采用springboot+flowable快速实现工作流 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › workflow工作流 › 采用springboot+flowable快速实现工作流 |
采用springboot+flowable快速实现工作流
|
前言
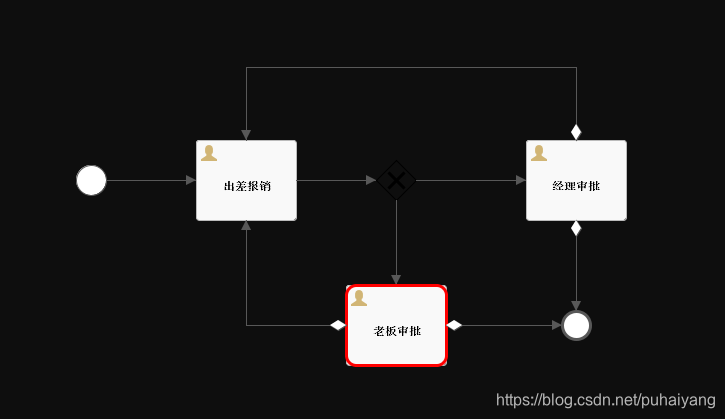
工作流框架大家一定不陌生,各种OA系统里我们常常用到。 对于JAVA领域来说一说起工作流框架第一浮现我在脑海中的便是大名鼎鼎的Activiti了。很久以前学习Activiti框架时我也曾记录过一篇文章。见链接:工作流框架Activiti常用功能初探 尽管当时只是学习了一下在之后的相关工作和项目中并没有用到,通过学习后了解了下, 仅对于知识广度进行了扩宽。 最近在一个开源项目里见到有使用另一个工做流框架:flowable 。简单用了下感觉还是挺方便的,于是乎决定还是要来使用下并在此做下记录,便于后面用到时可以“拿来主义”,哈哈! 什么是flowable?对于flowable是什么以及关于此框架的具体信息可以参看此项目的官方文档:https://www.flowable.org/docs/userguide/index.html 官网对于此项目如何使用有非常详细的描述,只是目前还没有对应的中文文档。 Flowable is a light-weight business process engine written in Java.这是官网文档对此框架的完美解释:Flowable是一个用java语言写的轻量级工作流引擎。 在简单了解flowable后与activiti框架相比的第一感觉就是开发方便快速,易与springBoot等各种框架快速整合。如果项目中需要快速实现一些工作流的相关功能那么用此框架是一个不错的选择。 使用版本用测试方便,这里都使用springBoot和flowable最新的稳定版本 springBoot版本:2.0.1.RELEASE flowable版本:6.3.0 Flowable与springBoot项目整合 添加依赖将flowable的依赖加入到POM中即可,flowable使用需要一个数据库,这里为了方便我选择mysql org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.flowable flowable-spring-boot-starter 6.3.0 mysql mysql-connector-java 5.1.45 org.flowable flowable-spring-boot-starter 6.3.0 mysql mysql-connector-java 5.1.45 flowable配置测试方便flowable配置为默认的即可。为了测试时方便看日志信息,我这里将flowable的定时job功能暂时关闭,其他的都用默认的 当然记得要添加一个数据源,我这里添加的mysql,并且记得建好对应的mysql库,如果没有建就自己建一个吧 like this: CREATE DATABASE `flowable-spring-boot` DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci; spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/flowable-spring-boot?characterEncoding=UTF-8 username: root password: root flowable: #关闭定时任务JOB async-executor-activate: false这样操作后,flowable与springBoot的整个就完成了! 个人非常方便! 然后就可以运行了,初次运行时flowable会将自动执行flowable中的初始化脚本完成工作流所需要的数据表的建立,如果指定的数据库中还未创建过flowable的相关数据表的话。 定义流程文件上面已经完成了flowable与springboot的整合了,接下来就可以使用此框架进行流程需要开发了! 同样在flowable官方文档中对于流程文件它有这样的建议: The Flowable engine expects processes to be defined in the BPMN 2.0 format, which is an XML standard that is widely accepted in the industry. flowable建议采用业界标准BPMN2.0的XML来描述需要定义的工作流。 那么BPMN这个流程文件应该怎么写呢? Typically, such a process definition is modeled with a visual modeling tool, such as the Flowable Designer (Eclipse) or the Flowable Modeler (web application). 上官方文档中有看到这样的描述后即便我不会写也不怕了。通常都是通过专门的流程建模工具来画出来的,可以用Eclipse里的流程插件来画。同时Flowable也提供了对应的web管理台可以对流程文件进行创建。详见: Flowable UI applications 为了方便测试,这里采用一个开源项目中的流程文件,其描述如下: 报销流程 500}]]>其中的两个代理类为: import org.flowable.engine.delegate.TaskListener; import org.flowable.task.service.delegate.DelegateTask; public class ManagerTaskHandler implements TaskListener { @Override public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { delegateTask.setAssignee("经理"); } } public class BossTaskHandler implements TaskListener { @Override public void notify(DelegateTask delegateTask) { delegateTask.setAssignee("老板"); } }为了方便,也可以去掉这两个JAVA类,将其对应的task改写为如下的形式: 尽管上面的BPMN文件很长,但放心,毕竟那是通过相关的工具生成出来的,对于核心的逻辑部分也很少(主要在process 标签内) ,如需要详细了解的可自行学习下BPMN的标签即可!当然,在flowable的使用文档中也有相关的描述,详见:Creating a ProcessEngine 如上定义好一个流程文件后,将其命令为ExpenseProcess.bpmn20.xml并将其放于项目中的resource目录下的processes(如此目录不存在自行创建)目录下就可以了。 like this:
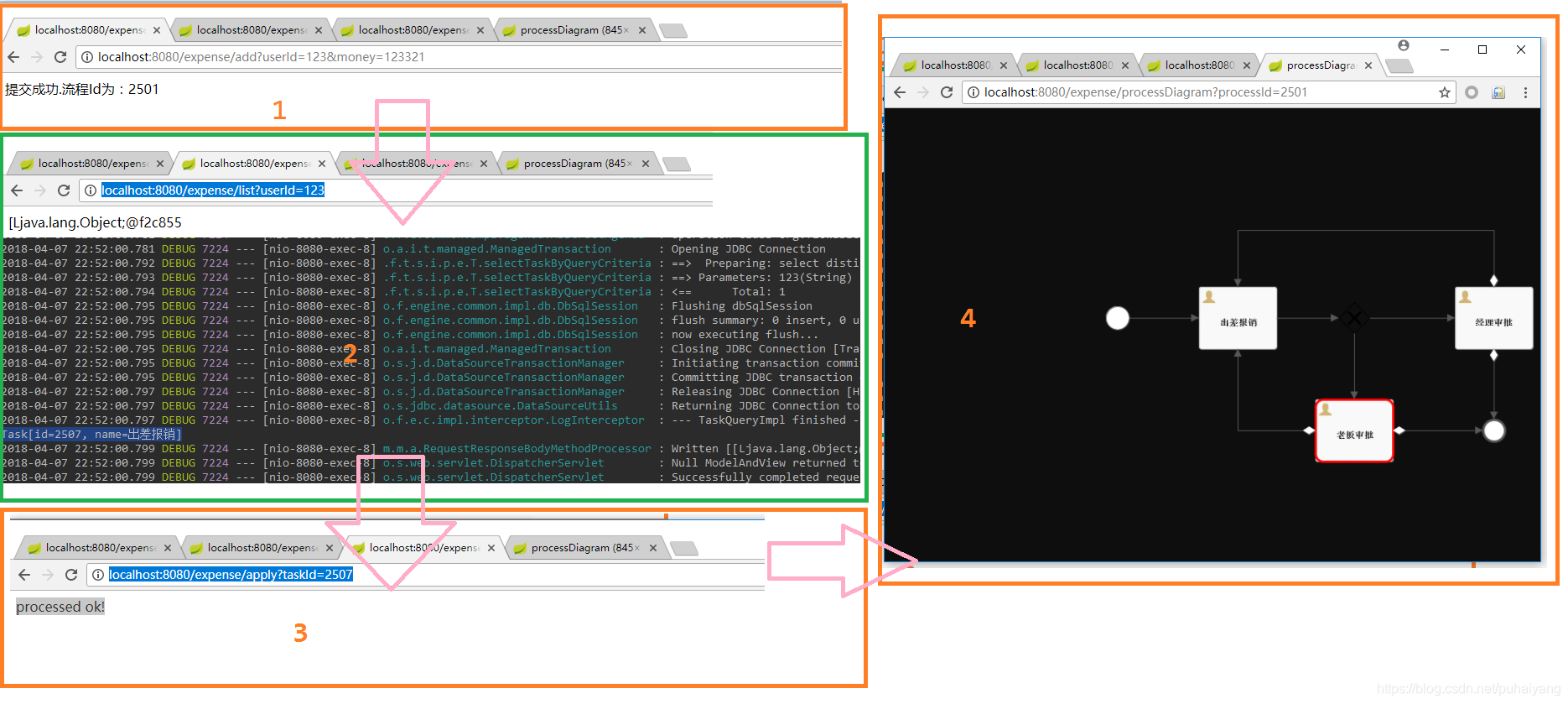
这样当此框架启动的时候它会默认加载resource目录下的processes时就可以将此流程配置加载到数据库进行持久化了 测试controller为了方便这里通过一个controller来完成此DEMO的快速编写 @Controller @RequestMapping(value = "expense") public class ExpenseController { @Autowired private RuntimeService runtimeService; @Autowired private TaskService taskService; @Autowired private RepositoryService repositoryService; @Autowired private ProcessEngine processEngine; /***************此处为业务代码******************/ }写一个controller,并注入由flowable框架启动时自动注册的几个bean,下面的功能将会用到! 开始流程 /** * 添加报销 * * @param userId 用户Id * @param money 报销金额 * @param descption 描述 */ @RequestMapping(value = "add") @ResponseBody public String addExpense(String userId, Integer money, String descption) { //启动流程 HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("taskUser", userId); map.put("money", money); ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("Expense", map); return "提交成功.流程Id为:" + processInstance.getId(); }上面的代码通过接收用户的一个请求传入用户的ID和金额以及描述信息来开启一个报销流程,并返回给用户这个流程的Id 查询流程列表,待办列表 /** * 获取审批管理列表 */ @RequestMapping(value = "/list") @ResponseBody public Object list(String userId) { List tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee(userId).orderByTaskCreateTime().desc().list(); for (Task task : tasks) { System.out.println(task.toString()); } return tasks.toArray().toString(); }通过上面的代码获取出此用户需要处理的流程 批准,同意 /** * 批准 * * @param taskId 任务ID */ @RequestMapping(value = "apply") @ResponseBody public String apply(String taskId) { Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskId(taskId).singleResult(); if (task == null) { throw new RuntimeException("流程不存在"); } //通过审核 HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("outcome", "通过"); taskService.complete(taskId, map); return "processed ok!"; }通过前端传入的任务ID来对此流程进行同意处理 拒绝,不同意 /** * 拒绝 */ @ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "reject") public String reject(String taskId) { HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("outcome", "驳回"); taskService.complete(taskId, map); return "reject"; } 生成当前流程图表 /** * 生成流程图 * * @param processId 任务ID */ @RequestMapping(value = "processDiagram") public void genProcessDiagram(HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, String processId) throws Exception { ProcessInstance pi = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processInstanceId(processId).singleResult(); //流程走完的不显示图 if (pi == null) { return; } Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery().processInstanceId(pi.getId()).singleResult(); //使用流程实例ID,查询正在执行的执行对象表,返回流程实例对象 String InstanceId = task.getProcessInstanceId(); List executions = runtimeService .createExecutionQuery() .processInstanceId(InstanceId) .list(); //得到正在执行的Activity的Id List activityIds = new ArrayList(); List flows = new ArrayList(); for (Execution exe : executions) { List ids = runtimeService.getActiveActivityIds(exe.getId()); activityIds.addAll(ids); } //获取流程图 BpmnModel bpmnModel = repositoryService.getBpmnModel(pi.getProcessDefinitionId()); ProcessEngineConfiguration engconf = processEngine.getProcessEngineConfiguration(); ProcessDiagramGenerator diagramGenerator = engconf.getProcessDiagramGenerator(); InputStream in = diagramGenerator.generateDiagram(bpmnModel, "png", activityIds, flows, engconf.getActivityFontName(), engconf.getLabelFontName(), engconf.getAnnotationFontName(), engconf.getClassLoader(), 1.0); OutputStream out = null; byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int legth = 0; try { out = httpServletResponse.getOutputStream(); while ((legth = in.read(buf)) != -1) { out.write(buf, 0, legth); } } finally { if (in != null) { in.close(); } if (out != null) { out.close(); } } }通过传入流程ID生成当前流程的流程图给前端,如果流程中使用到中文且生成的图片是乱码的,则需要进配置下字体: /** * @author haiyangp * date: 2018/4/7 * desc: flowable配置----为放置生成的流程图中中文乱码 */ @Configuration public class FlowableConfig implements EngineConfigurationConfigurer { @Override public void configure(SpringProcessEngineConfiguration engineConfiguration) { engineConfiguration.setActivityFontName("宋体"); engineConfiguration.setLabelFontName("宋体"); engineConfiguration.setAnnotationFontName("宋体"); } } 整体演示上面的代码写好后就可以演示下整体流程了 1.先启动好此项目,然后创建一个流程: 访问:http://localhost:8080/expense/add?userId=123&money=123321 返回:提交成功.流程Id为:2501 2.查询待办列表: 访问:http://localhost:8080/expense/list?userId=123 输出:Task[id=2507, name=出差报销] 3.同意: 访问:http://localhost:8080/expense/apply?taskId=2507 返回:processed ok! 4.生成流程图: 访问:http://localhost:8080/expense/processDiagram?processId=2501 返回如下图片:
整体流程截图如下:
通过springBoot与flowable的整合体验到了工作流的开发原来如此简单方便。 给此框架点赞,向巨人们致敬! 本文源码地址:https://github.com/puhaiyang/flowable-springboot |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |