鸡传染性法氏囊炎变异株的最新研究进展 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 最新变异株的毒量 › 鸡传染性法氏囊炎变异株的最新研究进展 |
鸡传染性法氏囊炎变异株的最新研究进展
|
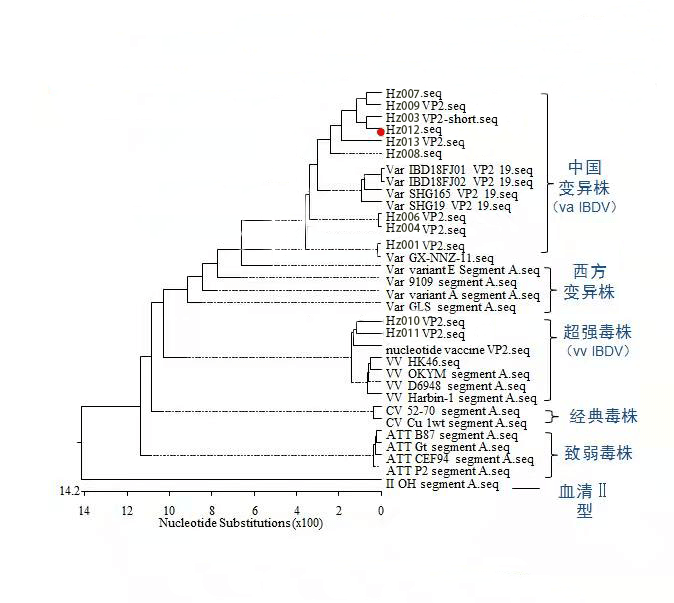
IBDV新型变异株的序列分析结果 在报道的IBDV变异株中,可分为两个明显的亚群,美国早期变异株为一个亚群,国内报道形成了另一个亚群。范林进等人对于分离到的IBDV新型变异株的VP2基因高变区进行氨基酸序列分析发现,血清I型IBDV明显分为经典株、超强株、减毒株和变异株4个分支。中国变异株的核苷酸序列的同源性与美国早期变异株的同源率最高可达到94.8%,而与经典株、超强株、减毒株的同源率在92%以下。中国分离株中具有变异株特征性氨基酸222T、249K、286I和318D位点[13-15],并发现了221K、252I和299S三个新变异位点,证明我国新流行的IBDV变异株属于IBDV新型变异株[9]。
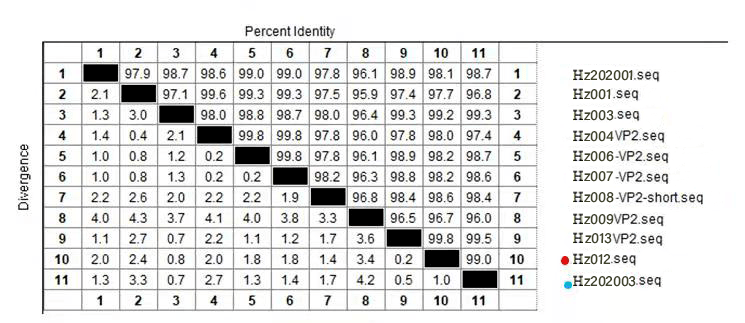
惠中生物2019年已经开始跟踪IBDV新型变异株的情况。对市场上收集9个毒株进行VP2片段测序(Hz001-Hz009),由图1可见9个分离株均属于中国变异毒株。
惠中生物通过对VP2核苷酸序列分析,发现分离的市场流行株与种毒库中的毒株之间基因同源性在96-99%之间,表明其可以对市场流行的鸡传染性法氏囊变异株进行保护。 IBDV新型变异株的危害 组织病理学切片显示,感染组萎缩的法氏囊中滤泡结构受到破坏,淋巴细胞显著减少,个别滤泡髓质可见少量异嗜细胞浸润,局部成纤维细胞增生。研究还发现早期感染会引起脾脏肿胀,后期引起脾脏萎缩。 IBDV新型变异株引起的非典型IBD的危害不容忽视。虽然IBDV新型变异株致死率低,但因引起的不可逆的法氏囊损伤和其严重的免疫抑制,导致鸡群免疫力低下,增加了其他病原的感染几率,影响鸡群的生长,导致体重下降、均匀度变差、料肉比升高等,严重影响了经济效益。 另一方面,IBDV新型变异株会干扰其它重要疫病疫苗的免疫效果。有报道显示,禽流感H5/H7二联疫苗的抗体产生会被IBDV新型变异株的感染干扰[14]。 对变异株的防控由于变异株的出现,目前市场上现有的疫苗保护率不理想,存在免疫后发病的情况。因此在选择疫苗的时候,尽量选取与变异株基因序列相近的疫苗进行预防,提高免疫后的鸡群保护力。 同时做好鸡舍的生物安全措施,改进饲养管理,减少鸡群应激。对于发病的鸡舍做到严格的消毒和空舍措施,并改进免疫方案。在下批次的养殖中密切关注鸡传染性法氏囊病的发生情况,出现问题第一时间使用高免血清进行治疗,减少损失。 参考文献 [1]、Muller H, Islam M R, Raue R. Research on infectious bursal disease--the past, the present and the future [J]. Vet Microbiol, 2003, 97(1-2): 153-165. [2]Brandt M, Yao Kun, Liu Mei-hong, et al. Molecular determinants of virulence, cell tropism, and pathogenic phenotype of infectious bursal disease virus [J]. J Virol, 2001, 75 (24): 11974-11982. [3]Qi Xiao-le, Gao Hong-lei, Gao Yu-long, et al. Naturally occurring mutations at residues 253 and 284 in VP2 contribute to the cell tropism and virulence of very virulent infectious bursal disease virus [J]. Antiviral Res, 2009, 84(3): 225-233. [4]Qi Xiao-le, Zhang Li-zhou, Chen Yu-ming, et al. Mutations of residues 249 and 256 in VP2 are involved in the replication and virulence of infectious Bursal disease virus [J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e70982. [5]、MCFERRAN J B, MCNULTY M S, MCK ILLOP E R, etal. Isolation and serological studies with infectious bursal disease viruses from fowl, turkeys and ducks: demonstration of a second serotype[J]. Avian pathology: journal of the W.V.P.A, 1980, 9(3): 395-404. [6]Jackwood D J. Advances in vaccine research against economically important viral diseases of food animals: Infectious bursal disease virus [J]. Vet Microbiol, 2017, 206: 121-125. [7]祁小乐,高立,王笑梅. 传染性法氏囊病病毒的自然重组 [J]. 微生物学报,2016,56(5):740-746. [8]GOMIS S, AHMED K A, WILLSON P, et al. A 5- year study of the incidence and economic impact of variant infectious bursal disease viruses on broiler production in Saskatchewan, Canada[J]. Canadian journal of veterinary research, 2016, 80(4): 255-261. [9]FAN L, WU T, HUSSAIN A, et al. Novel variant strains of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China[J]Veterinary microbiology, 2020, 230: 212-220. [10]范林进,王雨龙,吴甜甜,等. 我国传染性法氏囊病病毒新型变异株分析研究[J].中国预防兽医学报,2019,41(11):1164-1169. [11] 曹永长,毕英佐,罗文新,等. 传染性法氏囊病病毒变异株主要免疫原基因 cDNA 的克隆及鉴定[J]. 中国兽医杂志,1997(9):3-5 [12]FAN L, WU T, WANG Y, et al. Novel variants of infectious bursal disease virus can severely damage the bursa of fabricius of immunized chickens[J]. Veterinary microbiology, 2020, 240: 108507 [13]JACKWOOD D J. Molecular epidemiologic evidence of homologous recombination in infectious bursal disease viruses[J]. Avian diseases, 2012, 56(3): 574-577. [14]JACKWOOD, COOKSON, SOMMER- WAGNER. Molecular characteristics of infectious bursal disease viruses from asymptomatic broiler flocks in Europe[J]. Avian diseases, 2006, 50(4): 532-536. [15]Fan Lin-jin, Wu Tian-tian, Hussain A, et al. Novel variant strains of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China [J]. Vet Microbiol, 2019, 230: 212-220.返回搜狐,查看更多 |
【本文地址】