Verilog 文件操作 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › verilog输出文件 › Verilog 文件操作 |
Verilog 文件操作
|
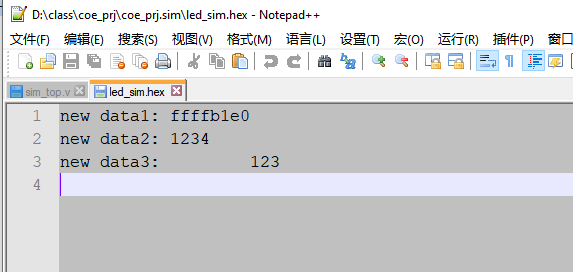
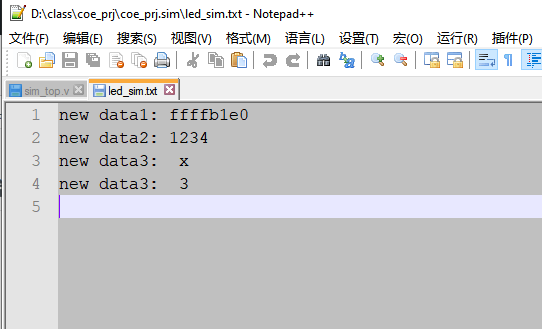
原文网站: Verilog 文件操作-$fdisplay,$fwrite,$fstrobe,$fmonitor – 芯片天地 在Verilog 仿真中, 我们有时需要将仿真得到的数据回写到文件中去,在Verilog 语法中提供$fdisplay,$fwrite,$fstrobe,$fmonitor 等系统函数,帮助开发者将数据写回到文件中。 $display 函数使用:语法解析: $fdisplay(, "", variables); file_desc :文件句柄,表示要对哪个文件进行写操作 string:为写入文件的格式 variables: 为写入的数值。$fdisplay 的使用方法和$display系统函数的使用方法很类似,$display是将格式化的结果输出到控制台上,而$fdisplay 是将格式化的输出结果写入到文件中。 打开一个文本文件,并写入相关的数据: `timescale 1ns / 1ps module sim_top( ); localparam FILE_NAME = "../../../led_sim.txt"; integer file_handle = 0; initial begin file_handle = $fopen(FILE_NAME,"w"); if(!file_handle) begin $display("Could not open File \r"); $stop; end $fdisplay (file_handle, "new data1: %h", file_handle); $fdisplay (file_handle, "new data2: %h", 16'h1234); $fdisplay (file_handle, "new data3: %d", 123); $fclose(file_handle); #200; $stop; end endmodule$fopen 用来打开操作系统上的文件,$fdisplay 将数据格式化写入到文件中去。$fclose 用于将文件关闭。由于打开的文件为文本格式的。 所以存储的文件也是可以被文本工具打开的。
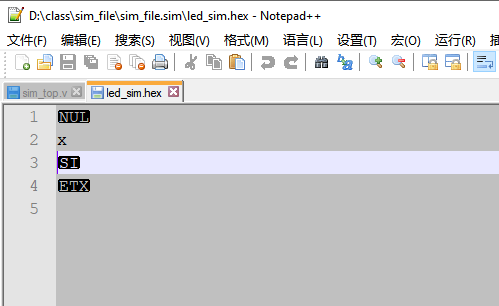
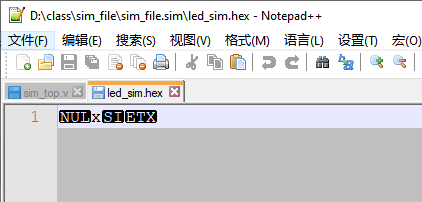
打开一个二进制文件,并写入相关的数据: `timescale 1ns / 1ps module sim_top( ); wire [3:0] y; reg [2:0] a = 1, b = 2; assign y = a + b; localparam FILE_NAME = "../../../led_sim.hex"; integer file_handle = 0; initial begin file_handle = $fopen(FILE_NAME,"wb+"); if(!file_handle) begin $display("Could not open File \r"); $stop; end $fdisplay (file_handle, "%c", $time); $fdisplay (file_handle, "%c", 16'h5678); $fdisplay (file_handle, "%c", y); #10; $fdisplay (file_handle, "%c", y); $fclose (file_handle); #200; $stop; end endmodule
$fwrite 和$write 的使用也是很类似的,和$display,$fdisplay 系统函数比较,但没有自动换行操作。 $fwrite 函数的使用方法与$fdisplay 类似, 只是$fwrite 信号没有缺省的换行操作。 `timescale 1ns / 1ps module sim_top( ); wire [3:0] y; reg [2:0] a = 1, b = 2; assign y = a + b; localparam FILE_NAME = "../../../led_sim.hex"; integer file_handle = 0; initial begin file_handle = $fopen(FILE_NAME,"wb+"); if(!file_handle) begin $display("Could not open File \r"); $stop; end $fwrite(file_handle, "%c", $time); $fwrite(file_handle, "%c", 16'h5678); $fwrite(file_handle, "%c", y); #10; $fwrite(file_handle, "%c", y); $fclose (file_handle); #200; $stop; end endmodule
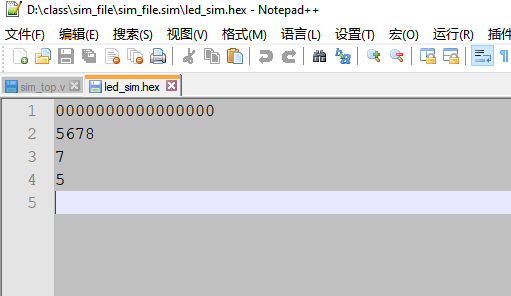
$fstrobe 使用 $fstrobe(, "", variables); file_desc: 文件句柄,表示对哪个文件进行写操作 string:输出文件的格式,可以参考$display 的格式用法 variables:准备写入的变量$fstrobe 和 $strobe 使用函数使用类似,都是在时间节点到达时,执行函数。 `timescale 1ns / 1ps module sim_top( ); wire [3:0] y; reg [2:0] a = 1, b = 2; assign y = a + b; localparam FILE_NAME = "../../../led_sim.hex"; integer file_handle = 0; initial begin file_handle = $fopen(FILE_NAME,"wb+"); if(!file_handle) begin $display("Could not open File \r"); $stop; end $fstrobe (file_handle, "%h", $time); $fstrobe (file_handle, "%h", 16'h5678); $fstrobe (file_handle, "%h", y); a = 5; $fstrobe (file_handle, "%h", y); #10; a = 9; $fstrobe (file_handle, "%c", y); $fclose (file_handle); #200; $stop; end endmodule
从上面的仿真结果可以看出:$fstrobe 系统函数的使用和$strobe 函数的使用非常类似, 也就是说只有到得了时间节点后,才进行统一的赋值输出(a= 1是作废了)。当 a = 9时,虽然后面还有$fstrobe 函数, 但是这时文件已经关闭了, 所以 最新的y 值并没有被写入到文件中去。 $fmonitor函数使用 $fmonitor(, "", variables); file_desc: 文件句柄,需要写入的文件 string:字符表达式,具体可以参考$display variables:写入的数据$fmonitor和$monitor 系统函数的使用类似,只有但variables 列表中发生变化,时间节点到达时,才执行函数。优点是,不必纠结在那里打印输出, 只要出发条件,就可以自动打印输出。 `timescale 1ns / 1ps module sim_top( ); wire [3:0] y; reg [2:0] a = 1, b = 2; assign y = a + b; localparam FILE_NAME = "../../../led_sim.hex"; integer file_handle = 0; initial begin file_handle = $fopen(FILE_NAME,"wb+"); if(!file_handle) begin $display("Could not open File \r"); $stop; end $fmonitor (file_handle, "%h", $time); $fmonitor (file_handle, "%h", 16'h5678); $fmonitor (file_handle, "%h", y); a = 5; #10; a = 3; #10; a = 4; $fclose (file_handle); end endmodule
上例中, 我们可以看到,$fmonitor 可以监控数据的改变,不需要每次都调用$fmonitor。 注意当a = 4时,文件就关闭了, 所以最后一次的计算,并没有写入到文件中。 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |