利用A*算法解决迷宫问题(附代码) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 迷宫函数 › 利用A*算法解决迷宫问题(附代码) |
利用A*算法解决迷宫问题(附代码)
|
人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到网站 https://www.captainai.net/shuai 《人工智能》实验报告 实验名称: 利用A*算法解决迷宫问题 班 级: 软件工程191 2022 年 3 月 29 日 先看一下效果: 利用A*算法在迷宫中找到一条最优路径。其中1代表墙,0代表路。出发位置为左上角,终点为右下角。
学习并实现A*算法,实现使用java语言。 三、实验内容 3.1数据导入将map.txt中的迷宫地图存入二维数组中。 String filename = in.next(); File file=new File(filename); //读取文件里面的数据,将其存入map二维数组中 Scanner input = new Scanner(file); int[][] map = new int[n][n]; for (int i = 0; i map[i][j] = input.nextInt(); } } 3.2数据预处理根据导入的地图数据进行地图的初始化。 // 定义地图的基本数据,长宽高,大小 MapStructure QuestionMap = new MapStructure(map, map.length, new Point(0, 0), new Point(map.length-1, map.length-1)); //MapStructure定义结构 class MapStructure{ int[][] map; int n; //地图的宽和高 Point start; Point end; MapStructure(int [][]map, int n, Point start,Point end){ this.map = map; this.n = n; this.start = start; this.end = end; } void setMapStructure(Point start,Point end){ this.start = start; this.end = end; } } 3.3算法描述之前写过一篇算法的详细分析:A搜索算法和A*搜索算法概述 采用A*算法。公式为: 这里面的d(n)代表状态的深度,也就是到终点的距离。一般有两种计算的方式。 曼哈顿距离:就是上横向格子数+纵向格子数。 欧式距离:这个名字听起来也很高端,说白了,就是两点间的直线距离sqrt((x1-x2)2 + (y1-y2)2) w(n)是一种启发式的度量。是一种启发式函数,表示从任意顶点 n n n到目标点的估算成本。值得注意的是,启发式的信息给的越多,估价函数的数值就越大,执行的效率页越高。这是算法的核心。 3.4核心代码 int calcHx(Coord goal, Coord end){ // 欧式距离 return Math.abs(goal.x - end.x) + Math.abs(goal.y - end.y); } // 增加可移动的路径列表 void addPointInopenList(MapStructure map, Point current, int x, int y){ if(canAddopenList(map, x, y)){ Point end = map.end; Point goal = new Point(x, y); // 当前的距离加1 int Gx = current.Gx + value; // 这是与目标的距离 int Hx = calcHx(current.coord, end.coord); // 判断是否在终点 if(isEndCoord(goal.coord, end.coord)){ goal = end; goal.last = current; goal.Gx = Gx; goal.Hx = calcHx(goal.coord, end.coord); } else // 如果不在,继续寻找 goal = new Point(goal.coord, current, Gx, Hx); // 加入放入可移动的路径 openList.add(goal); } } //获得路径信息 void getPathInformation(int[][] map, Point end){ int path = 1; System.out.println("The shortest path needs " + end.Gx + " steps."); while(end != null){ // 可移动路径进行遍历 for(Point point : openList){ if(point.Hx == end.Hx && point.Gx == end.Gx){ path++; } } map[end.coord.y][end.coord.x] = sign; end = end.last; } System.out.println("The shortest path number is " + path); }四、实验结果及分析 项目目录: 这里需要说明,在打印最终地图的时候,对二维数组进行判断,1代表墙体,0代表路,2代表搜索出的路劲,让其打印相应的符号代表,以提高直观性。以下为代码: public static void printAnswer(int[][] maps) { for (int i = 0; i if (maps[i][j] == 1) { // 这个代表墙体 System.out.print("🟦"); } if (maps[i][j] == 0) { // 这个代表路 System.out.print("0️⃣"); } if (maps[i][j] == 2) { // 这个代表最终的路径 System.out.print("*️⃣"); } // System.out.print(maps[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } 演示视频 五、实验所有代码下面为完整代码: map.txt 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 package maze_solution; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class MazeSolution { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Please enter the size(不能大于20) and name of your maze(数据的文件名)"); int n = in.nextInt(); String filename = in.next(); File file=new File(filename); //读取文件里面的数据,将其存入map二维数组中 Scanner input = new Scanner(file); int[][] map = new int[n][n]; for (int i = 0; i map[i][j] = input.nextInt(); } } // 这是开始时间,用于记录搜索耗费的时间 long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 定义地图的基本数据,长宽高,大小 MapStructure QuestionMap = new MapStructure(map, map.length, new Point(0, 0), new Point(map.length-1, map.length-1)); new Algorithm().Go(QuestionMap); // 打印最后的map printAnswer(map); // 记录结束时间 long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("This program takes " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms."); } public static void printAnswer(int[][] maps) { for (int i = 0; i if (maps[i][j] == 1) { // 这个代表墙体 System.out.print("🟦"); } if (maps[i][j] == 0) { // 这个代表路 System.out.print("0️⃣"); } if (maps[i][j] == 2) { // 这个代表最终的路径 System.out.print("*️⃣"); } // System.out.print(maps[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } class Coord{ int x; int y; Coord(int x, int y){ this.x = x; this.y = y; } //判断是否已经到达了终点 boolean isEquals(Coord goal){ if(goal.x == x && goal.y == y) return true; return false; } } class Point{ Coord coord; Point last; // A*算法的两个参数 int Gx; //移动距离 int Hx; //离终点的距离 int air; //节点坐标 Point(int x, int y){ this.coord = new Coord(x,y); } Point(Coord coord, Point parent, int Gx, int Hx){ this.coord = coord; this.last = parent; this.Gx = Gx; this.Hx = Hx; } Point(int air){ this.air = air; } } //MapStructure定义结构 class MapStructure{ int[][] map; int n; //地图的宽和高 Point start; Point end; MapStructure(int [][]map, int n, Point start,Point end){ this.map = map; this.n = n; this.start = start; this.end = end; } void setMapStructure(Point start,Point end){ this.start = start; this.end = end; } } //完成A*算法,并求出路径 class Algorithm{ // 1代表墙 final static int bar = 1; // 2代表选中,走的路径 final static int sign = 2; final static int value = 1; //只能上下左右移动 ArrayList openList = new ArrayList(); //放入可移动的路径 ArrayList closeList = new ArrayList(); //放入走过的路径 boolean isEndCoord(Coord coord, Coord end){ if(coord != null && end.isEquals(coord)) // 已经倒带终点 return true; return false; } //是否能加入移动路径 boolean canAddopenList(MapStructure map, int x, int y){ if(x=map.n || y=map.n) // 不能越界 return false; if(map.map[y][x] == bar) // 不能等于墙 return false; if(isIncloseList(x, y)) return false; if(isInopenList(x, y)) return false; // 以上判断判断都不符合,可以加入 return true; } // 是否在放入可移动的路径 boolean isInopenList(int x, int y){ for(Point point : openList){ if(x == point.coord.x && y == point.coord.y) return true; } return false; } // 是否在放入走过的路径 boolean isIncloseList(int x, int y){ if(closeList.isEmpty()) return false; for(Point point : closeList){ if(x == point.coord.x && y == point.coord.y) return true; } return false; } int calcHx(Coord goal, Coord end){ // 欧式距离 return Math.abs(goal.x - end.x) + Math.abs(goal.y - end.y); } // 增加可移动的路径列表 void addPointInopenList(MapStructure map, Point current, int x, int y){ if(canAddopenList(map, x, y)){ Point end = map.end; Point goal = new Point(x, y); // 当前的距离加1 int Gx = current.Gx + value; // 这是与目标的距离 int Hx = calcHx(current.coord, end.coord); // 判断是否在终点 if(isEndCoord(goal.coord, end.coord)){ goal = end; goal.last = current; goal.Gx = Gx; goal.Hx = calcHx(goal.coord, end.coord); } else // 如果不在,继续寻找 goal = new Point(goal.coord, current, Gx, Hx); // 加入放入可移动的路径 openList.add(goal); } } void addPointInopenList(MapStructure map, Point current){ int x = current.coord.x; int y = current.coord.y; addPointInopenList(map, current, x-1, y); //左 addPointInopenList(map, current, x+1, y); //右 addPointInopenList(map, current, x, y-1); //上 addPointInopenList(map, current, x, y+1); //下 } void drawPath(int[][] map, Point end){ while(end != null){ map[end.coord.y][end.coord.x] = sign; end = end.last; } } //获得路径信息 void getPathInformation(int[][] map, Point end){ int path = 1; System.out.println("The shortest path needs " + end.Gx + " steps."); while(end != null){ // 可移动路径进行遍历 for(Point point : openList){ if(point.Hx == end.Hx && point.Gx == end.Gx){ path++; } } map[end.coord.y][end.coord.x] = sign; end = end.last; } System.out.println("The shortest path number is " + path); } //从地图左上角为所有的0赋予 void addBreathbyLeft(MapStructure map){ int i = 0; int j = 0; Point zero = new Point(j, i); for (i = 1; i zero.air = 0; if(map.map[i][j] == 0){ if(map.map[i][j+1] == 0) zero.air++; if(j >= 1 && map.map[i][j-1] == 0) zero.air++; if(map.map[i+1][j] == 0) zero.air++; if(i >= 1 && map.map[i-1][j] == 0) zero.air++; } if(zero.air int i = 0; int j = 0; Point zero = new Point(j, i); for (i = map.n-2; i > 0; i--) { for (j = map.n-2; j > 0; j--) { zero.air = 0; if(map.map[i][j] == 0){ if(map.map[i][j+1] == 0) zero.air++; if(j >= 1 && map.map[i][j-1] == 0) zero.air++; if(map.map[i+1][j] == 0) zero.air++; if(i >= 1 && map.map[i-1][j] == 0) zero.air++; } if(zero.air for (int i = 0; i if(map == null){ // 初始化失败 System.out.println("The map structure is wrong!"); return; } openList.clear(); closeList.clear(); changeBreath(map); openList.add(map.start); movePoint(map); getPathInformation(map.map, map.end); System.out.println("This is all maze paths (The sign of the pathway is '2'):"); } void Back(MapStructure map){ openList.clear(); closeList.clear(); openList.add(map.start); movePoint(map); } Point findMinInopenList(){ Point goal = openList.get(0); for(Point point : openList){ if(point.Gx + point.Hx Point goal = findMinInopenList(); openList.remove(goal); closeList.add(goal); addPointInopenList(map, goal); if(isIncloseList(map.end.coord.x, map.end.coord.y)){ drawPath(map.map, map.end); break; } } } }如果是在不会弄,就资源下载吧! 资源下载 |
【本文地址】
 整体图:
整体图: 

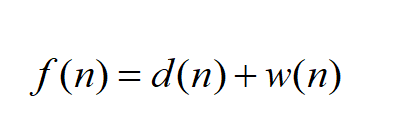
 运行截图:
运行截图: 


