LocalDateTime获取时间类(当前时间) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 获取当前年月日时间戳 › LocalDateTime获取时间类(当前时间) |
LocalDateTime获取时间类(当前时间)
|
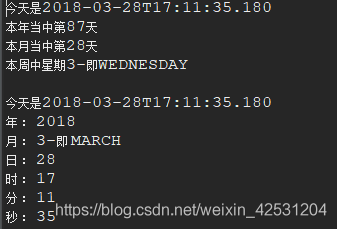
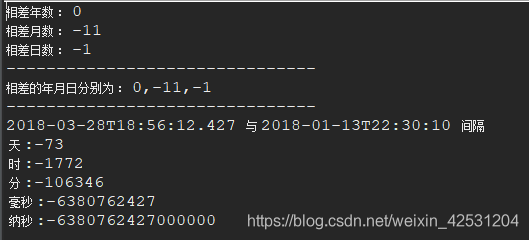
LocalDateTime获取时间类 LocalDateTime获取时间类是java8提供的一个新的获取时间类,该类可以获取任意格式的时间,使用非常方便。 获取当前当前时间 public void timeNow() { //输出当前时间 LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(dateTime); }2.获取指定格式时间 public void formatDateTime() { //格式化格式 String format = "YYYY-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"; // DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern方法根据指定的格式输出时间 String formatDateTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(format)); System.out.println(formatDateTime); }3.获取某个日期的时间 获取某个日期的时间可以通过选择不同的plus方法一直选择下去。 public void getDateTime() { //获取当前日期后一天的后一个小时 LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(1).plusHours(1); System.out.println(dateTime); //格式化格式 String format = "YYYY-MM-dd hh:mm:ss"; //获取当前日期后三天以后3小时的时间并格式化输出 String formatDate = LocalDateTime.now().plusDays(3).plusHours(3).format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(format)); System.out.println(formatDate); } ```在java8以前,或许: 当你在做有关时间日期的操作时,你会想到用Date; 当你在做日期、月份、天数相加减时,你会想到用Calendar; 当你需要对时间日期进行格式化时,你会想到使用SimpleDateFormat或DateFormat下的其他子类; 但是,你必须知道,以上有关的时间日期操作对象,都是可变的、线程不安全的,同时,如果作为一个经常写过类似代码的人来说,尽管有相关对象提供某些操作,但并不能很快、很简单的就能得到最终想要的结果,如:要计算两个时间点之间相差的年、月、日、周、时、分、秒等,这些计算尽管原有API也能够实现,但原有API除了线程不安全之外,另外一个不足之处就是代码繁琐,性能低! **为何我们总提多线程下,线程不安全?**对于初学者来说,可能觉得能够简单实现出功能就已经足够,但是真正的开发项目是不可能仅仅考虑功能的实现的,还要考虑项目的安全性、稳定性、高性能、高可用性等等!因此,作为java开发者,多线程的知识是必不可少的。而也正因为多线程,才会出现一大堆问题(简称线程安全性问题),作为开发者,就应该写出不仅能实现功能的代码,还要是线程安全的代码。那么,学习并熟悉掌握新的线程安全的API就显得非常重要了! 没错,java8出的新的时间日期API都是线程安全的,并且性能更好,代码更简洁! 新时间日期API常用、重要对象介绍 ZoneId: 时区ID,用来确定Instant和LocalDateTime互相转换的规则Instant: 用来表示时间线上的一个点(瞬时)LocalDate: 表示没有时区的日期, LocalDate是不可变并且线程安全的LocalTime: 表示没有时区的时间, LocalTime是不可变并且线程安全的LocalDateTime: 表示没有时区的日期时间, LocalDateTime是不可变并且线程安全的Clock: 用于访问当前时刻、日期、时间,用到时区Duration: 用秒和纳秒表示时间的数量(长短),用于计算两个日期的“时间”间隔Period: 用于计算两个“日期”间隔其中,LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime是新API里的基础对象,绝大多数操作都是围绕这几个对象来进行的,有必要搞清楚: LocalDate : 只含年月日的日期对象 LocalTime :只含时分秒的时间对象 LocalDateTime : 同时含有年月日时分秒的日期对象 本文将以实例讲解日常开发中常用到的时间日期操作,如: 获取当前日期、时间 指定时间日期创建对应的对象 计算两个时间点的间隔 判断两个时间的前后 时间日期的格式化 获取时间戳 时间、日期相加减 获取给定时间点的年份、月份、周、星期等 新时间日期API详解与示例 获取当前时间 LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now(); LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now(); LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(); System.out.println(localDate); System.out.println(localTime); System.out.println(localDateTime);运行结果: 结果: 运行结果: 结果: 结果: 时间戳 事实上Instant就是java8以前的Date, 可以使用以下两个类中的方法在这两个类型之间进行转换, 比如Date.from(Instant)就是用来把Instant转换成java.util.date的, 而new Date().toInstant()就是将Date转换成Instant的 Instant instant = Instant.now(); //2019-06-08T16:50:19.174Z System.out.println(instant); Date date = Date.from(instant); Instant instant2 = date.toInstant(); //Sun Jun 09 00:50:19 CST 2019 System.out.println(date); //2019-06-08T16:50:19.174Z System.out.println(instant2);计算时间、日期间隔 Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔 Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔 //计算两个日期的日期间隔-年月日 LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2018, 2, 13); LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.of(2017, 3, 12); //内部是用date2-date1,所以得到的结果是负数 Period period = Period.between(date1, date2); System.out.println("相差年数 : " + period.getYears()); System.out.println("相差月数 : " + period.getMonths()); System.out.println("相差日数 : " + period.getDays()); //还可以这样获取相差的年月日 System.out.println("-------------------------------"); long years = period.get(ChronoUnit.YEARS); long months = period.get(ChronoUnit.MONTHS); long days = period.get(ChronoUnit.DAYS); System.out.println("相差的年月日分别为 : " + years + "," + months + "," + days); //注意,当获取两个日期的间隔时,并不是单纯的年月日对应的数字相加减,而是会先算出具体差多少天,在折算成相差几年几月几日的 //计算两个时间的间隔 System.out.println("-------------------------------"); LocalDateTime date3 = LocalDateTime.now(); LocalDateTime date4 = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 1, 13, 22, 30, 10); Duration duration = Duration.between(date3, date4); System.out.println(date3 + " 与 " + date4 + " 间隔 " + "\n" + " 天 :" + duration.toDays() + "\n" + " 时 :" + duration.toHours() + "\n" + " 分 :" + duration.toMinutes() + "\n" + " 毫秒 :" + duration.toMillis() + "\n" + " 纳秒 :" + duration.toNanos() + "\n" ); //注意,并没有获得秒差的,但既然可以获得毫秒,秒就可以自行获取了结果: 将时间日期对象转为格式化后的时间日期对象 将时间日期对象转为格式化后的时间日期对象 //新的格式化API中,格式化后的结果都默认是String,有时我们也需要返回经过格式化的同类型对象 LocalDateTime ldt1 = LocalDateTime.now(); DateTimeFormatter dtf1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); String temp = dtf1.format(ldt1); LocalDateTime formatedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(temp, dtf1); System.out.println(formatedDateTime);结果: 结果: |
【本文地址】
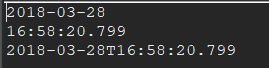
 日期时间的加减 对于LocalDate,只有精度大于或等于日的加减,如年、月、日; 对于LocalTime,只有精度小于或等于时的加减,如时、分、秒、纳秒; 对于LocalDateTime,则可以进行任意精度的时间相加减;
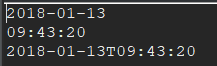
日期时间的加减 对于LocalDate,只有精度大于或等于日的加减,如年、月、日; 对于LocalTime,只有精度小于或等于时的加减,如时、分、秒、纳秒; 对于LocalDateTime,则可以进行任意精度的时间相加减;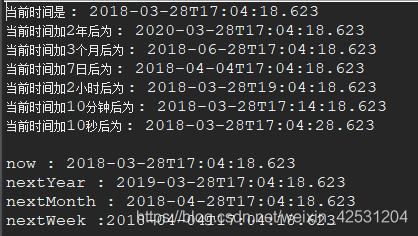 将年、月、日等修改为指定的值,并返回新的日期(时间)对象 析: 其效果与时间日期相加减差不多,如今天是2018-01-13,要想变为2018-01-20有两种方式 a. localDate.plusDays(20L) -> 相加指定的天数 b. localDate.withDayOfYear(20) -> 直接指定到哪一天
将年、月、日等修改为指定的值,并返回新的日期(时间)对象 析: 其效果与时间日期相加减差不多,如今天是2018-01-13,要想变为2018-01-20有两种方式 a. localDate.plusDays(20L) -> 相加指定的天数 b. localDate.withDayOfYear(20) -> 直接指定到哪一天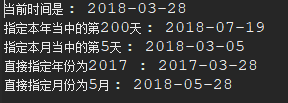
 long毫秒值转换为日期
long毫秒值转换为日期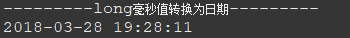 借鉴:https://www.cnblogs.com/mark5/p/11865833.html
借鉴:https://www.cnblogs.com/mark5/p/11865833.html