门限回归及Stata操作汇总与空间门槛回归模型简介 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 置信区间画图stata › 门限回归及Stata操作汇总与空间门槛回归模型简介 |
门限回归及Stata操作汇总与空间门槛回归模型简介
|
在这些文章中,Hansen介绍了包含个体固定效应的静态平衡面板数据门限回归模型,阐述了计量分析方法。方法方面,首先要通过减去时间均值方程,消除个体固定效应,然后再利用OLS(最小二乘法)进行系数估计。如果样本数量有限,那么可以使用自举法(Bootstrap)重复抽取样本,提高门限效应的显著性检验效率。在Hansen(1999)的模型中,解释变量中不能包含内生解释变量,无法扩展应用领域。Caner和Hansen在2004年解决了这个问题。他们研究了带有内生变量和一个外生门限变量的面板门限模型。与静态面板数据门限回归模型有所不同,在含有内生解释变量的面板数据门限回归模型中,需要利用简化型对内生变量进行一定的处理,然后用2SLS(两阶段最小二乘法)或者GMM(广义矩估计)对参数进行估计。 二.显著性检验 门槛回归模型显著性检验的目的是,检验以门檻值划分的两组样本其模型估计参数是否显著不同。 因此,不存在门槛值的零假设为:Ho:两个系数相同。同时构造LM统计量:
其中,So是在零假设下的残差平方和。由于LM统计量并不服从标准的分布。因此, Hansen(2000)提出了通过“自举法”( Bootstrap)来获得渐进分布的想法,进而得出相应的概率p值,也称为 Bootstrap P值。 这种方法的基本思想是:在解释变量和门槛值给定的前提下,模拟( Simulate)产生一组因变量序列,并使其满足N(0,e2),其中e是式(4)的残差项。每得到一个自抽样样本,就可以计算出一个模拟的エM统计量。将这一过程重复1000次。Hansen(1996)认为模拟产生的LM统计量大于式(6)的次数占总模拟次数的百分比就是“自举法”估计得到的P值。这里的Bootstrap P值类似于普通计量方法得出的相伴概率P值。例如,当 Bootstrap P值小于0.01时,表示在1 %的显著性水平下通过了LM检验,以此类推。 三.置信区间
以上的检验过程为只有一个门槛值的检验过程,为了能确定是否存在两个门槛值或者是更多的门槛值,我们应当检验是否存在两个门槛值,拒绝意味着至少存在一个门槛值。我们可以假设己经估计的第一个门槛值,然后开始寻找第二个门槛值。在确定有两个门槛值后,再寻找第三个门槛值,方法都和前面的一样,直至我们不能拒绝零假设。 四、门槛回归:threshold 阈值将一个状态从另一个状态描述出来。有一个效应(一组系数)达到阈值和另一个效应(另一组系数)。Stata的新门限命令适用于时间序列。门槛模型常用于时间序列数据。 门槛可以是一个时间 。例如,如果你认为投资策略在某个未知的日期发生了变化,你可以用一个模型来获得日期的估计,并在它前后得到不同系数的估计。或者 门槛值可以用另一个变量来表示 。例如,在一定程度的通货膨胀之外,央行会提高利率。你可以用一个模型来得到 门槛值的估计值和两边的系数。 在Stata 15中,进行门槛回归的命令为 threshold,语法格式为:threshold depvar [indepvars] [if] [in], threshvar(varname) [options] 其中,其中, depvar为被解释变量, indepvars为相关变量(解释变量)。必选项 threshvar( varname) 表示变量 varname为门槛变量,选项 nthresholds(#)指的是number of thresholds,这个命令默认只有一个门槛值( default is nthresholds(1))。也可以通过选择项 nthresholds(#) 来指定多个门槛值,比如 nthresholds(2) 表示有 2 个门槛值,not allowed with optthresh。 optthresh(#[, ictype]), select optimal number of thresholds less than or equal to #; not allowed with nthresholds,计算最优的门槛个数,一般有Bayesian information criterion (BIC)、Akaike information criterion (AIC) 、Hannan-Quinn information criterion (HQIC)三个信息准则。其中默认使用BIC信息准则进行选择。 菜单操作步骤为:Statistics > Time series > Threshold regression model 门槛回归Example
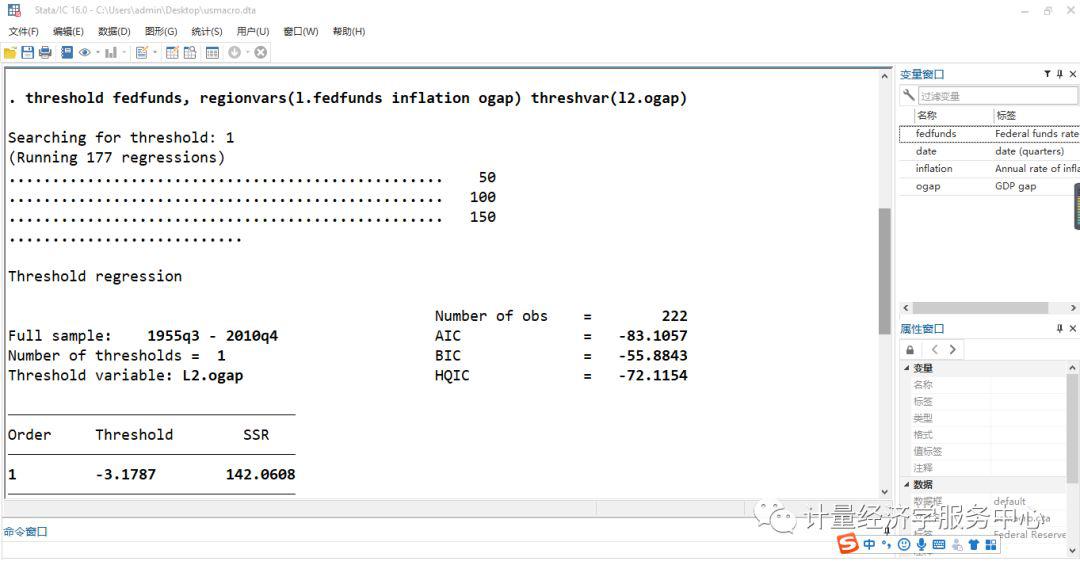
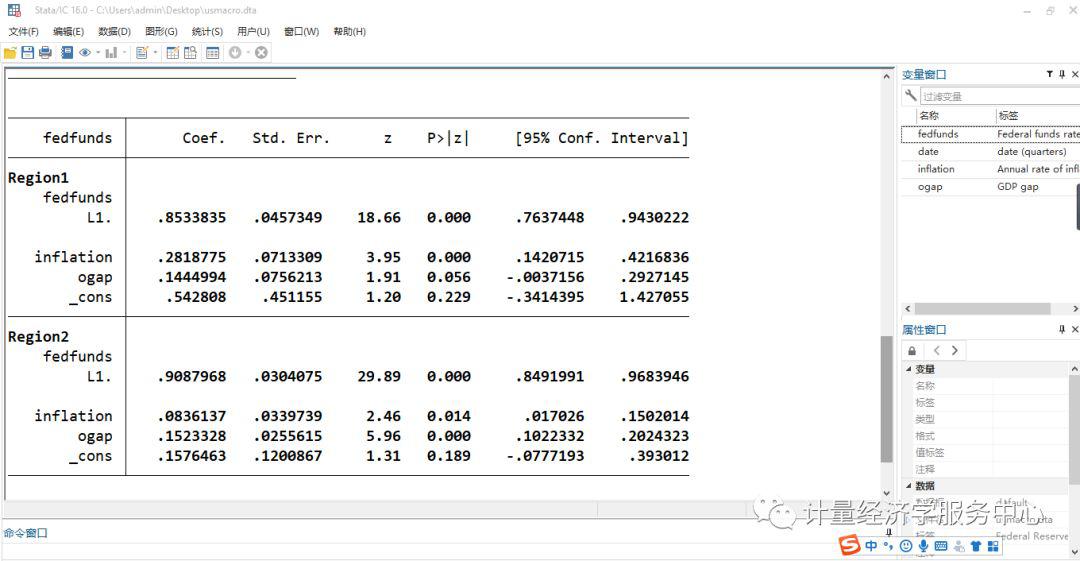
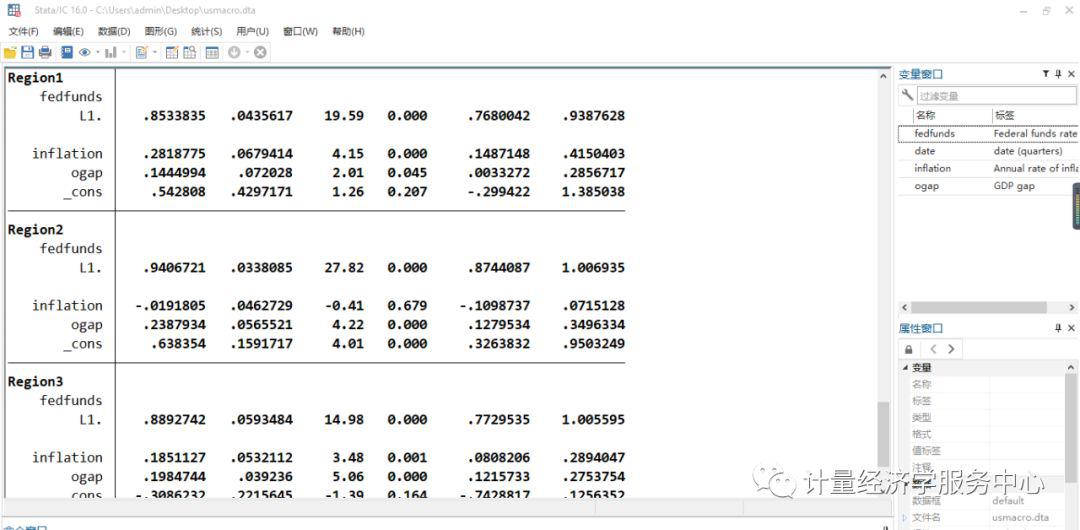
调用数据: webuse usmacro 下面进行门限回归 threshold fedfunds, regionvars(l.fedfunds inflation ogap) threshvar(l2.ogap)
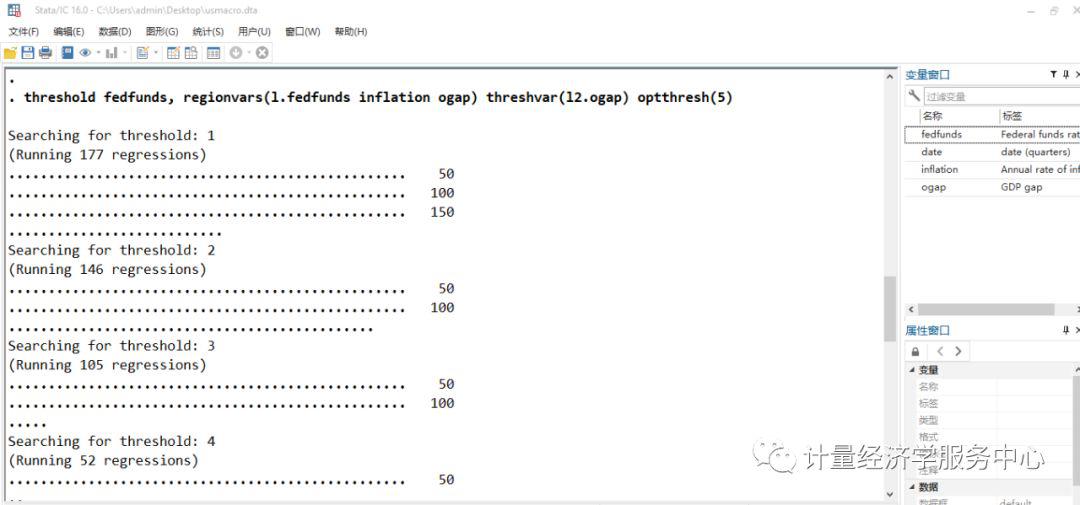
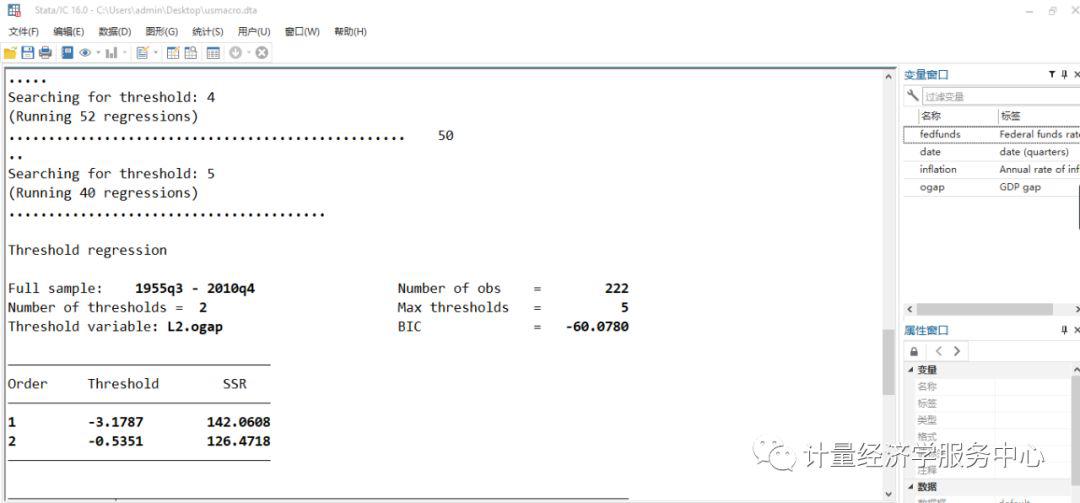
threshold fedfunds, regionvars(l.fedfunds inflation ogap) threshvar(l2.ogap) optthresh(5)
▲图:结果输出 五、xthreg命令 xthreg需要stata13及以上版本 语法格式为: xthreg depvar [indepvars] [if] [in], rx(varlist) qx(varname) [thnum(#) grid(#) trim(numlist) bs(numlist) thlevel(#) gen(newvarname) noreg nobslog thgiven options] depvar被解释变量,indepvars 解释变量,qx(varname) is the threshold variable,门限变量,thnum(#) is the number of thresholds,在stata13.0中门槛值是必要项目,需要等于大于1,小于等于3,默认值为1,也就是至少存在三个门槛值。 rx(varlist) is the regime-dependent variable. Time-series operators are allowed. rx is required. 区制变量或者制度变量 qx(varname) is the threshold variable. Time-series operators are allowed. qx is required. 门限变量或者门槛变量 thnum(#) is the number of thresholds. In the current version (Stata 13), # must be equal to or less than 3. The default is thnum(1). 门槛个数 grid(#) is the number of grid points. grid is used to avoid consuming too much time when computing large samples. The default is grid(300). 网格点数 trim(numlist) is the trimming proportion to estimate each threshold. The number of trimming proportions must be equal to the number of thresholds specified in thnum. The default is trim(0.01) for all thresholds. For example, to fit a triple-threshold model, you may set trim(0.01 0.01 0.05). bs(numlist) is the number of bootstrap replications. If bs is not set, xthreg does not use bootstrap for the threshold-effect test. bootstrap迭代次数 thlevel(#) specifies the confidence level, as a percentage, for confidence intervals of the threshold. The default is thlevel(95). 置信区间,默认为95%,即thlevel(95) gen(newvarname) generates a new categorical variable with 0, 1, 2, ... for each regime. The default is gen(_cat). noreg suppresses the display of the regression result. 不显示回归结果 nobslog suppresses the iteration process of the bootstrap. 不显示bootstrap迭代过程 thgiven fits the model based on previous results. options are any options available for [XT] xtreg. Time-series operators are allowed in depvar, indepvars, rx, and qx.
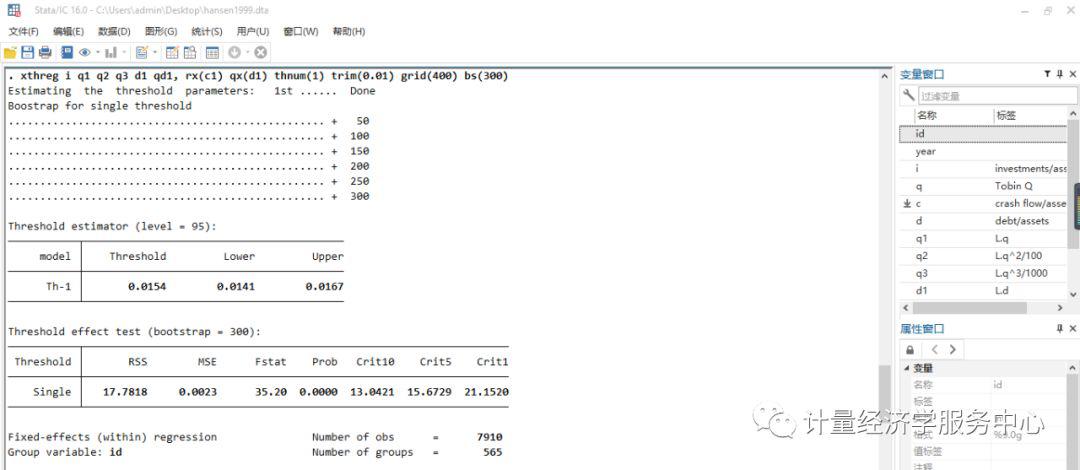
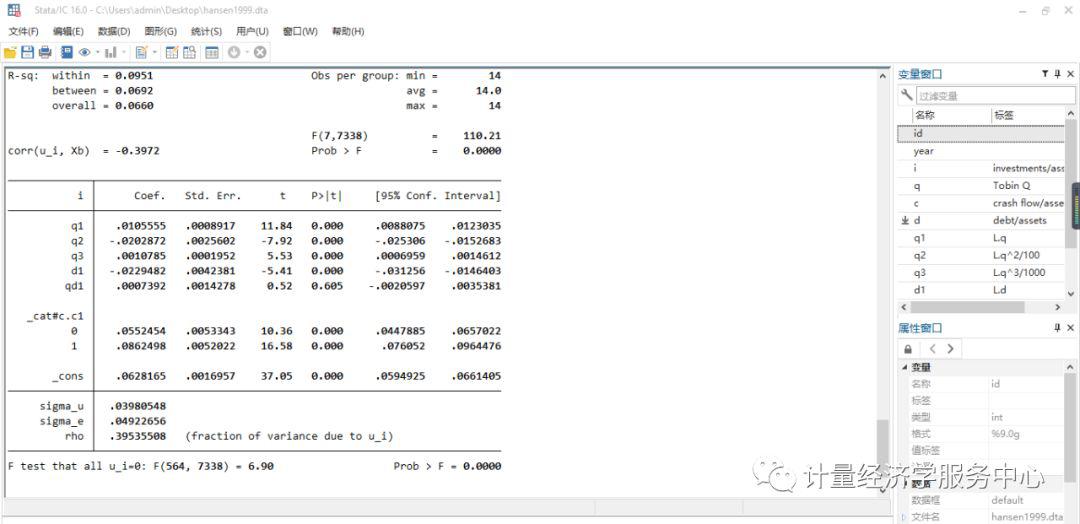
门槛回归的案例 use hansen1999 Estimate a single-threshold model xthreg i q1 q2 q3 d1 qd1, rx(c1) qx(d1) thnum(1) trim(0.01) grid(400) bs(300)
输出结果包括四个部分。第一部分输出门限估计值和自举法的结果。第二部分列表输出门限值及置信区间,Th-1代表单一门限估计值,Th-21 和Th-22代表双门限回归的两个估计值,有时Th-21和Th-1相同。第三部分列出了门限检验,包括RSS、MSE、F统计量及概率值,以及10%、5%、1%的置信水平。第四部分是固定效应回归结果。 六、xtthres命令 语法格式为:xtthres varlist [if] [in] , thres(varname) dthres(varname) [ qn(#) bs1(#) bs2(#) bs3(#) levle(#) minobs(#) ] thres(varname) specifies threshold variable, as denoted by q_it in Hansen(1999). Note that this option should not be omitted. dthres(varname) specifies the variable that will show threshold effects, as denoted by x_it in Hansen(1999). This variable will be multipled by the indicator function I(.). Note that this option should not be omitted either. qn(#) specifies the number of distinct values to be search in finding out the optimal estimate of threshold effects, r_hat, which will minimize the sum of square residuals of the model. The default value is 400. bs1(#), bs2(#), bs3(#) specify the Bootstrap times in single threshold, double threshold and triple threshold model respectively. The default values are all 300. level(#) specifies the confidence level, in percent, for confidence intervals. The default is level(95) or as set by set level; see help level. minobs specifies the minimum number of observations in each of the regimes when searching for r_hats. The default is 10. 案例介绍1 xtthres tobin size tang prof, th(grow) d(tl) xtthres tobin size tang prof, th(grow) d(tl) bs2(200) bs3(100) minobs(30) xtthres tobin size tang prof if year |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |