Android文件基本操作(创建文件(夹)、复制文件(夹)、设置文件访问权限) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 解压缩支持文件时出错:无法创建目录或文件 › Android文件基本操作(创建文件(夹)、复制文件(夹)、设置文件访问权限) |
Android文件基本操作(创建文件(夹)、复制文件(夹)、设置文件访问权限)
|
Android文件基本操作
一、创建文件夹和文件二、复制文件三、复制文件夹及其文件四、删除文件或文件夹五、设置文件的访问权限
一、创建文件夹和文件
// 获取当前包名的files路径:/data/user/0/com.exa.myapplication/files
val PATH = this.filesDir.absolutePath
// 创建src和dst文件夹
// 【注】需要有PATH目录的权限才能创建子目录
// 若PATH文件夹权限为root权限,则使用adb shell chown命令修改权限
val src = File(PATH + "/" + "src")
// 判断文件夹是否存在,不存在就进行创建
if (!src.exists()) {
if (!src.mkdirs()){
Log.e(TAG, "create directory failed.")
}
}
val dst = File(PATH + "/" + "dst")
if (!dst.exists()) {
if (!dst.mkdirs()){
Log.e(TAG, "create directory failed.")
}
}
// 创建info.txt文件,并写入数据———"hello info"
val srcPath = File("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src/info.txt")
val fos = FileOutputStream(srcPath)
fos.write("hello info".toByteArray())
fos.close()
二、复制文件
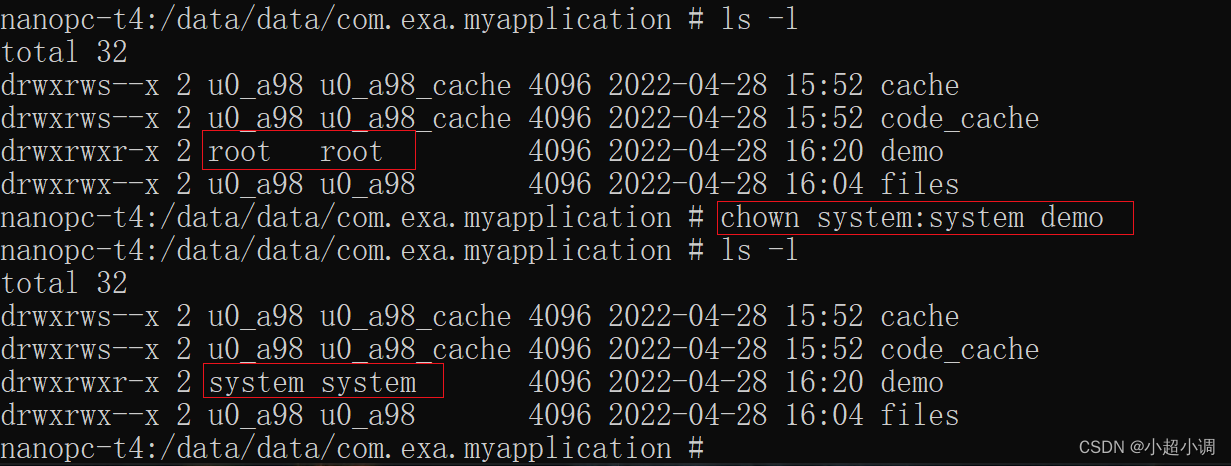
将src目录下的info.txt复制到dst目录并重命名为info_dst.txt 1、 方法一:调用java.nio.file.Files.copy() val srcPath = File("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src/info.txt") // 判断源文件是否存在、可读 if (!srcPath.exists()){ Log.i(TAG, "file is not exist.") return } else if (!srcPath.isFile){ Log.i(TAG, "Not a file.") return } else if (!srcPath.canRead()){ Log.i(TAG, "file is not readable.") return } val fos = FileOutputStream(srcPath) fos.write("hello info".toByteArray()) fos.close() // 设置目标文件路径 val dstPath = File("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/dst/info_dst.txt") // 复制文件,第一个和第二个参数为PATH类型 Files.copy(srcPath.toPath(), dstPath.toPath(), StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING)2、方法二:使用输入输出流 val srcPath = File("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src/info.txt") // 判断源文件是否存在、可读 if (!srcPath.exists()){ Log.i(TAG, "file is not exist.") return } else if (!srcPath.isFile){ Log.i(TAG, "Not a file.") return } else if (!srcPath.canRead()){ Log.i(TAG, "file is not readable.") return } val input = FileInputStream(srcPath) // 设置目标文件路径 val output = FileOutputStream("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/dst/info_dst.txt") var length = -1 val buf = ByteArray(1024) while(input.read(buf).also { length = it } != -1){ output.write(buf, 0, length) } output.flush() input.close() output.close() 三、复制文件夹及其文件 /** * 复制文件夹及其中的文件 * @param oldPath String 原文件夹路径 如:data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src * @param newPath String 复制后的路径 如:data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/dst * @return `true` if and only if the directory and files were copied; * `false` otherwise */ fun copyFolder(oldPath: String, newPath: String): Boolean { return try { val newFile = File(newPath) if (!newFile.exists()) { if (!newFile.mkdirs()) { Log.e(TAG, "create directory failed.") return false } } val oldFile = File(oldPath) // 获取oldPath路径下的全部文件 val files = oldFile.list() var temp: File for (file in files) { temp = if (oldPath.endsWith(File.separator)) { File(oldPath + file) } else { File(oldPath + File.separator + file) } if (temp.isDirectory) { // 如果temp是子文件夹,则继续递归调用 copyFolder("$oldPath/$file", "$newPath/$file") }else if (temp.isFile && temp.exists() && temp.canRead()){ val fileInputStream = FileInputStream(temp) val fileOutputStream = FileOutputStream(newPath + "/" + temp.name) val buffer = ByteArray(1024) var byteRead: Int while (fileInputStream.read(buffer).also { byteRead = it } != -1) { fileOutputStream.write(buffer, 0, byteRead) } fileInputStream.close() fileOutputStream.flush() fileOutputStream.close() } } true } catch (e: Exception) { e.printStackTrace() false } } 四、删除文件或文件夹1、删除文件 只需要调用File的delete方法即可删除指定文件 File("x.txt").delete()2、删除文件夹 如果文件夹不为空,调用delete方法是无法删除文件夹的。需要先删除文件夹中包含的所有文件,最后再删掉文件夹。 fun deleteDirWihtFile(dir: File?) { if (dir == null || !dir.exists() || !dir.isDirectory) return for (file in dir.listFiles()) { if (file.isFile) { file.delete() // 删除所有文件 } else if (file.isDirectory) { deleteDirWihtFile(file) // 递规的方式删除文件夹 } } dir.delete() // 删除目录本身 } 五、设置文件的访问权限1、方法一:使用File中的方法 val file = File("data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src/info.txt") /** * 参数一是executable:为true时设置权限;为false时没有该权限 * 参数二是ownerOnly:为true时只对所有者生效;为false时对所有者,所在组和其它组都生效 */ file.setReadable(true, false) file.setWritable(true, false) file.setExecutable(true, false)2、方法二:执行授权命令 val permissionsCmd = "chmod 777 data/data/com.exa.myapplication/files/src/info.txt" Runtime.getRuntime().exec(permissionsCmd)需要说明的是: 读写文件的前提是该文件具有读写权限 复制文件和设置文件访问权限则需要app具有src和dst目录的拥有者权限,一般的,app默认是具有所在包名的权限为u0_a*:u0_a*(我这里是u0_a98:u0_a98),若目录的拥有者权限为root:root,则app是无法在该目录完成复制文件操作的,但可以通过Linux命令重新设置目录权限,如下 adb shell chown system:system 目录名 // app的AndroidManifest.xml需要添加android:sharedUserId="android.uid.system"
当app去写new.txt文件时,会提示 W/System.err: java.io.FileNotFoundException: data/data/com.test.pac/files/new.txt: open failed: EACCES (Permission denied)【解决办法】 方法一:app自己创建文件,完成写操作 方法二:adb shell chown u0_a98:u0_a98 data/data/com.test.pac/files/new.txt |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |
 最后,给出linux中文件系统基本权限的说明图,方便查阅
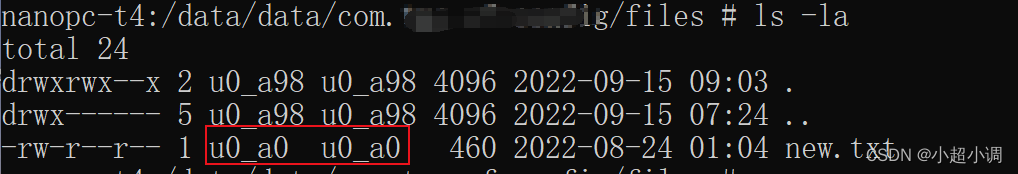
最后,给出linux中文件系统基本权限的说明图,方便查阅  【注意】 如果通过adb去push文件,该文件权限的拥有者和所属组就不是u0_a98,而是其他,如u0_a0(如果执行adb root成功了,会是root)。只要文件拥有者和所属组不是u0_a98,app虽然可以读,但没有写权限,具体如下。 adb push new.txt data/data/com.test.pac/files
【注意】 如果通过adb去push文件,该文件权限的拥有者和所属组就不是u0_a98,而是其他,如u0_a0(如果执行adb root成功了,会是root)。只要文件拥有者和所属组不是u0_a98,app虽然可以读,但没有写权限,具体如下。 adb push new.txt data/data/com.test.pac/files