Water Pump : Types, Working, Characteristics & Applications |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 末日游戏安卓 › Water Pump : Types, Working, Characteristics & Applications |
Water Pump : Types, Working, Characteristics & Applications
|
In before the discovery of internal combustion engines, these water pumps were invented. At that time itself, the water pumps were utilized for multiple purposes, while the quick forerunner of the contemporary water pump was implemented for the purpose of water circulation in steam engines. As there are few drawbacks in the internal combustion engines such as more water necessity, water pumps are more preferred as they have minimal water loss. So, this is the article that clearly explains the concepts of water pump working, types, and the motor in it. What is Water Pump?A water pump is a mechanical tool that is constructed to distribute coolant all through water-cooled engines. For many of the cooling systems, these water pumps act as a core for systems. There exist multiple approaches to driving water pumps, but the extensively used method is the revolution of the crankshaft. So, either for irrigational or drainage systems, these water pumps serve as best. The water pump diagram can be shown as: 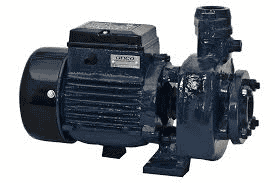
Water Pump Water Pump WorkingEven though there are various kinds of water pumps, the basic functionality is similar in all the types. Mechanical energy is carried to the crankshaft, which is in the water pump, mostly through the belt which is for the water pump. In a few situations, the water pump will be fuelled up through the camshaft and for a few cases, the pump is fuelled by the timing belt instead of an accessory belt. Either in any kind of water pump, the pump circulation is utilized to stimulate the fluid circulation all across the cooling system. The internal mechanism of the water pump differs extensively for each design and they might operate like a centrifugal, scroll, and many other kinds. Coolant is usually pulled into the pump from the engine compartment and directed towards the radiator. From here, it moves via thin tubes that are constructed to offer an extensively viable surface area. When there is the passage of more warm liquid into the radiator, then the cooler liquid moves from the radiator and comes back to the engine. Here, it holds the ability to pull out additional heat from the engine. Failure Conditions of Water PumpEven the modern-day water pumps are water-tight, they will also come across a few failing conditions. The few scenarios that lead to water pump failure are: Gasket Pump bearings Bearing sealA gasket is a component that is placed in between the engine and the water pump. The deterioration happens in the water pump because of gasket decays and this decay is because of various conditions such as polluted coolant, electrolysis, ground issues, and many others. The other failure condition is because of bearing seals and pump bearings. Failure of bearings leads to leakage which eventually damages the engine. TypesThe other important concept that has to be discussed is water pump types. The basic classification of water pumps is a positive displacement, axial flow, and centrifugal pumps. In general, in centrifugal pumps, the fluid flow direction gets altered by 900 when it passes through the impeller, whereas in axial flow pumps the fluid flow direction is not altered. Positive Displacement PumpsHere, the fluid movement is happened by confining a specific amount and then pushing the confined volume into the discharge tube. Few of these kinds of water pumps make use of enlarging and decreasing cavities on the suction and discharge sides. The fluid flow happens into the pump when the suction enlarges and flows out when the cavity contracts. This operation provides a balanced condition for the entire cycle activity. Without considering the discharge pressure value, the pumps offer a similar flow rate at the provided speed (RPM). So, these are termed as constant fluid flow pumps. Though, a minimal increment in the internal outflow as the pressure value enhances avoids balanced fluid flow rate. Depending on the approach used for fluid movement, these are further categorized as: Rotary type Reciprocating type Linear typeThe rotary type of positive displacement pumps falls into the classification of gear pumps, rotary vane, screw pumps, hollow disk, and vibratory pumps. While reciprocating pumps are categorized as a piston, radial piston, diaphragm, and plunger pumps. Few of the other kinds in this water pump are Hydraulic pump Rope pump Flexible impeller Progressive cavity Rotary lobe Peristaltic pumps Axial Flow PumpsThese are also called all-fluid pumps. These pumps are mainly considered for applications that need increased flow rates and minimal pressure values. These pumps cannot be operated at a speed having any specific protection. When operated at minimal flow rates, the complete head enhances and the increased torque related to the pipe will indicate that the initial torque needs to perform as the acceleration function for the entire fluid quantity in the water pipe. Whereas when there is a huge fluid quantity, it speeds up the water pump in a slow manner. 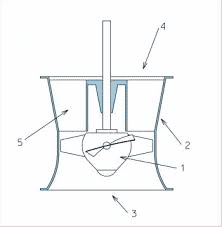
Axial Flow Water Pump Centrifugal PumpThese water pumps are also called as radial flow water pumps. The fluid that enters into the pump through the center is stimulated by the exits which are in the right-angled position and by the impeller. The same principle is employed in a centrifugal fan that is used for the implementation of a vacuum cleaner. 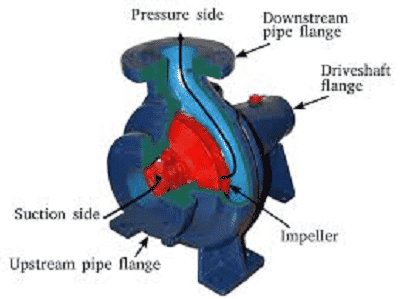
Centrifugal Pump The other kind of centrifugal pump is the vortex pump. The fluid has a movement across the functioning wheel in a tangential way. The transformation of the motor’s mechanical energy to that of potential energy for the movement is received by the number of whirls that are accelerated by the impeller in the water pump. Mostly, the radial-flow water pumps function at incremented pressures and minimal flow rates when compared with axial-flow water pumps. Water Pump CharacteristicsFew characteristics that are to be considered while choosing the water pump are as follows: Power consumption rate – It is measured in Watts(W)or Kilowatts (kW) Grain size – It states the greatest size of dust particles present in water and measured in millimeters (mm) Fluid flow rate – At the time of perfect operating conditions, fluid has the greatest flow rate. It is represented as Qmax and measured in liters per second/hour (l/h or l/s) ApplicationsWater pumps have a wide variety of uses. The past applications of the water pumps are in the watermill for water pumping and in windmills. These days, with the invention of various sizes, approaches, motor designs, and shapes, these pumps are implemented in irrigational purposes, air conditioning, coolers, marine activities, gasoline industry, refrigerators, chemical purposes, and many others. Every kind of water pump has its own applications such as: Dive pumps for drainage systems Submersible pumps for greater pressure applications Fire pumps used in pipe wells Self-priming garden pumps are utilized for sucking the water via a hose Pond pumps are implemented in the functionality of water games or streams Rain barrel and cistern pumps are employed for irrigating a garden Petrol motor water pumps are used in the cases when an electric pump has no power distributionSo, this is all about the concept of water pumps. Being so adaptable for many commercial and household purposes, these pumps gain more importance. As water pumps provide greater efficiency and performance these are more preferred than that internal combustion engines. So, know the additional concepts such as how to make a water pump and other related concepts? |
【本文地址】