SpringBoot项目后端开发逻辑梳理总结 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 如何写后端业务接口 › SpringBoot项目后端开发逻辑梳理总结 |
SpringBoot项目后端开发逻辑梳理总结
|
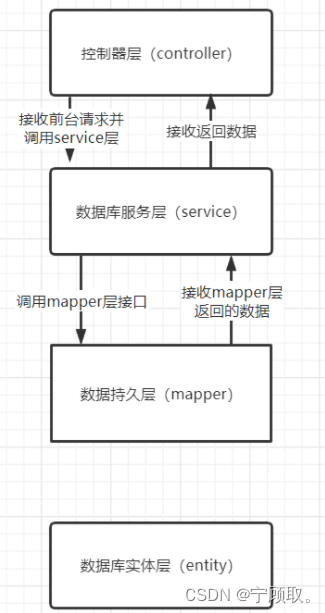
SpringBoot项目中包含Mapper层(Dao层)、Entity层(model层)、DTO层、VO层、Service层和Controller层(本篇以学生信息表增删改查为例,梳理各个层之间的逻辑关系、开发流程和注意事项)。 目录 一、各层之间的逻辑关系 1.Controller层、Service层、Mapper层、Entity层的逻辑关系 2.每层的理解 1.mapper层(Dao层)。 2.Entity层(model层) 3.DTO层 4.VO层 5.service层 6.Controller层 二、运行流程 三、开发流程 1、实体类 2、Service接口 3、xml文件 4、Mapper接口 5、ServiceImpl实现类 6、Controller层调用接口 一、各层之间的逻辑关系 1.Controller层、Service层、Mapper层、Entity层的逻辑关系
mapper层是操作数据库的一层。想要访问数据库并且操作,只能通过mapper层向数据库发送sql语句,将这些通过接口传给service层,对数据库进行操作。主要实现增删改查操作,在mybatis中与xxx.xml内相互一一映射。 mapper层包含xxxDao.java文件和xxxDao.xml (.xml文件中写sql语句,配置通用查询映射结果) (Dao.java相当于xml文件的抽象类) StudentBaseDao.xml id, name, sex, age, chinese, math, tenglish select * from student select name from student where name = #{abc} and id != #{id}StudentBaseDao.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.dao.student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.rs.RsCheckListInfo; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.student.studentDTO; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.vo.student.studentBaseForm; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.Student.StudentBase; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.quote.QuoteBase; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Mapper @Repository public interface StudentBaseDao extends BaseMapper { List queryList(studentBaseForm v); //studentDTO queryRepeat(Map param); //List queryRepeat(studentBaseForm v); List queryRepeat(String abc,int id); }注意: namespace和resultMap的type要指向正确的地址:namespace指向mapper文件,type指向实体类。parameterType用于对应的mapper接口方法接收的参数类型,将信息存入到数据库中。resultType用于指定sql输出的结果类型,从数据库中提取相应的数据。.xml文件命名的id与.java文件中的名称对应 2.Entity层(model层)也叫作pojo层,是数据库在项目中的类,在文件包含实体类的属性和对应属性的get、set方法。 实体类中属性同数据库表字段一一对应,对于相应的get、set方法一般不需要书写,实体类上引入@Data注解,会自动注入get、set以及toString方法,减少代码量。 entity表示对数据库中所有标的映射,是根据数据库表字段设计出来的实体(要求表名和类名相同,字段名与成员变量名相同) StudentBase.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.Student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.BaseEntity; import lombok.*; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName; import java.math.BigDecimal; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @TableName (value ="student") public class StudentBase { //private static final long serialVersionUID = 1999600885795452253L; @TableField(value = "id") @TableId private int id; @TableField(value = "name") private String name; @TableField(value = "sex") private String sex; @TableField(value = "age") private String age; @TableField(value = "chinese") private String chinese; @TableField(value = "math") private String math; @TableField(value = "english") private String english; } 3.DTO层数据对象传输层,负责屏蔽后端实体类,将UI要的数据进行重新定义和封装。 DTO里的每个字段,与前端页面对应。 因为后端在实际业务场景中需要储存大量数据,而用户需要的只是一部分,为了快速获取用户需要的数据,应该把用户经常用到的数据在DTO层进行封装,在调用服务时,只需要调用依次便可完成所有的逻辑操作。 逻辑关系如下:
studentDTO.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.common.model.BaseInfo; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.util.List; @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class studentDTO { private int id; private String name; private String sex; private String age; private String chinese; private String math; private String english; private String sumGrade; // private String sGrade; } 4.VO层视图对象,用于展示层返回给前端。 把某个指定页面的所有数据封装起来,方便前端获取数据,后端将前端需要的数据做整合,打包成一个类。 使用场景:如果在前端页面需要展示经过某些数据库操作才能展示的特定数据,一般在vo层中把操作过程中涉及到的数据进行封装,方便前端获取。在controller层定义对应接口时把返回类型规定为vo类。 studentBaseForm.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.vo.student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.utils.ManagePageRequest; import lombok.Data; @Data public class studentBaseForm extends ManagePageRequest { private int id; private String name; private int sex; private int age; private int chinese; private int math; private int english; } 5.service层业务服务层,调用mapper层API并提供给controller层使用,间接和数据库打交道。 包括两部分,接口文件(Service.java)和接口实现类文件(ServiceImpl.java)。 接口文件中定义在controller层中调用的service层方法;接口实现类文件中完成service层接口中定义的方法的实现。 在该层进行复杂的业务逻辑处理,在对多个mapper层查到的数据进行组装、处理,然后将结果返回给controller。因此,在一般情况下,一个controller中可能包括多个Service,而一个Service中又或许包含多个mapper。 注意:这里接口实现类中方法的实现是指业务逻辑的实现,可能有些方法并不能在实现类里完成真正意义上的实现,还需要在mapper层文件完成其真正意义上的实现(主要是和数据库交互)。 StudentBaseService.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.service.student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.student.studentDTO; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.vo.student.studentBaseForm; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.utils.ManagePageResult; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.Student.StudentBase; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService; import java.util.List; public interface StudentBaseService extends IService { ManagePageResult studentList(studentBaseForm vo); studentDTO studentDetail(int name); void saveStudent(studentDTO studentDTO) throws Exception; void delUser(int name); }StudentBaseServiceImpl.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.service.impl.student; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.student.studentDTO; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.vo.student.studentBaseForm; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.utils.ManagePageResult; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.dao.student.StudentBaseDao; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.entity.Student.StudentBase; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.exception.ManageException; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.service.UserInfoService; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.service.student.StudentBaseService; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl; import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper; import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.apache.commons.lang3.ObjectUtils; import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.List; @Slf4j @Service("studentBaseService") public class StudentBaseServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements StudentBaseService { @Autowired StudentBaseService studentBaseService; @Autowired UserInfoService userInfoService; @Override public ManagePageResult studentList(studentBaseForm vo) { PageHelper.startPage(vo.getPageNum(), vo.getPageSize()); List pageList = this.baseMapper.queryList(vo); for(studentDTO item : pageList){ int chinese = Integer.parseInt(item.getChinese()); int math = Integer.parseInt(item.getMath()); int english = Integer.parseInt(item.getEnglish()); int sum = chinese+math+english; if((sum)>180){ item.setSumGrade("及格"); }else{ item.setSumGrade("不及格"); } } PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo(pageList); return ManagePageResult.getPageResult(pageInfo); } @Override public studentDTO studentDetail(int studentNo) { if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(studentNo)) { throw new ManageException("error!"); } QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper(); wrapper.eq("id", studentNo); StudentBase studentBase = this.baseMapper.selectOne(wrapper); if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(studentBase)) { throw new ManageException("未找到对应的信息,请检查输入是否正确!"); } studentDTO studentDTO = new studentDTO(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(studentBase, studentDTO); return studentDTO; } @Override @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void saveStudent(studentDTO studentDTO) throws Exception { //保存信息 StudentBase studentBase = new StudentBase(); BeanUtils.copyProperties(studentDTO, studentBase); List result = this.baseMapper.queryRepeat(studentBase.getName(),studentBase.getId()); if(ObjectUtils.isEmpty(result)){ this.save(studentBase); }else{ throw new ManageException("用户名重复"); } } //删除 @Override @Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class) public void delUser(int name) { log.info("删除信息入参:【{}】", name); if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(name)) { throw new ManageException("入参错误!"); } // QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper(); // wrapper.eq("id", name); // StudentBase studentBase = this.baseMapper.selectOne(wrapper); this.removeById(name); } } 6.Controller层本层定义接口并调用service逻辑设计层的接口来控制业务流程。 功能:接收前端请求,调用service,接收service返回的数据,再将处理结果返回到前端(接收前端数据,返回页面请求信息)。 Controller层是不允许直接操作数据库的!它就像一个服务员,有客人需要点菜,就喊服务员;对前端需要完成什么业务,就告诉Controller。Controller只是一个中间者或转发者。 不能在Controller里暴露Service的业务逻辑,而应该直接转发Service的业务处理结果。 QuoteBaseController11.java package com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.controller.quote; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.dto.student.studentDTO; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.model.vo.student.studentBaseForm; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.utils.ManagePageResult; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.remote.utils.ResponseResult; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.enumeration.common.RespStatus; import com.ai.citicnet.boss.manage.service.service.student.StudentBaseService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("/studentBase") public class QuoteBaseController11 { @Autowired // spring自动注入studentBaseService赋值 private StudentBaseService studentBaseService; //PostMapping用于认证方法,将http post请求映射到特定处理程序 @PostMapping("/studentList") public ResponseResult queryList(@RequestBody studentBaseForm vo) { try { ManagePageResult page = studentBaseService.studentList(vo); return ResponseResult.ok().put(page); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return ResponseResult.error(RespStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage()); } } @PostMapping("/studentDetail") public ResponseResult studentDetail(@RequestParam("name") int studentNo) { try { studentDTO studentDTO = studentBaseService.studentDetail(studentNo); return ResponseResult.ok().put(studentDTO); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return ResponseResult.error(RespStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage()); } } //保存数据 @PostMapping("/saveStudent") public ResponseResult saveStudent(@RequestBody studentDTO studentDTO) { try { studentBaseService.saveStudent(studentDTO); return ResponseResult.ok().put(true); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return ResponseResult.error(RespStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage()); } } //删除数据 @PostMapping("/deleteStudent") public ResponseResult deleteStudent(@RequestParam("name") int name) { try { studentBaseService.delUser(name); return ResponseResult.ok().put(true); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return ResponseResult.error(RespStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), e.getMessage()); } } } 二、运行流程1.控制层接收前端请求,调用对应的业务层接口方法 2.业务层实现类去实现业务层接口 3.业务层实现类的方法调用数据层的接口 4.数据层实现文件(mapper.xml)实现数据层接口 5.处理结果,逐层返回。 三、开发流程1.实体类 2.service接口 3.XML文件 4.mapper接口 5.serviceImpl实现类 6.controller层调用接口 7.最终接口展示 1、实体类实体类连接着前端接口内容,返回的响应参数、参数的数据类型和注释都来自于这里;所以我们把创建实体类作为开始编码的第一步。 建立实体类,就能知道我们最终是想要得到什么值返回给前端,这样,我们以后的步骤都是围绕着如何得到我们的实体类而来。 注意: 因为很多时候返回给前端的是一个集合类型,存储着很多的数据。这个时候,我们一般建立两个实体类,一个用来存储List集合,另一个用来存储该集合里的内部数据。 package com.hncr.system.domain.vo; //用户集合实体类 @Data public class UserVo { @ApiModelProperty("用户集合") private List userListVos; } package com.hncr.system.domain.vo; //用户类 @Data public class UserListVo { @ApiModelProperty("姓名") private String name; @ApiModelProperty("年龄") private Integer age; @ApiModelProperty("性别:(0:男,1:女)") private Integer sex; } 2、Service接口“接口编程”思想大概就是基于Service接口进行的吧! 返回值类型是UserVo实体类(因为最终要得到的值就是要返回一个集合给前端,所以这里的返回类型就是该实体类) package com.hncr.system.service; import com.hncr.system.domain.vo.UserVo; //Service接口 public interface IUserService { UserVo userSummary(); } 3、xml文件接下来,我们将sql语句写好(很重要!!!) 确定需要多少个sql语句才能解决具体的Service接口问题。 可以先在Navicate中做一些实力操作(根据年龄进行排序) SELECT name, age, sex FROM `user` ORDER BY age DESC(在实际项目中,要查询或者改变的操作会很多,数据量也会很大,很多时候要对某个字段做索引操作才会缩短查询时间,查询时间超过3秒或4秒的sql,在前端来看就是一个相当慢的接口了。) 数据量大的数据库,我们尽量做到只访问一次,以免浪费不必要的时间,影响用户体验。 在Navicat中查到想要的数据后,把sql语句加入到我们的XML文件中,结合我们的namespace、id、resultType(第四步会配置)。 SELECT name, age, sex FROM `user` ORDER BY age DESC 4、Mapper接口第三步确定,一条sql语句就可以搞定想要的效果,那Mapper接口写一个即可(反正就是sql写了几个,我们对应的就得写几个Mapper接口)。 package com.hncr.system.mapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; //Mapper接口 @Repository public interface UserMapper { List userSummaryMapper(); }可以看到,这里的返回值类型不太一样了,我们要确保xml文件中的resultType要和Mapper接口中的一一对应上,否则查询不到数据,接口报错。 (在实际项目中,后续的这种接口方式用的较多,list、Map、List) 集合很重要,项目中大多数都会使用集合!!! id对应上我们的Mapper接口名字,这里是“userSUmmaryMapper” 注意: xml文件多少个sql,mapper接口就写多少个。mapper接口返回类型,接口名称要与xml文件中resultType、id 等属性一一对上。 5、ServiceImpl实现类至关重要的一步!!! 在这里要实现数据的交互、代码逻辑。 package com.hncr.system.service.impl; import com.hncr.system.domain.vo.UserListVo; import com.hncr.system.domain.vo.UserVo; import com.hncr.system.mapper.UserMapper; import com.hncr.system.service.IUserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; List userSummaryMapper(){ return userMapper.userSummaryMapper(); } public UserVo userSummary(){ UserVo userVo = new UserVo(); List list1 = userSummaryMapper(); List list2 = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++) { UserListVo userListVo = new UserListVo(); Map map = list1.get(i); userListVo.setName((String) map.get("name")); userListVo.setAge((Integer) map.get("age")); userListVo.setSex((Integer) map.get("sex")); list2.add(userListVo); } userVo.setUserListVos(list2); return userVo; } } 6、Controller层调用接口走到这里,基本就迎来了收尾工作。 Controller层就是一个调用的过程,将相关的注解写好,注入相关的接口方法,然后返回给前端。这样我们就完成了其中一个接口。同理再逐个完成其他接口就可以啦。 package com.hncr.web.controller.system; import com.hncr.system.domain.JsonResult; import com.hncr.system.domain.vo.UserVo; import com.hncr.system.service.IUserService; import io.swagger.annotations.Api; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @Api(value = "用户信息", tags = "用户信息") @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @Autowired private IUserService userService; @ApiOperation(value = "用户信息汇总", notes = "{" + " \"msg\": \"操作成功\"," + " \"code\": 200," + " \"data\": {" + " }" + "}") @GetMapping("UserSummary") public JsonResult userSummary(){ UserVo userVo = userService.userSummary(); return JsonResult.success(userVo); } }一个完整的SpringBoot项目的完整后端开发就这样完成啦!!! 参考文章: https://huaweicloud.csdn.net/63874ec5dacf622b8df8a935.html?spm=1001.2101.3001.6650.1&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~activity-1-126849368-blog-120290351.235^v38^pc_relevant_sort_base2&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~CTRLIST~activity-1-126849368-blog-120290351.235^v38^pc_relevant_sort_base2&utm_relevant_index=2&#devmenu4 基于SpringBoot_后端接口流程_springboot后端接口怎么写_Fish_Vast的博客-CSDN博客 controller层,service层,mapper层,entity层的作用与联系。_mapper层的作用_要努力变强-的博客-CSDN博客 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |