前端实战:React 多页签缓存处理 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 前端页面缓存 › 前端实战:React 多页签缓存处理 |
前端实战:React 多页签缓存处理
|
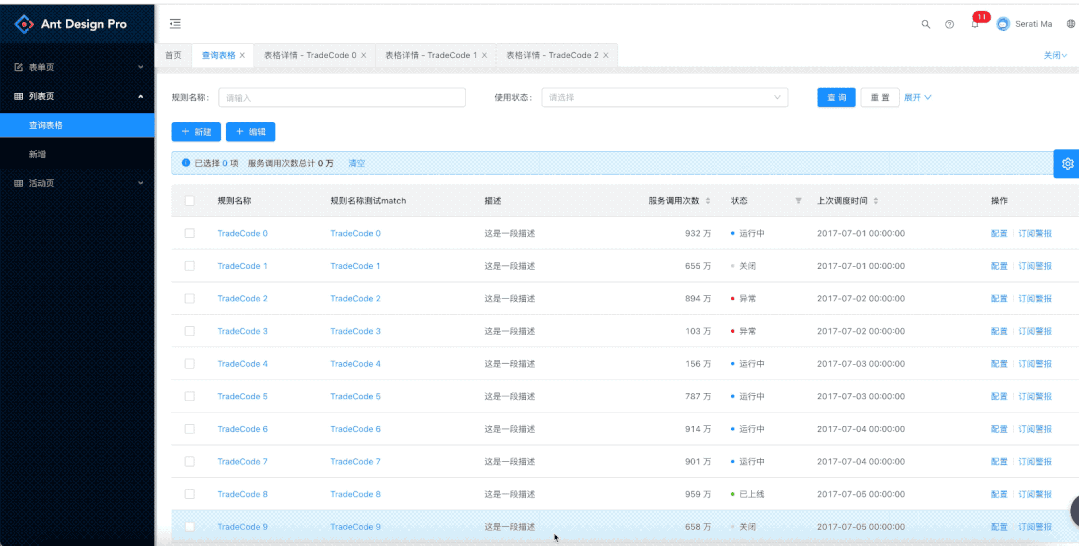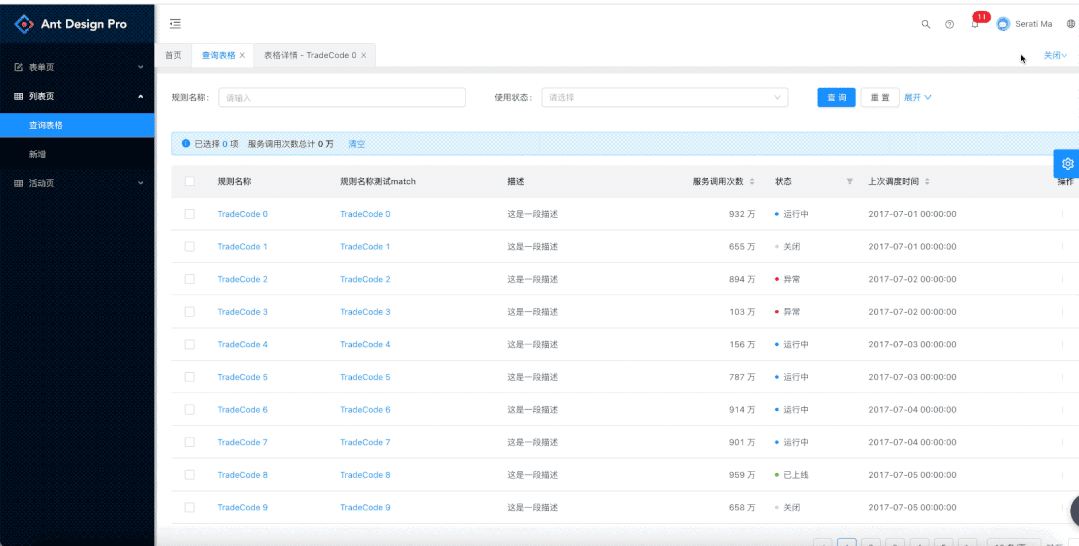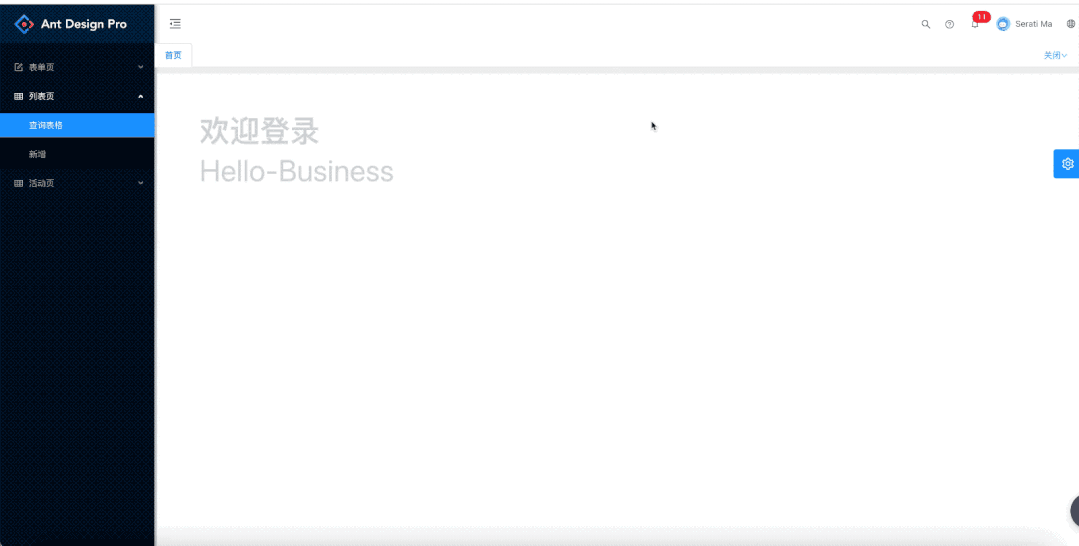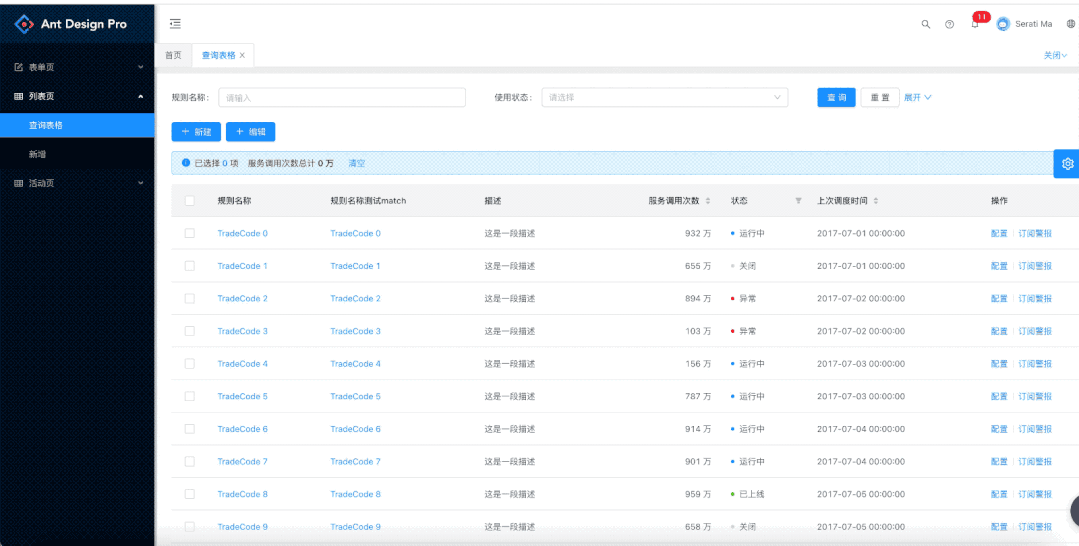
关注并将「趣谈前端」设为星标 每天定时分享技术干货/优秀开源/技术思维 1. 背景ant design pro v2的项目需要多页签显示页面而且还需要页面能够缓存下来。 多页面展示 不同数据会对应不同的详情页面 代码里面的路由跳转可以正常进行页面切换 页签可以关闭
这里主要是考虑多页面+缓存问题。 这里是借用了ant tabs标签的缓存作用。tabs的多页面只是显示和隐藏,组件本身还存在。 路由这一块,其实路由目前的基本使用页面只是会渲染当前匹配成功的路由节点。 这里钻了一个空子。Route在没有标注path的情况下会作为没有匹配路径的url进行渲染,作为没有匹配任何路由的情况下渲染节点。 因为我们通过路由path去匹配是不行,只有使用不带path的情况下渲染节点,而且不能使用switch。 而且不使用path的情况下,路由对应渲染的组件则不能依赖于react-router的机制来自动匹配,页面的渲染就需要我们进行手动处理。因为打开多少个页面就会有多少个no path的Route的节点。 3. 讲解回到具体的实现:BasicLayout.js 3.1 原先的版本 const layout = ( {isTop && !isMobile ? null : ( )} { ...this.getLayoutStyle(), minHeight: '100vh', }} > { background: '#fff' }} tabPosition="top" tabBarGutter={-1} onEdit={this.onEdit} hideAdd > {listenRouterState.map(item => ( ))}这里使用的是tab + 路由 with no path的方式。现在我们需要将组件和path进行关联起来。因为没有使用路由匹配了。代码里的listenRouterState就是我们打开页面的key和对应组件的mapping关系。这里path的处理我使用的是路由监控,因为是对于整个系统的页面多页签,所以我使用了路由监控。 3.2.2 componentDidMount路由监控 UN_LISTTEN = history.listen(route => { const { listenRouterState, listenRouterKey, customerMatchs } = this.state; let replaceRouter = routerArray.filter(itemRoute => pathToRegexp(itemRoute.key || '').test(route.pathname), )[0]; let currentKey = ''; if (replaceRouter && replaceRouter.isOnlyOnePage) { currentKey = route.pathname; } else { currentKey = route.pathname + this.parseQueryString(route.search); } if (!listenRouterKey.includes(currentKey)) { if (!replaceRouter) { replaceRouter = routerArray.filter(itemroute => itemroute.key === '/404')?.[0]; this.setState({ listenRouterState: [ ...listenRouterState, { ...replaceRouter, key: currentKey, tab: '404' }, ], activeKey: currentKey, listenRouterKey: [...listenRouterKey, currentKey], }); } else { const match = matchPath(route.pathname, { path: replaceRouter.key }); this.setState({ listenRouterState: [ ...listenRouterState, { ...replaceRouter, key: currentKey, tab: this.getPageTitle(route.pathname, breadcrumbNameMap) + this.getDetailPagePrimaryId(route, match), }, ], activeKey: currentKey, listenRouterKey: [...listenRouterKey, currentKey], customerMatchs: [...customerMatchs, { key: currentKey, match }], }); } } this.setState({ activeKey: currentKey, }); }); } 3.2.2.1 主要介绍这里主要是在做什么,监控路由然后进行路由匹配,获取对应的组件。先介绍一下这里面用到的一些state变量 listenRouterState:打开页面数据对象,也是在layout渲染的数组,存储了pathname和component的mapping关系 activeKey:当前打开的页面key listenRouterKey:listenRouterState对象key属性的数组集合,用于一些数据判断。 customerMatchs:适配match,这里可以先不管,因为这个是服务于下面实际问题的。 这里的主要逻辑就是,监控路由,判断路由是否已经打开,如果已经打开就不会重新打开。这里的key是全路径,是加上查询参数的。如下面的这个地址:
但是匹配组件内容不能使用这个进行匹配的,还是需要使用pathname进行匹配的。还是先看一下具体路由监控的到的route数据是什么?
针对路由的匹配,因为有match参数的存在,所以这里我用的是pathToRegexp,可以很好的解决这个问题。 3.2.2.4 listenRouterState的逻辑判断 if (!listenRouterKey.includes(currentKey)) { if (!replaceRouter) { replaceRouter = routerArray.filter(itemroute => itemroute.key === '/404')?.[0]; this.setState({ listenRouterState: [ ...listenRouterState, { ...replaceRouter, key: currentKey, tab: '404' }, ], activeKey: currentKey, listenRouterKey: [...listenRouterKey, currentKey], }); } else { const match = matchPath(route.pathname, { path: replaceRouter.key }); this.setState({ listenRouterState: [ ...listenRouterState, { ...replaceRouter, key: currentKey, tab: this.getPageTitle(route.pathname, breadcrumbNameMap) + this.getDetailPagePrimaryId(route, match), }, ], activeKey: currentKey, listenRouterKey: [...listenRouterKey, currentKey], customerMatchs: [...customerMatchs, { key: currentKey, match }], }); } } this.setState({ activeKey: currentKey, });这里做的就是对当前的key进行判断,如果不存在,那就是页面没有打开,则添加新的数据进行,如果已经打开,则跳转到新的页面,如果匹配路径获取组件没有成功,则跳转到404。 3.2.2.5 不同详情页面的title如何处理因为详情页有多个,但是tab的标签页title要不同  tab: this.getPageTitle(route.pathname, breadcrumbNameMap)
+ this.getDetailPagePrimaryId(route, match),
tab: this.getPageTitle(route.pathname, breadcrumbNameMap)
+ this.getDetailPagePrimaryId(route, match),
getPageTitle主要用的还是之前的逻辑,主要说明一下getDetailPagePrimaryId getDetailPagePrimaryId = (route, match) => { const detailPageIdEnum = ['id', 'title', 'activityNo']; let titleValue = ''; // 处理query类型 Object.keys(route.query).forEach(item => { if (detailPageIdEnum.includes(item) && !titleValue) { titleValue = route.query[item]; } }); // 处理match Object.keys(match.params).forEach(item => { if (detailPageIdEnum.includes(item) && !titleValue) { titleValue = match.params[item]; } }); return titleValue ? ` - ${titleValue}` : ''; };这里的逻辑主要是从query和match中间变量值,只要匹配成功,就会返回匹配的数据值。detailPageIdEnum主要是系统层级可能对应的变量名称比如query中的title
其他的就不是核心代码,基本分为两块,一块是初始化处理,另外一块是table的menu的处理 3.2.3.1 初始化处理 constructor(props) { super(props); this.getPageTitle = memoizeOne(this.getPageTitle); this.matchParamsPath = memoizeOne(this.matchParamsPath, isEqual); routerArray = this.updateTree(props.route.routes); const homeRouter = routerArray.filter(itemroute => itemroute.key === '/')[0]; this.state = { listenRouterState: [{ ...homeRouter, key: '/', tab: '首页', closable: false }], listenRouterKey: ['/'], activeKey: '/', customerMatchs: [], }; }主要就是会将routers的数据做一个基础处理,第二个就是添加一个首页在tab标签页面。 3.2.3.2 tab menu的处理主要处理,关闭打开的页签,关闭当前页面,关闭全部页面,关闭其他页面
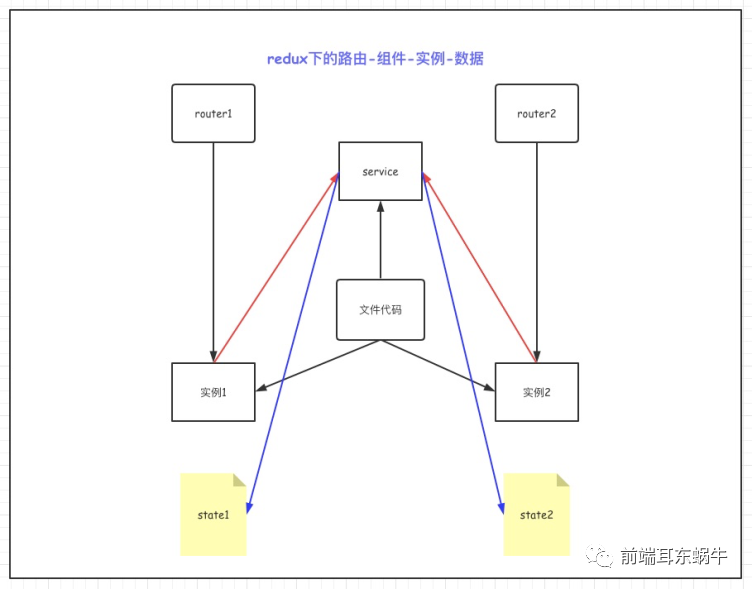
这一块比较简单,就不介绍了。 onClickHover = e => { // message.info(`Click on item ${key}`); const { key } = e; const { activeKey, listenRouterState, listenRouterKey, routeKey } = this.state; if (key === '1') { this.setState({ activeKey: routeKey, listenRouterState: listenRouterState.filter( v => v.key !== activeKey || v.key === routeKey || !v.closable, ), listenRouterKey: listenRouterKey.filter( v => v !== activeKey || v === routeKey || !v.closable, ), }); } else if (key === '2') { this.setState({ activeKey, listenRouterState: listenRouterState.filter( v => v.key === activeKey || v.key === routeKey || !v.closable, ), listenRouterKey: listenRouterKey.filter( v => v === activeKey || v === routeKey || v === '/', ), customerMatchs: listenRouterState.filter( v => v.key === activeKey || v.key === routeKey || !v.closable, ), }); } else if (key === '3') { this.setState({ activeKey: '/', listenRouterState: listenRouterState.filter(v => v.key === routeKey || !v.closable), listenRouterKey: listenRouterKey.filter(v => v === routeKey || v === '/'), customerMatchs: listenRouterState.filter(v => v.key === routeKey || !v.closable), }); } }; onEdit = (targetKey, action) => { this[action](targetKey); }; remove = targetKey => { const { activeKey, listenRouterState } = this.state; let newActiviKey = activeKey; let lastIndex; listenRouterState.forEach((pane, i) => { if (pane.key === targetKey) { lastIndex = i - 1; } }); const tabList = []; const tabListKey = []; listenRouterState.forEach(pane => { if (pane.key !== targetKey) { tabList.push(pane); tabListKey.push(pane.key); } }); if (lastIndex >= 0 && activeKey === targetKey) { newActiviKey = tabList[lastIndex].key; } router.push(newActiviKey); this.setState({ listenRouterState: tabList, activeKey: newActiviKey, listenRouterKey: tabListKey, }); }; 4. redux应用 4.1 问题redux在多页签的页面里会存在问题,比如以下两种情况: 详情页面:因为详情页面可以打开多个,但是都是公用同一个redux。 多列表页面共用同一个model 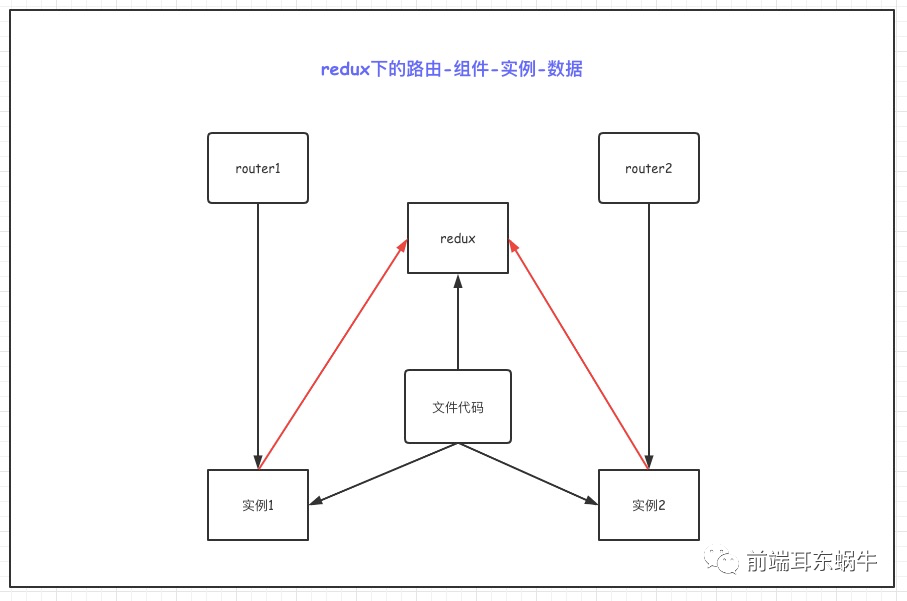
 4.2 解决思路
4.2 解决思路
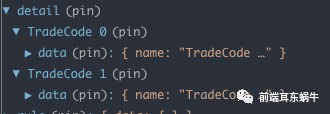
动态路由,手动注册model实现,但是在ant design pro内部不是很好实现。提了一个官方issue问题:ant design pro多页签缓存问题 不使用redux,大部分页面是不需要使用redux。只通过页面调用接口请求,数据存储都放在组件state中去。 使用redux,同一个model通过关键key进行数据区分 4.3 公用同一个model的具体操作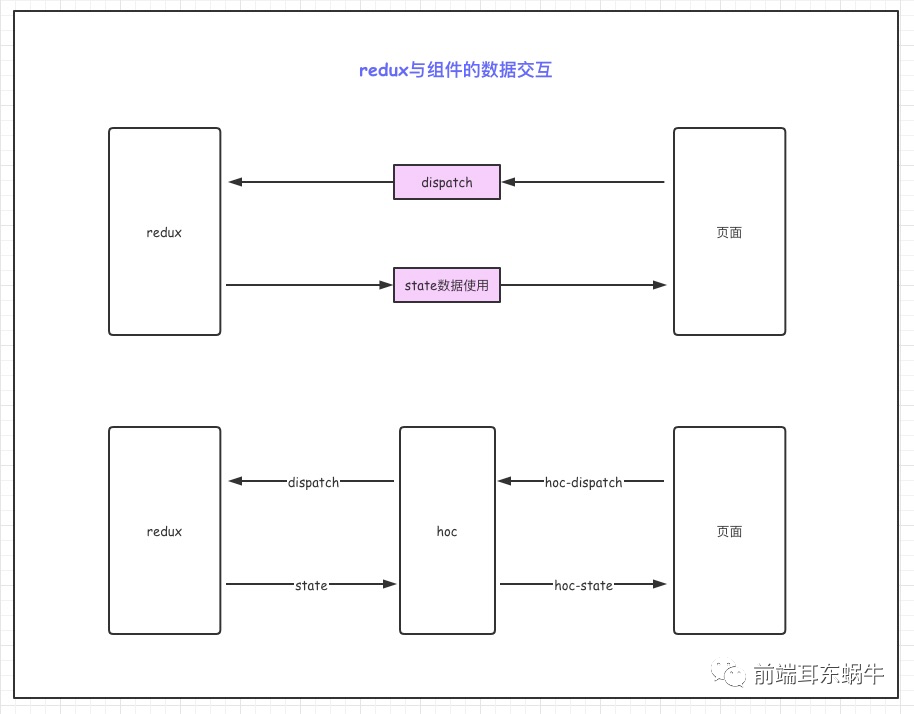
 4.3.1 hoc
4.3.1 hoc
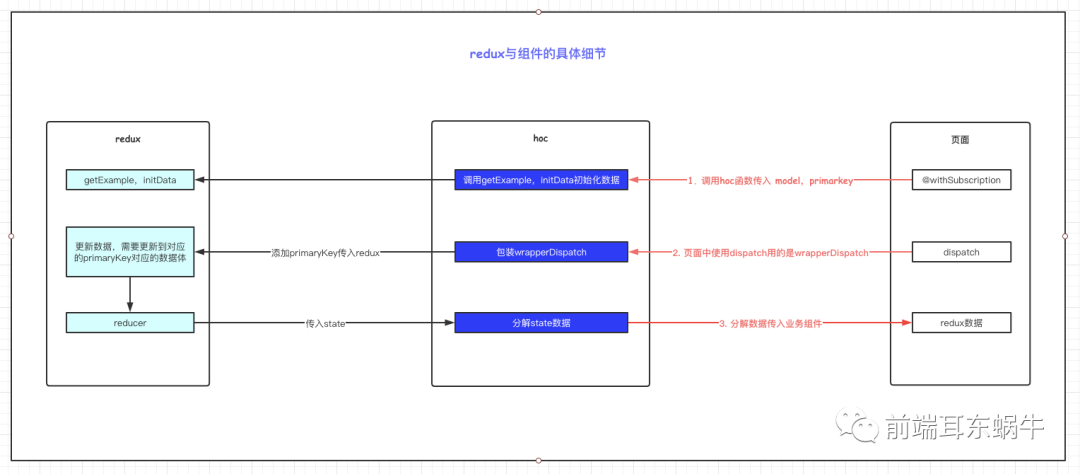
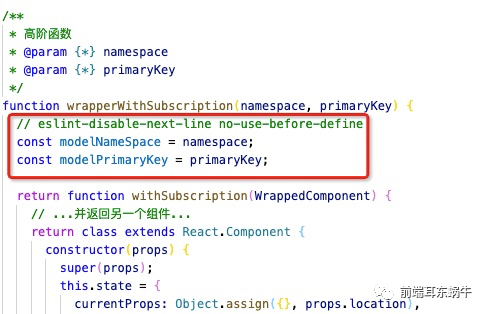
为什么使用hoc,这里是为了不影响业务页面做修改,将修改的地方放在hoc统一处理掉。这里主要是两个问题: dispatch需要将当前primaryKey传到redux,因为对应的数据更新需要放到对应的primarykey对应的state里面去。 业务组件使用state数据的时候,需要将当前primaryKey对应的数据传入到props里面 /** * 高阶函数 * @param {*} namespace * @param {*} primaryKey */ function wrapperWithSubscription(namespace, primaryKey) { // eslint-disable-next-line no-use-before-define const modelNameSpace = namespace; const modelPrimaryKey = primaryKey; return function withSubscription(WrappedComponent) { // ...并返回另一个组件... return class extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { currentProps: Object.assign({}, props.location), initData: {}, }; } componentWillMount() { const { dispatch, location } = this.props; dispatch({ type: `${modelNameSpace}/initData`, payload: { primaryKey: location.query[modelPrimaryKey], }, }); dispatch({ type: `${modelNameSpace}/getExample`, payload: {}, callback: result => { this.setState({ initData: result, }); }, }); } componentWillUnmount() { // 可以自定扩展如何消除当前primarykey对应的数据 // 一般情况下,前端业务组件会自己清除state的数据 } wrapperDispatch = (dispatchPrams) => { const { dispatch, } = this.props; const { currentProps: { query } } = this.state; dispatch({ ...dispatchPrams, primaryKey: query[modelPrimaryKey], }); }; render() { const { initData, currentProps: { query }, } = this.state; const modelNameSpaceProps = { // eslint-disable-next-line react/destructuring-assignment [modelNameSpace]: this.props[modelNameSpace][query[modelPrimaryKey]] || initData, }; return ( ); } }; }; } 4.3.1.1 wrapperDispatch其实页面组件的dispatch会走当前的页面,这里会统一将primaryKey传入进去 wrapperDispatch = (dispatchPrams) => { const { dispatch, } = this.props; const { currentProps: { query } } = this.state; dispatch({ ...dispatchPrams, primaryKey: query[modelPrimaryKey], }); }; 4.3.1.2 renderrender函数会处理redux的state,将对应当前页面的数据传回,页面组件还按照之前直接访问,下面的detail就是当前页面对应的model的namespace名称 const { history, location, detail } = this.props; render() { const { initData, currentProps: { query }, } = this.state; const modelNameSpaceProps = { // eslint-disable-next-line react/destructuring-assignment [modelNameSpace]: this.props[modelNameSpace][query[modelPrimaryKey]] || initData, }; return ( ); } 4.3.2 model文件会做哪些改变呢? 4.3.2.1 初始state的不同 const initDataExample = { data: { name: '', }, }; export default { namespace: 'detail', state: {}, ***** }现在我们的state里面初始是没有值,因为state的一级属性值使我们页面对应的primaryKey。我们会定义一个基础结构,initDataExample。用于在组件初始化的时候使用这个初始值添加到state对应的primaryKey。 4.3.2.2 新增两个服务于hoc方法effects *getExample({ callback }) { if (callback) callback({ ...initDataExample }); }, *initData({ payload }, { put }) { yield put({ type: 'init', payload: { [payload.primaryKey]: { ...initDataExample, }, }, }); },getExample:获取初始数据结构initData:初始化数据结构getExample呢,是因为hoc内部初始化函数的时候,state是异步的,不会直接在页面render的时候直接初始成功,所以这里的getExample是为了在state还没有更新的情况下,使用初始函数去拿到值,传递给组件。hoc componentWillMount() { const { dispatch, location } = this.props; dispatch({ type: `${modelNameSpace}/initData`, payload: { primaryKey: location.query.title, }, }); dispatch({ type: `${modelNameSpace}/getExample`, payload: {}, callback: result => { this.setState({ initData: result, }); }, }); } ***** render() { const { initData, currentProps: { query }, } = this.state; const modelNameSpaceProps = { // eslint-disable-next-line react/destructuring-assignment [modelNameSpace]: this.props[modelNameSpace][query[modelPrimaryKey]] || initData, }; return ( ); } 4.3.2.3 更新state的不同 *fetch({ payload, primaryKey }, { put, select }) { const currentPrimaryKeyState = yield select(state => state.detail[primaryKey]); yield put({ type: 'save', payload: updateWrapperModel('data', payload, primaryKey, currentPrimaryKeyState), }); }现在更新数据,需要定位到更新到哪一个primaryKey。所以这里提供了一个函数:更新的时候传入对应的值,然后更新对应primaryKey下的具体的key / value /** * updateWrapperModel * @param {*} updateKey * @param {*} updateValue * @param {*} primaryKey * @param {*} currentPrimaryKeyState */ export function updateWrapperModel(updateKey, updateValue, primaryKey, currentPrimaryKeyState) { return { [primaryKey]: { ...currentPrimaryKeyState, [updateKey]: updateValue, }, }; } 4.4 业务组件的修改我们使用hoc就是为了尽量少的减少业务组件的改动。hoc内部是一个统一的函数处理,所以hoc是不知道具体当前业务组件对应的modelspace是什么,以及当前路由下对应的primaryKey的key是什么,因为有的页面可能是id,有的页面取得是title。所以modelNamespace和primaryKey需要传入到hoc。业务组件只需要添加下面的一行代码进行hoc的传递就可以了。 @withSubscription('detail', 'title')
 5. 实际问题
5.1 控制是否使用多页签
5. 实际问题
5.1 控制是否使用多页签
这里其实是想可以控制部分页面不需要根据key进行判断,而是根据pathname进行判断就好了。解决的代码提交是https://github.com/rodchen-king/ant-design-pro-v2/commit/86430c03d3c13f2aed1090c71fb96cf95f195853路由需要进行只会存在一个页面标示: 
路由监控的地方,判断当前路由如果是isOnlyOnePage,则采用pathname进行key标示
这里其实就是为了处理参数在pathname里面的参数 
这里主要的问题是采用目前的这种方式,match的数据是不会正常返回的 所以这里对于项目中用到的props.match都需要单独处理一下。 所以在BasicLayout里面做了单独的处理,就是上面说的customerMatch。其实是为了处理这个问题的。 5.2.1 具体实现整体的思想和redux应用里面有类似的思路。不同的是监控路由匹配的时候会处理得到当前路由的match值。 const match = matchPath(route.pathname, { path: replaceRouter.key });这里其实是处理当前url和匹配的路由pathname处理得到一个match的结果。 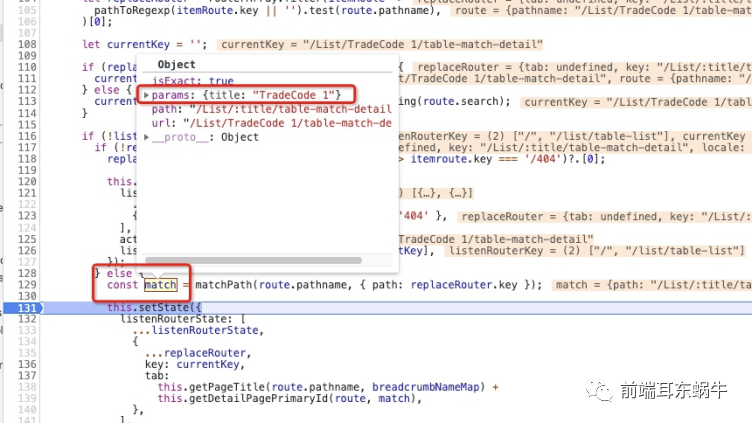
至于matchPath这个方法,其实是我从react-router源码里面复制出来的: import pathToRegexp from 'path-to-regexp'; const cache = {}; const cacheLimit = 10000; let cacheCount = 0; function compilePath(path, options) { const cacheKey = `${options.end}${options.strict}${options.sensitive}`; const pathCache = cache[cacheKey] || (cache[cacheKey] = {}); if (pathCache[path]) return pathCache[path]; const keys = []; const regexp = pathToRegexp(path, keys, options); const result = { regexp, keys }; if (cacheCount { if (!path && path !== '') return null; if (matched) return matched; const { regexp, keys } = compilePath(path, { end: exact, strict, sensitive, }); const match = regexp.exec(pathname); if (!match) return null; const [url, ...values] = match; const isExact = pathname === url; if (exact && !isExact) return null; return { path, // the path used to match url: path === '/' && url === '' ? '/' : url, // the matched portion of the URL isExact, // whether or not we matched exactly params: keys.reduce((memo, key, index) => { // eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign memo[key.name] = values[index]; return memo; }, {}), }; }, null); } export default matchPath;然后不同页面的match值会存储在customerMatchs。然后通过context进行数据传递。 HOC函数进行消费withRouterMath import React from 'react'; import { RouterContext } from '@/layouts/BasicLayout'; /** * 高阶函数: 适配match */ function withRouterMath() { // eslint-disable-next-line no-use-before-define return function withSubscription(WrappedComponent) { // ...并返回另一个组件... return class extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { currentLocation: Object.assign({}, props.location), }; } getMatch = value => { const { currentLocation: { pathname }, } = this.state; const returnValue = value.filter(item => item.key === pathname); if (returnValue.length) { return returnValue[0].match; } return {}; }; render() { return ( {_value => } ); } }; }; } export default withRouterMath;使用的时候 @withRouterMatth() @withSubscription('detail', 'title') class ListDetail extends React.PureComponent { componentDidMount() { const { match, dispatch } = this.props; dispatch({ type: 'detail/fetch', payload: { name: match.params.title, }, }); } }这样页面就可以正常使用match,和原先的location一样获取值,然后系统层级也会匹配query和match的数据进行primarykey处理。 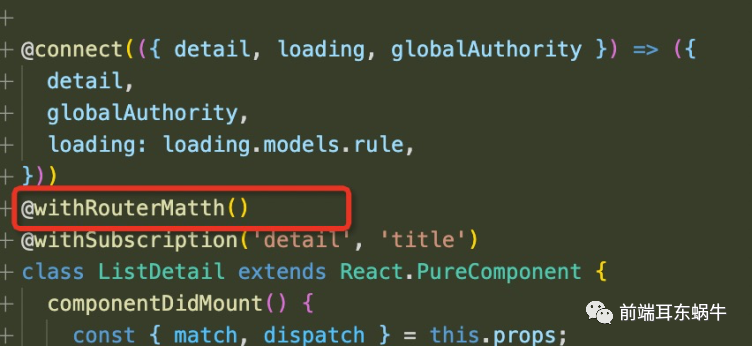 5.3 业务页面不是由单个的参数进行唯一表示,而是多个业务参数进行唯一表示
5.3 业务页面不是由单个的参数进行唯一表示,而是多个业务参数进行唯一表示
前面说的都是单个primarykey作为唯一页面标示的,但是可能部分代码存在很复杂的情况。 举个例子,存在一个业务组件既是详情页面,也是新增页面,而且业务上还存在多个。 类似营销活动:为了更好的说明,我在单独加一个字段,templateName 满减活动【templateName:满减】 activityType:1; 详情的时候会有一个activityNo 新增的时候则没有activityNo 满折活动【templateName:满折】 activityType:2: 详情的时候会有一个activityNo, 新增的时候则没有activityNo 5.3.1 具体实现https://github.com/rodchen-king/ant-design-pro-v2/commit/d0ecfd2e795cb90837b0ed94de5f4ad13012af31这里主要是支持多个参数:修改BasicLayout.js
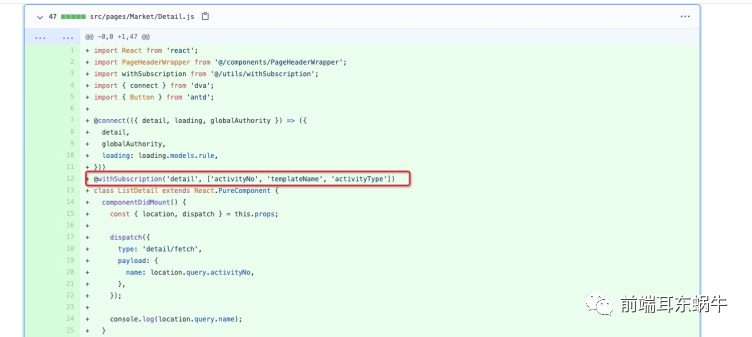 6. 优化
6.1 dispatch.then的使用
6. 优化
6.1 dispatch.then的使用
代码:https://github.com/rodchen-king/ant-design-pro-v2/commit/5f160db67aaad31cb1ac04d4d01a66a1fc6d0582开发过程中存在dispatch().then的方式:所以这里支持也要优化一下: wrapperDispatch = dispatchPrams => { const { dispatch } = this.props; const { primaryKeyValue } = this.state; dispatch({ ...dispatchPrams, primaryKey: primaryKeyValue, }); }; 6.2 redux-state更新多个参数代码:https://github.com/rodchen-king/ant-design-pro-v2/commit/5f160db67aaad31cb1ac04d4d01a66a1fc6d0582 /** * model相关的处理函数 */ /** * updateWrapperModel * @param {*} updateStateObject 要更新state的健值对 * @param {*} primaryKey 当前页面对应的primaryKey * @param {*} currentPrimaryKeyState primaryKey对应的数据源 */ export function updateWrapperModel(updateStateObject, primaryKey, currentPrimaryKeyState) { return { [primaryKey]: { ...currentPrimaryKeyState, ...updateStateObject, }, }; } 7. Ant design pro v5 如何做?https://procomponents.ant.design/components/layout 因为最新的v5 菜单已经采用ProLayout作为布局。所以这里一种方式是利用配置项目的childRender 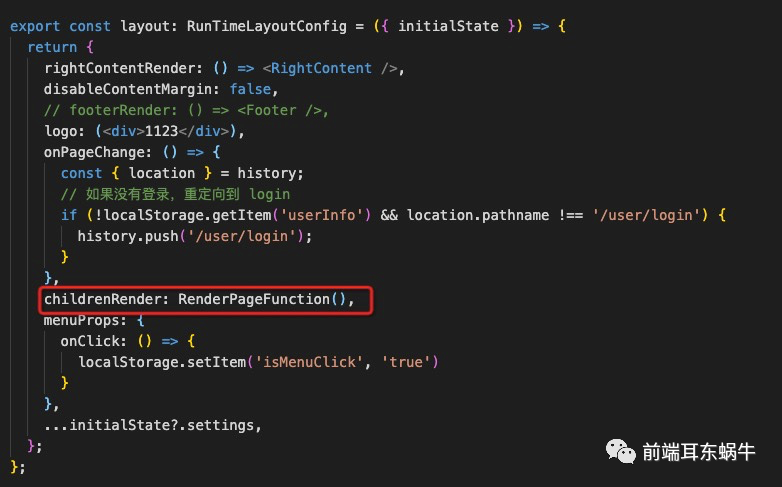
另一种方式则是注释这里的代码,然后重新写以前版本的BasicLayout.js 好了,今天的分享就到这里了,如果文章对你有帮助,你也可以点赞 + 转发, 鼓励作者持续创作。
从零搭建全栈可视化大屏制作平台V6.Dooring 从零设计可视化大屏搭建引擎 Dooring可视化搭建平台数据源设计剖析 可视化搭建的一些思考和实践 基于Koa + React + TS从零开发全栈文档编辑器(进阶实战 创作不易,加个点赞、在看 支持一下哦! |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |
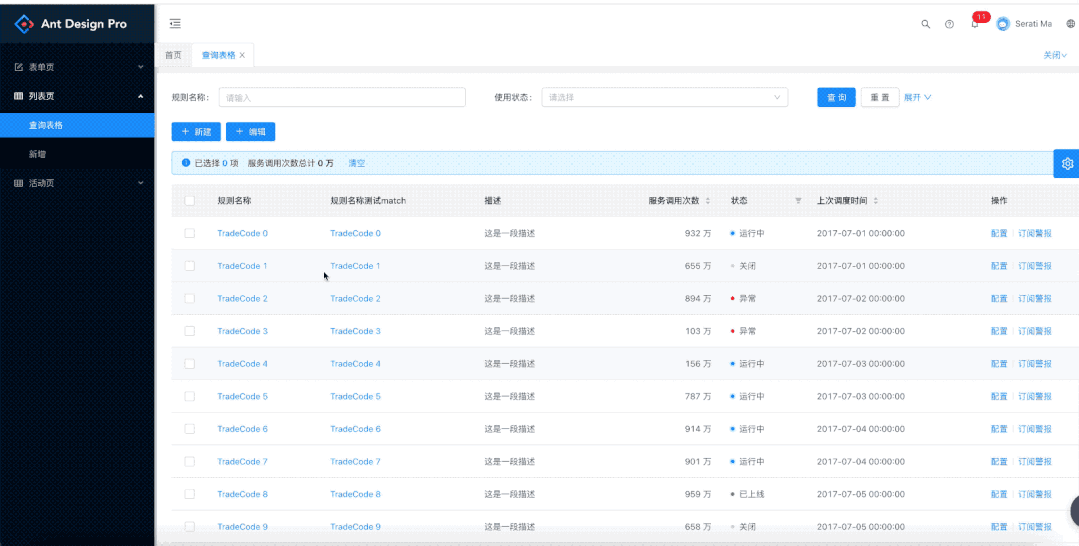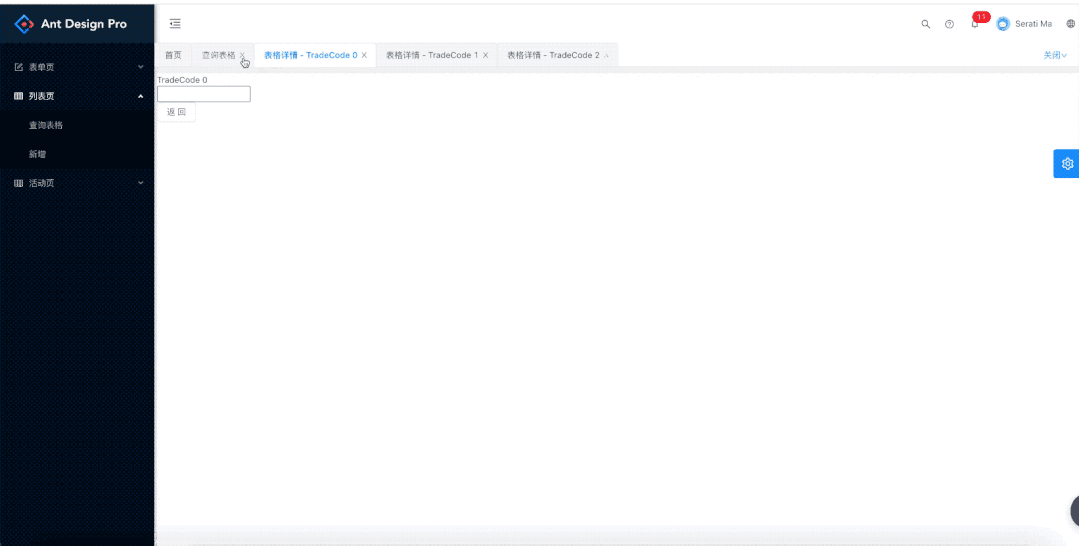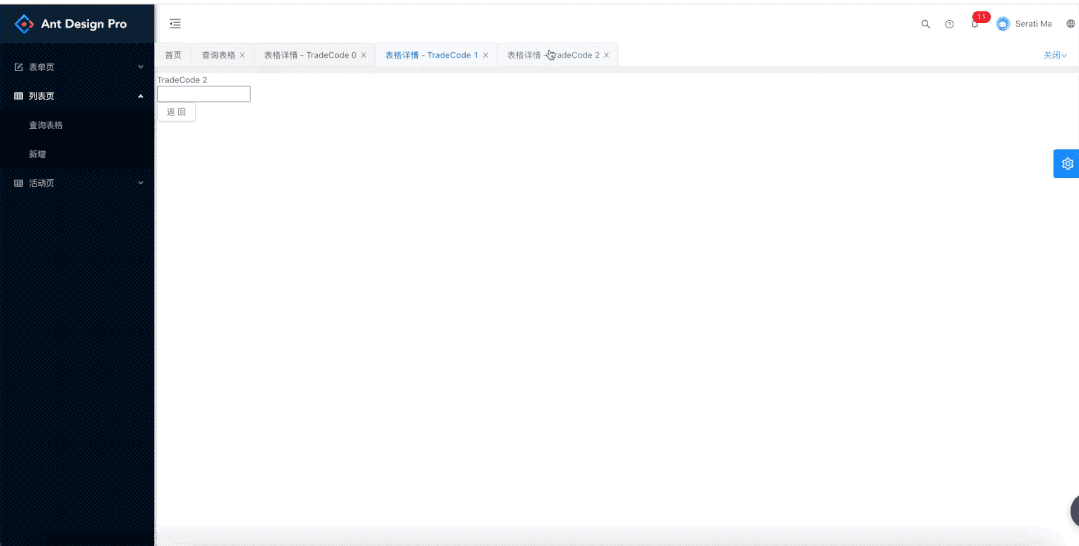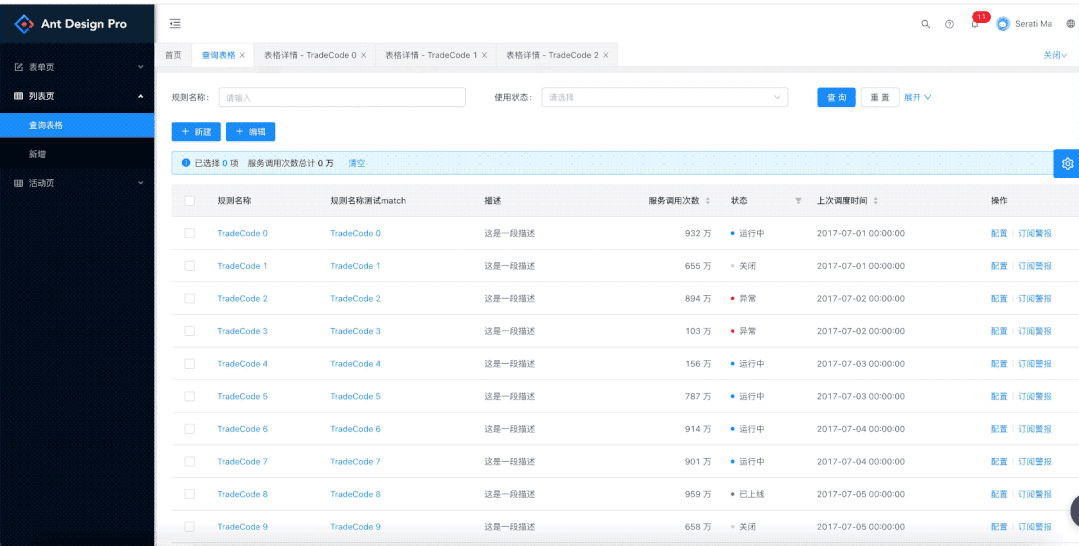
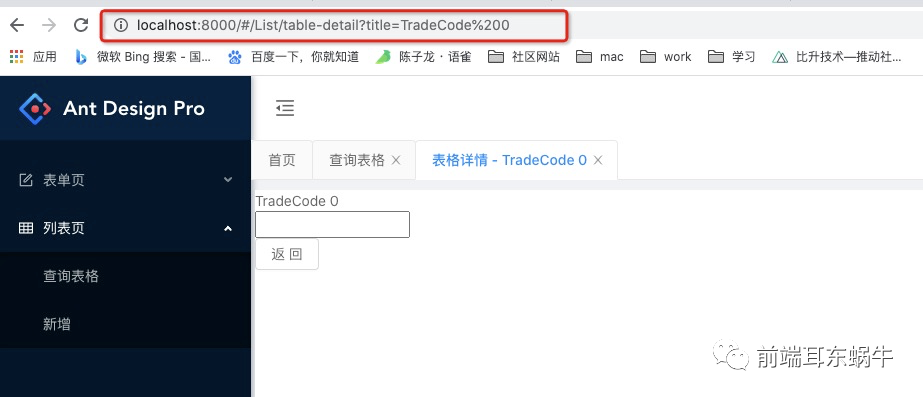
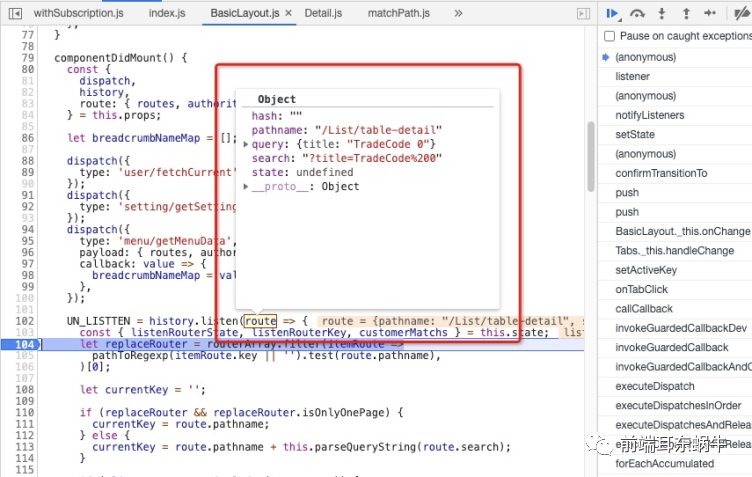 所以我们上面说的key:是pathname + query。这里要分清key和pathname的区别,因为pathname是用来匹配获取组件的,key是为了进行多个详情页面的区分,如果不是全路径是没有办法区分不同详情页面的。当然我们这个pathname是比较好匹配的,假如是下面的这种,下面的路由对应的是:
所以我们上面说的key:是pathname + query。这里要分清key和pathname的区别,因为pathname是用来匹配获取组件的,key是为了进行多个详情页面的区分,如果不是全路径是没有办法区分不同详情页面的。当然我们这个pathname是比较好匹配的,假如是下面的这种,下面的路由对应的是: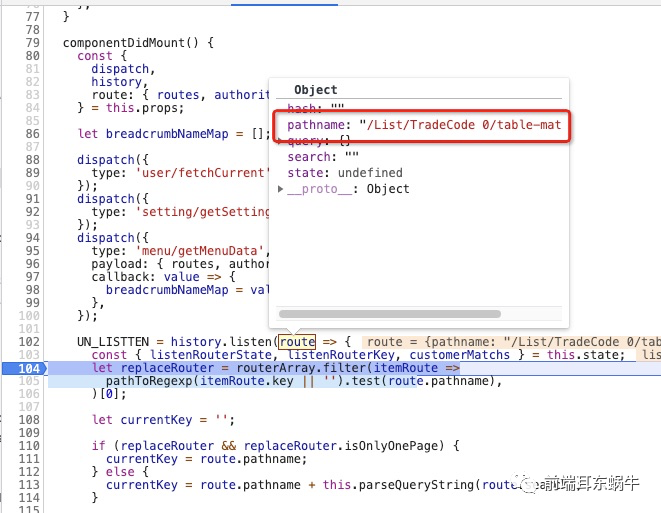
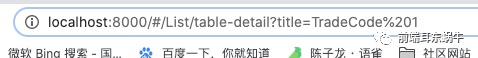 或者match中title 【当然这里的match是有问题的,在下面实际问题的时候会说明一下】
或者match中title 【当然这里的match是有问题的,在下面实际问题的时候会说明一下】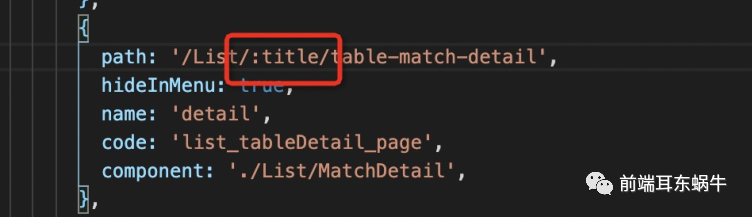
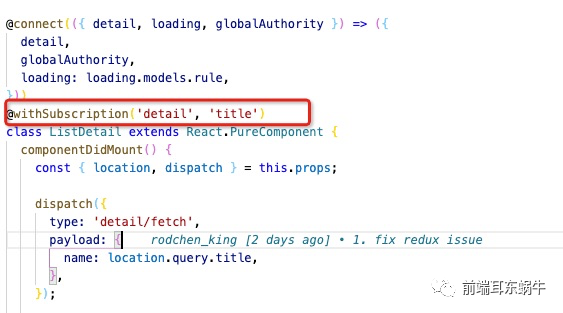 高阶函数会接受这两个值使用
高阶函数会接受这两个值使用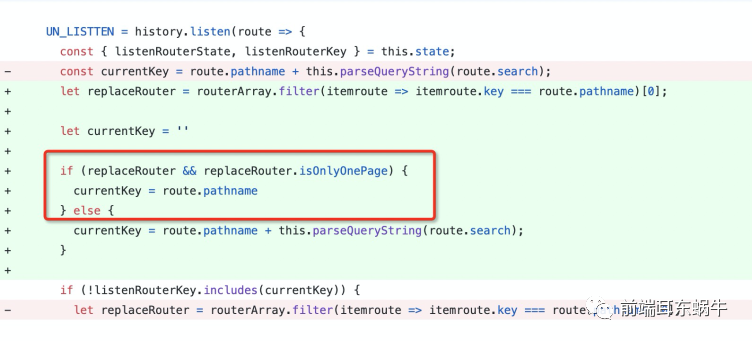
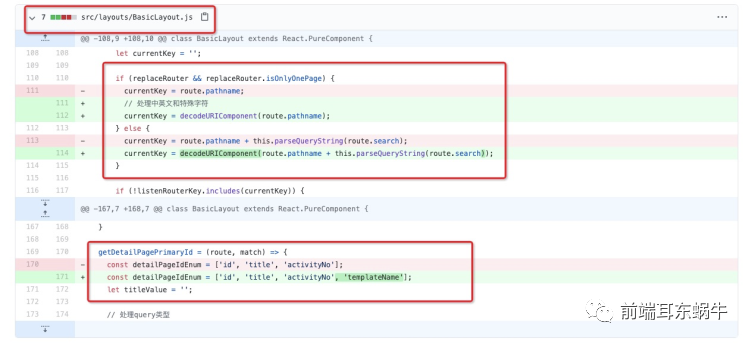 因为可能参数当中涉及到中文,所以判断key的逻辑用了decodeURIComponent方法解析。第二个在getDetailPagePrimaryId,这里加上这个是为了适配新的查询参数。修改wrapperWithSubscription
因为可能参数当中涉及到中文,所以判断key的逻辑用了decodeURIComponent方法解析。第二个在getDetailPagePrimaryId,这里加上这个是为了适配新的查询参数。修改wrapperWithSubscription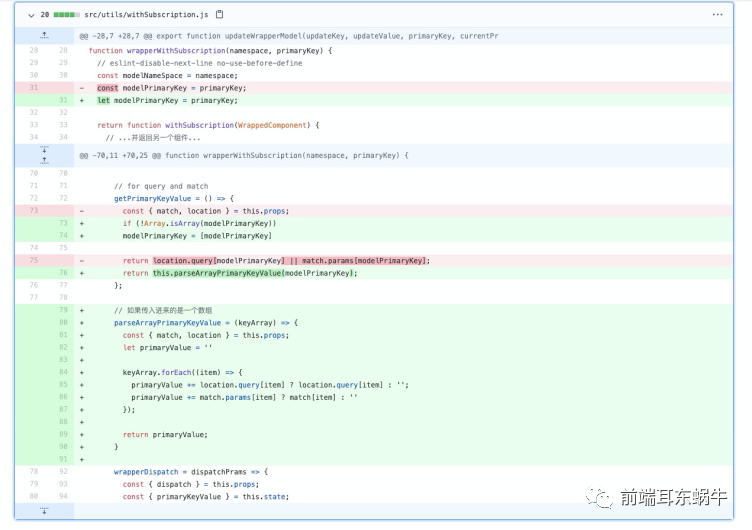 主要是兼容多个参数的情况,传进来的是一个数组。调用的方式参考新增的业务Maket组件的调用方式
主要是兼容多个参数的情况,传进来的是一个数组。调用的方式参考新增的业务Maket组件的调用方式