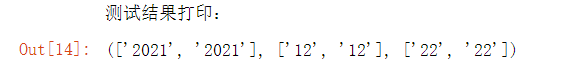python爬取中国地震网 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 中国地震台网速报一 › python爬取中国地震网 |
python爬取中国地震网
|
(一)选题背景 地震(earthquake)又称地动、地振动,是地壳快速释放能量过程中造成的振动,期间会产生地震波的一种自然现象。地球上板块与板块之间相互挤压碰撞,造成板块边沿及板块内部产生错动和破裂,是引起地震的主要原因。 地震开始发生的地点称为震源,震源正上方的地面称为震中。地震常常造成严重人员伤亡,能引起火灾、水灾、有毒气体泄漏、细菌及放射性物质扩散,还可能造成海啸、滑坡、崩塌、地裂缝等次生灾害。给人们带来灾难。 (二)主题式网络爬虫设计方案 1、爬虫名称:爬取中国地震网2013年到2021年的地震 2、爬取内容:爬取中国地震网的震级、发震时刻、维度、经度、深度、参考位置等 3、主题式网络爬虫设计方案概述:数据的爬取与清洗、数据模型分析,数据可视化处理,绘制分布图等 技术难点:数据化的分析还有可视化等不好解决
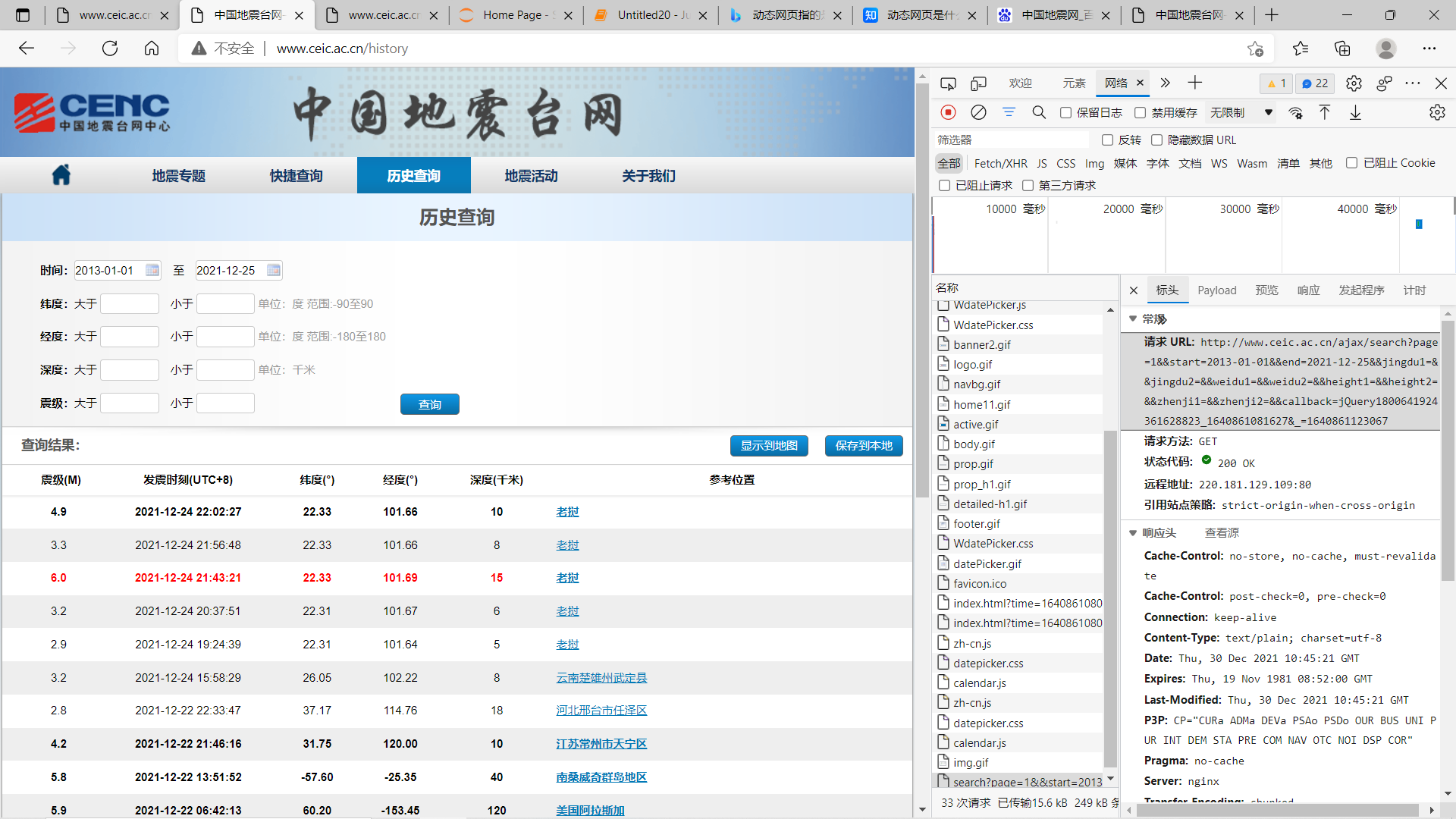
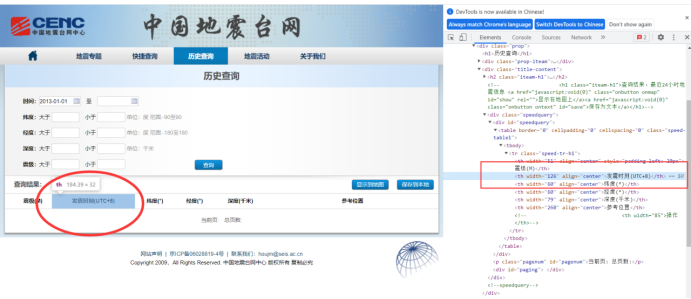
(三)、主题页面的结构特征分析 爬取网址首页地址:https://news.ceic.ac.cn 爬取的网址URL:http://www.ceic.ac.cn/ajax/search?page=1&&start=2013-01-01&&end=2021-12-25&&jingdu1=&&jingdu2=&&weidu1=&&weidu2=&&height1=&&height2=&&zhenji1=&&zhenji2=&&callback=jQuery1800641924361628823_1640861081627&_=1640861123067 1、主题页面的结构与特征分析 通过解析HTML代码,找到table标签里的tr,没一个包含一行地震数据,里的是每一条地震数据的具体信息,比如震级,日期,经度,纬度等等
2、页面解析:
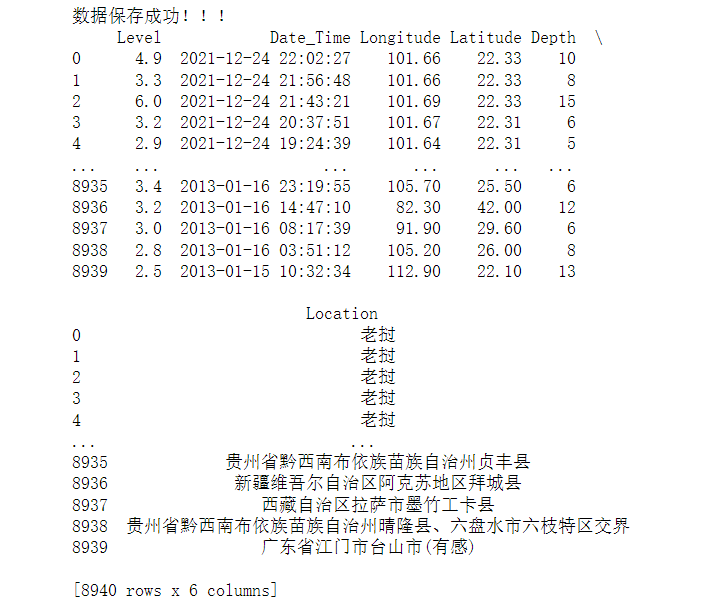
(四)、网络爬虫程序设计 1 import requests 2 import pandas as pd 3 import re 4 5 6 # 获取所有的页面url 7 def get_url(): 8 list = [] 9 for i in range(1, 448): # 448 10 url = "http://www.ceic.ac.cn/ajax/search?page={}&&start=2013-01-01&&end=2021-12-25&&jingdu1=&&jingdu2=&&weidu1=&&weidu2=&&height1=&&height2=&&zhenji1=&&zhenji2=&&".format( 11 i) 12 list.append(url) 13 return list 14 # 爬取所有url 15 def crawl_data(ls): 16 list = [] 17 for i in ls: 18 resp = requests.get(i) 19 list.append(resp.text) 20 return list 21 # 将Unicode编码转化为中文 22 def conversion(ls): 23 list = [] 24 for i in ls: 25 s = eval('u"%s"' % i) 26 list.append(s) 27 return list 28 # 程序主体 29 if __name__ == '__main__': 30 all_url = get_url() 31 resp = crawl_data(all_url) 32 # 通过正则抓取所有的数据 33 Level = re.findall('"M":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 地震等级 34 Date_Time = re.findall('"O_TIME":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 时刻 35 Longitude = re.findall('"EPI_LON":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 经度 36 Latitude = re.findall('"EPI_LAT":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 纬度 37 Depth = re.findall('"EPI_DEPTH":([0-9]+)', str(resp)) # 深度 38 Location_U = re.findall('"LOCATION_C":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 地址 39 Location = conversion(conversion(conversion(Location_U))) # 解码 40 # 将数据转化为datafram格式 41 df = pd.DataFrame( 42 {'Level': Level, 'Date_Time': Date_Time, 'Longitude': Longitude, 'Latitude': Latitude, 'Depth': Depth, 43 'Location': Location}) 44 # 将数据保存为Excel 45 writer = pd.ExcelWriter('./earthquake.xlsx') 46 df.to_excel(writer, columns=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'], index=False, 47 encoding='utf-8') 48 writer.save() 49 print("数据保存成功!!!") 50 print(df)
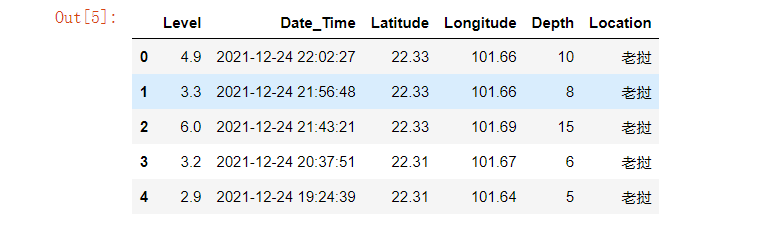
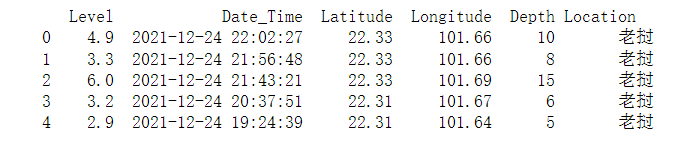
1 #读取csv文件 2 earthquake=pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel('./Desktop/earthquake.xlsx')) 3 earthquake.head()
1 #检查是否有重复值 2 earthquake.duplicated()
1 #检查是否有空值 2 print(earthquake['Depth'].isnull().value_counts())
1 df = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel('./earthquake.xlsx')) 2 print(df.head())
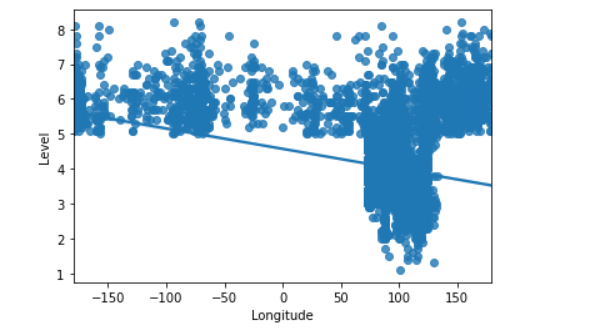
1 #绘制日期与深度回归图 2 import seaborn as sns 3 sns.regplot(earthquake.Longitude,earthquake.Level)
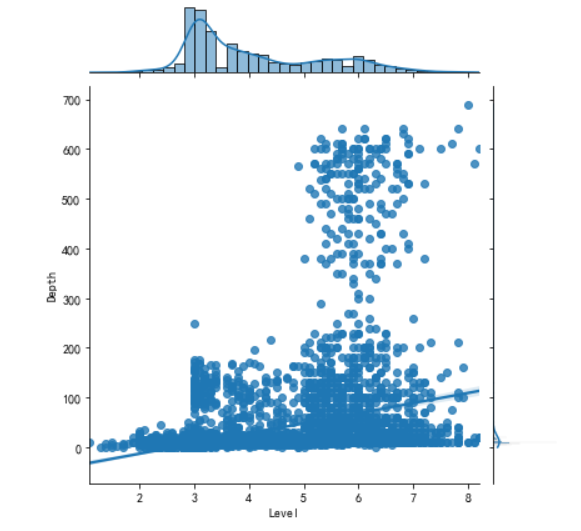
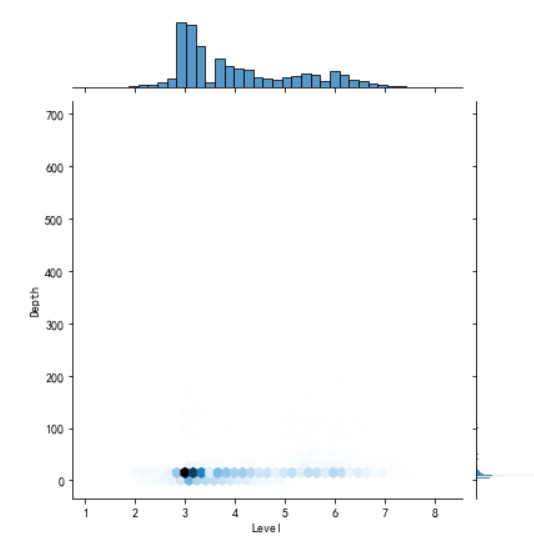
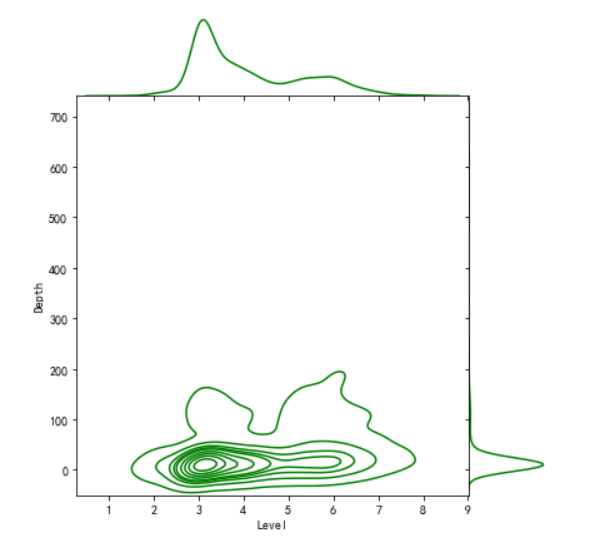
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 #画出散点图 4 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 5 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 6 N=10 7 x=np.random.rand(N) 8 y=np.random.rand(N) 9 size=50 10 plt.xlabel("Level") 11 plt.ylabel("Depth") 12 plt.scatter(x,y,size,color='r',alpha=0.5,marker="o") 13 #散点图 kind='reg' 14 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind='reg') 15 # kind='hex' 16 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind='hex') 17 # kind='kde' 18 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind="kde",space=0,color='g')
1 #选择个特征变量,绘制分布图,用最小二乘法分析两个变量间的二次拟合方程和拟合曲线 2 colnames=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'] 3 df = pd.read_excel('./earthquake.xlsx',skiprows=0,names=colnames) 4 X = df.Latitude 5 Y = df.Level 6 Z = df.Depth 7 def A(): 8 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="blue",linewidth=2) 9 plt.title("RM scatter",color="blue") 10 plt.grid() 11 plt.show() 12 A()
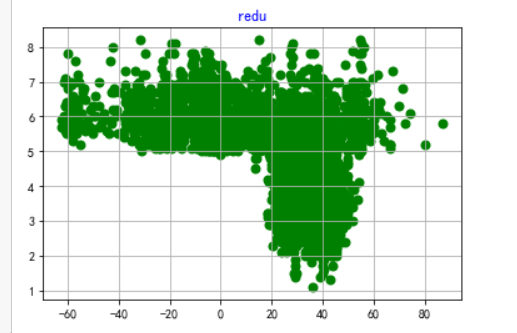
1 def B(): 2 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="green",linewidth=2) 3 plt.title("redu",color="blue") 4 plt.grid() 5 plt.show() 6 B()
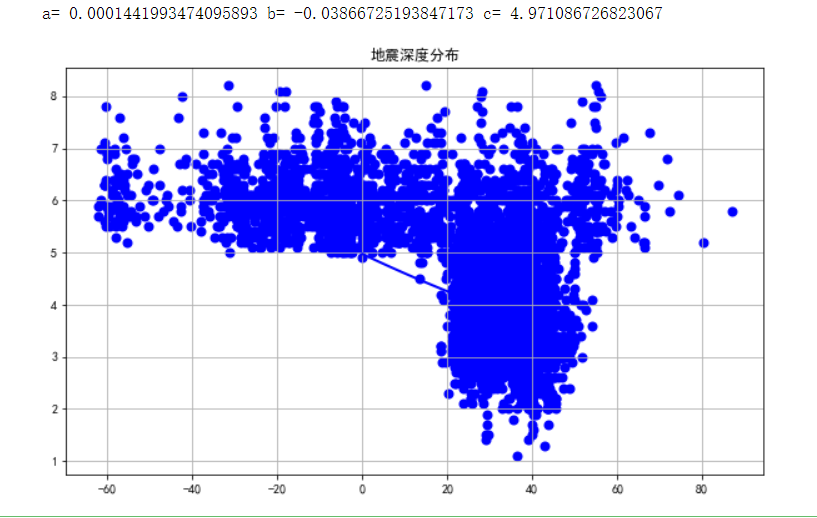
1 from scipy.optimize import leastsq 2 def func(p,x): 3 a,b,c=p 4 return a*x*x+b*x+c 5 def error(p,x,y): 6 return func(p,x)-y 7 def main(): 8 plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) 9 p0=[0,0,0] 10 Para = leastsq(error,p0,args=(X,Y)) 11 a,b,c=Para[0] 12 print("a=",a,"b=",b,"c=",c) 13 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="blue",linewidth=2) 14 x=np.linspace(0,20,20) 15 y=a*x*x+b*x+c 16 plt.plot(x,y,color="blue",linewidth=2,) 17 plt.title("地震深度分布") 18 plt.grid() 19 plt.show() 20 21 main()
1 # 用来清洗数据DateTime 2 s = ['2021-12-22 22:33:47', '2021-12-22 21:46:16'] # 用来测试函数的数据 3 def clear_datetime(date_list): 4 # 为了拆分年月日,用来存放year、month 、day的空列表 5 year = [] 6 month = [] 7 day=[] 8 for s in date_list: 9 # 通过split函数简单清洗数据 10 # 清洗年数据 11 s1 = s.split('-')[0] 12 # 清洗月数据 13 s2 = s.split('-')[1] 14 # 清洗日数据 15 ss = s.split('-')[2] 16 s3 = ss.split(' ')[0] 17 # 把数据添加到列表中 18 year.append(s1) 19 month.append(s2) 20 day.append(s3) 21 # 返回三元组,元组里的每一个元素是对应年月日的列表 22 return year,month,day 23 24 s = clear_datetime(s) # 用于测试结果 25 print('测试结果打印:') 26 s
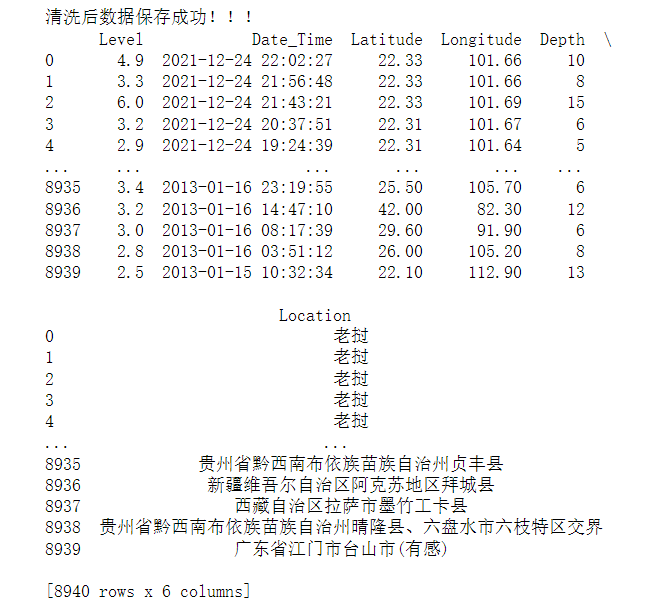
1 # all_url = get_url() 2 # resp = crawl_data(all_url) 3 # 通过正则抓取所有的数据 4 # 地震等级 5 Level = re.findall('"M":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 6 # 时刻 7 Date_Time = re.findall('"O_TIME":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 8 # 返回的是一个三元组 9 date_result = clear_datetime(Date_Time) 10 # 元组里的每一元素是一个列表,对应年 月 日 11 Year = date_result[0] 12 Month = date_result[1] 13 Day = date_result[2] 14 # 经度 15 Longitude = re.findall('"EPI_LON":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 16 # 纬度 17 Latitude = re.findall('"EPI_LAT":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 18 # 深度 19 Depth = re.findall('"EPI_DEPTH":([0-9]+)', str(resp)) 20 # 地址 21 Location_U = re.findall('"LOCATION_C":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 22 # 解码 23 Location = conversion(conversion(conversion(Location_U))) 24 # 将数据转化为datafram格式 25 df1 = pd.DataFrame( 26 {'Level': Level, 'Date_Time': Date_Time,'Year': Year,'Month': Month,'Day': Day, 27 'Longitude': Longitude, 'Latitude': Latitude, 'Depth': Depth, 'Location': Location}) 28 # 将数据保存为Excel 29 # 清洗后的数据增加了年月日字段 30 writer = pd.ExcelWriter('./earthquakeData.xlsx') 31 df1.to_excel(writer, columns=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Year', 'Month', 'Day', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'], index=False, 32 encoding='utf-8') 33 writer.save() 34 print("清洗后数据保存成功!!!") 35 print(df)
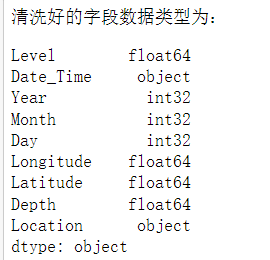
1 # 对爬取的数据进行类型转换,为后面做比较做准备 2 # 毕竟下载下来的数据是字符串类型,所以要转换为float类型和int类型 3 # 把震级数据改成float浮点类型 4 df1['Level'] = df1['Level'].astype('float') 5 # 把年数据改成int整数类型 6 df1['Year'] = df1['Year'].astype('int') 7 # 把月数据改成int整数类型 8 df1['Month'] = df1['Month'].astype('int') 9 # 把日数据改成int整数类型 10 df1['Day'] = df1['Day'].astype('int') 11 # 把经度数据改成float浮点类型 12 df1['Latitude'] = df1['Latitude'].astype('float') 13 # 把维度数据改成float浮点类型 14 df1['Longitude'] = df1['Longitude'].astype('float') 15 # 把地震深度数据改成float浮点类型 16 df1['Depth'] = df1['Depth'].astype('float') 17 # 查看数据列类型 18 print('清洗好的字段数据类型为:') 19 df1.dtypes
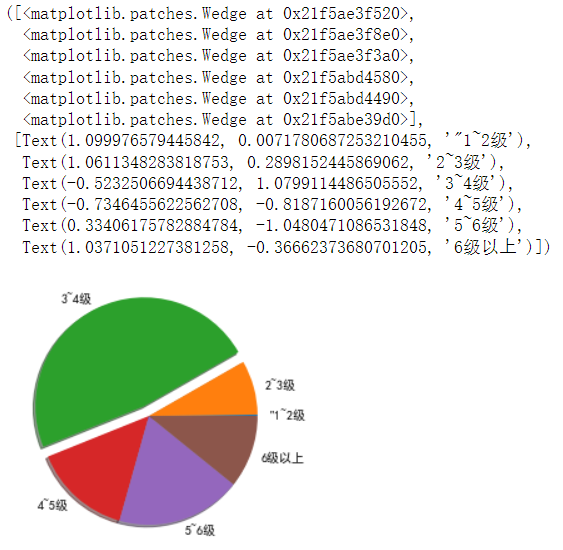
1 all_data = df1 2 # 统计2013~2021年的震级分布占比 3 level_12 = all_data.query("Level >=1 and Level =2 and Level =3 and Level =4 and Level =5 and Level =6") 14 # print(level_up_6) 15 16 # result 17 print("1~2级震级占比为:", len(level_12)) 18 print("2~3级震级占比为:", len(level_23)) 19 print("3~4级震级占比为:", len(level_34)) 20 print("4~5级震级占比为:", len(level_45)) 21 print("5~6级震级占比为:", len(level_56)) 22 print("6级及以上震级占比为:", len(level_up_6))
1 # 导入绘图库 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plit 3 # 设置中文字体 4 plt.rcParams['font.family']=['SimHei'] 5 # 各种震级列表 6 level = ['"1~2级','2~3级','3~4级','4~5级','5~6级','6级以上'] 7 # 各种震级所占数量列表 8 slices= [14,544,3222,981,1250,729] 9 # 绘制饼状图 10 plt.pie(slices, labels=level,shadow=True,explode=[0,0,0.1,0,0,0])
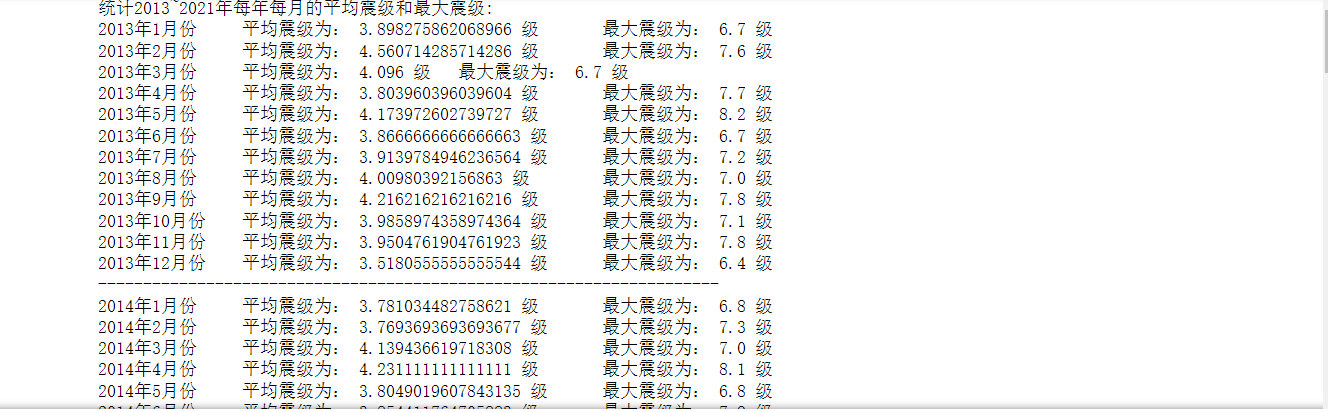
1 # 统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均震级和最大震级 2 print('统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均震级和最大震级:') 3 for j in range(2013, 2022): 4 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 5 for i in range(1, 13): 6 average_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Level'].mean() 7 max_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Level'].max() 8 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份\t" + "平均震级为:", str(average_level), 9 "级\t" + "最大震级为:", str(max_level), "级") 10 print("---------------------------------------------------------------------")
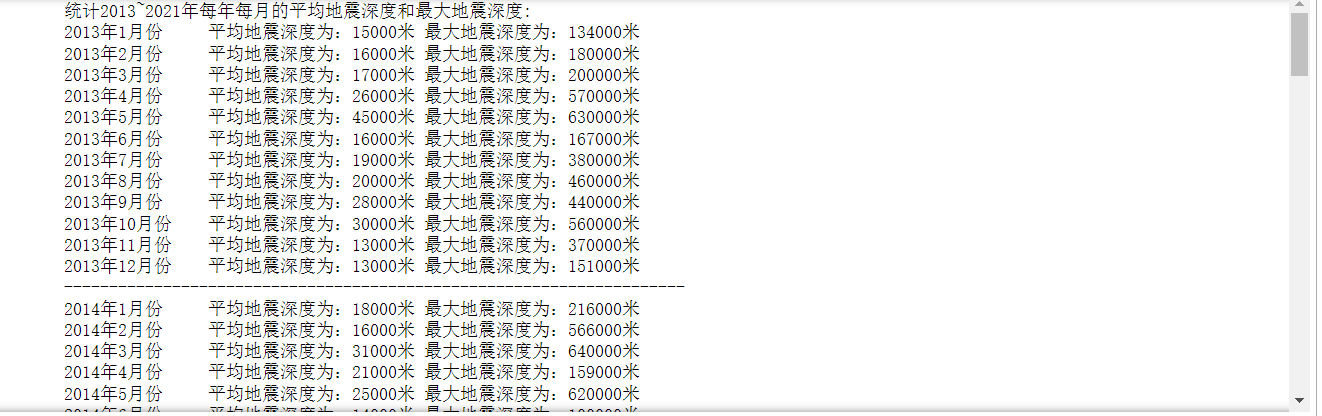
1 # 统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均地震深度和最大地震深度 2 print('统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均地震深度和最大地震深度:') 3 for j in range(2013, 2022): 4 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 5 for i in range(1, 13): 6 average_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Depth'].mean() 7 max_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Depth'].max() 8 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份\t" + "平均地震深度为:"+ str(int(average_level)*1000)+"米\t" 9 + "最大地震深度为:"+ str(int(max_level)*1000)+"米") 10 print("---------------------------------------------------------------------")
1 # 尝试 2 print("统计2021年11月每日平均地震深度和最大地震深度:") 3 data_2021_11 = all_data.query("Year == 2021 and Month == 11") 4 for i in range(1, 31): 5 average_level = data_2021_11.query("Day == {}".format(i))['Depth'].mean() 6 max_level = data_2021_11.query("Day == {}".format(i))['Depth'].max() 7 print("2021年11月" + str(i) + "日\t平均地震深度为:" + str(int(average_level)*1000) + "米\t" 8 + "最大地震深度为:" + str(int(max_level)*1000) + "米")
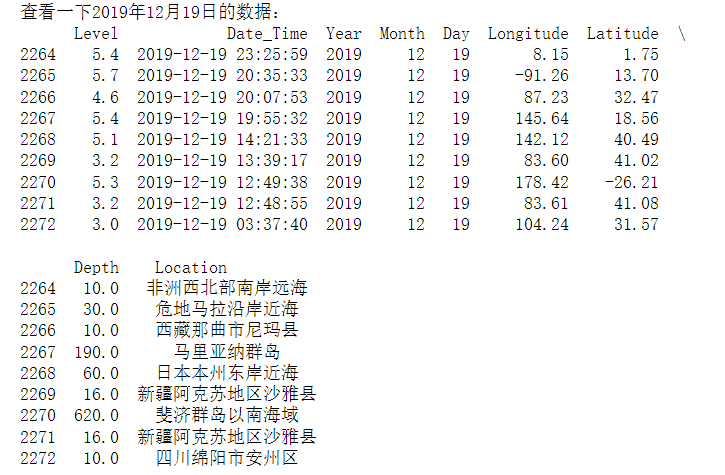
1 # 其中有一天数据比较离谱,查一下发现没错 2 print('查看一下2019年12月19日的数据:') 3 data_2019_12_19 = all_data.query("Year == 2019 and Month ==12 and Day == 19") 4 print(data_2019_12_19)
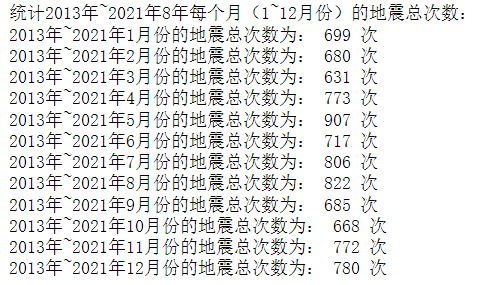
1 # 统计2013年~2021年7年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数 2 print("统计2013年~2021年8年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数:") 3 for i in range(1, 13): 4 month_data = all_data.query("Month == {}".format(i)) 5 print("2013年~2021年" + str(i) + "月份的地震总次数为:", len(month_data), "次")
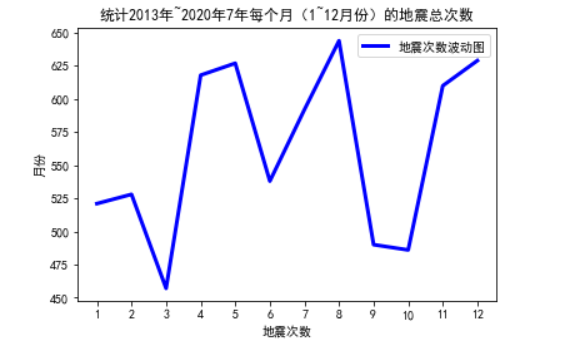
1 # 导入绘图库 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plit 3 # 设置中文字体 4 plt.rcParams['font.family']=['SimHei'] 5 # x轴坐标数据 6 x = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10','11','12'] 7 # y轴坐标数据 8 y = [521,528,457,618,627,538,592,644,490,486,610,629] 9 # 绘制线段 10 plt.plot(x,y,'b',label='地震次数波动图',linewidth=3) 11 # 设置标题 12 plt.title('统计2013年~2021年7年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数') 13 # 添加y轴标题 14 plt.ylabel('月份') 15 # 添加x轴标题 16 plt.xlabel('地震次数') 17 # 设置图例 18 plt.legend() 19 # 显示图片 20 plt.show()
1 # 统计每年地震总次数以及每年每月份的地震总次数 2 print("统计每年地震总次数以及每年每月份的地震总次数") 3 for j in range(2013, 2022): 4 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 5 print("{}年总共地震次数为:".format(j), len(data_year), "次") 6 for i in range(1, 13): 7 data_month = data_year.query("Year == {} and Month == {}".format(j, i)) 8 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份的地震次数为:", len(data_month), "次") 9 print("---------------------------------------------")
1 # 统计平均每年地震次数 2 print('统计平均每年地震次数') 3 earthquake_times = 0 4 for i in range(2013, 2022): 5 every_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(i)) 6 earthquake_times += len(every_year) 7 earthquake_average_times = earthquake_times / 7 8 print("平均每年地震次数:" + str(round(earthquake_average_times)) + "次")
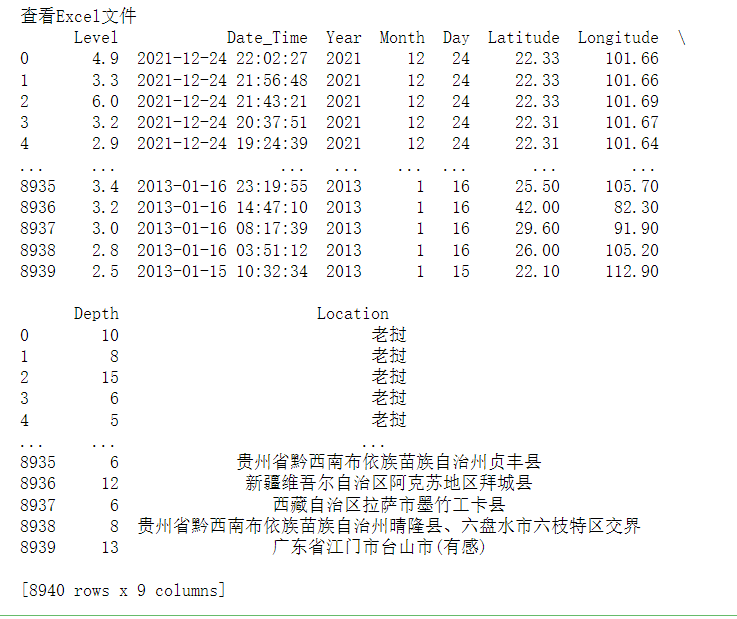
1 # 导入需要的库 2 import codecs # 解码库 3 import collections # 词频统计库 4 import csv # 读取csv格式和写入csv表格数据 5 import re # 正则表达式库 6 7 import jieba # 中文分词 8 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 图像展示库 9 import numpy as np # numpy数据处理库 10 import pandas as pd # 数据分析库 11 import wordcloud # 词云展示库 12 from PIL import Image # 图像处理库 1 data = pd.read_excel('./earthquakeData.xlsx') # 读取Excel文件 2 print('查看Excel文件') 3 print(data)
1 # 这是为了得到数据中的字符串 2 data_str = '' 3 # 数据有多少条就取多少条 4 for i in data.index: 5 # 取出每一条的地震位置 6 location = data.at[i, 'Location'] 7 # 得到地震位置的字符串 8 data_str += location + "\n" 1 # 设置停用词 2 # 空集合用来存放停用词 3 stopwords = set() 4 # stopwords.txt里包括了:中文停用词表、哈工大停用词表、百度停用词表、四川大学机器智能实验室停用词库 5 # codecs是一个解码库,文件读尽量用codecs.open方法,一般不会出现编码的问题 6 stopw = codecs.open(r'./stopwords.txt', 'r', 'utf-8') 7 for word in stopw: 8 # 把每一个停用词转换成字符串并且去掉空格,然后添加到停用词的集合中 9 stopwords.add(str(word).strip()) 10 # 关闭文件 11 stopw.close() 1 # 地震位置的词频统计和词云制作 2 # 定义正则表达式匹配模式 3 pattern = re.compile(u'\t|\n|\.|-|:|;|\)|\(|\?|"|\d|\W') 4 # 将符合模式的字符去除,得到纯文字 5 string_data = re.sub(pattern, '', data_str) 6 # 文本分词:精确模式分词 7 seg_list_exact = jieba.cut(string_data, cut_all=False) 8 # 用来存放非停用词,以便于做词频统计和词云 9 object_list = [] 10 # 循环读出每个分词 11 for word in seg_list_exact: 12 # 如果不在要去除的停用词库中 13 if word not in stopwords: 14 # 分词追加到列表 15 object_list.append(word) 16 # 用collections.Counter()对分词做词频统计 17 word_counts = collections.Counter(object_list) 18 # 获取前20最高频的词,most_common()来实现Top n功能 19 word_counts_top20 = word_counts.most_common(20) 20 # 输出检查 21 print(word_counts_top20)
1 # 词频展示 2 # mask = np.array(Image.open('./词云背景图.png')) # 定义词频背景 3 wc = wordcloud.WordCloud( 4 font_path='C:/Windows/Fonts/simhei.ttf', # 设置字体格式 5 # mask=mask, # 设置背景图 6 max_words=250, # 最多显示词数 7 background_color='black', # 背景颜色 8 max_font_size=50 # 字体最大值 9 ) 10 wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_counts) # 根据字典生成词云 11 # image_colors = wordcloud.ImageColorGenerator(mask) # 从背景图建立颜色方案 12 # wc.recolor(color_func=image_colors) # 将词云颜色设置为背景图方案 13 # 去除图像周围的白边 14 plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) 15 plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) 16 plt.subplots_adjust(top=1, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0) 17 plt.margins(0, 0) 18 # 显示词云 19 print("多次出现的地震地区词云图:") 20 plt.imshow(wc) 21 # 关闭坐标轴 22 plt.axis('off') 全部代码 1 import requests 2 import pandas as pd 3 import re 4 5 6 # 获取所有的页面url 7 def get_url(): 8 list = [] 9 for i in range(1, 448): # 448 10 url = "http://www.ceic.ac.cn/ajax/search?page={}&&start=2013-01-01&&end=2021-12-25&&jingdu1=&&jingdu2=&&weidu1=&&weidu2=&&height1=&&height2=&&zhenji1=&&zhenji2=&&".format( 11 i) 12 list.append(url) 13 return list 14 # 爬取所有url 15 def crawl_data(ls): 16 list = [] 17 for i in ls: 18 resp = requests.get(i) 19 list.append(resp.text) 20 return list 21 # 将Unicode编码转化为中文 22 def conversion(ls): 23 list = [] 24 for i in ls: 25 s = eval('u"%s"' % i) 26 list.append(s) 27 return list 28 # 程序主体 29 if __name__ == '__main__': 30 all_url = get_url() 31 resp = crawl_data(all_url) 32 # 通过正则抓取所有的数据 33 Level = re.findall('"M":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 地震等级 34 Date_Time = re.findall('"O_TIME":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 时刻 35 Longitude = re.findall('"EPI_LON":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 经度 36 Latitude = re.findall('"EPI_LAT":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 纬度 37 Depth = re.findall('"EPI_DEPTH":([0-9]+)', str(resp)) # 深度 38 Location_U = re.findall('"LOCATION_C":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) # 地址 39 Location = conversion(conversion(conversion(Location_U))) # 解码 40 # 将数据转化为datafram格式 41 df = pd.DataFrame( 42 {'Level': Level, 'Date_Time': Date_Time, 'Longitude': Longitude, 'Latitude': Latitude, 'Depth': Depth, 43 'Location': Location}) 44 # 将数据保存为Excel 45 writer = pd.ExcelWriter('./earthquake.xlsx') 46 df.to_excel(writer, columns=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'], index=False, 47 encoding='utf-8') 48 writer.save() 49 print("数据保存成功!!!") 50 print(df) 51 earthquake=pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel('./earthquake.xlsx')) 52 earthquake.head() 53 #检查是否有重复值 54 earthquake.duplicated() 55 #检查是否有空值 56 print(earthquake['Depth'].isnull().value_counts()) 57 df = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel('./earthquake.xlsx')) 58 print(df.head()) 59 #绘制日期与深度回归图 60 import seaborn as sns 61 sns.regplot(earthquake.Longitude,earthquake.Level) 62 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 63 import numpy as np 64 #画出散点图 65 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 66 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 67 N=10 68 x=np.random.rand(N) 69 y=np.random.rand(N) 70 size=50 71 plt.xlabel("Level") 72 plt.ylabel("Depth") 73 plt.scatter(x,y,size,color='r',alpha=0.5,marker="o") 74 #散点图 kind='reg' 75 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind='reg') 76 # kind='hex' 77 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind='hex') 78 # kind='kde' 79 sns.jointplot(x="Level",y="Depth",data=earthquake,kind="kde",space=0,color='g') 80 #选择个特征变量,绘制分布图,用最小二乘法分析两个变量间的二次拟合方程和拟合曲线 81 colnames=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'] 82 df = pd.read_excel('./earthquake.xlsx',skiprows=0,names=colnames) 83 X = df.Latitude 84 Y = df.Level 85 Z = df.Depth 86 def A(): 87 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="blue",linewidth=2) 88 plt.title("RM scatter",color="blue") 89 plt.grid() 90 plt.show() 91 A() 92 def B(): 93 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="green",linewidth=2) 94 plt.title("redu",color="blue") 95 plt.grid() 96 plt.show() 97 B() 98 from scipy.optimize import leastsq 99 def func(p,x): 100 a,b,c=p 101 return a*x*x+b*x+c 102 def error(p,x,y): 103 return func(p,x)-y 104 def main(): 105 plt.figure(figsize=(10,6)) 106 p0=[0,0,0] 107 Para = leastsq(error,p0,args=(X,Y)) 108 a,b,c=Para[0] 109 print("a=",a,"b=",b,"c=",c) 110 plt.scatter(X,Y,color="blue",linewidth=2) 111 x=np.linspace(0,20,20) 112 y=a*x*x+b*x+c 113 plt.plot(x,y,color="blue",linewidth=2,) 114 plt.title("地震深度分布") 115 plt.grid() 116 plt.show() 117 118 main() 119 # 用来清洗数据DateTime 120 s = ['2021-12-22 22:33:47', '2021-12-22 21:46:16'] # 用来测试函数的数据 121 def clear_datetime(date_list): 122 # 为了拆分年月日,用来存放year、month 、day的空列表 123 year = [] 124 month = [] 125 day=[] 126 for s in date_list: 127 # 通过split函数简单清洗数据 128 # 清洗年数据 129 s1 = s.split('-')[0] 130 # 清洗月数据 131 s2 = s.split('-')[1] 132 # 清洗日数据 133 ss = s.split('-')[2] 134 s3 = ss.split(' ')[0] 135 # 把数据添加到列表中 136 year.append(s1) 137 month.append(s2) 138 day.append(s3) 139 # 返回三元组,元组里的每一个元素是对应年月日的列表 140 return year,month,day 141 142 s = clear_datetime(s) # 用于测试结果 143 print('测试结果打印:') 144 s 145 # all_url = get_url() 146 # resp = crawl_data(all_url) 147 # 通过正则抓取所有的数据 148 # 地震等级 149 Level = re.findall('"M":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 150 # 时刻 151 Date_Time = re.findall('"O_TIME":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 152 # 返回的是一个三元组 153 date_result = clear_datetime(Date_Time) 154 # 元组里的每一元素是一个列表,对应年 月 日 155 Year = date_result[0] 156 Month = date_result[1] 157 Day = date_result[2] 158 # 经度 159 Longitude = re.findall('"EPI_LON":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 160 # 纬度 161 Latitude = re.findall('"EPI_LAT":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 162 # 深度 163 Depth = re.findall('"EPI_DEPTH":([0-9]+)', str(resp)) 164 # 地址 165 Location_U = re.findall('"LOCATION_C":"(.*?)"', str(resp)) 166 # 解码 167 Location = conversion(conversion(conversion(Location_U))) 168 # 将数据转化为datafram格式 169 df1 = pd.DataFrame( 170 {'Level': Level, 'Date_Time': Date_Time,'Year': Year,'Month': Month,'Day': Day, 171 'Longitude': Longitude, 'Latitude': Latitude, 'Depth': Depth, 'Location': Location}) 172 # 将数据保存为Excel 173 # 清洗后的数据增加了年月日字段 174 writer = pd.ExcelWriter('./earthquakeData.xlsx') 175 df1.to_excel(writer, columns=['Level', 'Date_Time', 'Year', 'Month', 'Day', 'Latitude', 'Longitude', 'Depth', 'Location'], index=False, 176 encoding='utf-8') 177 writer.save() 178 print("清洗后数据保存成功!!!") 179 print(df) 180 # 对爬取的数据进行类型转换,为后面做比较做准备 181 # 毕竟下载下来的数据是字符串类型,所以要转换为float类型和int类型 182 # 把震级数据改成float浮点类型 183 df1['Level'] = df1['Level'].astype('float') 184 # 把年数据改成int整数类型 185 df1['Year'] = df1['Year'].astype('int') 186 # 把月数据改成int整数类型 187 df1['Month'] = df1['Month'].astype('int') 188 # 把日数据改成int整数类型 189 df1['Day'] = df1['Day'].astype('int') 190 # 把经度数据改成float浮点类型 191 df1['Latitude'] = df1['Latitude'].astype('float') 192 # 把维度数据改成float浮点类型 193 df1['Longitude'] = df1['Longitude'].astype('float') 194 # 把地震深度数据改成float浮点类型 195 df1['Depth'] = df1['Depth'].astype('float') 196 # 查看数据列类型 197 print('清洗好的字段数据类型为:') 198 df1.dtypes 199 all_data = df1 200 # 统计2013~2021年的震级分布占比 201 level_12 = all_data.query("Level >=1 and Level =2 and Level =3 and Level =4 and Level =5 and Level =6") 212 # print(level_up_6) 213 214 # result 215 print("1~2级震级占比为:", len(level_12)) 216 print("2~3级震级占比为:", len(level_23)) 217 print("3~4级震级占比为:", len(level_34)) 218 print("4~5级震级占比为:", len(level_45)) 219 print("5~6级震级占比为:", len(level_56)) 220 print("6级及以上震级占比为:", len(level_up_6)) 221 # 导入绘图库 222 import matplotlib.pyplot as plit 223 # 设置中文字体 224 plt.rcParams['font.family']=['SimHei'] 225 # 各种震级列表 226 level = ['"1~2级','2~3级','3~4级','4~5级','5~6级','6级以上'] 227 # 各种震级所占数量列表 228 slices= [14,544,3222,981,1250,729] 229 # 绘制饼状图 230 plt.pie(slices, labels=level,shadow=True,explode=[0,0,0.1,0,0,0]) 231 # 统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均震级和最大震级 232 print('统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均震级和最大震级:') 233 for j in range(2013, 2022): 234 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 235 for i in range(1, 13): 236 average_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Level'].mean() 237 max_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Level'].max() 238 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份\t" + "平均震级为:", str(average_level), 239 "级\t" + "最大震级为:", str(max_level), "级") 240 print("---------------------------------------------------------------------") 241 # 统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均地震深度和最大地震深度 242 print('统计2013~2021年每年每月的平均地震深度和最大地震深度:') 243 for j in range(2013, 2022): 244 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 245 for i in range(1, 13): 246 average_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Depth'].mean() 247 max_level = data_year.query("Month == {}".format(i))['Depth'].max() 248 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份\t" + "平均地震深度为:"+ str(int(average_level)*1000)+"米\t" 249 + "最大地震深度为:"+ str(int(max_level)*1000)+"米") 250 print("---------------------------------------------------------------------") 251 # 尝试 252 print("统计2021年11月每日平均地震深度和最大地震深度:") 253 data_2021_11 = all_data.query("Year == 2021 and Month == 11") 254 for i in range(1, 31): 255 average_level = data_2021_11.query("Day == {}".format(i))['Depth'].mean() 256 max_level = data_2021_11.query("Day == {}".format(i))['Depth'].max() 257 print("2021年11月" + str(i) + "日\t平均地震深度为:" + str(int(average_level)*1000) + "米\t" 258 + "最大地震深度为:" + str(int(max_level)*1000) + "米") 259 # 其中有一天数据比较离谱,查一下发现没错 260 print('查看一下2019年12月19日的数据:') 261 data_2019_12_19 = all_data.query("Year == 2019 and Month ==12 and Day == 19") 262 print(data_2019_12_19) 263 # 统计2013年~2021年7年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数 264 print("统计2013年~2021年8年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数:") 265 for i in range(1, 13): 266 month_data = all_data.query("Month == {}".format(i)) 267 print("2013年~2021年" + str(i) + "月份的地震总次数为:", len(month_data), "次") 268 # 导入绘图库 269 import matplotlib.pyplot as plit 270 # 设置中文字体 271 plt.rcParams['font.family']=['SimHei'] 272 # x轴坐标数据 273 x = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','10','11','12'] 274 # y轴坐标数据 275 y = [521,528,457,618,627,538,592,644,490,486,610,629] 276 # 绘制线段 277 plt.plot(x,y,'b',label='地震次数波动图',linewidth=3) 278 # 设置标题 279 plt.title('统计2013年~2021年7年每个月(1~12月份)的地震总次数') 280 # 添加y轴标题 281 plt.ylabel('月份') 282 # 添加x轴标题 283 plt.xlabel('地震次数') 284 # 设置图例 285 plt.legend() 286 # 显示图片 287 plt.show() 288 # 统计每年地震总次数以及每年每月份的地震总次数 289 print("统计每年地震总次数以及每年每月份的地震总次数") 290 for j in range(2013, 2022): 291 data_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(j)) 292 print("{}年总共地震次数为:".format(j), len(data_year), "次") 293 for i in range(1, 13): 294 data_month = data_year.query("Year == {} and Month == {}".format(j, i)) 295 print("{}年".format(j) + str(i) + "月份的地震次数为:", len(data_month), "次") 296 print("---------------------------------------------") 297 # 统计平均每年地震次数 298 print('统计平均每年地震次数') 299 earthquake_times = 0 300 for i in range(2013, 2022): 301 every_year = all_data.query("Year == {}".format(i)) 302 earthquake_times += len(every_year) 303 earthquake_average_times = earthquake_times / 7 304 print("平均每年地震次数:" + str(round(earthquake_average_times)) + "次") 305 # 导入需要的库 306 import codecs # 解码库 307 import collections # 词频统计库 308 import csv # 读取csv格式和写入csv表格数据 309 import re # 正则表达式库 310 311 import jieba # 中文分词 312 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 图像展示库 313 import numpy as np # numpy数据处理库 314 import pandas as pd # 数据分析库 315 import wordcloud # 词云展示库 316 from PIL import Image # 图像处理库 317 data = pd.read_excel('./earthquakeData.xlsx') # 读取Excel文件 318 print('查看Excel文件') 319 print(data) 320 # 这是为了得到数据中的字符串 321 data_str = '' 322 # 数据有多少条就取多少条 323 for i in data.index: 324 # 取出每一条的地震位置 325 location = data.at[i, 'Location'] 326 # 得到地震位置的字符串 327 data_str += location + "\n" 328 # 设置停用词 329 # 空集合用来存放停用词 330 stopwords = set() 331 # stopwords.txt里包括了:中文停用词表、哈工大停用词表、百度停用词表、四川大学机器智能实验室停用词库 332 # codecs是一个解码库,文件读尽量用codecs.open方法,一般不会出现编码的问题 333 stopw = codecs.open(r'./stopwords.txt', 'r', 'utf-8') 334 for word in stopw: 335 # 把每一个停用词转换成字符串并且去掉空格,然后添加到停用词的集合中 336 stopwords.add(str(word).strip()) 337 # 关闭文件 338 stopw.close() 339 # 地震位置的词频统计和词云制作 340 # 定义正则表达式匹配模式 341 pattern = re.compile(u'\t|\n|\.|-|:|;|\)|\(|\?|"|\d|\W') 342 # 将符合模式的字符去除,得到纯文字 343 string_data = re.sub(pattern, '', data_str) 344 # 文本分词:精确模式分词 345 seg_list_exact = jieba.cut(string_data, cut_all=False) 346 # 用来存放非停用词,以便于做词频统计和词云 347 object_list = [] 348 # 循环读出每个分词 349 for word in seg_list_exact: 350 # 如果不在要去除的停用词库中 351 if word not in stopwords: 352 # 分词追加到列表 353 object_list.append(word) 354 # 用collections.Counter()对分词做词频统计 355 word_counts = collections.Counter(object_list) 356 # 获取前20最高频的词,most_common()来实现Top n功能 357 word_counts_top20 = word_counts.most_common(20) 358 # 输出检查 359 print(word_counts_top20) 360 # 词频展示 361 # mask = np.array(Image.open('./词云背景图.png')) # 定义词频背景 362 wc = wordcloud.WordCloud( 363 font_path='C:/Windows/Fonts/simhei.ttf', # 设置字体格式 364 # mask=mask, # 设置背景图 365 max_words=250, # 最多显示词数 366 background_color='black', # 背景颜色 367 max_font_size=50 # 字体最大值 368 ) 369 wc.generate_from_frequencies(word_counts) # 根据字典生成词云 370 # image_colors = wordcloud.ImageColorGenerator(mask) # 从背景图建立颜色方案 371 # wc.recolor(color_func=image_colors) # 将词云颜色设置为背景图方案 372 # 去除图像周围的白边 373 plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) 374 plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator()) 375 plt.subplots_adjust(top=1, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0) 376 plt.margins(0, 0) 377 # 显示词云 378 print("多次出现的地震地区词云图:") 379 plt.imshow(wc) 380 # 关闭坐标轴 381 plt.axis('off')
(五)总结 通过这次爬取中国地震网可以知道,地震震级频率最高的是3到4级,六级的相对来说比较少,并且新疆地震频率相对来说比较高 在编写代码的过程中,python相对于其他编程来说更明了,爬取的年份比较多,得出来数据很杂,可视化也比较繁杂。编程这门语言,需要不断地动手敲打,才能熟能生巧,通过上机来编程来判断自己是否正确,完成编程的编写不一定万事大吉,只能靠自己的上机经验来分析判断错误的所在,通过这次的设计,只要努力,任何东西都不会太难。
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |