|
基本原理
 一切都要从基本原理说起 一切都要从基本原理说起 

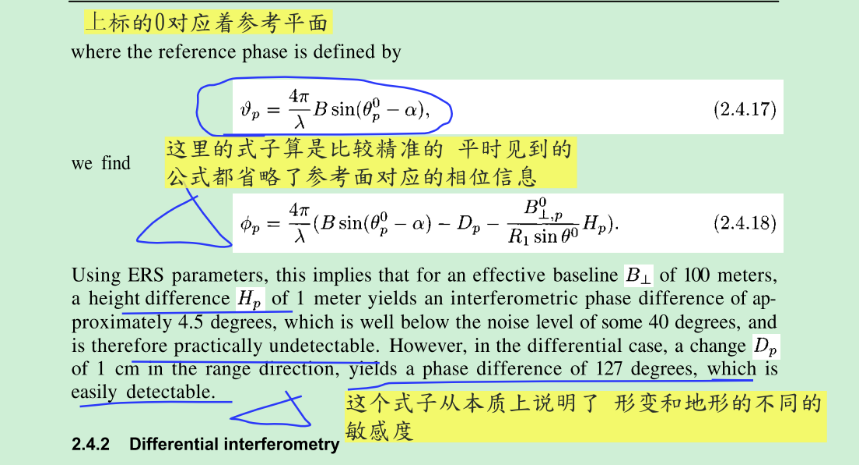 上面的基本原理给出了干涉相位和高程与形变的关系,与此同时也给出干涉相位和基线(或者是轨道数据)的关系。这里的基本原理是下面的分析以及其他分析的基础。 上面的基本原理给出了干涉相位和高程与形变的关系,与此同时也给出干涉相位和基线(或者是轨道数据)的关系。这里的基本原理是下面的分析以及其他分析的基础。
轨道误差的处理办法
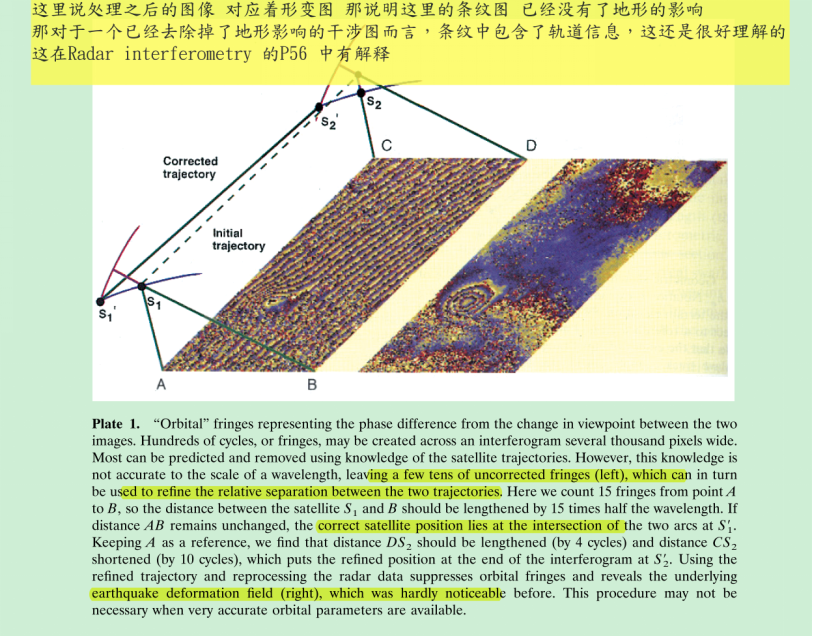 上面的基本思想就是“自洽”,这个里面有一个原理,即上面公式描述的基线、地形以及相位等的关系,那么在这个公式的前提下,整个系统内部要自洽,不能相互矛盾。当然了这里的处理只能提高相对精度,而不能提高绝对精度,不过对于某些应用好像是已经够了。 上面的步骤只能得到某些点上的轨道纠正信息,要得到每一个点上的轨道纠正信息需要进行一个拟合: To eliminate the residual orbital contribution in an interferogram, we count the residual fringes on the interferogram and attribute them to an error in the slave orbit (Plate 1). This approximation is acceptable because the phenomenon depends mainly on the relative, rather than absolute, positions of the orbits. We seek two corrections to the slave orbit, a vertical and a lateral deviation, both of which change linearly with time along track as a * bt and c * dt. To determine the four coefficients a, b, c, and d, we choose four points as far apart as possible in the final image, typically at the corners. We then count the residual fringes between them. The four coefficients are the solution of a linear system of four equations involving the positions of the four points and the number of cycles at each of them. The orbit can then be corrected for any epoch in time, and the interferogram can be adequately corrected everywhere. Usually, we apply the correction to the final product, because the error committed on the slave orbit is too small to alter the previous processing steps. If necessary, we could completely reiterate the processing with the corrected slave orbit, but a single correction is sufficient in practice. 这是一种方法 这种方法必须要估计DEM辅助数据的精度吧。 其他的方法: In a slightly different approach, Murakami et al. [1996] use GPS measurements of surface displacement at seven bench marks within about 15 km of the Northridge earthquake epicenter to adjust the orbital parameters. They obtain residual differences (GPS minus JERS-1 radar) of less than 3 cm in range, smaller than the 3.5-cm uncertainty of the GPS measurements. More widely separated control points (e.g., the four corners of the 100 by 100 km image) provide a better estimate of the orbital separation, which varies mostly over long wavelengths [Massonnet et al., 1996a]. 上面的基本思想就是“自洽”,这个里面有一个原理,即上面公式描述的基线、地形以及相位等的关系,那么在这个公式的前提下,整个系统内部要自洽,不能相互矛盾。当然了这里的处理只能提高相对精度,而不能提高绝对精度,不过对于某些应用好像是已经够了。 上面的步骤只能得到某些点上的轨道纠正信息,要得到每一个点上的轨道纠正信息需要进行一个拟合: To eliminate the residual orbital contribution in an interferogram, we count the residual fringes on the interferogram and attribute them to an error in the slave orbit (Plate 1). This approximation is acceptable because the phenomenon depends mainly on the relative, rather than absolute, positions of the orbits. We seek two corrections to the slave orbit, a vertical and a lateral deviation, both of which change linearly with time along track as a * bt and c * dt. To determine the four coefficients a, b, c, and d, we choose four points as far apart as possible in the final image, typically at the corners. We then count the residual fringes between them. The four coefficients are the solution of a linear system of four equations involving the positions of the four points and the number of cycles at each of them. The orbit can then be corrected for any epoch in time, and the interferogram can be adequately corrected everywhere. Usually, we apply the correction to the final product, because the error committed on the slave orbit is too small to alter the previous processing steps. If necessary, we could completely reiterate the processing with the corrected slave orbit, but a single correction is sufficient in practice. 这是一种方法 这种方法必须要估计DEM辅助数据的精度吧。 其他的方法: In a slightly different approach, Murakami et al. [1996] use GPS measurements of surface displacement at seven bench marks within about 15 km of the Northridge earthquake epicenter to adjust the orbital parameters. They obtain residual differences (GPS minus JERS-1 radar) of less than 3 cm in range, smaller than the 3.5-cm uncertainty of the GPS measurements. More widely separated control points (e.g., the four corners of the 100 by 100 km image) provide a better estimate of the orbital separation, which varies mostly over long wavelengths [Massonnet et al., 1996a].
精确的轨道数据对干涉处理的意义
Note that, when co-registering parameters derived from orbits are sufficiently accurate, it is possible to include the co-registration in the focusing operator. 计算基线 图像匹配 图像定位(相位模拟)
参考文献
Hooper, A., Bekaert, D., Spaans, K., & Arıkan, M. (2012). Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. Tectonophysics, 514, 1-13. Zhong, L., & Dzurisin, D. (2014). Insar imaging of aleutian volcanoes. Springer Praxis Books, 2014(8), 1778–1786. Ketelaar, V. (2009). Satellite radar interferometry : subsidence monitoring techniques. 博主目前在慕尼黑读博士,非常欢迎大家和我交流。
|  一切都要从基本原理说起
一切都要从基本原理说起 

 上面的基本原理给出了干涉相位和高程与形变的关系,与此同时也给出干涉相位和基线(或者是轨道数据)的关系。这里的基本原理是下面的分析以及其他分析的基础。
上面的基本原理给出了干涉相位和高程与形变的关系,与此同时也给出干涉相位和基线(或者是轨道数据)的关系。这里的基本原理是下面的分析以及其他分析的基础。 上面的基本思想就是“自洽”,这个里面有一个原理,即上面公式描述的基线、地形以及相位等的关系,那么在这个公式的前提下,整个系统内部要自洽,不能相互矛盾。当然了这里的处理只能提高相对精度,而不能提高绝对精度,不过对于某些应用好像是已经够了。 上面的步骤只能得到某些点上的轨道纠正信息,要得到每一个点上的轨道纠正信息需要进行一个拟合: To eliminate the residual orbital contribution in an interferogram, we count the residual fringes on the interferogram and attribute them to an error in the slave orbit (Plate 1). This approximation is acceptable because the phenomenon depends mainly on the relative, rather than absolute, positions of the orbits. We seek two corrections to the slave orbit, a vertical and a lateral deviation, both of which change linearly with time along track as a * bt and c * dt. To determine the four coefficients a, b, c, and d, we choose four points as far apart as possible in the final image, typically at the corners. We then count the residual fringes between them. The four coefficients are the solution of a linear system of four equations involving the positions of the four points and the number of cycles at each of them. The orbit can then be corrected for any epoch in time, and the interferogram can be adequately corrected everywhere. Usually, we apply the correction to the final product, because the error committed on the slave orbit is too small to alter the previous processing steps. If necessary, we could completely reiterate the processing with the corrected slave orbit, but a single correction is sufficient in practice. 这是一种方法 这种方法必须要估计DEM辅助数据的精度吧。 其他的方法: In a slightly different approach, Murakami et al. [1996] use GPS measurements of surface displacement at seven bench marks within about 15 km of the Northridge earthquake epicenter to adjust the orbital parameters. They obtain residual differences (GPS minus JERS-1 radar) of less than 3 cm in range, smaller than the 3.5-cm uncertainty of the GPS measurements. More widely separated control points (e.g., the four corners of the 100 by 100 km image) provide a better estimate of the orbital separation, which varies mostly over long wavelengths [Massonnet et al., 1996a].
上面的基本思想就是“自洽”,这个里面有一个原理,即上面公式描述的基线、地形以及相位等的关系,那么在这个公式的前提下,整个系统内部要自洽,不能相互矛盾。当然了这里的处理只能提高相对精度,而不能提高绝对精度,不过对于某些应用好像是已经够了。 上面的步骤只能得到某些点上的轨道纠正信息,要得到每一个点上的轨道纠正信息需要进行一个拟合: To eliminate the residual orbital contribution in an interferogram, we count the residual fringes on the interferogram and attribute them to an error in the slave orbit (Plate 1). This approximation is acceptable because the phenomenon depends mainly on the relative, rather than absolute, positions of the orbits. We seek two corrections to the slave orbit, a vertical and a lateral deviation, both of which change linearly with time along track as a * bt and c * dt. To determine the four coefficients a, b, c, and d, we choose four points as far apart as possible in the final image, typically at the corners. We then count the residual fringes between them. The four coefficients are the solution of a linear system of four equations involving the positions of the four points and the number of cycles at each of them. The orbit can then be corrected for any epoch in time, and the interferogram can be adequately corrected everywhere. Usually, we apply the correction to the final product, because the error committed on the slave orbit is too small to alter the previous processing steps. If necessary, we could completely reiterate the processing with the corrected slave orbit, but a single correction is sufficient in practice. 这是一种方法 这种方法必须要估计DEM辅助数据的精度吧。 其他的方法: In a slightly different approach, Murakami et al. [1996] use GPS measurements of surface displacement at seven bench marks within about 15 km of the Northridge earthquake epicenter to adjust the orbital parameters. They obtain residual differences (GPS minus JERS-1 radar) of less than 3 cm in range, smaller than the 3.5-cm uncertainty of the GPS measurements. More widely separated control points (e.g., the four corners of the 100 by 100 km image) provide a better estimate of the orbital separation, which varies mostly over long wavelengths [Massonnet et al., 1996a].