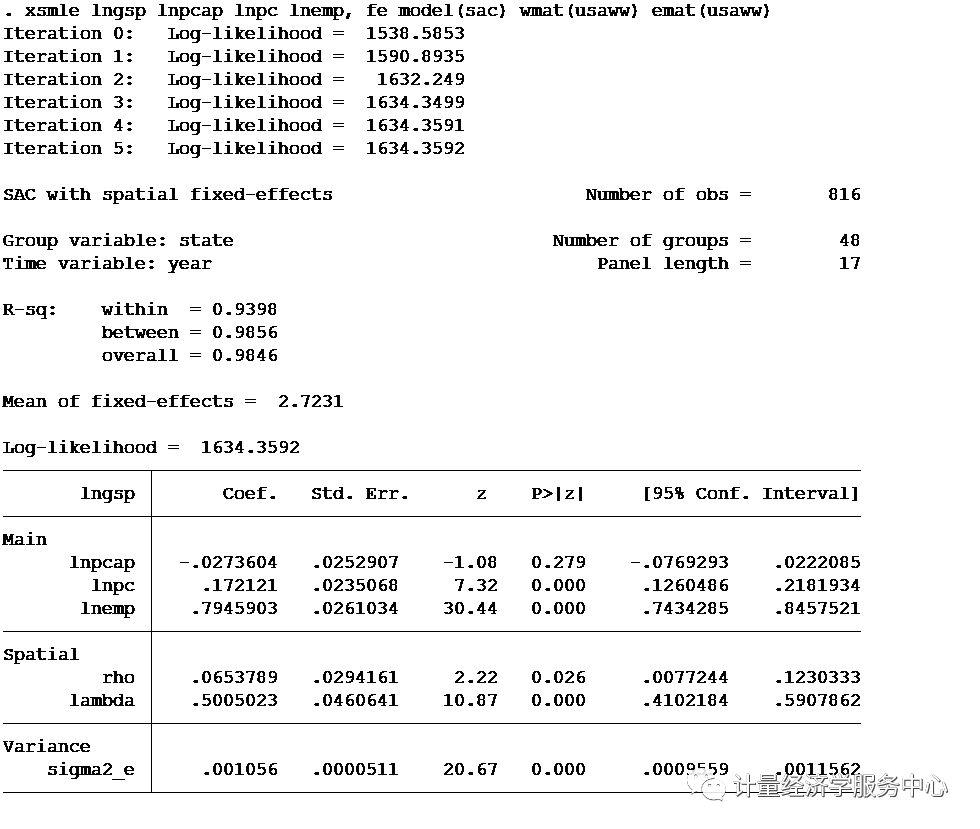
SAC model xsmle lngsp lnpcap lnpc lnemp, fe model(sac) wmat(usaww) emat(usaww)
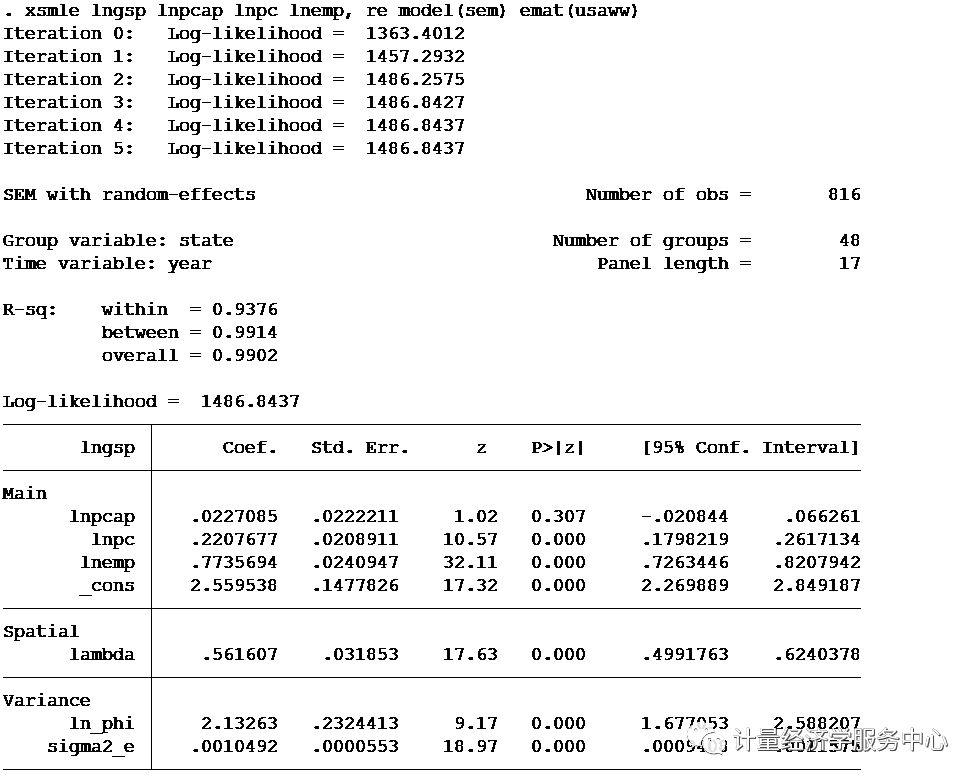
SEM model xsmle lngsp lnpcap lnpc lnemp, re model(sem) emat(usaww)
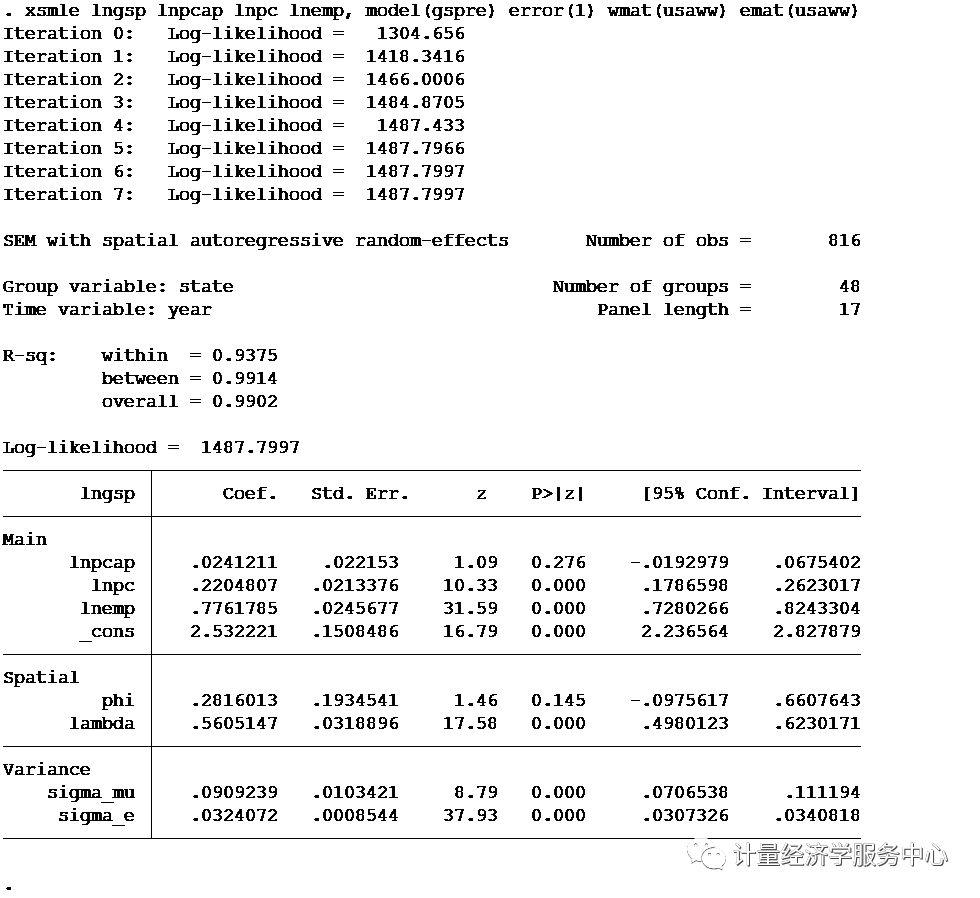
GSPRE model xsmle lngsp lnpcap lnpc lnemp, model(gspre) error(1) wmat(usaww) emat(usaww)
◆◆◆◆返回搜狐,查看更多 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |