Python常用遥感模块Rasterio与Rioxarray的安装与使用 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › spyder如何使用安装的模块 › Python常用遥感模块Rasterio与Rioxarray的安装与使用 |
Python常用遥感模块Rasterio与Rioxarray的安装与使用
|
1. Rasterio与Rioxarray安装
Rasterio 是一个很多模块是基于 GDAL 的 Python 包,可用于处理地理空间栅格数据,例如 GeoTIFF 文件。为此,可以使用许多模块和函数,例如,处理来自卫星的原始数据、读取栅格数据、检索地理元数据、转换坐标、裁剪图像、合并多个图像以及以其他格式保存数据。大量的功能和易于实施使 Rasterio 成为卫星数据分析的标准工具。 首先安装 Rasterio 模块,(本人使用 conda 安装时遇到过报错 ImportError: cannot import name 'CRS' from 'pyproj' (unknown location),是由于 pyproj 模块安装不全,因此建议采用后面的离线安装方式或者之后遇到问题时删除 pyproj 模块后再离线安装该模块): conda install gdal conda install rasterio如果安装失败可以采用离线安装的方式,Rasterio 依赖很多第三方库,所以比较麻烦,按下面的顺序依次安装即可,可以尝试使用 pip 安装或者下载 .whl 文件离线安装(注意对上 Python 版本): pyproj Shapely GDAL Fiona rasterio
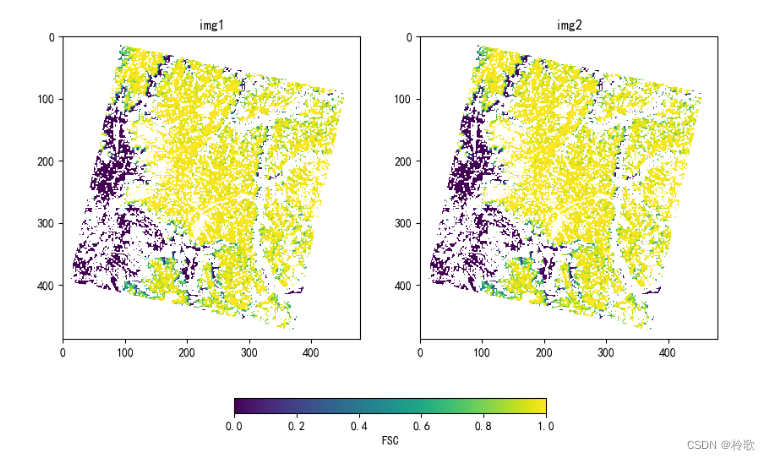
各个模块的链接:Pyproj、Shapely、GDAL、Fiona、Rasterio。 离线安装指令: pip install E:\GDAL-1.2.10-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl在 Python 中使用 Anaconda 安装 rioxarray 包时,首先需要安装 GDAL 和 rasterio,然后再安装 rioxarray: pip install rioxarray 2. 使用教程(1)使用 Rioxarray 读取并展示图像: import rasterio import rioxarray import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False img_path = '../images/tiff_img.tif' img = rioxarray.open_rasterio(img_path) print(img.shape) # (22, 488, 480),第一维为通道数 print(type(img)) # print(type(img.values)) # fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 6)) for ax in axes.flat: ax_img = ax.imshow(img[0], cmap='viridis') for ax, title in zip(axes.flat, ['img1', 'img2']): ax.set_title(title) fig.colorbar(mappable=ax_img, label='FSC', orientation='horizontal', ax=axes, fraction=0.04) # 图例,fraction可调整大小 plt.show()
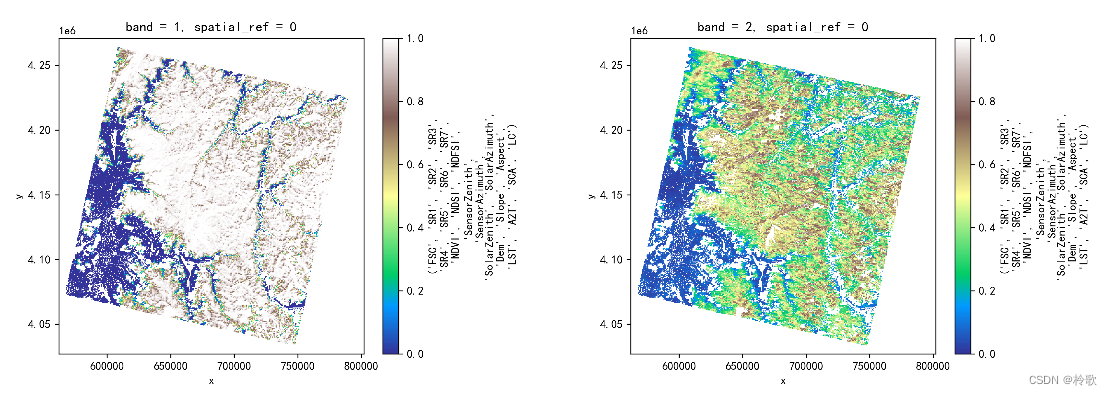
也可以用另一种形式展示(注意如果使用 Rasterio 读取图像则无法使用该方式展示图像): plt.figure(dpi=300, figsize=(15, 5)) plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.5) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) img[0].plot(cmap='terrain') # getting the first band plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) img[1].plot(cmap='terrain') # plt.savefig('1.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight', pad_inches=0) plt.show()
(2)使用 Rasterio 读取图像: img = rasterio.open(img_path).read() print(img.shape) # (22, 488, 480) print(type(img)) #(3)转换为 Tensor 类型: import torch import numpy as np img_torch = torch.tensor(np.array(img.values), dtype=torch.float32) # Rioxarray转Tensor print(img_torch.shape) # torch.Size([22, 488, 480]) img_torch = torch.tensor(img, dtype=torch.float32) # Rasterio转Tensor print(img_torch.shape) # torch.Size([22, 488, 480])(4)将 TIFF 图像逐像素提取出数据构建 CSV 文件: import os import tqdm import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def read_image(img_path): img = rasterio.open(img_path).read() band, height, width = np.shape(img) img_data_list = [] for x in tqdm.trange(height): for y in range(width): temp = img[::, x, y] if np.array(np.isnan(temp), dtype=np.int8).sum() > 0: # 过滤nan值 continue else: img_data_list.append(temp.tolist()) img_arr = np.array(img_data_list) img_arr = np.around(img_arr, 6) # 将数据四舍五入保留6位小数 labels = img_arr[:, 0] # 第一个特征为标签 dataset = img_arr[:, 1:] # 之后的特征为训练数据 print(os.path.basename(img_path), '读取成功!') # return dataset, labels return img_arr total_dataset = np.zeros((1, 22), dtype=np.float32) img_data = read_image(img_path) total_dataset = np.append(total_dataset, img_data, axis=0) total_dataset = np.delete(total_dataset, obj=0, axis=0) # 按行(axis=0)删除第一行(obj=0)元素 print(total_dataset, '\n', np.shape(total_dataset)) # [[0.570768 0.14354 0.159068 ... 0.458602 1. 0.4 ] # [0.307365 0.14354 0.159068 ... 0.458602 1. 0.4 ] # [0.005285 0.14354 0.159068 ... 0.428406 1. 0.4 ] # ... # [0.993229 0.393478 0.370807 ... 0.243081 1. 0.8 ] # [0.967867 0.370807 0.356894 ... 0.243081 1. 0.8 ] # [0.945627 0.321429 0.305714 ... 0.243081 1. 0.8 ]] # (116082, 22) # 一张影像22个波段,每一波段为一种特征,特征名如下,其中FSC既是模型训练时的标签数据也是模型输出数据 feature_name = ['FSC', 'SR1', 'SR2', 'SR3', 'SR4', 'SR5', 'SR6', 'SR7', 'NDVI', 'NDSI', 'NDFSI', 'SensorZenith', 'SensorAzimuth', 'SolarZenith', 'SolarAzimuth', 'Dem', 'Slope', 'Aspect', 'LST', 'A2T', 'SC', 'LCT'] df = pd.DataFrame(total_dataset, columns=feature_name) df.to_csv('../data/MODIS_total_data.csv', index=False) print(df) # FSC SR1 SR2 SR3 ... LST A2T SC LCT # 0 0.570768 0.143540 0.159068 0.165776 ... 0.447205 0.458602 1.0 0.4 # 1 0.307365 0.143540 0.159068 0.165776 ... 0.447205 0.458602 1.0 0.4 # ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... # 116080 0.967867 0.370807 0.356894 0.384162 ... 0.252946 0.243081 1.0 0.8 # 116081 0.945627 0.321429 0.305714 0.327329 ... 0.252946 0.243081 1.0 0.8 # [116082 rows x 22 columns] train_data, valid_data = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.3, random_state=1) # 按7:3的比例划分train_data与valid_data train_data.to_csv('../data/MODIS_train_data.csv', index=False) valid_data.to_csv('../data/MODIS_valid_data.csv', index=False) print(train_data) print(valid_data) # FSC SR1 SR2 ... A2T SC LCT # 65463 1.000000 0.868261 0.860124 ... 0.306415 0.954102 0.4 # 71636 0.000000 0.074969 0.090683 ... 0.492837 0.021780 0.4 # ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... # 77708 0.836359 0.252298 0.268199 ... 0.400243 1.000000 0.4 # 98539 0.004958 0.048758 0.073168 ... 0.547051 0.000000 0.4 # [81257 rows x 22 columns] # FSC SR1 SR2 ... A2T SC LCT # 24035 0.907556 0.579814 0.588075 ... 0.332088 1.000000 0.8 # 26625 0.988592 0.708696 0.702981 ... 0.334435 0.999297 0.4 # ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... # 22745 0.000000 0.054348 0.127143 ... 0.494257 0.532436 0.4 # 31068 0.994422 0.562795 0.532174 ... 0.384267 1.000000 0.4 # [34825 rows x 22 columns] |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |