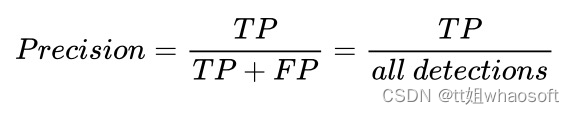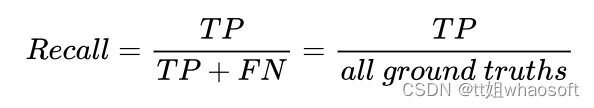YOLOv5~目标检测模型精确度 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › yolov5检测精度低 › YOLOv5~目标检测模型精确度 |
YOLOv5~目标检测模型精确度
|
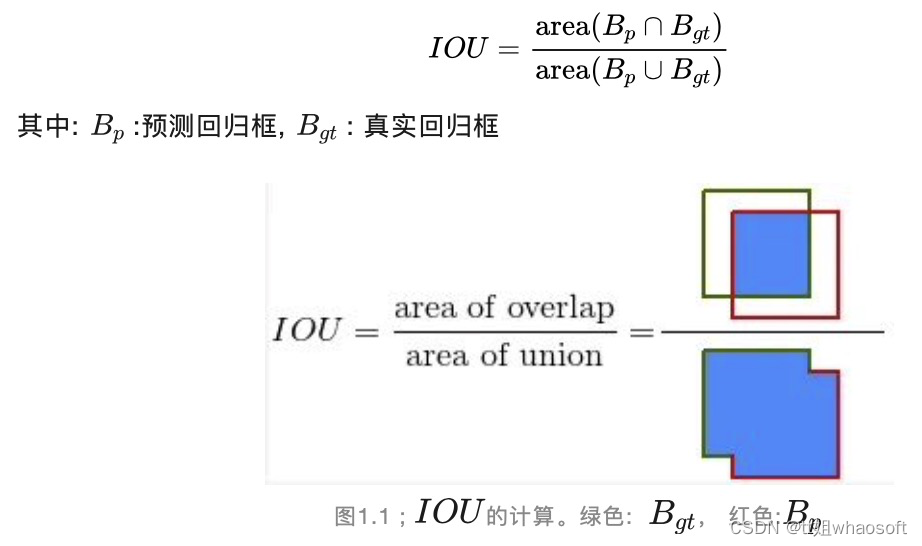
还是yolo5的基础啊~~ 一些关于目标检测模型的评估指标:IOU、TP&FP&FN&TN、mAP等,并列举了目标检测中的mAP计算。 指标评估(重要的一些定义) IOU
也称重叠度表示计算预测回归框和真实回归框的交并比,计算公式如下: TP&FP&FN&TN
指标的一些基本概念: TP(True Postives):分类器把正例正确的分类-预测为正例。(IOU >= 阈值) FN(False Negatives):分类器把正例错误的分类-预测为负例。(IOU < 阈值) FP(False Postives):分类器把负例错误的分类-预测为正例 TN(True Negatives):分类器把负例正确的分类-预测为负例(_yolov5中没有应用到_) yolov5中没有应用TN的原因: TN代表的是所有可能的未正确检测到的边界框。然而在yolo在目标检测任务中,每个网格会生成很多的预测边界框,有许多的预测边界框是没有相应的真实标签框,导致未正确检测到的边界框数量远远大于正确检测到的边界框,这就是为什么不使用TN的原因。 threshold: depending on the metric, it is usually set to 50%, 75% or 95%. PrecisionPrecision 定义:模型识别相关目标的能力。分类正确的样本在所有样本中的数量比例,公式如下:
Recall 定义:是模型找到真实回归框(即标签标注的框)的能力。计算公式如下:
多标签图像分类任务中图片的标签不止一个,因此评价不能用普通单标签图像分类的标准,即mean accuracy,该任务采用的是和信息检索中类似的方法—mAP,虽然其字面意思和mean average precision看起来差不多,但是计算方法要繁琐得多,mAP 会统计所有 Confidence 值下的 PR值,而实际使用时,会设定一个 Confidence 阈值,低于该阈值的目标会被丢弃,这部分目标在统计 mAP 时也会有一定的贡献。 Confidence(置信度):在统计学中,一个概率样本的置信区间(Confidence interval)是对这个样本的某个总体参数的区间估计。置信区间展现的是这个参数的真实值有一定概率落在测量结果的周围的程度。置信区间给出的是被测量参数测量值的可信程度范围,即前面所要求的“一定概率”。这个概率也被称为置信水平。
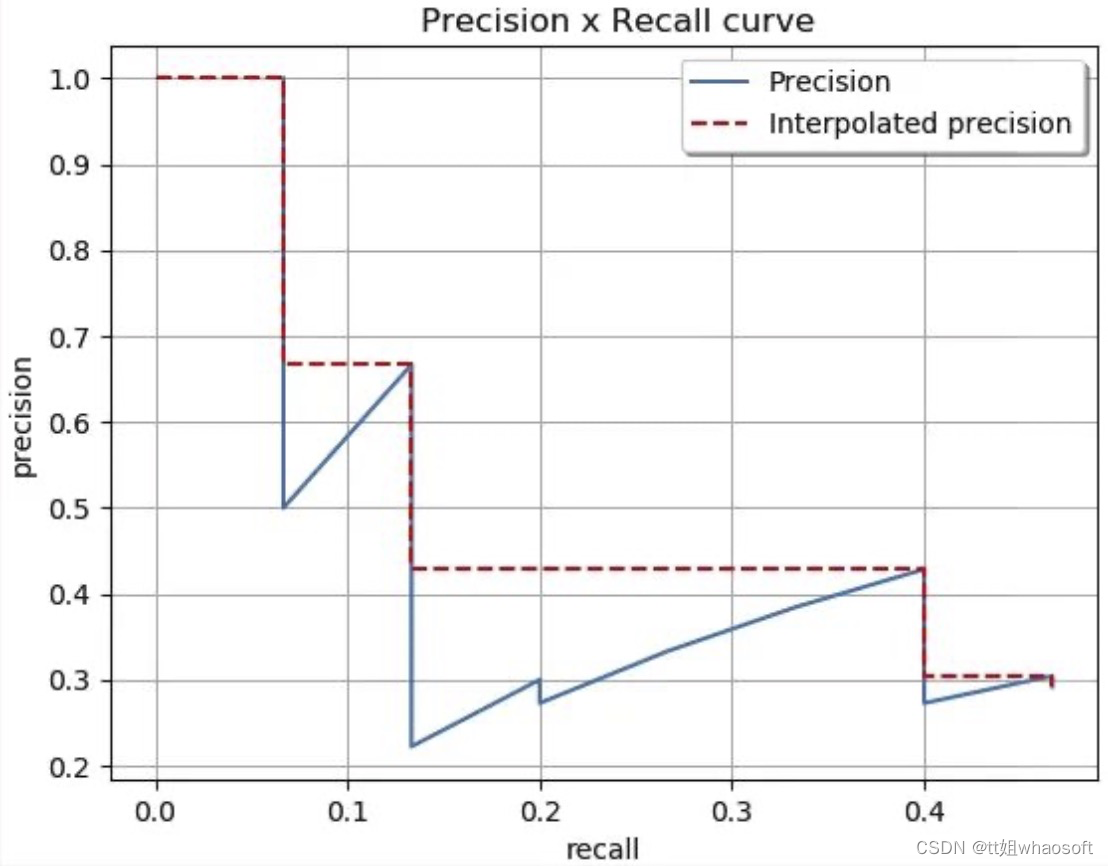
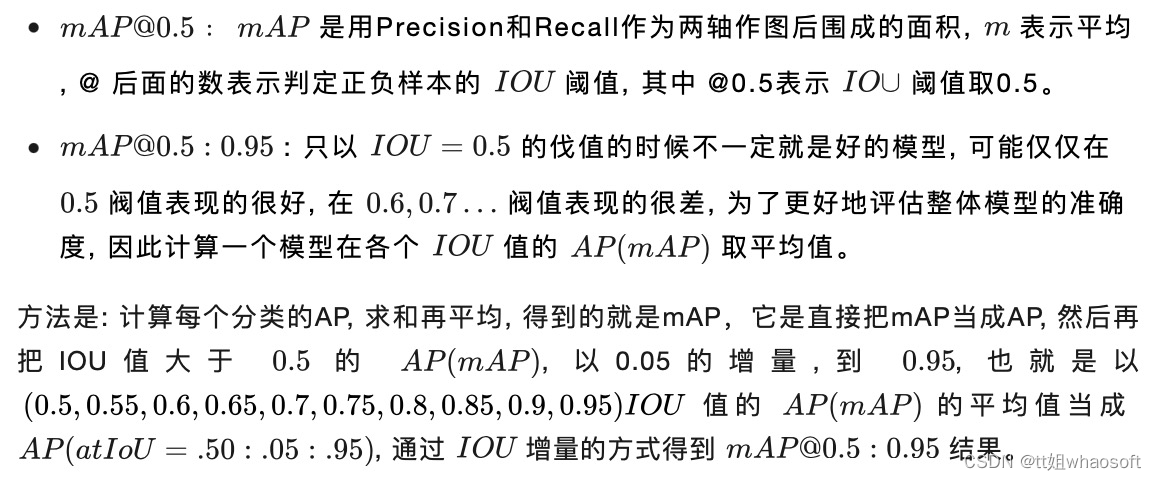
(红色曲线代表,人为的方式将PR曲线变成单调递减,使得计算面积更容易。) AP(Average Percision):AP为平均精度,指的是所有图片内的具体某一类的PR曲线下的面积(横轴为Recall,纵轴为Precision)。 AP衡量的是对一个类检测好坏,mAP就是对多个类的检测好坏。在多类多目标检测中,计算出每个类别的AP后,再除于类别总数,即所有类别AP的平均值,比如有两类,类A的AP值是0.5,类B的AP值是0.2,那么 =(0.5+0.2)/2=0.35。 MAP: 是指所有图片内的所有类别的AP的平均值,map越高代表模型预测精度值越高。
目标检测中的mAP计算 yolov5计算IOU源码解析 源代码地址:https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/one-yolov5/blob/main/utils/metrics.py#L224-L261 # 计算两框的特定iou (DIou, DIou, CIou) def bbox_iou(box1, box2, xywh=True, GIoU=False, DIoU=False, CIoU=False, eps=1e-7): # Returns Intersection over Union (IoU) of box1(1,4) to box2(n,4) # Get the coordinates of bounding boxes 下面条件语句作用是:进行坐标转换从而获取yolo格式边界框的坐标 if xywh: # transform from xywh to xyxy (x1, y1, w1, h1), (x2, y2, w2, h2) = box1.chunk(4, 1), box2.chunk(4, 1) w1_, h1_, w2_, h2_ = w1 / 2, h1 / 2, w2 / 2, h2 / 2 b1_x1, b1_x2, b1_y1, b1_y2 = x1 - w1_, x1 + w1_, y1 - h1_, y1 + h1_ b2_x1, b2_x2, b2_y1, b2_y2 = x2 - w2_, x2 + w2_, y2 - h2_, y2 + h2_ else: # x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1 b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1.chunk(4, 1) b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2.chunk(4, 1) w1, h1 = b1_x2 - b1_x1, b1_y2 - b1_y1 w2, h2 = b2_x2 - b2_x1, b2_y2 - b2_y1 # Intersection area 获取两个框相交的面积。 """ left_line = max(b1_x1, b2_x1) reft_line = min(b1_x2, b2_x2) top_line = max(b1_y1, b2_y1) bottom_line = min(b1_y2, b2_y2) intersect = (reight_line - left_line) * (bottom_line - top_line) """ inter = (flow.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - flow.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \ (flow.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - flow.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0) # Union Area 两个框并到面积 union = w1 * h1 + w2 * h2 - inter + eps # IoU iou = inter / union if CIoU or DIoU or GIoU: cw = flow.max(b1_x2, b2_x2) - flow.min(b1_x1, b2_x1) # convex (smallest enclosing box) width ch = flow.max(b1_y2, b2_y2) - flow.min(b1_y1, b2_y1) # convex height if CIoU or DIoU: # Distance or Complete IoU https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287v1 c2 = cw ** 2 + ch ** 2 + eps # convex diagonal squared rho2 = ((b2_x1 + b2_x2 - b1_x1 - b1_x2) ** 2 + (b2_y1 + b2_y2 - b1_y1 - b1_y2) ** 2) / 4 # center dist ** 2 if CIoU: # https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-SSD-pyflow.blob/master/utils/box/box_utils.py#L47 v = (4 / math.pi ** 2) * flow.pow(flow.atan(w2 / (h2 + eps)) - flow.atan(w1 / (h1 + eps)), 2) with flow.no_grad(): alpha = v / (v - iou + (1 + eps)) return iou - (rho2 / c2 + v * alpha) # CIoU return iou - rho2 / c2 # DIoU c_area = cw * ch + eps # convex area return iou - (c_area - union) / c_area # GIoU https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf return iou # IoU yolov5计算AP源码逐行解析源代码地址: https://github.com/Oneflow-Inc/one-yolov5/blob/main/utils/metrics.py#L96-L121 # 根据PR曲线计算AP def compute_ap(recall, precision): """ Compute the average precision, given the recall and precision curves # Arguments recall: The recall curve (list) precision: The precision curve (list) # Returns Average precision, precision curve, recall curve """ # Append sentinel values to beginning and end 将开区间给补上,补成闭合的区间。 mrec = np.concatenate(([0.0], recall, [1.0])) mpre = np.concatenate(([1.0], precision, [0.0])) # Compute the precision envelope """ 人为的把PR曲线变成单调递减的,例如: np.maximum(accumulate(np.array([21, 23, 18, 19, 20, 13, 12, 11]) ) => np.array([23, 23, 20, 20, 20, 13, 12, 11]) """ mpre = np.flip(np.maximum.accumulate(np.flip(mpre))) # Integrate area under curve method = 'interp' # methods: 'continuous', 'interp' if method == 'interp': # 默认采用 interpolated-precision 曲线, x = np.linspace(0, 1, 101) # 101-point interp (COCO) ap = np.trapz(np.interp(x, mrec, mpre), x) # integrate else: # 'continuous' i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0] # points where x axis (recall) changes ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1]) # area under curve return ap, mpre, mrecwhaosoft aiot http://143ai.com |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |