使用opencv和dlib进行人脸姿态估计(python) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 人脸3d模型怎么展示出来 › 使用opencv和dlib进行人脸姿态估计(python) |
使用opencv和dlib进行人脸姿态估计(python)
|
概述
在计算机视觉中,物体的姿态是指相对于相机的相对取向和位置。 本文主要参考了《Head Pose Estimation using OpenCV and Dlib》这篇文章。 进行人脸姿态估计的目的就是获取人脸相对相机的朝向: 人脸姿态估计的思想:旋转三维标准模型一定角度,直到模型上“三维特征点”的“2维投影”,与待测试图像上的特征点(图像上的特征点显然是2维)尽量重合。 从笔记本摄像头取视频,每一帧用dlib检测人脸关键点,用opencv做姿态估计。并实时显示在屏幕上。 opencv输出的是旋转向量,我参考《基于Dlib和OpenCV的人脸姿态估计(HeadPoseEstimation)》这篇文章的方法,将旋转向量转化为4元数,再转化为欧拉角(弧度)。 这篇文章的坑就是,最终转化出来的欧拉角单位是弧度,需要除以Pi乘以180得到度的单位值。原文的代码是c++,我转化为python3了。 下面的例子是我最终测试完毕没问题的代码。 #!/usr/bin/env python import cv2 import numpy as np import dlib import time import math detector = dlib.get_frontal_face_detector() predictor = dlib.shape_predictor("shape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat") POINTS_NUM_LANDMARK = 68 # 获取最大的人脸 def _largest_face(dets): if len(dets) == 1: return 0 face_areas = [ (det.right()-det.left())*(det.bottom()-det.top()) for det in dets] largest_area = face_areas[0] largest_index = 0 for index in range(1, len(dets)): if face_areas[index] > largest_area : largest_index = index largest_area = face_areas[index] print("largest_face index is {} in {} faces".format(largest_index, len(dets))) return largest_index # 从dlib的检测结果抽取姿态估计需要的点坐标 def get_image_points_from_landmark_shape(landmark_shape): if landmark_shape.num_parts != POINTS_NUM_LANDMARK: print("ERROR:landmark_shape.num_parts-{}".format(landmark_shape.num_parts)) return -1, None #2D image points. If you change the image, you need to change vector image_points = np.array([ (landmark_shape.part(30).x, landmark_shape.part(30).y), # Nose tip (landmark_shape.part(8).x, landmark_shape.part(8).y), # Chin (landmark_shape.part(36).x, landmark_shape.part(36).y), # Left eye left corner (landmark_shape.part(45).x, landmark_shape.part(45).y), # Right eye right corne (landmark_shape.part(48).x, landmark_shape.part(48).y), # Left Mouth corner (landmark_shape.part(54).x, landmark_shape.part(54).y) # Right mouth corner ], dtype="double") return 0, image_points # 用dlib检测关键点,返回姿态估计需要的几个点坐标 def get_image_points(img): #gray = cv2.cvtColor( img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY ) # 图片调整为灰色 dets = detector( img, 0 ) if 0 == len( dets ): print( "ERROR: found no face" ) return -1, None largest_index = _largest_face(dets) face_rectangle = dets[largest_index] landmark_shape = predictor(img, face_rectangle) return get_image_points_from_landmark_shape(landmark_shape) # 获取旋转向量和平移向量 def get_pose_estimation(img_size, image_points ): # 3D model points. model_points = np.array([ (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), # Nose tip (0.0, -330.0, -65.0), # Chin (-225.0, 170.0, -135.0), # Left eye left corner (225.0, 170.0, -135.0), # Right eye right corne (-150.0, -150.0, -125.0), # Left Mouth corner (150.0, -150.0, -125.0) # Right mouth corner ]) # Camera internals focal_length = img_size[1] center = (img_size[1]/2, img_size[0]/2) camera_matrix = np.array( [[focal_length, 0, center[0]], [0, focal_length, center[1]], [0, 0, 1]], dtype = "double" ) print("Camera Matrix :{}".format(camera_matrix)) dist_coeffs = np.zeros((4,1)) # Assuming no lens distortion (success, rotation_vector, translation_vector) = cv2.solvePnP(model_points, image_points, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs, flags=cv2.SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE ) print("Rotation Vector:\n {}".format(rotation_vector)) print("Translation Vector:\n {}".format(translation_vector)) return success, rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs # 从旋转向量转换为欧拉角 def get_euler_angle(rotation_vector): # calculate rotation angles theta = cv2.norm(rotation_vector, cv2.NORM_L2) # transformed to quaterniond w = math.cos(theta / 2) x = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[0][0] / theta y = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[1][0] / theta z = math.sin(theta / 2)*rotation_vector[2][0] / theta ysqr = y * y # pitch (x-axis rotation) t0 = 2.0 * (w * x + y * z) t1 = 1.0 - 2.0 * (x * x + ysqr) print('t0:{}, t1:{}'.format(t0, t1)) pitch = math.atan2(t0, t1) # yaw (y-axis rotation) t2 = 2.0 * (w * y - z * x) if t2 > 1.0: t2 = 1.0 if t2 < -1.0: t2 = -1.0 yaw = math.asin(t2) # roll (z-axis rotation) t3 = 2.0 * (w * z + x * y) t4 = 1.0 - 2.0 * (ysqr + z * z) roll = math.atan2(t3, t4) print('pitch:{}, yaw:{}, roll:{}'.format(pitch, yaw, roll)) # 单位转换:将弧度转换为度 Y = int((pitch/math.pi)*180) X = int((yaw/math.pi)*180) Z = int((roll/math.pi)*180) return 0, Y, X, Z def get_pose_estimation_in_euler_angle(landmark_shape, im_szie): try: ret, image_points = get_image_points_from_landmark_shape(landmark_shape) if ret != 0: print('get_image_points failed') return -1, None, None, None ret, rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs = get_pose_estimation(im_szie, image_points) if ret != True: print('get_pose_estimation failed') return -1, None, None, None ret, pitch, yaw, roll = get_euler_angle(rotation_vector) if ret != 0: print('get_euler_angle failed') return -1, None, None, None euler_angle_str = 'Y:{}, X:{}, Z:{}'.format(pitch, yaw, roll) print(euler_angle_str) return 0, pitch, yaw, roll except Exception as e: print('get_pose_estimation_in_euler_angle exception:{}'.format(e)) return -1, None, None, None if __name__ == '__main__': # rtsp://admin:[email protected]:554 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) while (cap.isOpened()): start_time = time.time() # Read Image ret, im = cap.read() if ret != True: print('read frame failed') continue size = im.shape if size[0] > 700: h = size[0] / 3 w = size[1] / 3 im = cv2.resize( im, (int( w ), int( h )), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC ) size = im.shape ret, image_points = get_image_points(im) if ret != 0: print('get_image_points failed') continue ret, rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs = get_pose_estimation(size, image_points) if ret != True: print('get_pose_estimation failed') continue used_time = time.time() - start_time print("used_time:{} sec".format(round(used_time, 3))) ret, pitch, yaw, roll = get_euler_angle(rotation_vector) euler_angle_str = 'Y:{}, X:{}, Z:{}'.format(pitch, yaw, roll) print(euler_angle_str) # Project a 3D point (0, 0, 1000.0) onto the image plane. # We use this to draw a line sticking out of the nose (nose_end_point2D, jacobian) = cv2.projectPoints(np.array([(0.0, 0.0, 1000.0)]), rotation_vector, translation_vector, camera_matrix, dist_coeffs) for p in image_points: cv2.circle(im, (int(p[0]), int(p[1])), 3, (0,0,255), -1) p1 = ( int(image_points[0][0]), int(image_points[0][1])) p2 = ( int(nose_end_point2D[0][0][0]), int(nose_end_point2D[0][0][1])) cv2.line(im, p1, p2, (255,0,0), 2) # Display image #cv2.putText( im, str(rotation_vector), (0, 100), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1 ) cv2.putText( im, euler_angle_str, (0, 120), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN, 1, (0, 0, 255), 1 ) cv2.imshow("Output", im) cv2.waitKey(1) 参考资料人脸姿态估计浅谈~ opencv官方文档: Pose Estimation dlib+opencv头部姿态估计的国外博客: Head Pose Estimation using OpenCV and Dlib 中文翻译: 使用OpenCV和Dlib进行人头姿态估计 将旋转向量转换为欧拉角参考了:基于Dlib和OpenCV的人脸姿态估计(HeadPoseEstimation) 这个和上面方法不一样,我没试:怎么计算脸部姿势 with cv2.solvePnP in python3 原理讲解:四元数与欧拉角之间的转换 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |

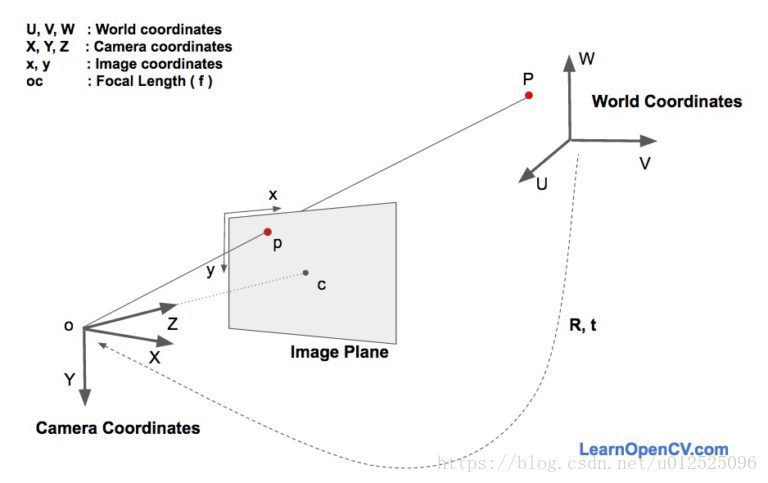
 姿态估计部分的代码参考了《Head Pose Estimation using OpenCV and Dlib》这篇文章。
姿态估计部分的代码参考了《Head Pose Estimation using OpenCV and Dlib》这篇文章。