Scala语言进阶(二):单词计数WordCount案例 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 句子制作 › Scala语言进阶(二):单词计数WordCount案例 |
Scala语言进阶(二):单词计数WordCount案例
|
目录
wordCount基本版
需求分析
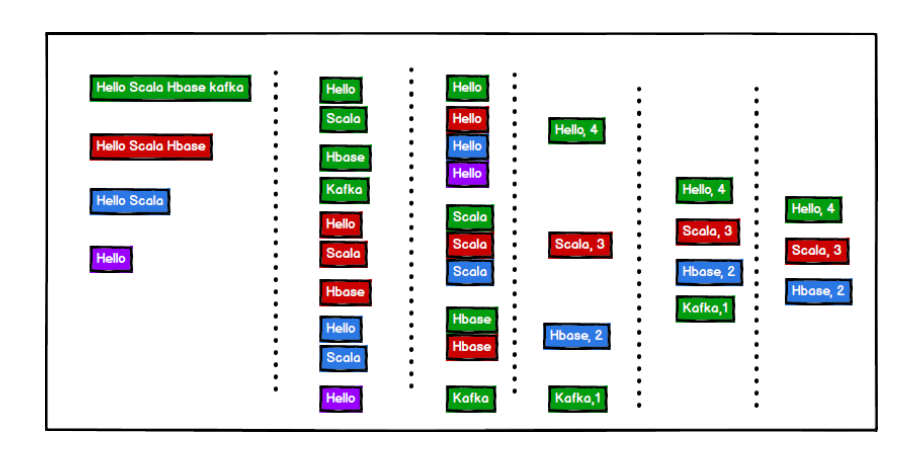
思路解析
代码编写
复杂版WordCount
方法 1
方法 2
1.wordCount基本版
1.1 需求分析
需求:从一个集合中计算出每个单词的个数,并输出前三的单词 集合中的形式: val stringList: List[String] = List( "hello world", "beautiful city", "I a chinese", "you is a good man", "I is a kind woman", "thanks for you", "forgive you", "hello world,I am student in a beautiful city", "whatever I will keep happy" ) 1.2思路解析
1. 先对每一行以空格切割,获得每一个单词,此时返回的是一个字符串数组。 2. 将每个字符串数组扁平化处理 3. 对单词进行分组操作 4.统计 1.3代码编写 // 简单版本:单词计数:将集合中出现的相同的单词统计其个数 val stringList: List[String] = List( "hello world", "beautiful city", "I a chinese", "you is a good man", "I is a kind woman", "thanks for you", "forgive you", "hello world,I am student in a beautiful city", "whatever I will keep happy" ) // 1. 将单词按空格切割 val stringSplit: List[Array[String]] = stringList.map((strings) => { strings.split(" ") }) println(stringSplit) // 2. 扁平化 val stringListFlatten: List[String] = stringSplit.flatten println(stringListFlatten) // 3.将相同的单词放在一起 groupby val stringGroupBy: Map[String, List[String]] = stringListFlatten.groupBy((word) => word) println(stringGroupBy) // 4.统计相同元素的个数,并返回map val stringCountList: Map[String, Int] = stringGroupBy.map((kv) => (kv._1, kv._2.size)) // 5.排序 取出前三个 val toList = stringCountList.toList val resultList = toList.sortWith((x, y) => { x._2 > y._2 }).take(3) println(resultList) 2. 复杂版WordCount与简单版本不一样的是复杂版本中,它的集合格式如下:数字代表该字符串重复的次数,这里提供两种解法。 val tupleList: List[(String, Int)] = List((("Hello Scala Spark World"), 7), (("Hello Scala"), 3), (("Hello china"), 5) 2.1 方法 1它先把集合中的字符串转成如下格式(简单版中的格式),其他的步骤与简单版一致: val tupleList: List[String] = List("hello world", "beautiful city") // 方法一:(不通用) val tupleList: List[(String, Int)] = List((("Hello Scala Spark World"), 7), (("Hello Scala"), 3), (("Hello china"), 5)) tupleList.map((elem) => (elem._1 + " ") * elem._2) .flatMap(_.split(" ")) .groupBy(word => word) .map((kv) => (kv._1, kv._2.length)) .toList.sortWith(_._2 > _._2) .take(3) .foreach(println) 2.2 方法 2这种方法就是先计算每个元组中单词的个数,再进行累加即可 // 方法二:先计算每个元组中单词的个数,再把相同的key的value累加起来 // ("Hello Scala Spark World"), 7) // ("Hello",7) ("Scala",7) ("Spark",7) ("World", 7) val tupleList: List[(String, Int)] = List((("Hello Scala Spark World"), 7), (("Hello Scala"), 3), (("Hello china"), 5)) val wordToCountList: List[(String, Int)] = tupleList.flatMap(t => { val strings: Array[String] = t._1.split(" ") strings.map(word => (word, t._2)) }) println(wordToCountList) // 分组 val wordGroupBy: Map[String, List[(String, Int)]] = wordToCountList.groupBy(_._1) println(wordGroupBy) // 把数字合并成列表 类似于(“hello” => List(7,7,7)) val wordToCountMap = wordGroupBy.map(t => { (t._1, t._2.map(t1 => t1._2)) }) val wordToTotalCountMap:Map[String, Int] = wordToCountMap.map(t => (t._1,t._2.sum)) println(wordToTotalCountMap) wordToTotalCountMap .toList .sortWith(_._2 > _._2) .take(3) .foreach(println) |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |