获取Java程序运行的路径 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 运行jar包指定生成目录文件 › 获取Java程序运行的路径 |
获取Java程序运行的路径
|
获取Java程序运行的路径 | 获取当前jar包的路径 转自 Itype 用户snoopy7713 http://marsvaadin.iteye.com/blog/1671046 不管是否是 Jar 包,不管是否是 Tomcat 部署,以下三个方法均可实现。 package test; public class MyPath { /** * 获取项目所在路径(包括jar) * * @return */ public static String getProjectPath() { java.net.URL url = MyPath.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource() .getLocation(); String filePath = null; try { filePath = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(url.getPath(), "utf-8"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } if (filePath.endsWith(".jar")) filePath = filePath.substring(0, filePath.lastIndexOf("/") + 1); java.io.File file = new java.io.File(filePath); filePath = file.getAbsolutePath(); return filePath; } /** * 获取项目所在路径 * * @return */ public static String getRealPath() { String realPath = MyPath.class.getClassLoader().getResource("") .getFile(); java.io.File file = new java.io.File(realPath); realPath = file.getAbsolutePath(); try { realPath = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(realPath, "utf-8"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return realPath; } public static String getAppPath(Class cls) { // 检查用户传入的参数是否为空 if (cls == null) throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException("参数不能为空!"); ClassLoader loader = cls.getClassLoader(); // 获得类的全名,包括包名 String clsName = cls.getName(); // 此处简单判定是否是Java基础类库,防止用户传入JDK内置的类库 if (clsName.startsWith("java.") || clsName.startsWith("javax.")) { throw new java.lang.IllegalArgumentException("不要传送系统类!"); } // 将类的class文件全名改为路径形式 String clsPath = clsName.replace(".", "/") + ".class"; // 调用ClassLoader的getResource方法,传入包含路径信息的类文件名 java.net.URL url = loader.getResource(clsPath); // 从URL对象中获取路径信息 String realPath = url.getPath(); // 去掉路径信息中的协议名"file:" int pos = realPath.indexOf("file:"); if (pos > -1) { realPath = realPath.substring(pos + 5); } // 去掉路径信息最后包含类文件信息的部分,得到类所在的路径 pos = realPath.indexOf(clsPath); realPath = realPath.substring(0, pos - 1); // 如果类文件被打包到JAR等文件中时,去掉对应的JAR等打包文件名 if (realPath.endsWith("!")) { realPath = realPath.substring(0, realPath.lastIndexOf("/")); } java.io.File file = new java.io.File(realPath); realPath = file.getAbsolutePath(); try { realPath = java.net.URLDecoder.decode(realPath, "utf-8"); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } return realPath; }// getAppPath定义结束 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getRealPath()); System.out.println(getProjectPath()); } }使用Jar包,在Tomcat的运行结果如下: ProjectPath: D:\J2EE\Tomcat 6.0\webapps\MyService1WebP\WEB-INF\lib RealPath: D:\J2EE\Tomcat 6.0\webapps\MyService1WebP\WEB-INF\classes Apppath: D:\J2EE\Tomcat 6.0\webapps\MyService1WebP\WEB-INF\classes java的System.getProperty()方法可以获取的值
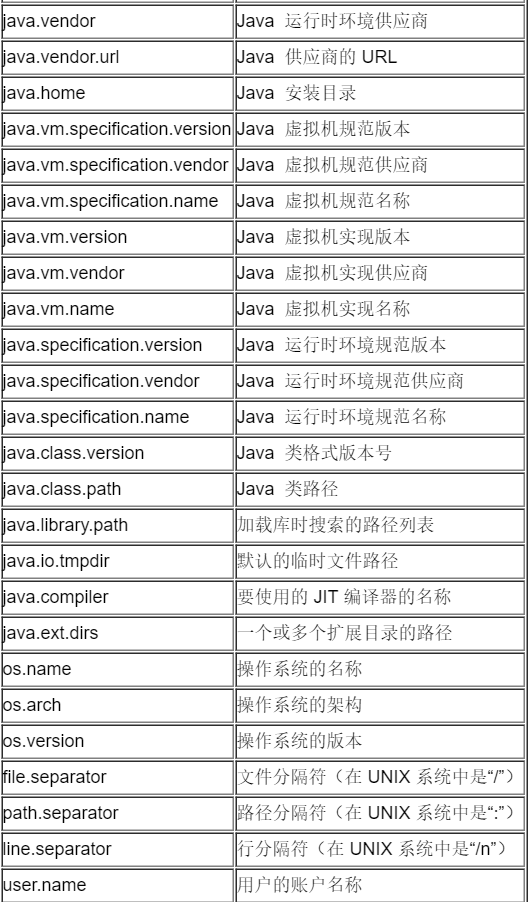
获取的代码示例: public class SystemProperty { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("java_vendor:" + System.getProperty( "java.vendor" )); System.out.println("java_vendor_url:" + System.getProperty("java.vendor.url" )); System.out.println("java_home:" + System.getProperty( "java.home" )); System.out.println("java_class_version:" + System.getProperty("java.class.version" )); System.out.println("java_class_path:" + System.getProperty("java.class.path" )); System.out.println("os_name:" + System.getProperty( "os.name" )); System.out.println("os_arch:" + System.getProperty( "os.arch" )); System.out.println("os_version:" + System.getProperty( "os.version" )); System.out.println("user_name:" + System.getProperty( "user.name" )); System.out.println("user_home:" + System.getProperty( "user.home" )); System.out.println("user_dir:" + System.getProperty( "user.dir" )); System.out.println("java_vm_specification_version:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.version" )); System.out.println("java_vm_specification_vendor:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.vendor" )); System.out.println("java_vm_specification_name:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.specification.name" )); System.out.println("java_vm_version:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.version" )); System.out.println("java_vm_vendor:" + System.getProperty("java.vm.vendor" )); System.out .println("java_vm_name:" + System.getProperty( "java.vm.name" )); System.out.println("java_ext_dirs:" + System.getProperty("java.ext.dirs" )); System.out.println("file_separator:" + System.getProperty("file.separator" )); System.out.println("path_separator:" + System.getProperty("path.separator" )); System.out.println("line_separator:" + System.getProperty("line.separator" )); }======================================================================= System.setProperties( “proxySet”, “true” ); System.setProperties( “proxyHost”, “192.168.31.117” ); System.setProperties( “proxyPort”, “80” ); 这里的proxySet,proxyHost,proxyPort等等这些系统的属性名称是从哪里知道的? ——通过JDK文档中对java.lang.system的static Properties getProperties()方法的介绍,可以获知所有可用属性的含义。 ——根本没有proxySet,proxyHost和proxyPort, 这些是user defined property,那么用户定义的属性如何起作用的? JavaVM实现Proxy的方法 要想让java应用使用代理连接网络,只需要设置一下system properties,有两种方法可以设置,一是直接在java代码里面调用System.setProperty()方法,还有就是通过-D选项添加 java虚拟机参数,如 java -Dhttp.proxyHost=192.168.254.254 -Dhttp.proxyPort=9000 ,当然也可以指定不使用代理访问的网站或者主机,http.nonProxyHosts属性指定不使用代理访问的域。示例如下所示: System.setProperty(“http.proxyHost”, “192.168.254.254”); System.setProperty(“http.proxyPort”, “9000”); System.setProperty(“http.nonProxyHosts”, “localhost”); 如果你想使用ftp代理可以以相同的方式设定如下系统属性:ftp.proxyHost, ftp.proxyPort , and 使用socket代理可以设定socks.ProxyHost socks.ProxyPort 也可以使用如下代码: Properties sysProperties = System.getProperties(); //Specify proxy settings sysProperties.put(“proxyHost”, “myhost”);//myhost设置为代理的地址 sysProperties.put(“proxyPort”, “myport”);//myport设置为代理端口 sysProperties.put(“proxySet”, “true”); 补充: Java网络代理服务器环境变量 Java 是一种面向对象的网络语言,Java 的JVM已经提供了可以设置与网络代理服务相关的环境变量,这些环境变量是按照键值名(Key)和值(Value)实现配置的。而这些环境变量与应用程序 息息相关。比如:大家比较熟悉的classpath环境变量等。从表面上看,JVM的环境变量有点类似Windows的*.ini,该环境变量是按照纯文 本的格式存储的。 Http 代理服务是目前Internet环境下,应有最为广泛的代理服务。一般的网络浏览器,如:微软的IE和网景的Netscape都提供对Http代理服务的 配置选项。在Java应用程序中,对Http代理服务的使用是通过配置Java 虚拟机的JVM的环境变量来实现的。针对http代理服务,Java 虚拟机提供了如下环境变量: http.proxySet 该环境变量用以设置应用程序是否使用http协议代理,值为True/False。 注意:在设置环境变量时候,变量值True/False是按照字符串的形式进行设置的。 http.proxyHost 该环境变量用以设置应用程序所使用的http协议代理服务器的主机,比如:我们使用 http://172.14.10.34 作为http的代理服务器主机。 http.proxyport 该环境变量用以设置应用程序所使用的http协议代理服务器的主机的端口号。比如:我们使用 http://172.14.10.34 的8080端口作为http的代理服务器。 如:将Java应用程序的Http代理服务器设为http://172.14.10.34 ,端口为8080,可以使用如下代码: String host=”http://172.14.10.34 “; String port=”8080”; System.setproperty(“http.proxySet”, “true”); System.setproperty(“http.proxyHost”, host); System.setproperty(“http.proxyport”, port); 一旦设置好了Java应用程序的http代理环境变量,Java应用程序就可以通过http代理服务透明地访问与http相关的网络资源。 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |