C#WPF 如何绘制几何图形 图示教程 绘制sin曲线 正弦 绘制2D坐标系 有图有代码 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 正弦sine产品测评 › C#WPF 如何绘制几何图形 图示教程 绘制sin曲线 正弦 绘制2D坐标系 有图有代码 |
C#WPF 如何绘制几何图形 图示教程 绘制sin曲线 正弦 绘制2D坐标系 有图有代码
|
C#WPF 如何绘制几何图形? 怎么绘制坐标系?绘制sin曲线(正弦曲线)? 这离不开Path(System.Windows.Shapes)和StreamGeometry(System.Windows.Media)类。 完成该工程,我们首先要建立并绘制一个坐标系,然后在该坐标系中绘制sin曲线的点(x,y),最后,把曲线的点转换为屏幕坐标并连接;这样坐标系和sin曲线就绘制完成了。 代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/wyx100/8320225 如果有帮助,别忘了给评价!
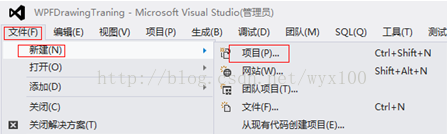
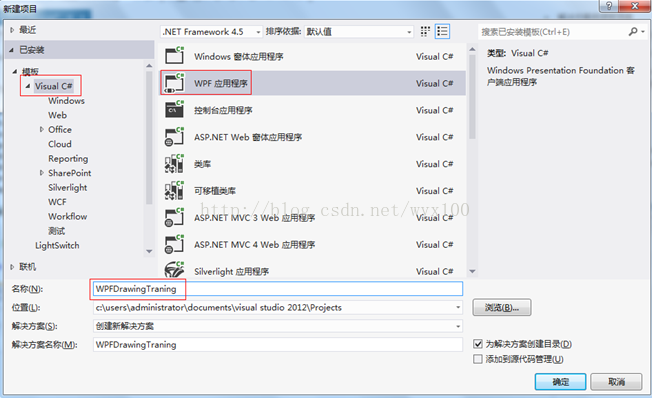
一、建立WPF工程
二、添加代码
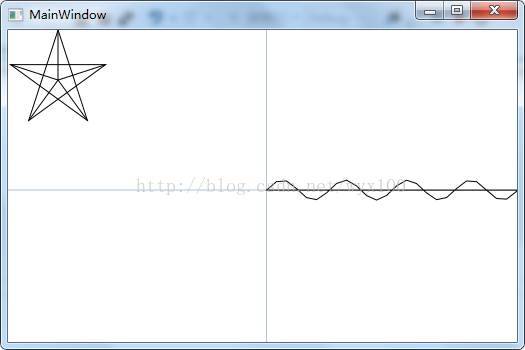
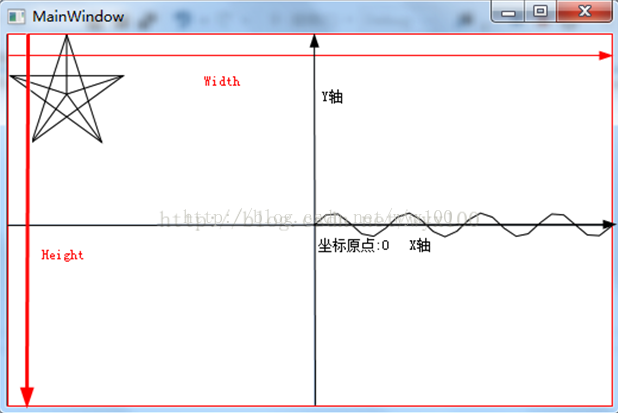
MainWindow.xaml 中代码 MainWindow.xaml.cs中代码 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows; using System.Windows.Controls; using System.Windows.Data; using System.Windows.Documents; using System.Windows.Input; using System.Windows.Media; using System.Windows.Media.Imaging; using System.Windows.Navigation; using System.Windows.Shapes; namespace WPFDrawingTraning { /// /// MainWindow.xaml 的交互逻辑 /// public partial class MainWindow : System.Windows.Window { //Canvas mainPanel = new Canvas(); public MainWindow() { InitializeComponent(); Drawsin();//绘制2D坐标系和sin曲线 Drawpentagon(); } /// /// 绘制一组线段 /// protected void Drawing() { PathFigure myPathFigure = new PathFigure(); myPathFigure.StartPoint = new Point(10, 50); LineSegment myLineSegment = new LineSegment(); myLineSegment.Point = new Point(200, 70); PathSegmentCollection myPathSegmentCollection = new PathSegmentCollection(); myPathSegmentCollection.Add(myLineSegment); myPathFigure.Segments = myPathSegmentCollection; PathFigureCollection myPathFigureCollection = new PathFigureCollection(); myPathFigureCollection.Add(myPathFigure); PathGeometry myPathGeometry = new PathGeometry(); myPathGeometry.Figures = myPathFigureCollection; Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; myPath.Data = myPathGeometry; // Add path shape to the UI. StackPanel mainPanel = new StackPanel(); mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath); this.Content = mainPanel; } /// /// 绘制线段 /// protected void DrawingLine(Point startPt,Point endPt) { LineGeometry myLineGeometry = new LineGeometry(); myLineGeometry.StartPoint = startPt; myLineGeometry.EndPoint = endPt; Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; myPath.Data = myLineGeometry; mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath); } /// /// 绘制星状线 /// protected void DrawingAstroid(Point center,double r) { double h1 = r * Math.Sin(18 * Math.PI / 180); double h2 = r * Math.Cos(18*Math.PI/180); double h3 = r * Math.Sin(36 * Math.PI / 180); double h4 = r * Math.Cos(36 * Math.PI / 180); ; Point p1 = new Point(r, 0); Point p2 = new Point(r - h2, r - h1); Point p3 = new Point(r - h3, r + h4); Point p4 = new Point(r + h3, p3.Y); Point p5 = new Point(r + h2, p2.Y); Point[] values = new Point[] { p1, p2, p3, p4, p5 }; PathFigureCollection myPathFigureCollection = new PathFigureCollection(); PathGeometry myPathGeometry = new PathGeometry(); for (int i = 0; i < values.Length; i++) { //DrawingLine(center, values[i]); PathFigure myPathFigure = new PathFigure(); myPathFigure.StartPoint = center; LineSegment myLineSegment = new LineSegment(); myLineSegment.Point = values[i]; PathSegmentCollection myPathSegmentCollection = new PathSegmentCollection(); myPathSegmentCollection.Add(myLineSegment); myPathFigure.Segments = myPathSegmentCollection; myPathFigureCollection.Add(myPathFigure); } myPathGeometry.Figures = myPathFigureCollection; Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; myPath.Data = myPathGeometry; mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath); } /// /// 绘制坐标系和sin曲线 /// private void Drawpentagon() { Point center = new Point(50, 50); double r = 50; DrawingAstroid(center, r); double h1 = r * Math.Sin(18 * Math.PI / 180); double h2 = r * Math.Cos(18 * Math.PI / 180); double h3 = r * Math.Sin(36 * Math.PI / 180); double h4 = r * Math.Cos(36 * Math.PI / 180); ; Point p1 = new Point(r, 0); Point p2 = new Point(r - h2, r - h1); Point p3 = new Point(r - h3, r + h4); Point p4 = new Point(r + h3, p3.Y); Point p5 = new Point(r + h2, p2.Y); Point[] values = new Point[] { p1, p3, p5, p2, p4 }; // Create a path to draw a geometry with. Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; StreamGeometry theGeometry = BuildRegularPolygon(values, true, false); // Create a StreamGeometry to use to specify myPath. theGeometry.FillRule = FillRule.EvenOdd; // Freeze the geometry (make it unmodifiable) // for additional performance benefits. theGeometry.Freeze(); // Use the StreamGeometry returned by the BuildRegularPolygon to // specify the shape of the path. myPath.Data = theGeometry; // Add path shape to the UI. mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath); } /// /// 绘制连续的线段 /// /// /// private StreamGeometry BuildRegularPolygon(Point[] values, bool isClosed,bool isfilled) { // c is the center, r is the radius, // numSides the number of sides, offsetDegree the offset in Degrees. // Do not add the last point. StreamGeometry geometry = new StreamGeometry(); using (StreamGeometryContext ctx = geometry.Open()) { ctx.BeginFigure(values[0], isfilled /* is filled */, isClosed /* is closed */); for (int i = 1; i < values.Length; i++) { ctx.LineTo(values[i], true /* is stroked */, false /* is smooth join */); } } return geometry; } /// /// 绘制五角星 /// private void Drawsin() { Point point = new Point(this.mainPanel.Width, this.mainPanel.Height); Point xypoint = new Point(point.X / 2, point.Y / 2);//新坐标原点 //x轴坐标起点 Point xstartpoint = new Point(0, point.Y / 2); //x轴坐标终点 Point xendpoint = new Point(point.X, point.Y / 2); //y轴坐标起点 Point ystartpoint = new Point(point.X / 2, point.Y); //y轴坐标终点 Point yendpoint = new Point(point.X / 2, 0); Line xline = new Line(); xline.Stroke = System.Windows.Media.Brushes.LightSteelBlue; xline.X1 = 0; xline.Y1 = this.mainPanel.Height / 2; xline.X2 = this.mainPanel.Width; xline.Y2 = this.mainPanel.Height / 2; this.mainPanel.Children.Add(xline); Line yline = new Line(); yline.Stroke = System.Windows.Media.Brushes.LightSteelBlue; yline.X1 = this.mainPanel.Width / 2; yline.Y1 = this.mainPanel.Height; yline.X2 = this.mainPanel.Width / 2; yline.Y2 = 0; this.mainPanel.Children.Add(yline); Point[] points=new Point[1000]; //绘制sin曲线,从原点(0,0)开始 Point zpoint = new Point(0, 0); zpoint = XYTransf(zpoint, xypoint); points[0] = zpoint;//sin曲线的起点 for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) { //计算sin(x,y) point.X =10 * i;//x point.Y =10 * Math.Sin(i);//y //坐标转换 point = XYTransf(point, xypoint); points[i] = point; } Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; StreamGeometry theGeometry = BuildRegularPolygon(points, true, false); // Create a StreamGeometry to use to specify myPath. theGeometry.FillRule = FillRule.EvenOdd; // Freeze the geometry (make it unmodifiable) // for additional performance benefits. theGeometry.Freeze(); // Use the StreamGeometry returned by the BuildRegularPolygon to // specify the shape of the path. myPath.Data = theGeometry; // Add path shape to the UI. mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath); } //构建的XY坐标系中的坐标转换为界面坐标系 public Point XYTransf(Point point, Point xypoint) { point.X += xypoint.X; point.Y = xypoint.Y - point.Y; return point;//显示屏幕坐标系的位置 } } }三、页面效果
四、介绍 private void Drawsin() 函数中完成:坐标系绘制,sin曲线绘制; point是绘图坐标系中的点,xypoint(maincanvas.Width/2,maincanvas.Height/2)是绘图屏幕坐标的几何中心点( 图 坐标点转换,中x轴和y轴原点)的坐标。 public Point XYTransf(Point point, Point xypoint)函数返回值是在屏幕坐标绘制点的坐标。 //转换为界面坐标系 public Point XYTransf(Point point, Point xypoint) { point.X += xypoint.X; point.Y = xypoint.Y - point.Y; return point;//显示屏幕坐标系的位置 }
1.mainPanel 是一个Canvas面板,我们在该面板绘制图形。 2.绘制坐标系,以mainPanel 的图形中心为坐标原点;
图 坐标点转换
3.计算sin(x,y)并转换为屏幕坐标点,取1000个坐标点,并存在points数组中 for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) { //计算sin(x,y) point.X =10 * i;//sin x point.Y =10 * Math.Sin(i);//sin y //坐标转换 point = XYTransf(point, xypoint); points[i] = point; }4.连接1000个sin(x,y)的屏幕坐标点,并显示在Canvas中 StreamGeometry theGeometry = BuildRegularPolygon(points, true, false); 通过该函数连接points中所有的点; Path myPath = new Path(); myPath.Stroke = Brushes.Black; myPath.StrokeThickness = 1; StreamGeometry theGeometry = BuildRegularPolygon(points, true, false); // Create a StreamGeometry to use to specify myPath. theGeometry.FillRule = FillRule.EvenOdd; // Freeze the geometry (make it unmodifiable) // for additional performance benefits. theGeometry.Freeze(); // Use the StreamGeometry returned by the BuildRegularPolygon to // specify the shape of the path. myPath.Data = theGeometry; // Add path shape to the UI. mainPanel.Children.Add(myPath);5.执行显示效果 点击“启动”或按键盘“F5”执行工程,显示界面。
|
【本文地址】