Spring |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 对象存储是啥 › Spring |
Spring
|
JavaEE传送门
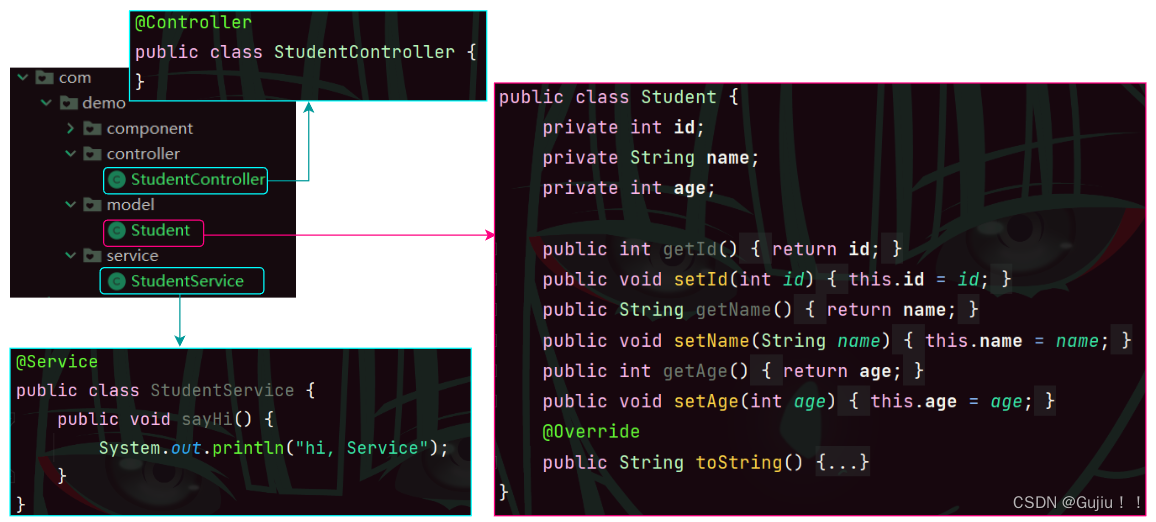
JavaEE Spring —— Spring 的创建与使用 Spring —— Spring简单的读取和存储对象Ⅰ 目录 Spring 简单的读取和存储对象获取 Bean 对象 (对象装配)属性注入构造方法注入Setter 注入@Resource 关键字同⼀类型多个 @Bean 报错处理 Spring 简单的读取和存储对象 获取 Bean 对象 (对象装配)获取 bean 对象也叫做对象装配,是把对象取出来放到某个类中,有时候也叫对象注⼊。 对象装配(对象注入)的实现方法以下 3 种: 属性注入构造方法注入Setter 注入我们先创建如下几个包和几个类:
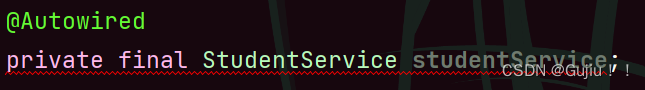
属性注⼊是使⽤ @Autowired 实现的,将 Service 类注⼊到 Controller 类中. @Controller public class StudentController { // 1.使用属性注入的方式获取 Bean @Autowired private StudentService studentService; public void sayHi() { // 调用 service 方法 studentService.sayHi(); } }
优点: 实现简单, 使用简单. 缺点: 功能性问题: 不能注入不可变 (final) 对象.
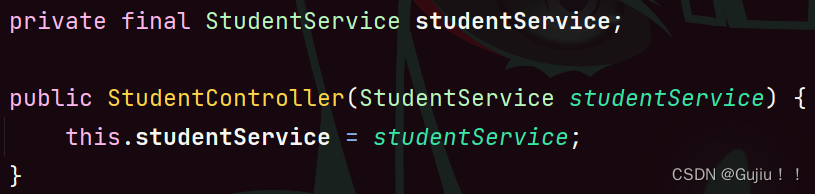
在 Java 中 final 对象(不可变)要么直接赋值,要么在构造方法中赋值,所以当使用属性注入 final 对象时,它不符合 Java 中 final 的使用规范,所以就不能注入成功了。 通用性问题: 只能适应于 IoC 容器. 设计原则问题: 更容易违背单一设计原则. (针对对象是类) 单一设计原则: 针对于类级别针对于方法级别 构造方法注入从 Spring 4.x 之后, Spring 官方推荐使用构造方法注入的形式. @Controller public class StudentController { // 2.构造方法注入 private StudentService studentService; // @Autowired 可省略 @Autowired public StudentController(StudentService studentService) { this.studentService = studentService; } public void sayHi() { // 调用 service 方法 studentService.sayHi(); } }# 注意 # @Autowired 可省略.但是如果类中有多个构造⽅法,那么需要添加 @Autowired 来明确指定到底使⽤哪个构造⽅法,否则程序会报错.
优点: 可注入不可变对象.
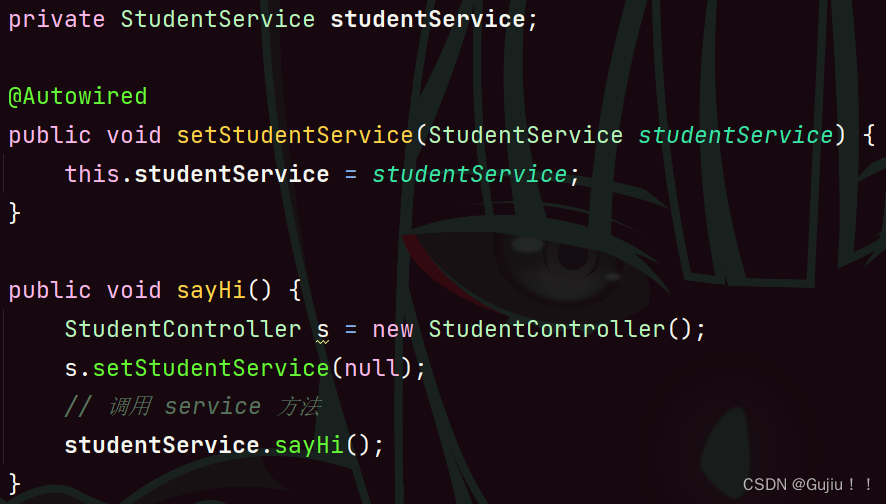
注入对象不会被修改. 加了 final 修饰符.构造方法是随着类加载只执行一次的.注入对象会被完全初始化. (使用构造方法带来的优点) 通用性更好. 缺点: 没有属性注入实现简单. Setter 注入Setter 注⼊和属性的 Setter ⽅法实现类似,只不过在设置 set ⽅法的时候需要加上 @Autowired 注解. @Controller public class StudentController { // 3.setter 注入 private StudentService studentService; @Autowired public void setStudentService(StudentService studentService) { this.studentService = studentService; } public void sayHi() { // 调用 service 方法 studentService.sayHi(); } }
优点: 更加符合单一设计原则. (针对对象是方法级别) 缺点: 不能注入不可变对象 (final 修饰的对象). 注入的对象可被修改. set 方法是普通 set 方法, 可以被重复调用, 有被修改的风险.
小结: 日常开发当中, 使用属性注入实现更简单的读取 Bean, 依然是主流的实现方式. @Resource 关键字在进⾏类注⼊时,除了可以使⽤ @Autowired 关键字之外,我们还可以使⽤ @Resource 进⾏注⼊. @Controller public class StudentController { @Resource private StudentService studentService; public void sayHi() { // 调用 service 方法 studentService.sayHi(); } }
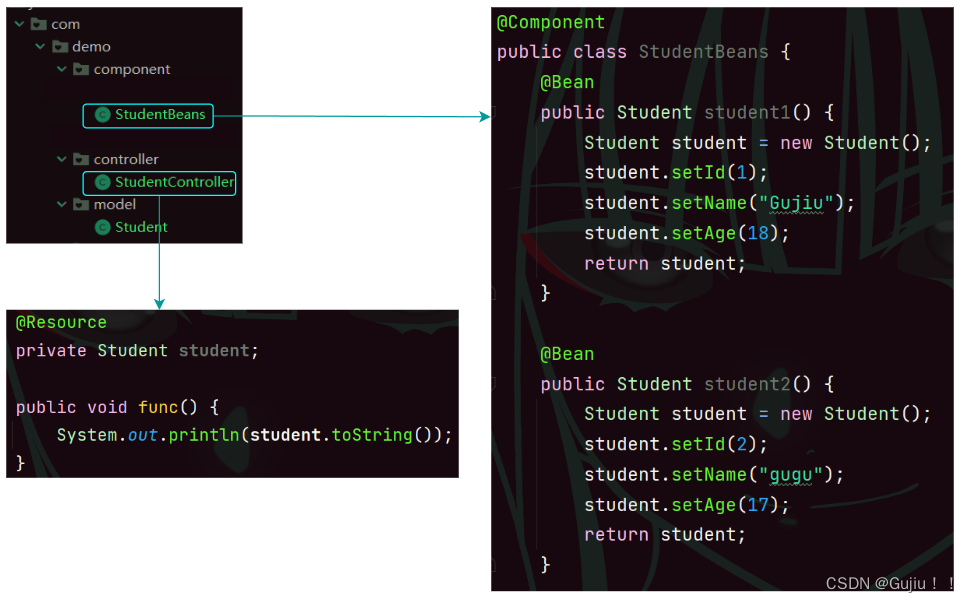
@Autowired 和 @Resource 的区别 相同点: 都是用来实现依赖注入的. 不同点: 功能支持不同: @Autowired 支持属性注入, setter 注入, 构造方法注入; @Resource 只支持属性注入和 setter 注入, 不支持构造方法注入.出身不同: @Autowired 来自于 Spring 框架; 而 @Resource 来自于 JDK.参数支持不同: @Resource 支持更多的参数设置; 而 @Autowired 只支持 required 参数. 同⼀类型多个 @Bean 报错处理当出现以下多个 Bean,返回同⼀对象类型时程序会报错
此时我们运行: public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml"); StudentController studentController = applicationContext.getBean("studentController", StudentController.class); studentController.func(); } }# 注意 # 会报错, 报错的原因是,非唯一的 Bean 对象。
同⼀类型多个 Bean 报错处理 解决同⼀个类型,多个 Bean 的解决⽅案有以下两个: 使⽤ @Resource(name="student1") 定义.使⽤ @Qualifier 注解定义名称.# 使⽤ @Resource(name="student1") 定义. @Controller public class StudentController { @Resource(name = "student2") private Student student; public void func() { System.out.println(student.toString()); } }# 使⽤ @Qualifier 注解定义名称. @Controller public class StudentController { @Resource @Qualifier("student2") private Student student; public void func() { System.out.println(student.toString()); } }# 如果我们想用 @Autowired 可以写成: @Autowired private Student student1; // 存在有耦合性问题 🌷(( ◞•̀д•́)◞⚔◟(•̀д•́◟ ))🌷以上就是今天要讲的内容了,希望对大家有所帮助,如果有问题欢迎评论指出,会积极改正!! |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |