使用python爬取高德POI数据,并转换为WGS84经纬度坐标的点矢量 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 经纬度坐标是唯一的吗 › 使用python爬取高德POI数据,并转换为WGS84经纬度坐标的点矢量 |
使用python爬取高德POI数据,并转换为WGS84经纬度坐标的点矢量
|
一,爬取高德POI数据(高德开放平台接口+ Python)
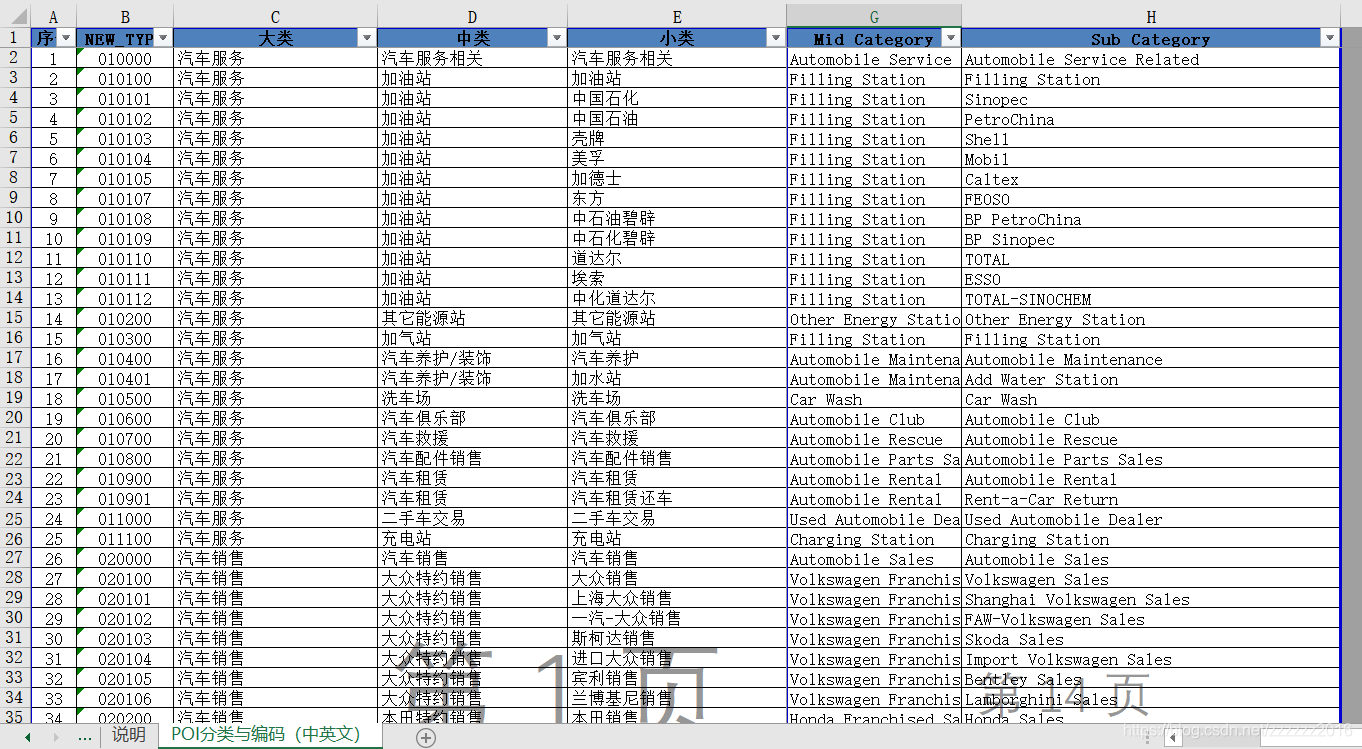
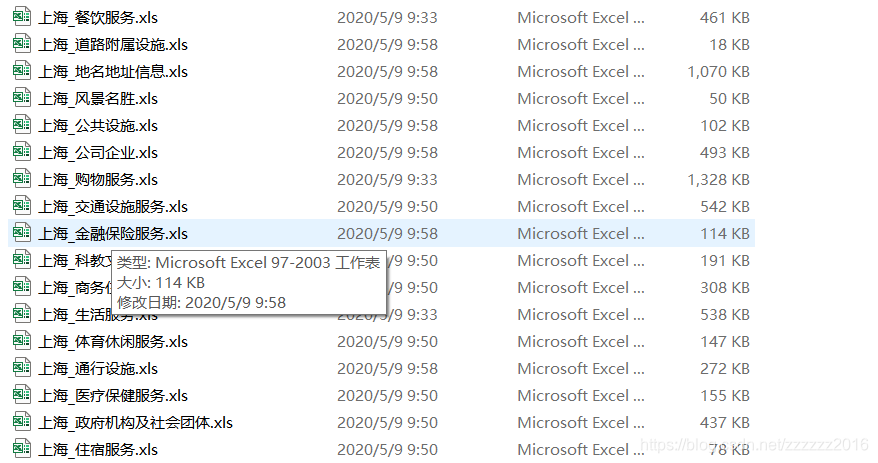
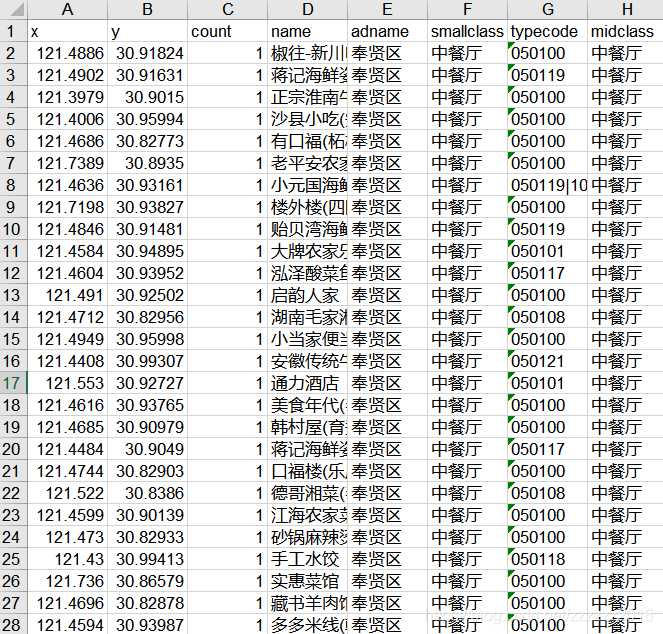
参考记者博客https://blog.csdn.net/hxx099/article/details/88974264 1,申请高德开放平台的数据接口1)申请高德地图API帐户https://lbs.amap.com/dev/key登录后—创建新应用在建立的应用中添加密钥类型选择Web服务![在这里插入图片描述(https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200629211526589.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark ,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3p6enp6ejIwMTY =,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)然后可以被要求提供服务的密钥 ![在这里插入图片描述(https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200629211931735.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3p6enp6ejIwMTY=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70) 2、下载高德地图POI分类编码表和城市编码表–下载地址为:https://lbs.amap.com/api/webservice/download 通过城市编码表,可以查看行政区划名称,以便在后面的代码中填写一致的城市名称; POI分类编码如下图所示,代码通过读取这个表中的大类、中类、小类的名称爬取POI数据,如有不需要的类别,可先将输入POI分类编码中的部分类别删除。 代码如下,更改输出文件夹、输入POI分类编码表、高德密钥、目标行政区范围 from urllib.parse import quote import urllib import pandas as pd import xlwt import json class getpoi: output_path="E:/out/" ##########输出文件夹名称########### path_class ="E:/in/amap_poicode.xlsx.xlsx" ##########输入的POI分类编码表(用以指示需要爬取的POI类型)########### amap_web_key = 'c8e8b1f7f265618cbb531517' ##########高德API的密钥########### poi_search_url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/text?key=%s&extensions=all&keywords=&types=%s&city=%s&citylimit=true&offset=25&page=%s&output=json" ##########不需要更改########## cityname = '上海' ############目标的城市(与城市编码表中的名称需要一致)############# areas = ['奉贤区'] ############目标城市的次级行政范围(与城市编码表中的名称需要一致)############# totalcontent = {} def __init__(self): data_class = self.getclass() for type_class in data_class: for area in self.areas: page = 1; if type_class['type_num'] / 10000 < 10: classtype = str('0') + str(type_class['type_num']) else: classtype = str(type_class['type_num']) while True: if classtype[-4:] =="0000": break; poidata = self.get_poi(classtype, area, page); poidata = json.loads(poidata) if poidata['count'] == "0": break; else: poilist = self.hand(poidata) print("area:" + area + " type:" + classtype + " page:第" + str(page) + "页 count:" + poidata['count'] + "poilist:") page += 1 for pois in poilist: if classtype[0:2] in self.totalcontent.keys(): pois['bigclass'] = type_class['bigclass'] pois['midclass'] = type_class['midclass'] pois['smallclass'] = type_class['smallclass'] list_total = self.totalcontent[classtype[0:2]] list_total.append(pois) else: self.totalcontent[classtype[0:2]] = [] pois['bigclass'] = type_class['bigclass'] pois['midclass'] = type_class['midclass'] pois['smallclass'] = type_class['smallclass'] self.totalcontent[classtype[0:2]].append(pois) for content in self.totalcontent: self.writeexcel(self.totalcontent[content], content) def writeexcel(self, data, classname): book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding='utf-8', style_compression=0) sheet = book.add_sheet(classname, cell_overwrite_ok=True) # 第一行(列标题) sheet.write(0, 0, 'x') sheet.write(0, 1, 'y') sheet.write(0, 2, 'count') sheet.write(0, 3, 'name') sheet.write(0, 4, 'adname') sheet.write(0, 5, 'smallclass') sheet.write(0, 6, 'typecode') sheet.write(0, 7, 'midclass') classname = data[0]['bigclass'] for i in range(len(data)): sheet.write(i + 1, 0, data[i]['lng']) sheet.write(i + 1, 1, data[i]['lat']) sheet.write(i + 1, 2, 1) sheet.write(i + 1, 3, data[i]['name']) sheet.write(i + 1, 4, data[i]['adname']) sheet.write(i + 1, 5, data[i]['smallclass']) sheet.write(i + 1, 6, data[i]['classname']) sheet.write(i + 1, 7, data[i]['midclass']) book.save(self.output_path + self.cityname + '_' + classname + '.xls') def hand(self, poidate): pois = poidate['pois'] poilist = [] for i in range(len(pois)): content = {} content['lng'] = float(str(pois[i]['location']).split(",")[0]) content['lat'] = float(str(pois[i]['location']).split(",")[1]) content['name'] = pois[i]['name'] content['adname'] = pois[i]['adname'] content['classname'] = pois[i]['typecode'] poilist.append(content) return poilist def readfile(self, readfilename, sheetname): data = pd.read_excel(readfilename, sheet_name=sheetname) return data def getclass(self): readcontent = self.readfile(self.path_class, "POI分类与编码(中英文)") data = [] for num in range(readcontent.shape[0]): content = {} content['type_num'] = readcontent.iloc[num]['NEW_TYPE'] content['bigclass'] = readcontent.iloc[num]['大类'] content['midclass'] = readcontent.iloc[num]['中类'] content['smallclass'] = readcontent.iloc[num]['小类'] data.append(content) return data def get_poi(self, keywords, city, page): poiurl = self.poi_search_url % (self.amap_web_key, keywords, quote(city), page) data = '' with urllib.request.urlopen(poiurl) as f: data = f.read().decode('utf8') return data if __name__ == "__main__": gp = getpoi()最后获得的结果如图所示:每个大类输出为一个单独的excel文件,每个EXCEL文件中包括POI数据的经纬度和相关信息。 参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37089628/article/details/88622304 原始的坐标系为火星坐标系,与平时使用的WGS84坐标系中间存在一个位置偏移,如果想要和别的WGS84坐标系的数据一起使用,需要先进行坐标系转换。 下述代码需要更改输入文件夹,输入EXCEL名称和输出名称。 #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import pandas as pd import json import math import os import csv ## 转换函数: x_pi = 3.14159265358979324 * 3000.0 / 180.0 pi = 3.1415926535897932384626 # π a = 6378245.0 # 长半轴 ee = 0.00669342162296594323 # 扁率 def gcj02towgs84(lng, lat): """ GCJ02(火星坐标系)转GPS84 :param lng:火星坐标系的经度 :param lat:火星坐标系纬度 :return: """ if out_of_china(lng, lat): return lng, lat dlat = transformlat(lng - 105.0, lat - 35.0) dlng = transformlng(lng - 105.0, lat - 35.0) radlat = lat / 180.0 * pi magic = math.sin(radlat) magic = 1 - ee * magic * magic sqrtmagic = math.sqrt(magic) dlat = (dlat * 180.0) / ((a * (1 - ee)) / (magic * sqrtmagic) * pi) dlng = (dlng * 180.0) / (a / sqrtmagic * math.cos(radlat) * pi) mglat = lat + dlat mglng = lng + dlng return [lng * 2 - mglng, lat * 2 - mglat] def transformlat(lng, lat): ret = -100.0 + 2.0 * lng + 3.0 * lat + 0.2 * lat * lat + \ 0.1 * lng * lat + 0.2 * math.sqrt(math.fabs(lng)) ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * lng * pi) + 20.0 * math.sin(2.0 * lng * pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0 ret += (20.0 * math.sin(lat * pi) + 40.0 * math.sin(lat / 3.0 * pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0 ret += (160.0 * math.sin(lat / 12.0 * pi) + 320 * math.sin(lat * pi / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0 return ret def transformlng(lng, lat): ret = 300.0 + lng + 2.0 * lat + 0.1 * lng * lng + \ 0.1 * lng * lat + 0.1 * math.sqrt(math.fabs(lng)) ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * lng * pi) + 20.0 * math.sin(2.0 * lng * pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0 ret += (20.0 * math.sin(lng * pi) + 40.0 * math.sin(lng / 3.0 * pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0 ret += (150.0 * math.sin(lng / 12.0 * pi) + 300.0 * math.sin(lng / 30.0 * pi)) * 2.0 / 3.0 return ret def out_of_china(lng, lat): """ 判断是否在国内,不在国内不做偏移 :param lng: :param lat: :return: """ if lng < 72.004 or lng > 137.8347: return True if lat < 0.8293 or lat > 55.8271: return True return False # 主程序: if __name__ == '__main__': filepath = 'E:\\out\\POI数据\\' poifile=filepath+'道路与交通设施用地.xlsx' print(poifile) # if not os.path.exists(path): # os.mkdir(path) poifile84=filepath+'上海_道路与交通设施用地_84.csv' pd_poifile=pd.read_excel(poifile) with open(poifile84,"w",newline="") as file: print(file) writter = csv.writer(file) writter.writerow(["x", "y", "name", "adname", "smallclass", "typecode", "midclass"]) for index,row in pd_poifile.iterrows(): i = gcj02towgs84(row["x"],row["y"]) writter.writerow([i[0],i[1],row["name"],row["adname"],row["smallclass"],row["typecode"],row["midclass"]]) file.close() print("坐标转换完毕") 三、将EXCEL文件转换为SHP矢量文件可以直接在ArcGIS中通过添加XY数据实现