计算机视觉特征图可视化与注意力图可视化(持续更新) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 樱花ins图 › 计算机视觉特征图可视化与注意力图可视化(持续更新) |
计算机视觉特征图可视化与注意力图可视化(持续更新)
|
1.YOLOv5 特征图可视化
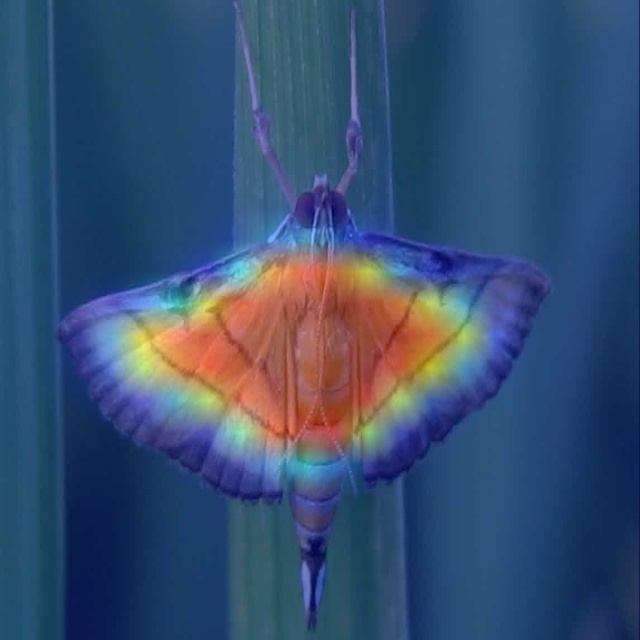
可视化代码: def feature_visualization(x, module_type, stage, n=2, save_dir=Path('runs/detect/exp')): """ x: Features to be visualized module_type: Module type stage: Module stage within model n: Maximum number of feature maps to plot save_dir: Directory to save results """ if 'Detect' not in module_type: batch, channels, height, width = x.shape # batch, channels, height, width if height > 1 and width > 1: f = save_dir / f"stage{stage}_{module_type.split('.')[-1]}_features.png" # filename blocks = torch.chunk(x[0].cpu(), channels, dim=0) # select batch index 0, block by channels n = min(n, channels) # number of plots fig, ax = plt.subplots(math.ceil(n / 2), 2, tight_layout=True) # 8 rows x n/8 cols ax = ax.ravel() plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05) for i in range(n): ax[i].imshow(blocks[i].squeeze()) # cmap='gray' ax[i].axis('off') LOGGER.info(f'Saving {f}... ({n}/{channels})') plt.savefig(f, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight') plt.close() np.save(str(f.with_suffix('.npy')), x[0].cpu().numpy()) # npy save使用: feature_visualization(features, name, stage_id, save_dir=ROOT / "visual")结果示例:
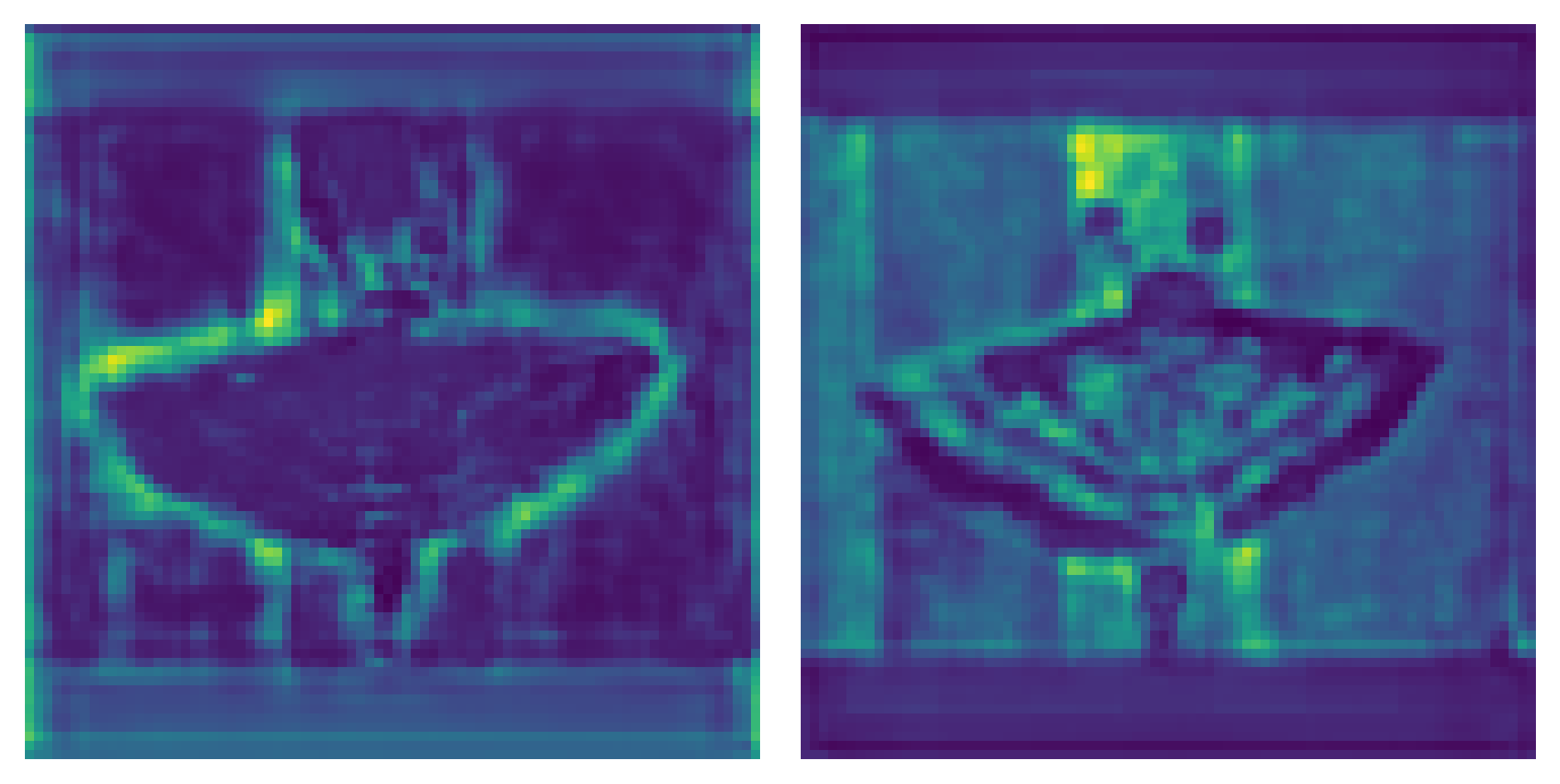
可视化代码: def feature_visualization(x, module_type, stage, n=2, save_dir=Path('runs/detect/exp')): """ x: Features to be visualized module_type: Module type stage: Module stage within model n: Maximum number of feature maps to plot save_dir: Directory to save results """ if 'Detect' not in module_type: batch, channels, height, width = x.shape # batch, channels, height, width if height > 1 and width > 1: f = save_dir / f"stage{stage}_{module_type.split('.')[-1]}_features.png" # filename blocks = torch.chunk(x[0].cpu(), channels, dim=0) # select batch index 0, block by channels n = min(n, channels) # number of plots fig, ax = plt.subplots(math.ceil(n / 2), 2, tight_layout=True) # 8 rows x n/8 cols ax = ax.ravel() plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.05, hspace=0.05) for i in range(n): block = blocks[i].squeeze().detach().numpy() block = (block - np.min(block)) / (np.max(block) - np.min(block)) temp = np.array(block * 255.0, dtype=np.uint8) temp = cv2.applyColorMap(temp, cv2.COLORMAP_JET) ax[i].imshow(temp, cmap=plt.cm.jet) # cmap='gray' ax[i].axis('off') LOGGER.info(f'Saving {f}... ({n}/{channels})') plt.savefig(f, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight') plt.close() np.save(str(f.with_suffix('.npy')), x[0].cpu().numpy()) # npy save使用: feature_visualization(features, name, stage_id, save_dir=ROOT / "visual")结果示例:
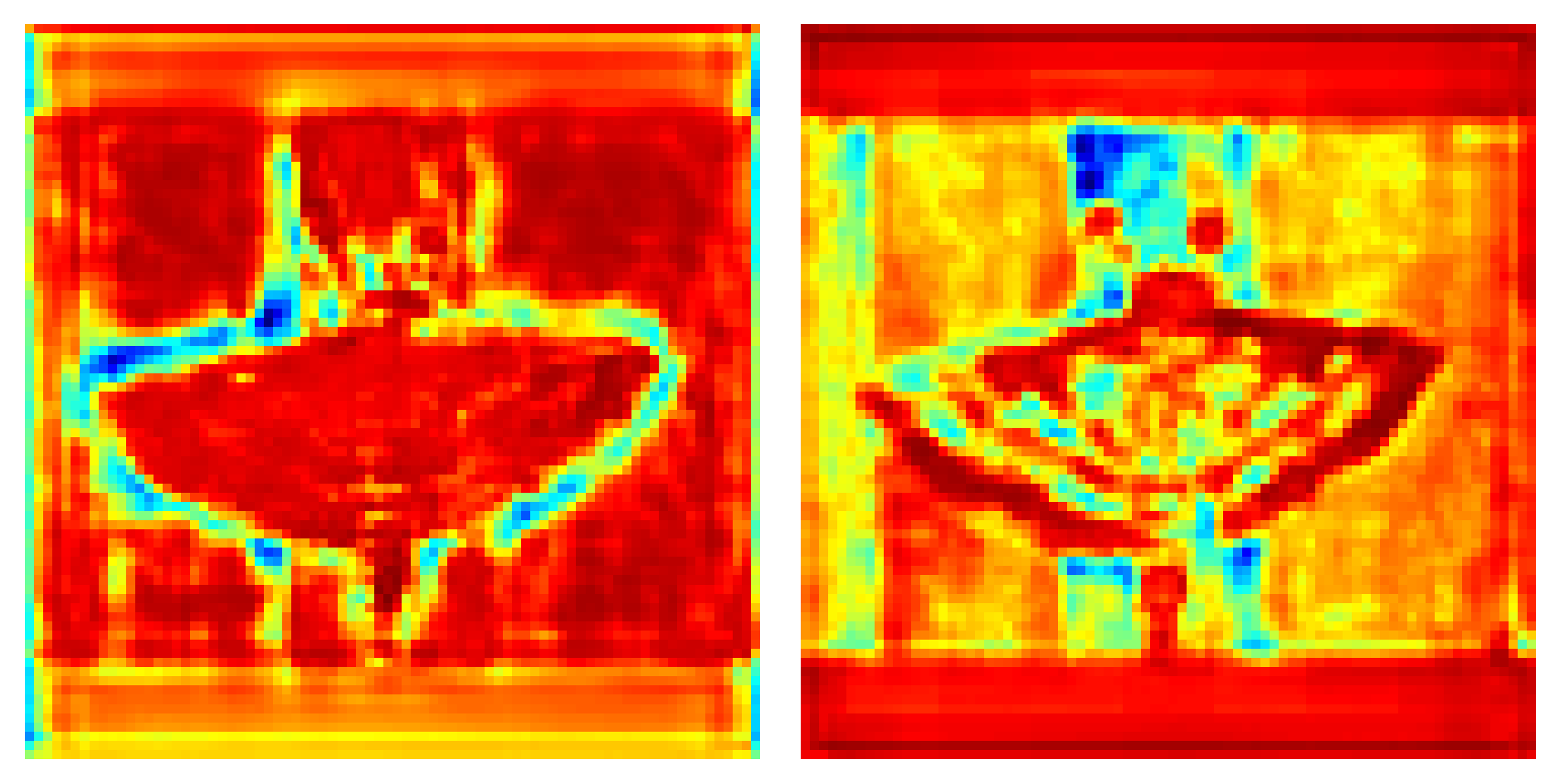
优化的可视化代码可视化结果更加清晰 参考:GitHub - z1069614715/objectdetection_script: 一些关于目标检测的脚本的改进思路代码,详细请看readme.md 3.注意力图可视化(YOLO)可视化代码: def show_CAM(save_img_path, image, feature_maps, class_id, all_ids=97, image_size=(640, 640), normalization=True): """ save_img_path: save heatmap images path feature_maps: this is a list [tensor,tensor,tensor], tensor shape is [1, 3, N, N, all_ids] normalization: Normalize score and class to 0 to 1 image_size: w, h """ SHOW_NAME = ["score", "class", "class*score"] img_ori = image layers0 = feature_maps[0].reshape([-1, all_ids]) layers1 = feature_maps[1].reshape([-1, all_ids]) layers2 = feature_maps[2].reshape([-1, all_ids]) layers = torch.cat([layers0, layers1, layers2], 0) if normalization: score_max_v = 1. score_min_v = 0. class_max_v = 1. class_min_v = 0. else: score_max_v = layers[:, 4].max() # compute max of score from all anchor score_min_v = layers[:, 4].min() # compute min of score from all anchor class_max_v = layers[:, 5 + class_id].max() # compute max of class from all anchor class_min_v = layers[:, 5 + class_id].min() # compute min of class from all anchor for j in range(3): # layers layer_one = feature_maps[j] # compute max of score from three anchor of the layer if normalization: anchors_score_max = layer_one[0, :, :, :, 4].max(0)[0].sigmoid() # compute max of class from three anchor of the layer anchors_class_max = layer_one[0, :, :, :, 5 + class_id].max(0)[0].sigmoid() else: anchors_score_max = layer_one[0, :, :, :, 4].max(0)[0] # compute max of class from three anchor of the layer anchors_class_max = layer_one[0, :, :, :, 5 + class_id].max(0)[0] scores = ((anchors_score_max - score_min_v) / ( score_max_v - score_min_v)) classes = ((anchors_class_max - class_min_v) / ( class_max_v - class_min_v)) layer_one_list = [] layer_one_list.append(scores) layer_one_list.append(classes) layer_one_list.append(scores * classes) for idx, one in enumerate(layer_one_list): layer_one = one.cpu().numpy() if normalization: ret = ((layer_one - layer_one.min()) / (layer_one.max() - layer_one.min())) * 255 else: ret = ((layer_one - 0.) / (1. - 0.)) * 255 ret = ret.astype(np.uint8) gray = ret[:, :, None] ret = cv2.applyColorMap(gray, cv2.COLORMAP_JET) ret = cv2.resize(ret, image_size) img_ori = cv2.resize(img_ori, image_size) show = ret * 0.50 + img_ori * 0.50 show = show.astype(np.uint8) cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_img_path, f"{j}_{SHOW_NAME[idx]}.jpg"), show)使用: show_CAM(ROOT/"visual", cv2.imread(path), ret[1], 0, # 指的是你想查看的类别 这个代码中我们看的是bear 所有在coco数据集中是21 80+ 5, # 80+5指的是coco数据集的80个类别+ x y w h score 5个数值 image_size=(640, 640), # 模型输入尺寸 # 如果为True将置信度和class归一化到0~1,方便按置信度进行区分热力图, # 如果为False会按本身数据分布归一化,这样方便查看相对置信度。 normalization=True )结果示例:
参考:GitHub - z1069614715/objectdetection_script: 一些关于目标检测的脚本的改进思路代码,详细请看readme.md |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |