使用redis Zset根据score和时间从多个维度进行排序(Zset榜单多维度排序) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 如何根据分数排序 › 使用redis Zset根据score和时间从多个维度进行排序(Zset榜单多维度排序) |
使用redis Zset根据score和时间从多个维度进行排序(Zset榜单多维度排序)
|
文章目录
1. 分段bit位实现排序2. 除数实现排序(推荐)3. 基于分段bit为实现的redis排序工具类
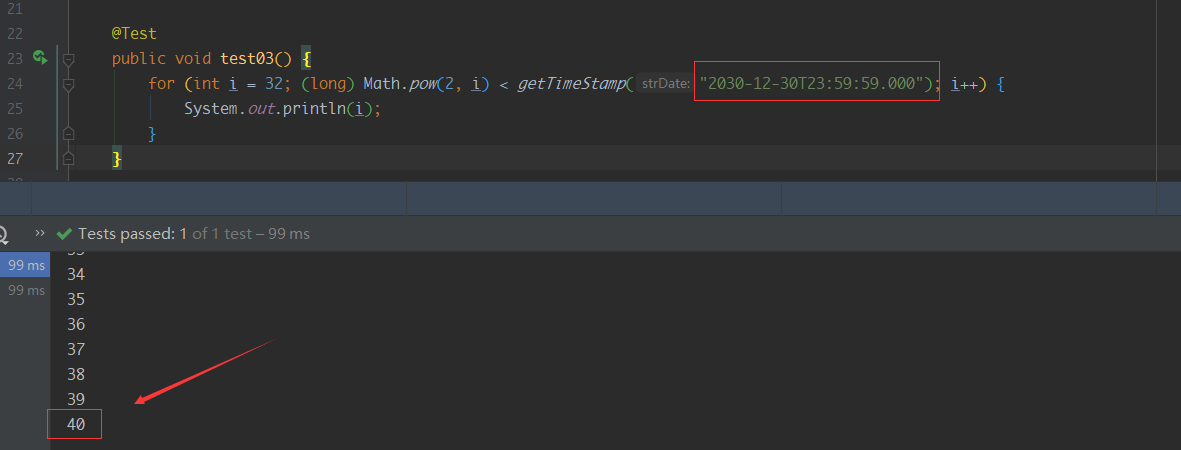
一般我们都会用redis的Zset这个数据结构来做排行榜 问题引入:使用zSet进行排序的时候一直有一个痛点,就是只能根据score进行排序,现实业务一般有多个维度,例如score一样按照先达到的时间排序 这里有两种常用的方法,推荐使用第二种: 参考雪花算法,用41位表示时间戳在低位,22位表示score在高位,这样当score相等时才会用时间戳比较,优点是可以拿到时间戳,缺点是22位只能存到417万,超出就需要压缩时间戳bit位了(本文中需要至少存到百亿,需要26个bit);当然有更多的维度可以继续拆分bit位用时间戳当做被除数,然后用一个标准值(例如1000d)除,得到一个小数放到score的小数部分,这样的话也是时间戳越小的小数部分越大,同样满足需求。这样的好处是方便,坏处是因为浮点数会进度丢失拿不到时间戳了,并且并发情况下由于得到的浮点数会精度丢失会导致排序不稳定,出现错排的情况 1. 分段bit位实现排序为了实现按照多个维度进行排序,特意封装此类,原理类似分布式ID雪花算法,即用一个long类型变量存储多个信息 一个long类型长度为8个字节(64bit),雪花算法使用其中41bit记录时间戳,其余bit位存储机房id、机器id、序列号Redis的ZSet支持分值为double类型,也是8字节,那么我们也可以使用41位存储时间戳,其他位存储用户的实际积分这里我们也可以用41位来存储时间戳,用22位来存储score,1位符号位,为什么要用41位来存储时间戳呢?首先我们要明确时间戳的概念: 时间戳是指格林威治时间1970年01月01日00时00分00秒(北京时间1970年01月01日08时00分00秒)起至现在的总秒数时间戳一般用10位和13位的,13位的时间戳,其精度是毫秒(ms),10位的时间戳,其精度是秒(s)我们来看一下这几个时间戳: - 2022-12-04T23:59:59.000 -> 1670169599000 - 2023-12-30T23:59:59.000 -> 1703951999000 - 2030-12-30T23:59:59.000 -> 1924876799000我们可以计算要存储13位的数字,其实最少需要40个bit位,再加上
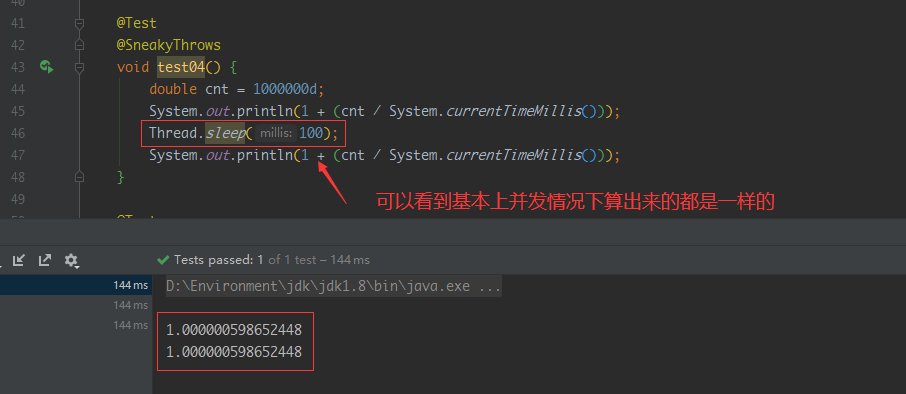
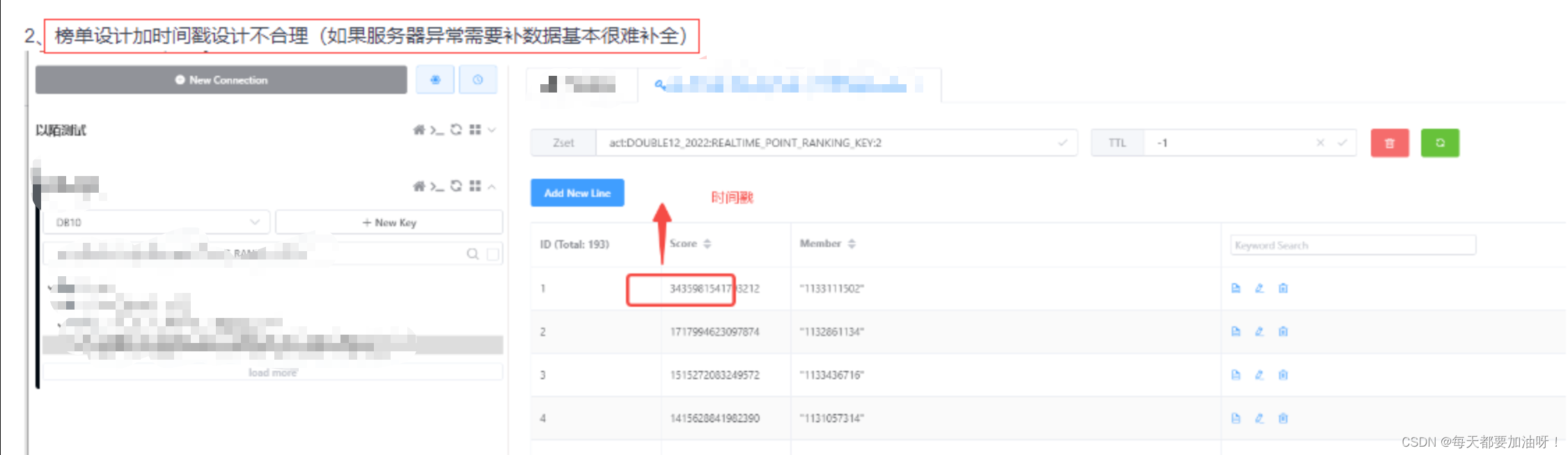
核心代码如下 /*** 64bit全为1的数,用来做移位操作 **/ private static final long FACTORS = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFL; // 高位存数字15 低位存数字14 long score = 0L; score = (score | 15) > 32这样在高并发情况下也能保证排序稳定,位运算性能也比较高效,但是缺点就是在redis中我们看不到score,不方便校验数据,也不方便测试同学测试,这点可以看笔者的第二种方式后面写的 2. 除数实现排序(推荐)这种方式排序并不稳定,特别是并发情况下及其不稳定 核心代码: public void increaseRankNum(long uid, int ponit) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); double baseScore = 1000000d; double suffixScore = baseScore / startTime; redisTemplate.opsForZSet().incrementScore(key, String.valueOf(uid), suffixScore + ponit); }并发情况下不稳定:
但是笔者最后还是使用了这种方式,无他,测试同学给我打bug了,我跟他谈并发,他跟我讲业务😭😭😭😭😭
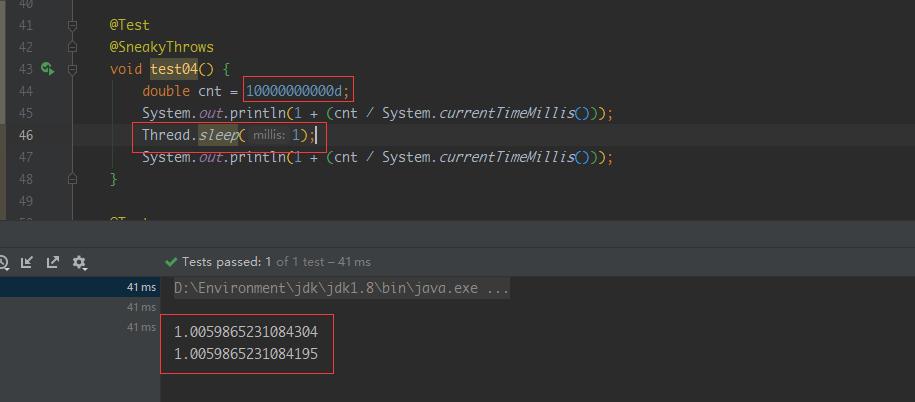
最后将被除数调整了一下,尽量让排序准确
其实真的好像测试同学说的对,其实这种方式也很好,难度较小,精度也还行,推荐使用这种
* 问题引入:使用zSet进行排序的时候一直有一个痛点,就是只能根据score进行排序,现实业务一般有多个维度,例如score一样按照先达到的时间排前面 * 为了实现按照多个维度进行排序,特意封装此类,原理类似分布式ID雪花算法,即用一个long类型变量存储多个信息。 * 一个long类型长度为8个字节(64bit),雪花算法使用其中41bit记录时间戳,其余bit位存储机房id、机器id、序列号。 * Redis的ZSet支持分值为double类型,也是8字节,那么我们也可以使用41位存储时间戳,其他位存储用户的实际积分 * * 1. 如果是用41bit表示时间戳,22bit表示积分的话,那么score的组成就是这样的: * 0(最高位不用)| 0000000 00000000 0000000(22bit表示积分)| 000000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000(41bit表示时间戳) * 因为排序首先按积分排再按时间排,所以积分在高位,时间戳在低位,这样不管时间戳的值是多少,积分越大,64bit表示的数值就越大 * * 2. 当score相等时,时间戳越大表示的数值越大,我们想要的是先达到的数值越大(越靠前),我们可以用一个时间周期(比如一天)和用户达到的 * score的时间进行做差,这样这个值会随着时间的推移而变小,而且不会出现负数的情况,刚好能够达到目的 * * 3. 这里使用三个月作为时间周期,由于使用作差计算的方式,所以时间戳不会超过11位数字,只需要34bit,score部分可以使用29bit,能够存储到5亿3千万 * 如果需要存储更大的值,可以用一个月作为时间周期进行作差,这样只需要28bit,score部分能够存储到三百四十多亿的数字 * 注意:时间周期一定不能超过当前时间往后推三个月,否则时间戳会溢出,导致排序出错 * * 4. 如果得分不超过四百一十万,建议使用41bit存储时间戳,需要将{@link RankOperator#LEFT}改为41 * 再将标准时间{@link RankOperator#STANDARD_DAY} 往后加50年即可,这样不会出现溢出的问题 * * @author xxx * @since 2022-12-02 16:29 **/@Slf4j public class RankOperator { protected final RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /*** 并发情况下,需要精确到毫秒 **/ private static final DateTimeFormatter DEFAULT_FORMAT = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss[.SSS]"); /*** 使用三个月作为标准时间进行作差,保证存储的时间戳在34位 **/ private static final LocalDateTime STANDARD_DAY = LocalDateTime.parse("2023-03-05T23:59:59.000", DEFAULT_FORMAT); /*** 2099年某一天的时间戳,用来做减法 **/ private static final long PERIOD_END_TIME_STAMP = getTimestampOfDateTime(STANDARD_DAY); /*** 64bit全为1的数,用来做移位操作 **/ private static final long FACTORS = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFL; /*** 左移位数,表示用多少位存储时间戳,如果用34位存,用来作差的时间不能高于三个月 **/ private static final int LEFT = 34; private static final int RIGHT = 64 - LEFT; /** * 子类初始化时 赋值泛型 * * @param redisTemplate redisTemplate */ protected RankOperator(RedisTemplate redisTemplate) { this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate; } /** * 实现积分 + 时间戳差值转score * * @param point 用户的得分,由于只有22个bit位,所以point不能超过2^22 - 1(4,194,303 四百一十万),如果超过可以压缩时间戳bit位 * @return 返回计算后的score */ protected long toScore(int point) { long score = 0L; score = (score | point) > LEFT); } /** * 拿到用户的真实得分 */ public int getPointByUserId(String redisKey, long userId) { Long score = Optional.ofNullable(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(redisKey, String.valueOf(userId))) .map(Double::longValue).orElse(0L); return getPoint(score); } /** * 获取用户得到此得分的最新时间 */ public LocalDateTime getDateByUserId(String redisKey, long userId) { Long score = Optional.ofNullable(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().score(redisKey, String.valueOf(userId))) .map(Double::longValue).orElse(0L); return getDate(getTimeStamp(score)); } /** * 拿到用户的排名,按照score降序,score相等先达到的排前面 */ public Long getRankByUserId(String redisKey, long userId) { return Optional.ofNullable(redisTemplate.opsForZSet().reverseRank(redisKey, String.valueOf(userId))) .map(e -> e + 1).orElse(-1L); } /** * 拿到低位的值(投票的时间戳),这里注意需要使用无符号右移 `>>>` * * @param score 在redis中实际保存的score * @return 投票的时间戳 */ protected long getTimeStamp(long score) { return PERIOD_END_TIME_STAMP - ((FACTORS >>> RIGHT) & score); } /** * 获得用户最新一次投票达到分数的时间 * * @param score 在redis中实际保存的score * @return 用户最新一次投票达到分数的时间 */ protected LocalDateTime getDate(long score) { long milli = getTimeStamp(score); return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.ofEpochMilli(milli), ZoneOffset.of("+8")); } /** * 拿到用户的得分,如果用户不存在则返回0 */ protected int getScore(Long userId, String randKey) { ZSetOperations zSetOperations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); return Optional.ofNullable(zSetOperations.score(randKey, String.valueOf(userId))) .map(Double::intValue).orElse(0); } /** * 更新用户的排名 * * 这里先读再写的操作并不是原子的,并发情况下多个请求同时读到同一个值再进行更改,会导致写操作丢失的情况 * 1. 可以使用分布式锁解决,但是性能低下 * 2. 基于`Multi、Exec、discard、watch` 实现乐观锁解决(CAS) * * @param accountId 用户账号 * @param addPoint 增加的分数 * @param redisKey 用来标记是那个排行榜 */ protected void updateRanking(Long accountId, Integer addPoint, String redisKey) { // 开启事物 redisTemplate.setEnableTransactionSupport(true); redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() { @Override @SuppressWarnings("all") public String execute(RedisOperations redisOperations) throws DataAccessException { // 用来保存每次用户cas后的值,如果和期望的不一样,则进行自旋重试 List result = null; // 自旋15次,如果自旋15次还是失败,则抛出异常并提示用户投票失败,防止空自旋导致CPU占用过高 AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(15); do { // 监视数据,如果其他线程修改会中断执行 redisOperations.watch((K) redisKey); ZSetOperations zSet = redisOperations.opsForZSet(); // 获取用户的得分,这里可能会脏读 Double score = zSet.score(redisKey, String.valueOf(accountId)); score = (score == null) ? 0d : score; int curPoint = getPoint(score.longValue()); long newScore = toScore(curPoint + addPoint); // 开始事务 redisOperations.multi(); zSet.add(redisKey, String.valueOf(accountId), newScore); try { // 提交事务 result = redisOperations.exec(); } catch (Exception e) { // 如果key被改变,提交事务时这里会报异常,自旋进行下一次修改 // noting to do ... } finally { if (atomicInteger.decrementAndGet() userId value -> score,这里的score是用户的真实分数 */ protected LinkedHashMap rank(Integer rankNum, String rankKey) { ZSetOperations zSetOperations = redisTemplate.opsForZSet(); Set typedTuples = zSetOperations.reverseRangeWithScores(rankKey, 0, rankNum - 1L); if (typedTuples == null || CollUtil.isEmpty(typedTuples)) { return Maps.newLinkedHashMapWithExpectedSize(0); } // userId score LinkedHashMap linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap(typedTuples.size()); typedTuples.forEach(typedTuple -> { long userId = Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(typedTuple.getValue())); // 用户的真实得分 int point = getPoint(Objects.requireNonNull(typedTuple.getScore()).longValue()); linkedHashMap.put(userId, point); }); return linkedHashMap; } /** * 获取一个标准时间字符串转换的时间戳 * * @param strDate 例如:2030-12-30T23:59:59.000 2022-12-04T23:59:59 * @return 时间戳 */ private static long getTimeStamp(String strDate) { DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(strDate); LocalDateTime date = LocalDateTime.parse(strDate, formatter); return getTimestampOfDateTime(date); } private static long getTimestampOfDateTime(LocalDateTime localDateTime) { ZoneId zone = ZoneId.systemDefault(); Instant instant = localDateTime.atZone(zone).toInstant(); return instant.toEpochMilli(); } } |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |