特征脸的人脸识别MATLAB程序(附完整代码和结果) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 脸型辨别方法图片 › 特征脸的人脸识别MATLAB程序(附完整代码和结果) |
特征脸的人脸识别MATLAB程序(附完整代码和结果)
|
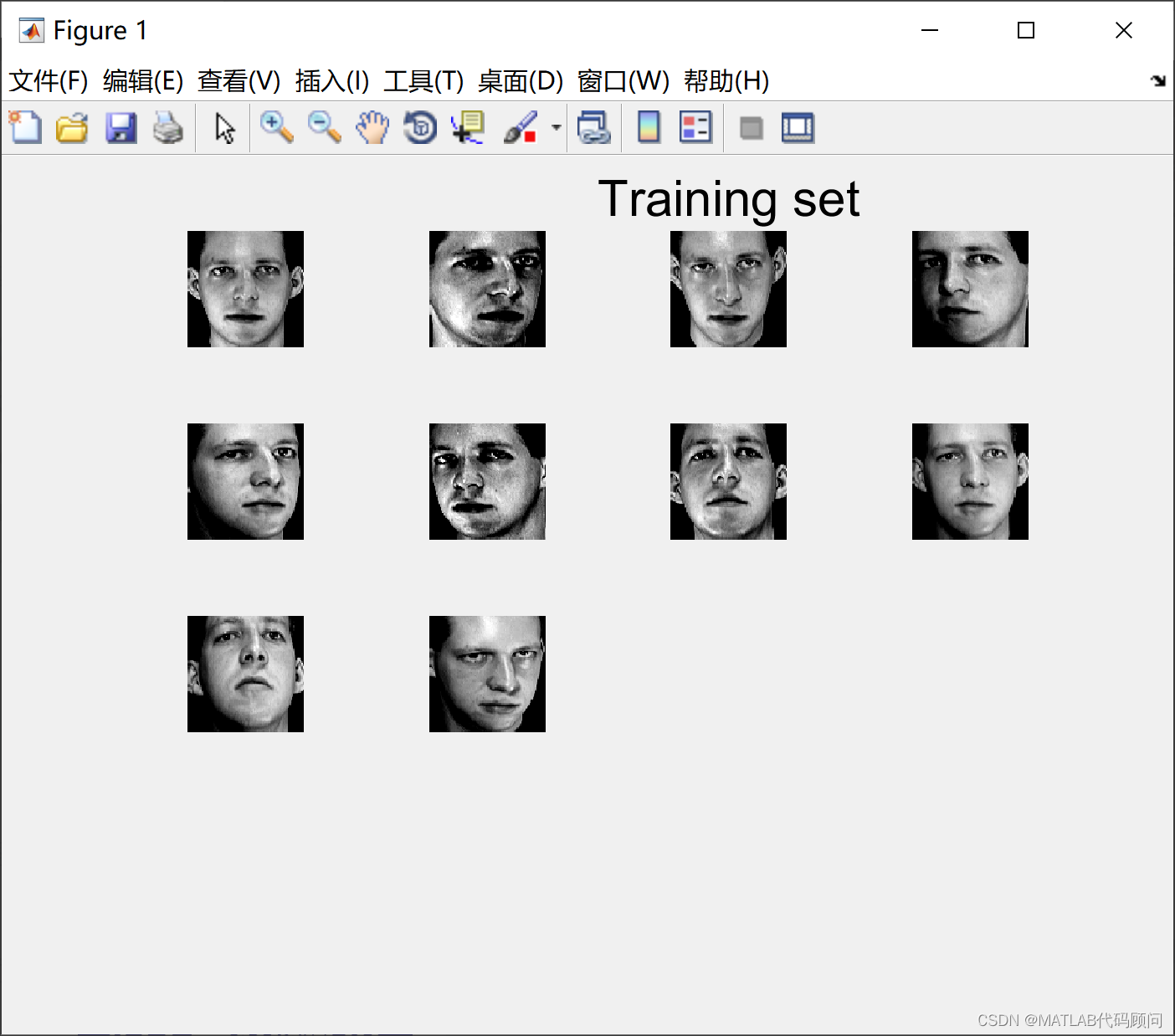
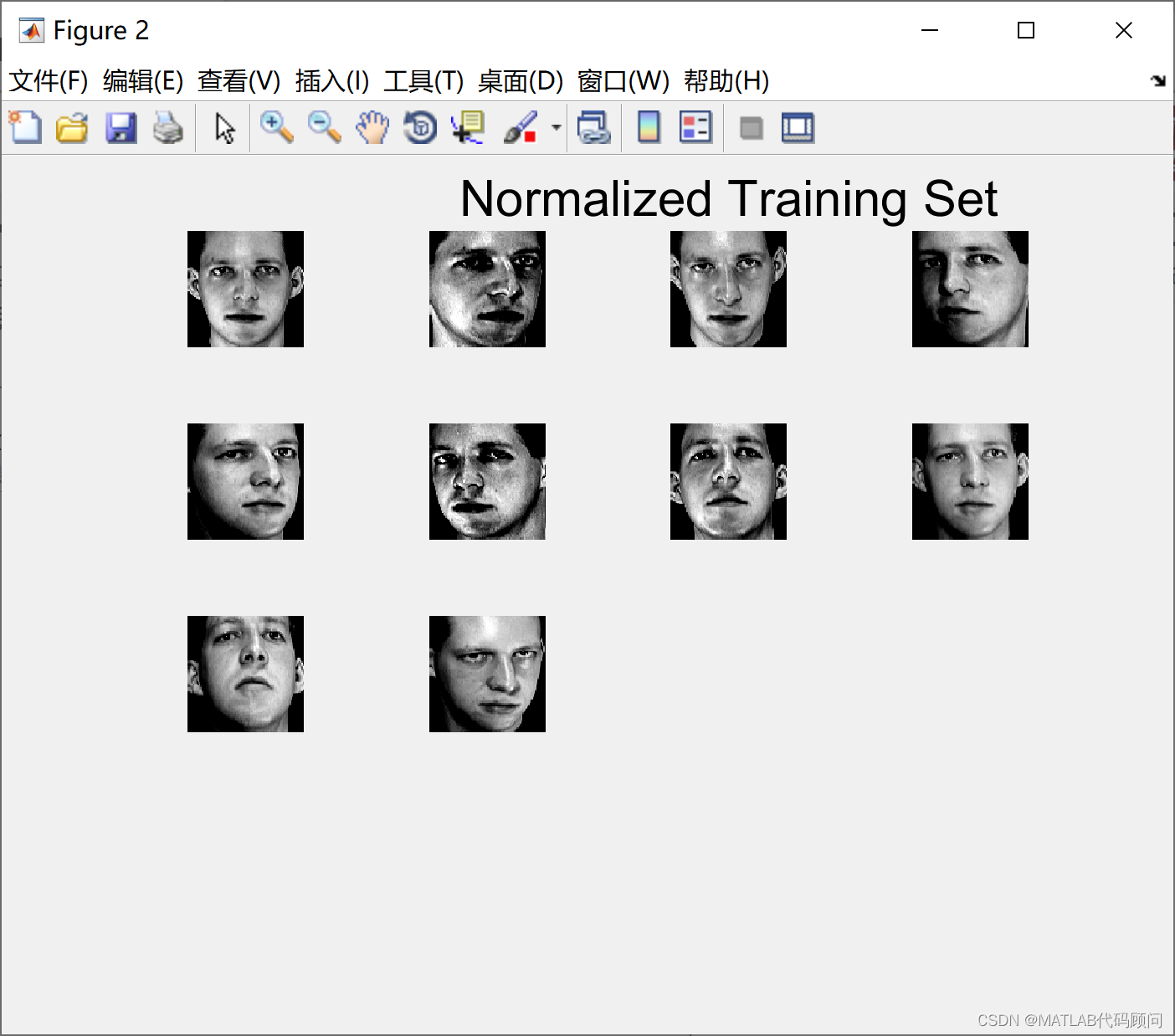
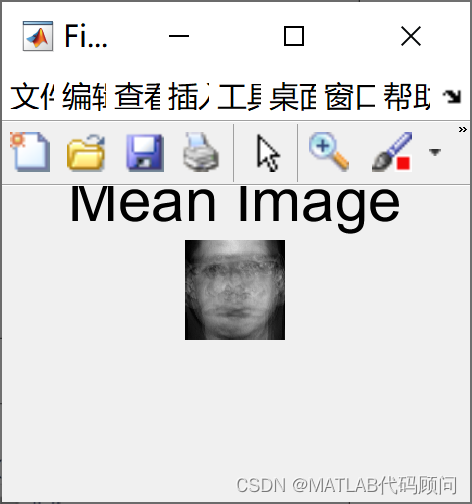
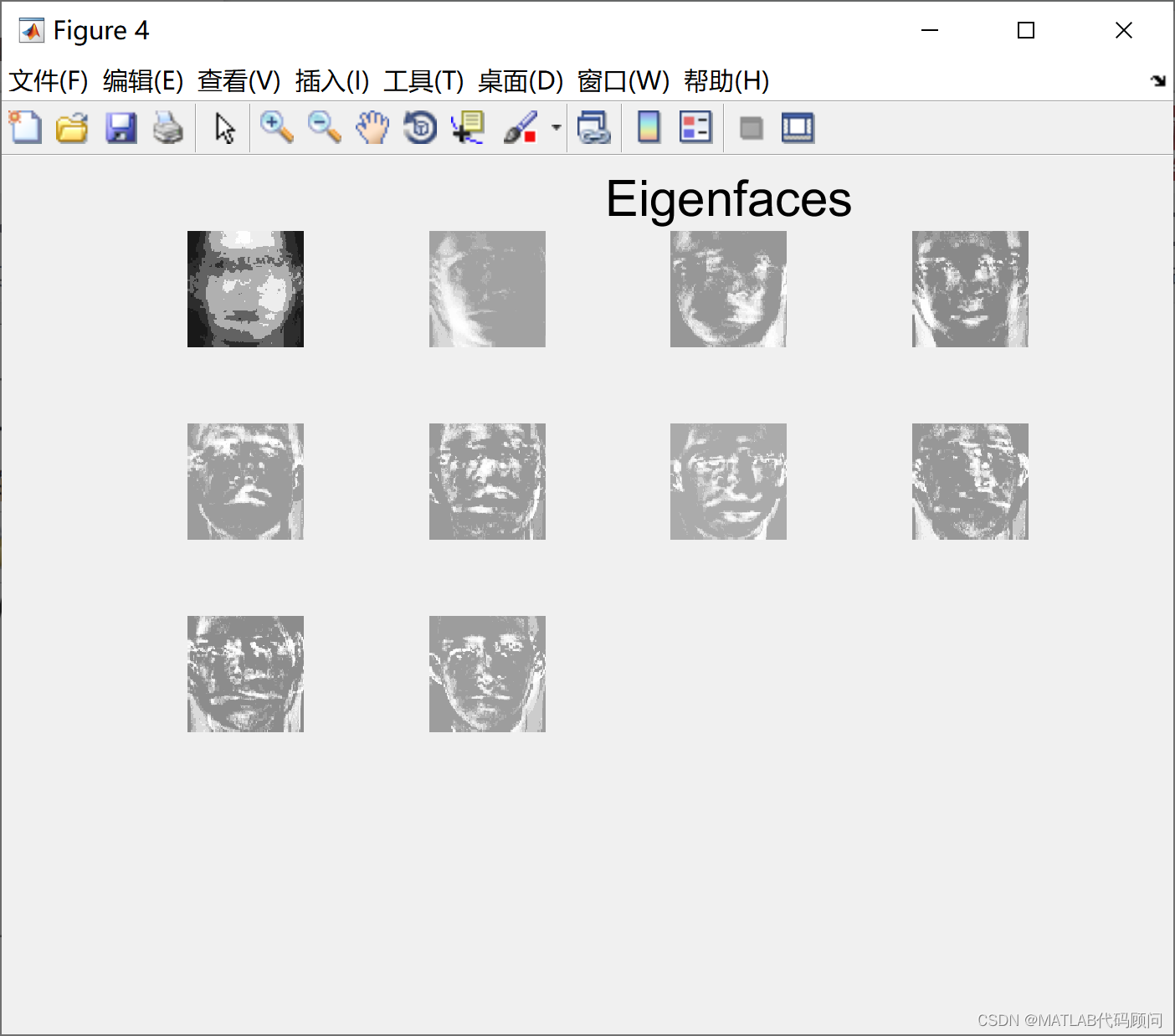
基于特征脸的人脸识别主体流程为: 1.读取训练数据和预处理:读取脸的图片数据后,将每个人脸转换为一个列向量,训练集人脸构成一个矩阵A。 2.求平均脸:对每一行都求平均值,得到一个列向量,我们称之为“平均脸”,是所有人脸的平均。 3.样本规范化:矩阵A的每一个脸都减去平均脸乘以标准差。 4.求特征脸:提高A的协方差矩阵C,再求C的特征向量。每一个特征向量就是“特征脸”。特点:也即原始的人脸都可表为特征脸的线性组合。 5.构造脸空间:取出特征值较大的特征脸,构成投影矩阵。 5. 脸投影:每一个训练集的脸投影到脸空间中,得到脸空间中的一个点。 6.识别:读取待识别的人脸图片数据,投影到脸空间,依次与脸空间中训练集的点进行比较距离,距离最小的即为识别出的脸 采用特征脸的人脸识别MATLAB程序如下: % Face recognition %人脸识别代码 clear all close all clc %训练集数目 M=10; % 选择标准差和均值 它可以是任何接近大多数图像的标准和平均值的数字。 um=100; ustd=80; % 读取和显示图像 %读入M个训练图像并显示在一个窗口上 S=[]; %img matrix figure; for i=1:M str=strcat(int2str(i),'.bmp'); %concatenates two strings that form the name of the image eval('img=imread(str);'); subplot(ceil(sqrt(M)),ceil(sqrt(M)),i) imshow(img) if i==3 title('Training set','fontsize',18) end drawnow; [irow icol]=size(img); % get the number of rows (N1) and columns (N2)获得图像的大小,所有图像的大小要一致 temp=reshape(img',irow*icol,1); %creates a (N1*N2)x1 matrix一幅图像构造一个向量 向量的大小和图像大小有关 S=[S temp]; %X is a N1*N2xM matrix after finishing the sequence 生成一个向量矩阵,M个图像有M列 %this is our S end %Here we change the mean and std of all images. We normalize all images. %This is done to reduce the error due to lighting conditions. %下面是对图像规范化,更具所有图像的的平均值和方差 for i=1:size(S,2) temp=double(S(:,i)); m=mean(temp); st=std(temp); S(:,i)=(temp-m)*ustd/st+um; end %show normalized images 显示规范化后的图像 figure; for i=1:M str=strcat(int2str(i),'.bmp'); img=reshape(S(:,i),icol,irow); img=img'; eval('imwrite(img,str)'); subplot(ceil(sqrt(M)),ceil(sqrt(M)),i) imshow(img) drawnow; if i==3 title('Normalized Training Set','fontsize',18) end end %mean image;显示平均图像,所有图像叠加在一起 m=mean(S,2); %obtains the mean of each row instead of each column tmimg=uint8(m); %converts to unsigned 8-bit integer. Values range from 0 to 255 img=reshape(tmimg,icol,irow); %takes the N1*N2x1 vector and creates a N2xN1 matrix img=img'; %creates a N1xN2 matrix by transposing the image. figure; imshow(img); title('Mean Image','fontsize',18) % Change image for manipulation % 对图像变换便于处理 dbx=[]; % A matrix for i=1:M temp=double(S(:,i)); dbx=[dbx temp]; end %求协方差矩阵 C=A'A, L=AA' A=dbx'; L=A*A'; [vv,dd]=eig(L);% vv是L的特征向量, dd是L=dbx'*dbx和C=dbx*dbx'的特征值; % 对特征值进行排序并去掉0 v=[]; d=[]; for i=1:size(vv,2) if(dd(i,i)>1e-4) v=[v vv(:,i)]; d=[d dd(i,i)]; end end %sort, will return an ascending sequence %排序并返回降序的 [B index]=sort(d); ind=zeros(size(index)); dtemp=zeros(size(index)); vtemp=zeros(size(v)); len=length(index); for i=1:len dtemp(i)=B(len+1-i); ind(i)=len+1-index(i); vtemp(:,ind(i))=v(:,i); end d=dtemp; v=vtemp; %对特征向量进行规范化 for i=1:size(v,2) % 每一列循环 kk=v(:,i); temp=sqrt(sum(kk.^2)); v(:,i)=v(:,i)./temp; end %得到C的特征向量矩阵 u=[]; for i=1:size(v,2) temp=sqrt(d(i)); u=[u (dbx*v(:,i))./temp]; end % Normalization of eigenvectors for i=1:size(u,2) kk=u(:,i); temp=sqrt(sum(kk.^2)); u(:,i)=u(:,i)./temp; end % show eigenfaces; %显示特征脸 figure; for i=1:size(u,2) img=reshape(u(:,i),icol,irow); img=img'; img=histeq(img,255); subplot(ceil(sqrt(M)),ceil(sqrt(M)),i) imshow(img) drawnow; if i==3 title('Eigenfaces','fontsize',18) end end % 找出训练集中每张脸的权重 omega = [];% 训练集中脸的权重 for h=1:size(dbx,2) WW=[]; for i=1:size(u,2) t = u(:,i)'; WeightOfImage = dot(t,dbx(:,h)'); WW = [WW; WeightOfImage]; end omega = [omega,WW]; end % Acquire new image % Note: the input image must have a bmp or jpg extension. % It should have the same size as the ones in your training set. % It should be placed on your desktop %获取一张新的脸 %注意:图像的大小和训练集中图像大小一样 % % InputImage = input('Please enter the name of the image and its extension \n','s'); InputImage='9.bmp';% 输入 InputImage = imread(strcat(InputImage)); figure; subplot(1,2,1); imshow(InputImage); colormap('gray'); title('Input image','fontsize',18); InImage=reshape(double(InputImage)',irow*icol,1); temp=InImage; me=mean(temp); st=std(temp); temp=(temp-me)*ustd/st+um; NormImage = temp; Difference = temp-m; NormImage = Difference; p = []; aa=size(u,2); for i = 1:aa pare = dot(NormImage,u(:,i)); p = [p; pare]; end ReshapedImage = m + u(:,1:aa)*p; %m is the mean image, u is the eigenvector ReshapedImage = reshape(ReshapedImage,icol,irow); ReshapedImage = ReshapedImage'; %show the reconstructed image. 显示重构的图像 subplot(1,2,2); imagesc(ReshapedImage); colormap('gray'); title('Reconstructed image','fontsize',18); InImWeight = []; for i=1:size(u,2) t = u(:,i)'; WeightOfInputImage = dot(t,Difference'); InImWeight = [InImWeight; WeightOfInputImage]; end ll = 1:M; figure; subplot(1,2,1) stem(ll,InImWeight) title('Weight of Input Face','fontsize',14) % 查找欧几里得距离 e=[]; for i=1:size(omega,2) q = omega(:,i); DiffWeight = InImWeight-q; mag = norm(DiffWeight); e = [e mag]; end kk = 1:size(e,2); subplot(1,2,2) stem(kk,e) title('Eucledian distance of input image','fontsize',14) MaximumValue=max(e) MinimumValue=min(e) 需要讨论的可以加Q1579325979 程序结果如下:
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |