东北师大吴兴隆|均匀Li+通量分布助力高稳定性耐温度变化锂负极 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › 三维网络结构电极更有利于电极电流的均匀分布吗 › 东北师大吴兴隆|均匀Li+通量分布助力高稳定性耐温度变化锂负极 |
东北师大吴兴隆|均匀Li+通量分布助力高稳定性耐温度变化锂负极
|
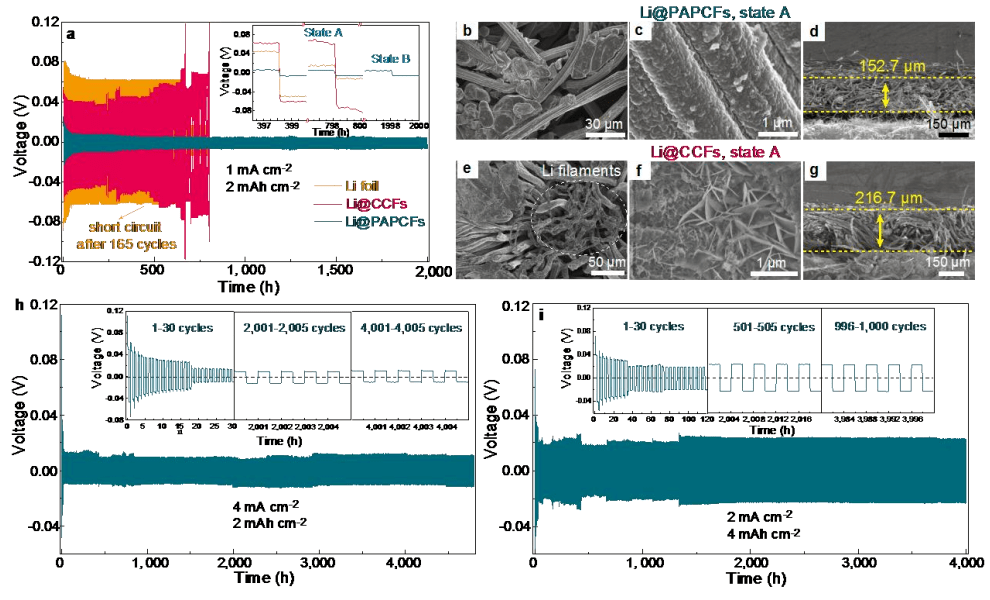
图文解析 图1展示了PAPCFs和CCFs上的结构和初始锂沉积的特性。(a-b) SEM 图像和 (c) 通过使用 PAPCFs 的 DFT 模型计算的 N2 吸附-解吸等温线和累积孔体积 (0.5-50 nm); (d-e) 在 PAPCFs 和 CCFs 电极上镀有 0.5 mA h cm-2 锂时的SEM 图,PAPCFs在镀锂后仍然显现出平整光滑的表面,而普通的CCFs则出现了疏松的锂枝晶,表明了PAPCFs对调控锂沉积有重要的意义。 PAPCFs 和 CCFs 电极界面信息的有限元模拟。(g) 分别用于 PAPCFs 和 CCFs 电极的 18 × 24 µm2 半电池电沉积系统下具有恒定反应电流和电极表面的电流密度矢量分布,轮廓中的箭头代表锂离子的运动。 (h) 分别具有多孔结构和不具有多孔结构的 PAPCFs 电极在 18 × 24 µm2 半电池电沉积系统下的平衡的锂离子浓度分布。在相同几何尺寸下,高比表面积将降低电极表面上的局部电流密度。因此,多孔电极上的电流密度设置为无孔电极上的一半。 (f) 多孔和非多孔电极中沿 Y 方向的一维横截面的锂离子浓度分布。 Y 方向表示垂直于电极。 (i) PAPCFs 在初始状态调节低浓度梯度和均匀的 Li+通量分布,实现均匀的锂沉积的示意图。 Fig. 1 The structure and initial Li deposition characteristic on PAPCFs and contrastive CCFs. (a-b) SEM images and (c) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm and cumulative pore volume (0.5-50 nm) calculated by the use of DFT-model of PAPCFs. (d, e) SEM images for Li deposition morphology with 0.5 mA h cm-2 of Li plated on PAPCFs and CCFs electrode. Finite element simulation for the interface information of PAPCFs and CCFs electrodes. (g) Current density vector profiles with constant-reaction-current electrode surfaces at 18 × 24 µm2 half cell electrodeposition system for PAPCFs and CCFs electrode, respectively. The arrows in the profiles stand for the movement of Li-ion. (h) Equilibrium Li-ion concentration profiles at 18 × 24 µm2 half cell electrodeposition system for PAPCFs electrode with and without porous structure, respectively. The high surface area will reduce the local current density on the electrode surface under the same geometry dimensions. Therefore, the current density on the porous electrode is set as a half of that on the non-porous electrode. (f) 1D cross-sectional Li-ion concentration profiles along Y direction in porous and non-porous electrodes. The Y direction is perpendicular to the electrode. (i) Schematic diagrams of PAPCFs to regulate low concentration gradient and even Li+ flux distribution for uniform Li deposition at initial state. 图2 展示了Li@PAPCFs复合负极的镀锂/脱锂稳定性与循环过程中的形貌演变。(a) 三种对称电池(Li@PAPCFs、Li@CCFs 和 Li 箔)在 1 mA cm-2 和 2 mA h cm-2 下的时间-电压曲线。(b-d) Li@PAPCFs 和 (e-g) Li@CCFs 在 200 次循环后的 SEM 图以及截面图(状态 A)。Li@PAPCFs 对称电池 (h) 在 4 mA cm-2 的电流密度下和 2 mA h cm-2 的容量下和 (i) 在 2 mA cm-2 的电流密度下和 4 mA h cm-2 的容量下的时间-电压图。 从所有的时间-电压曲线可知,该PAPCFs在不同的电流密度以及不同的容量下始终表现出最小的极化,说明具有平行排列且具有丰富孔结构的PAPCFs在重复的镀锂/脱锂循环过程中保持了优异的结构稳定性并始终维持着稳定的固体电解质膜。此外,其高的表面积很好地均匀了锂离子流,抑制了枝晶的生长。
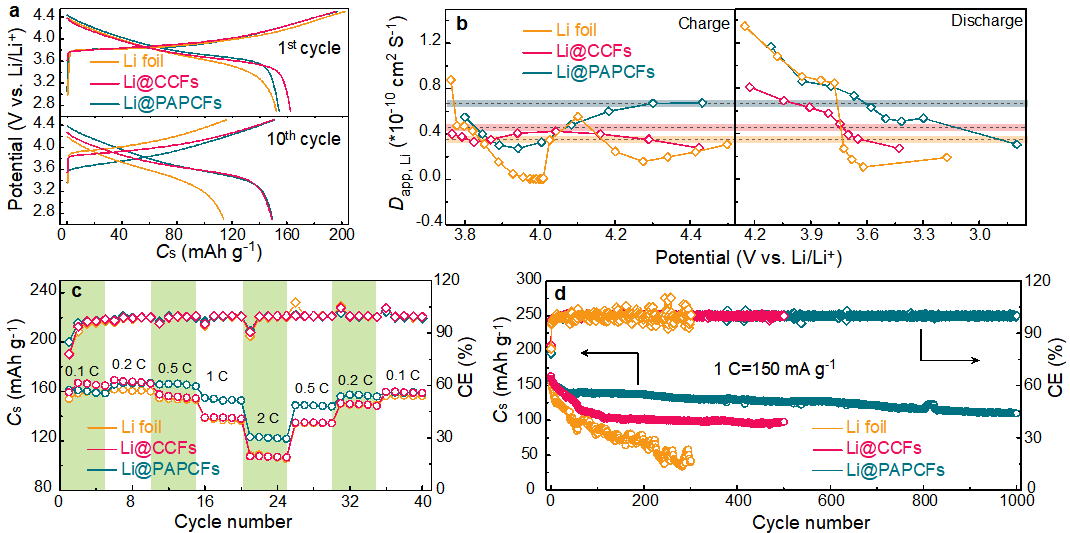
Fig. 2 The Li plating/stripping stability and morphology evolution of Li@PAPCFs. (a) Voltage profiles in three types of symmetrical cells (Li@PAPCFs, Li@CCFs, and Li foil) at 1 mA cm-2 and 2 mA h cm-2. Insert: Magnified voltage profiles at the 100th, 200th, and 500th cycle, respectively. Top view and cross section of SEM images of (b-d) Li@PAPCFs and (e-g) Li@CCFs after 200 cycles (state A). Voltage profiles of Li@PAPCFs symmetrical cell (h) at 4 mA cm-2 and 2 mA h cm-2 and (i) at 2 mA cm-2 and 4 mA h cm-2. Insert: Magnified voltage profiles at specific a certain cycles. 图3展示了NMC111-Li@PAPCFs、NMC111-Li@CCFs和NMC111-Li全电池的电化学性能。(a) 在电流密度为 1 C时,第 1 次和第 10 次循环的比容量-电压曲线。(b)GITT测试,从图中可以明显地看出NMC111-Li@PAPCFs的平均Dapp, Li在相同的测试环境下最高,表明Li@PAPCFs具有更好的Li+/电子传导性以及更好的界面稳定性;(c)不同倍率下的电化学性能。 (d) 1 C下的长循环稳定性。
Fig. 3 The electrochemical performance of NMC111-Li@PAPCFs, NMC111-Li@CCFs, and NMC111-Li full cells. (a) Voltage profiles at 1 C for the 1st and 10th cycle. (b) GITT tests of the Dapp, Li along with the galvanostatic charge-discharge process of 4th cycle at 0.5 C. (c) Rate performance at the different rates. (d) Long-term cycle stability at 1 C. 图4是 Li@PAPCFs 和其对应的全电池的低温性能。 Li@PAPCFs 对称电池在(a)1 mA cm-2 和 2 mA h cm-2 下0 ℃的时间-电压曲线,(b)0.25 mA cm-2 和 1 mA h cm-2 下-15 ℃的时间-电压曲线。 PAPCFs 在预先镀有10 mA h cm-2后(Li@PAPCFs)(c-e) 和在 0 ℃ 电镀/剥离循环后的SEM图和截面图(f-h)。NMC111-Li@PAPCFs 在(i)不同倍率和温度下的容量保持率,(j) 0.5 C不同温度下的充放电曲线。(k) NMC111-Li@CCFs 与 NMC111-Li@PAPCFs 在不同倍率和温度下的容量保持率。 NMC111-Li@PAPCFs 在电流密度为1 C时,温度为 (l) 0 ℃ 和 (m) -15 ℃时的长循环稳定性。 Fig. 4 LT tolerance of Li@PAPCFs and the corresponding full cell. Voltage profiles of Li@PAPCFs symmetrical cell (a) for 0 ℃ at 1 mA cm-2 and 2 mA h cm-2 and (b) for -15 ℃ at 0.25 mA cm-2 and 1 mA h cm-2. Insert: Magnified voltage profiles at specific a certain cycles. Top view and cross section of SEM images of Li@PAPCFs (c-e) after the initial Li plating of 10 mA h cm-2 and (f-h) after the plating/stripping cycles at 0 ℃. (i) Capacity retention (Cr) of NMC111-Li@PAPCFs at different rates and temperatures vs. 25 ℃. (j) Charge-discharge profiles at 0.5 C for different temperatures. (k) Cr of NMC111-Li@CCFs vs. NMC111-Li@PAPCFs at different rates and temperatures. Long-term cycle stability of NMC111-Li@PAPCFs at (l) 0 ℃ for 1 C and (m) -15 ℃ for 0.1 C. 总结与展望 从商业无纺布中提取的可再生、可伸缩的3D轻质碳骨架可以很好地实现Li的均匀成核和沉积,使HLCA在长期循环甚至低温条件下依然能够实现保持完整的结构,同时也能维持稳定的电极/电解液界面。其中,碳骨架的平行排列可以均匀化Li+分布;其大的比表面积可以大大降低有效电流密度,缓解电极界面的浓度梯度,从而形成稳定的富含LiF的 SEI 层。其对称电池和全电池的循环稳定性优于目前所报道的亲碳或亲锂修饰的碳宿主,表明HLCA的内在排列模式和微观结构对实现具有高稳定性以及高安全性的锂金属负极的重要性。本工作从实用角度出发,为一系列可充电金属电池提供了一种很有前途的碳主体材料。 作者介绍 吴兴隆,东北师范大学教授,教育部“青年长江学者”,课题组的研究领域包括纳米能源材料(用于锂离子电池、钠离子电池和电化学电容器等)、新型电化学储能器件、锂离子电池回收与再利用。已在《Adv. Mater.》(5篇)、《Energy Environ. Sci.》、《Sci. Bull.》、《Adv. Energy Mater.》(5篇)、《Adv. Funct. Mater.》、《Energy Storage Mater.》(2篇)、《Nano Energy》、《Small》(3篇)和《J. Mater. Chem. A》(12篇)等学术期刊发表通讯/第一作者论文110余篇。14篇论文被评选为ESI高引论文,文章被引用超过11000次,H指数为57;已获授权发明专利17项;负责了锂离子电池正极材料从实验室到中试,再到小规模工业化生产定型,开发了多款高性能锂离子电池产品。主持了国家自然科学基金委重大研究计划和吉林省省科技厅等十余项研究课题。曾获得教育部自然科学研究成果一等奖和中国科学院科技成果转化二等奖等科技奖励。 参考文献 Chao-Ying Fan, Dan Xie, Xiao-Hua Zhang, Wan-Yue Diao, Ru Jiang, Xing-Long Wu, Homogeneous Li+ Flux Distribution Enables Highly Stable and Temperature-Tolerant Lithium Anode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 2102158. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202102158返回搜狐,查看更多 |
【本文地址】