字符转字节数组与Base64 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 字符串转字节数组在线 › 字符转字节数组与Base64 |
字符转字节数组与Base64
|
文章目录
字符转字节数组与Base64
字符转字节数
需求原理解决过程单字符多字符转码
Base64
用处原理示例实现过程完整代码
参考
附
字符转字节数组与Base64
字符转字节数
需求
与接口交互时需要转成字节数组,然后Java在根据字节数组转成对应字符。 public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "姚鑫"; try { byte[] utf = str.getBytes("UTF-8"); for (int i = 0; i e.printStackTrace(); } } } 输入字符串"姚鑫" 转成对应字节数组如下。 -27-89-102-23-111-85 姚鑫 输入字符串"AB" 转成对应字节数组如下。 6566 AB需要用M来实现,先上结果: YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() [-27,-89,-102,-23,-111,-85] YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("AB").%ToJSON() [65,66] 原理unicode转换为utf-8编码的规则 UnicodeUTF-8——0000-007F0xxxxxxx0080-07FF110xxxxx10xxxxxx0800-FFFF1110xxxx10xxxxxx10xxxxxx如果字符对应编码值小于等于0x7F,则转换该为1个byte,最高位为0。该字符对应的二进制替换X,不足7位前面高位加0。 编码值在0080到07FF字符,会转换为2个字节,并且第一个字节以110开头,第二个字节以10开头,字符对应的编码值转换为2进制后的数据,填充X。不足位数的高位加0。 编码值在0800到FFFF字符,会转换为3个字节,并且第一个字节以1110开头,后面字节以10开头,字符对应的编码值转换为2进制后的数据,填充X。不足位数的高位加0。 也就是说大于07XX编码值的字符,转换为字节时,第一个字节中连续1的个数表示该字符对应字节的长度。 "姚"的unicode通过查unicode编码表可知为:59DA。 M来验证一下: YX>w $a("姚") 23002 YX>w $zhex(23002) 59DA通过转换为二进制为:101 1001 1101 1010。 YX>zw $factor(23002) $zwc(128,4)_$c(218,89,0,0)/*$bit(2,4,5,7..9,12,13,15)*/59DA落在了0800~ FFFF区间内,分成3段 101 100111 011010 再依据前面转换规则填充x。 高位填充 101 填充到 1110 不足补0 ,结果为:1110 0 101中位填充结果为:10 100111低位填充结果为:10 011010所以 "姚" 的UTF-8编码为 11100101 10100111 10011010 高位为符号位,1为-负: 计算 11100101 -2^7 + 2^6 + 2^5 + 2^2+ 2^0 = -128 + 64 +32 + 4 + 1 = -27 计算 10100111 -2^7 + 2^5 + 2^2 + 2^1+ 2^0 = -128 + 32 + 4 + 2 + 1 = -89 计算 10011010 -2^7 + 2^4 + 2^3 + 2^1 = -128 + 16 + 8 + 2 = -102 解决过程 单字符基于以上原理则来编写程序 获取字符ASCII。 /// w ##class(M.String2Bytes).GetStringASCII("姚") ClassMethod GetStringASCII(str) { q $ascii(str) } YX> w ##class(M.String2Bytes).GetStringASCII("姚") 23002 根据ASCII获取位串。 /// zw ##class(M.String2Bytes).GetBit("23002") ClassMethod GetBit(ascii) { q $factor(ascii) } YX>zw ##class(M.String2Bytes).GetBit("23002") $zwc(128,4)_$c(218,89,0,0)/*$bit(2,4,5,7..9,12,13,15)*/ 获取低6位。 s first = "" for i = 1 : 1 : 6 { s $bit(first, i) = $bit(bit, i) } zw first first=$zwc(410,1,0,2,5)/*$bit(2,4,5)*/ 根据位数转换成十进制,在用128减去。 ClassMethod bit2Decimal(bit) { s decimal = 0 for i = 1 : 1 : $bitcount(bit) { s num = $bit(bit, i) if (num = 1 ){ s decimal = decimal + $zpower(2, i - 1) } } q decimal } s firstDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(first) w firstDecimal,! firstDecimal=-102 获取中6位。 s second = "" for i = 7 : 1 : 12 { s $bit(second, i - 6) = $bit(bit, i) } zw second s secondDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(second) 获取剩余高位,补位为1110,因为高位为-128不用补,只补6、7为1即可,再计算结果。 s third = "" for i = 13 : 1 : 16 { s $bit(third, i - 12) = $bit(bit, i) } s $bit(third, 6) = 1 s $bit(third, 7) = 1 zw third s thirdDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(third)完整代码 /// w ##class(M.String2Bytes).CharBitString("姚") ClassMethod CharBitString(str) { #; 获取ascii s ascii = ..GetStringASCII(str) w ascii,! #; 根据ascii获取位串 s bit = ..GetBit(ascii) zw bStr #; 获取低6位并,并计算1-7位的结果在用再加上-128 s first = "" for i = 1 : 1 : 6 { s $bit(first, i) = $bit(bit, i) } zw first s firstDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(first) w firstDecimal,! #; 获取中6位并,并计算1-7位的结果在用再加上-128 s second = "" for i = 7 : 1 : 12 { s $bit(second, i - 6) = $bit(bit, i) } zw second s secondDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(second) w secondDecimal,! #; 获取剩余高位,并计算1-7位的结果在用再加上-128 s third = "" for i = 13 : 1 : 16 { s $bit(third, i - 12) = $bit(bit, i) } s $bit(third, 6) = 1 s $bit(third, 7) = 1 zw third s thirdDecimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(third) w thirdDecimal,! q $$$OK } YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes).CharBitString("姚") 23002 first=$zwc(410,1,0,2,5)/*$bit(2,4,5)*/ -102 second=$zwc(410,1,3,4)/*$bit(1..3,6)*/ -89 third=$zwc(409,1,1,3,4)/*$bit(1,3,6,7)*/ -27 1基于上面的例子我们解决了单个字符的UTF8的字节转码。 多字符转码 直接上完整代码,对上面的例子方法进行了一些抽取封装。进行了ascii范围了判断取字节不同,遍历输出。 /// w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() /// w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("AB").%ToJSON() ClassMethod Main(str) { s steam = ##class(%GlobalCharacterStream).%New() d steam.Write(str) q ..Char2Bytes(steam) } ClassMethod Char2Bytes(stream As %GlobalCharacterStream) { #define ASCII128 128 #define ASCII2048 2048 #define ASCII65536 65536 s bytes = [] while 'stream.AtEnd { s char = $a(stream.Read(1)) s bit = $factor(char) if (char d bytes.%Push(..GetHighByte(bit, 1)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 0)) } elseif ((char >= $$$ASCII2048) && (char d bytes.%Push(..GetHighByte(bit, 3)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 12)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 6)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 0)) } } q bytes } ClassMethod GetOffsetByte(bit, offset) { s decimalBit = "" for i = 1 + offset : 1 : 6 + offset { s $bit(decimalBit, i - offset) = $bit(bit, i) } s $bit(decimalBit, 7) = 0 s decimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(decimalBit) q decimal } ClassMethod GetHighByte(bit, wide) { s decimalBit = "" for i = (6 * wide + 1) : 1 : ((6 * (wide + 1) - wide)) { s $bit(decimalBit, i - (6 * wide)) = $bit(bit, i) } for i = 1 : 1 : wide { s $bit(decimalBit, 8 - i) = 1 } s decimal = -128 + ..bit2Decimal(decimalBit) q decimal } YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() [-27,-89,-102,-23,-111,-85] YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes).Main("AB").%ToJSON() [65,66]字节数组java这边也解析成功
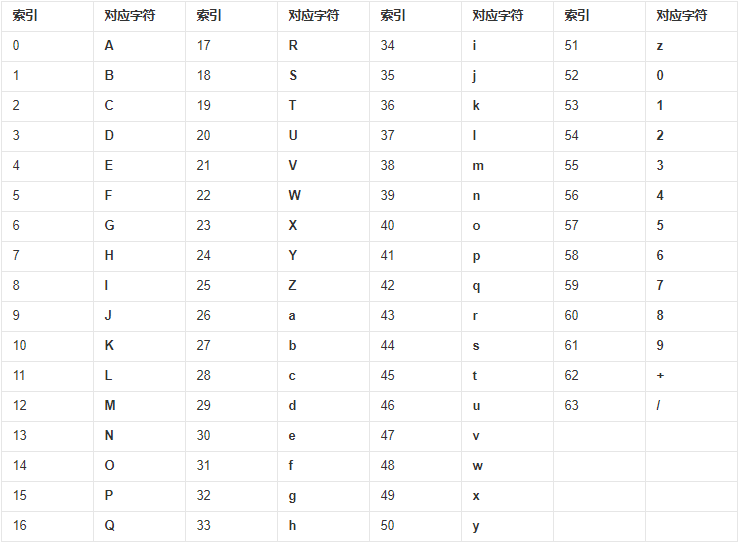
Base64是网络上最常见的用于传输8Bit字节码的编码方式之一,Base64就是一种基于64个可打印字符来表示二进制数据的方法。小写字母a-z、大写字母A-Z、数字0-9、符号"+“、”/“(再加上作为垫字的”=",实际上是65个字符)。 注:Base64作为编码而不是加密。 用处 将非ASCII字符的数据转换成ASCII字符;特别适合在http和mime协议下快速传输数据;数据内容进行编码来进行传输,安全简单。 电子邮件传输网络数据传输密钥存储数字证书存储OpenSSL操作Base64编码 原理 将每三个字节作为一组,一共是24个二进制位。将这24个二进制位分为四组,每个组有6个二进制位。在每组前面加两个00,扩展成32个二进制位,即4个字节。根据下表,得到扩展后的每个字节的对应符号,这就是Base64的编码值。
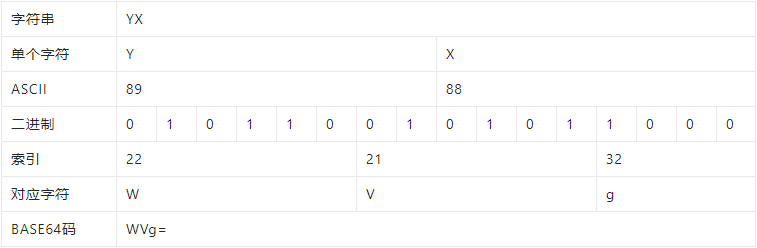
字符串 "YX" , -> ASCII码 -> 二进制 -> 按位数读取二进制再转十进制为索引表索引 -> 转为索引对应字符 。
思考:这里可以思考补位时不足如何加上=。 完整代码 Class M.String2Base64 Extends %RegisteredObject { /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).MainBase64("姚鑫") /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).MainBase64("YX") ClassMethod MainBase64(str) { #; base64转换对照表 s map = $lb( "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n", "o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z", "0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "+", "/" ) #; 声明流对象写入字符串。 #dim steam as %GlobalCharacterStream = ##class(%GlobalCharacterStream).%New() d steam.Write(str) #; 获取UTF8字节十进制字节数组。 #dim bytes as %DynamicArray = ..Char2Bytes(steam) w bytes.%ToJSON(),! #; 把二进制字节保存到流里 #dim saveBit as %GlobalCharacterStream = ##class(%GlobalCharacterStream).%New() s target = "" for i = 0 : 1 : bytes.%Size() - 1 { s bit = $factor(bytes.%Get(i)) for j = 8 : -1 : 1 { d saveBit.Write($bit(bit,j)) } } #; 每次取6位,并根据对照表查找值,进行输出。 while 'saveBit.AtEnd { s byte6Str = saveBit.Read(6) s byte6 = "" w byte6Str,! for i = 1 : 1 : 6 { s $bit(byte6, 7 - i) = $e(byte6Str, i) } s decimal = ..bit2Decimal(byte6) s target = target _ $lg(map,decimal + 1) } q target } /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).Main("YX").%ToJSON() ClassMethod Main(str) { s steam = ##class(%GlobalCharacterStream).%New() d steam.Write(str) q ..Char2Bytes(steam) } ClassMethod Char2Bytes(stream As %GlobalCharacterStream) { #define ASCII128 128 #define ASCII2048 2048 #define ASCII65536 65536 s bytes = [] while 'stream.AtEnd { s char = $a(stream.Read(1)) s bit = $factor(char) if (char d bytes.%Push(..GetHighByte(bit, 1)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 0)) } elseif ((char >= $$$ASCII2048) && (char d bytes.%Push(..GetHighByte(bit, 3)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 12)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 6)) d bytes.%Push(..GetOffsetByte(bit, 0)) } } q bytes } ClassMethod GetOffsetByte(bit, offset) { s first = "" for i = 1 + offset : 1 : 6 + offset { s $bit(first, i - offset) = $bit(bit, i) } s $bit(first, 7) = 0 s $bit(first, 8) = 1 s firstDecimal = ..bit2Decimal(first) q firstDecimal } ClassMethod GetHighByte(bit, wide) { s first = "" for i = (6 * wide + 1) : 1 : ((6 * (wide + 1) - wide)) { s $bit(first, i - (6 * wide)) = $bit(bit, i) } for i = 0 : 1 : wide { s $bit(first, 8 - i) = 1 } s firstDecimal = ..bit2Decimal(first) q firstDecimal } ClassMethod bit2Decimal(bit) { s decimal = 0 for i = 1 : 1 : $bitcount(bit) { s num = $bit(bit, i) if (num = 1 ){ s decimal = decimal + $zpower(2, i - 1) } } q decimal } /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).Base64Encryption("姚鑫") /// w ##class(M.String2Base64).Base64Encryption("YX") ClassMethod Base64Encryption(str As %String, capital As %String = "U") { /* 字符串有汉字需要转换UTF-8 */ s ret = $zcvt(str, "O", "UTF8") s ret = ##class(%SYSTEM.Encryption).Base64Encode(ret) q ret } } 参考utf8和字节数组的转换 ascii 和 byte以及UTF-8的转码规则 BASE64编码 base64解码 base64编码 在线base64解码/编码工具 UTF-8编码转换 UTF-8转换工具 在线UTF-8编码汉字互转工具 字符文本转二进制_汇享在线工具箱 javascript进行base64加密,解密 附 另外一种字符串和字节的互相转换。参考:js字符串和字节的互相转换 Class M.String2Bytes1 Extends %RegisteredObject { /// w ##class(M.String2Bytes1).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() ClassMethod Main(str) { s steam = ##class(%GlobalCharacterStream).%New() d steam.Write(str) q ..Stream2Bytes(steam) } /// 字符转字节数组 ClassMethod Stream2Bytes(stream) { s array = [] while 'stream.AtEnd { s char = $a(stream.Read(1)) if (char #; ba[n++] = (c >> 6) | 192; #; ba[n++] = (c & 63) | 128; s bit = $factor(char) s bit128 = $factor(128) s bit192 = $factor(192) s bit63 = $factor(63) s bitOffset6 = ..Offset(bit, 6) s a1 = $bitlogic(bitOffset6|bit192) s a21 = $bitlogic(bit&bit63) s a2 = $bitlogic(a21|bit128) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a1) - 256) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a2) - 256) } elseif ((char > 2047) && (char #; ba[n++] = (c >> 18) | 240; #; ba[n++] = ((c >> 12) & 63) | 128; #; ba[n++] = ((c >> 6) & 63) | 128; #; ba[n++] = (c & 63) | 128; s bit=$factor(char) s bit240 = $factor(240) s bit63 = $factor(63) s bit128 = $factor(128) s bitOffset18 = ..Offset(bit, 18) s bitOffset12 = ..Offset(bit, 12) s bitOffset6 = ..Offset(bit, 6) s a1 = $bitlogic(bitOffset18|bit240) s a21 = $bitlogic(bitOffset12&bit63) s a2 = $bitlogic(a21|bit128) s a31 = $bitlogic(bitOffset6&bit63) s a3 = $bitlogic(a31|bit128) s a41 = $bitlogic(bit&bit63) s a4 = $bitlogic(a41|bit128) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a1) - 256) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a2) - 256) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a3) - 256) d array.%Push(..Bit2Decimal(a4) - 256) } } q array } /// 位移 ClassMethod Offset(char, offset) { s bit = $factor(0) for i = 64 : -1 : 1{ s pos = i - offset if pos > 0 { s $bit(bit, pos) = $bit(char, i) } } q bit } /// 位转10进制 ClassMethod Bit2Decimal(char) { s decimal = 0 for i = 64 : -1 : 1{ s bit = $bit(char, i) if bit = 1{ s decimal = decimal + (2 ** (i - 1)) } } q decimal } } YX>w ##class(M.String2Bytes1).Main("YX").%ToJSON() [89,88] YX 3e1> w ##class(M.String2Bytes1).Main("姚鑫").%ToJSON() [-27,-89,-102,-23,-111,-85] |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |