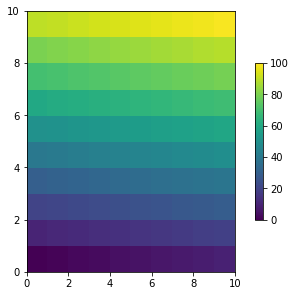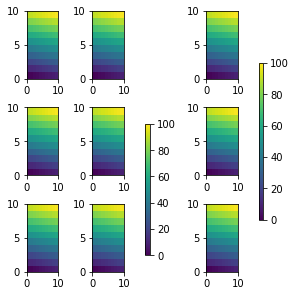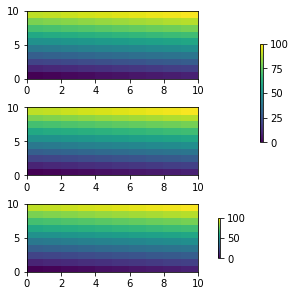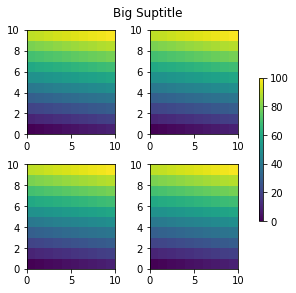matplotlib 进阶之Constrained Layout Guide |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › redraw是什么意思 › matplotlib 进阶之Constrained Layout Guide |
matplotlib 进阶之Constrained Layout Guide
|
文章目录
简单的例子ColorbarsSuptitleLegendsPadding and Spacingspacing with colobars
rcParamsUse with GridSpecManually setting axes positionsManually turning off constrained_layoutLimitaionsIncompatible functions管辖范围
函数链接
matplotlib教程学习笔记 如何干净利落地使用constrained_layout参数来画图 constrained_layout参数会自动地调整subplots和修饰的位置 import matplotlib.pyplot as pltconstrained_layout和tight_latout比较相似,不过是利用一个约束器?来完成。 在任意axex被添加到fig中,constrained_layout需要被激活,有俩种方式能够完成这个目的: plt.subplots(constrained_layout=True) plt.rcParams[‘figure.constrained_layout.use’] = True 简单的例子在matplotlib中,axes的位置是通过标准化的图像坐标轴定制的所以,有可能发生axes超出图片的边界而被剪切掉的情况: # sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 18 #import matplotlib #matplotlib.use('Qt5Agg') import warnings import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib.colors as mcolors import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec import matplotlib._layoutbox as layoutbox plt.rcParams['savefig.facecolor'] = "0.8" plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 4.5, 4. def example_plot(ax, fontsize=12, nodec=False): ax.plot([1, 2]) ax.locator_params(nbins=3) if not nodec: ax.set_xlabel('x-label', fontsize=fontsize) ax.set_ylabel('y-label', fontsize=fontsize) ax.set_title('Title', fontsize=fontsize) else: ax.set_xticklabels('') ax.set_yticklabels('') fig, ax = plt.subplots(constrained_layout=False) example_plot(ax, fontsize=24)
notebook会自动调整的? fig, ax = plt.subplots(constrained_layout=True) example_plot(ax, fontsize=24)
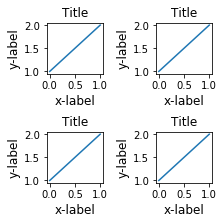
当你有多个子图的时候,你会发现,它们很可能是重叠在一起的 fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=False) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax)
将constrained_layout设置为True可以避免这一尴尬 fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax)
当你使用colorbar()创建colorbar的时候,需要为其预留一点空间,将constrained_layout为True,matplotlib会自动帮你完成这一项工作。 arr = np.arange(100).reshape((10, 10)) norm = mcolors.Normalize(vmin=0., vmax=100.) # see note above: this makes all pcolormesh calls consistent: pc_kwargs = {'rasterized': True, 'cmap': 'viridis', 'norm': norm} fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(4, 4), constrained_layout=True) im = ax.pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax, shrink=0.6);
我们可以利用ax=…来设定colorbar的位置,也就是colorbar所属的axes,这个时候 constrained_layout会给其留一个空,并且其他的图形大小依旧是一致的。 fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(4, 4), constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): im = ax.pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs[1:, ][:, 1], shrink=0.8) #等价于ax=axs[1:, :-1] fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs[:, -1], shrink=0.6);
通过shrink参数,我们可以调整colorbar的长度。 fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(4, 4), constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs[:2]: im = ax.pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs[:2], shrink=0.6) im = axs[2].pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs[2], shrink=0.6);
Suptitle用以设置整个图片的标题, t:str, x: default 0.5 y: default 0.98 constrained_layout 也会贴心地给大标题留出空间。 fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(4, 4), constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): im = ax.pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs, shrink=0.6) fig.suptitle('Big Suptitle');
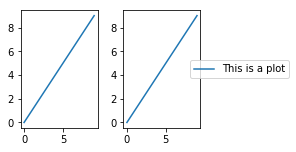
同样constrained_layout能够合适地处理legends fig, ax = plt.subplots(constrained_layout=True) ax.plot(np.arange(10), label='This is a plot') ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(0.8, 0.5));
但是,legend可能会偷取原本应该属于subplots的空间 fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(4, 2), constrained_layout=True) axs[0].plot(np.arange(10)) axs[1].plot(np.arange(10), label='This is a plot') axs[1].legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(0.8, 0.5));#这也不能怪legend啊,自己非要设置bbox_to_anchor作死
后面的没看懂啥意思 Padding and Spacing对于constrained_layout,我们为其设置内边距。Padding设置了边缘与画板的距离,以及plots的最小边距。 通过set_constrained_layout_pads设置: w_pad h_pad fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax, nodec=True) ax.set_xticklabels('') ax.set_yticklabels('') fig.set_constrained_layout_pads(w_pad=8./72., h_pad=8./72., hspace=0., wspace=0.) fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax, nodec=True) ax.set_xticklabels('') ax.set_yticklabels('') fig.set_constrained_layout_pads(w_pad=2./72., h_pad=2./72., hspace=0., wspace=0.)
subplots之间的空间,可以通过wspace和hspace来设置,传入一个比例,然后随着图片大小的变化,宽度也会按照比例进行变化 fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax, nodec=True) ax.set_xticklabels('') ax.set_yticklabels('') fig.set_constrained_layout_pads(w_pad=2./72., h_pad=2./72., hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)
如何我们希望colorbar再稍微远离一点,可以调整pad属性 fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, constrained_layout=True) for ax in axs.flatten(): pc = ax.pcolormesh(arr, **pc_kwargs) fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax, shrink=0.6, pad=0.05) ax.set_xticklabels('') ax.set_yticklabels('') fig.set_constrained_layout_pads(w_pad=2./72., h_pad=2./72., hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)
关于constrained_layout,有5个rcParams参数可以调整 use: 是否使用constrained_layout, 默认为False w_pad, h_pad: 内边距,默认为3./72. inches 3pts wspace, hspace: subplots之间的空间,默认为0.02 plt.rcParams['figure.constrained_layout.use'] = True fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(3, 3)) for ax in axs.flatten(): example_plot(ax)
明白了,就是说使用GridSpec的同时也设置constrained_layout=True是有意义的 plt.rcParams['figure.constrained_layout.use'] = False fig = plt.figure() gs1 = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 1, figure=fig) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[0]) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs1[1]) example_plot(ax1) example_plot(ax2)
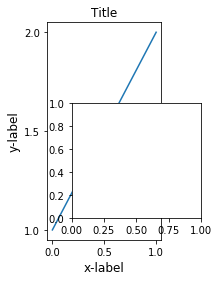
我们可以通过set_position来手动设置axes的位置 fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2) example_plot(axs[0], fontsize=12) axs[1].set_position([0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 0.4])
通过使用fig.execute_constrained_layout()函数,使得数据内的坐标能够被合理放置? from matplotlib.transforms import Bbox fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2) example_plot(axs[0], fontsize=12) fig.execute_constrained_layout() # put into data-space: bb_data_ax2 = Bbox.from_bounds(0.5, 1., 0.2, 0.4) disp_coords = axs[0].transData.transform(bb_data_ax2) fig_coords_ax2 = fig.transFigure.inverted().transform(disp_coords) bb_ax2 = Bbox(fig_coords_ax2) ax2 = fig.add_axes(bb_ax2)
通过fig.set_constrained_layout(False)来手动关闭constrained_layout Limitaions Incompatible functionssubplot函数和constrained_layout是不兼容的,因为constrained_layout是通过gridspecs来布局,而subplot会产生一个独立的gridspec? plt.rcParams['figure.constrained_layout.use']=True fig = plt.figure() ax1 = plt.subplot(221) ax2 = plt.subplot(223) ax3 = plt.subplot(122) example_plot(ax1) example_plot(ax2) example_plot(ax3)
同样的,subplot2grid函数也是不行的 fig = plt.figure() ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (0, 0)) ax2 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (0, 1), colspan=2) ax3 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (1, 0), colspan=2, rowspan=2) ax4 = plt.subplot2grid((3, 3), (1, 2), rowspan=2) example_plot(ax1) example_plot(ax2) example_plot(ax3) example_plot(ax4)
也是通过gridspec来改善 fig = plt.figure() gs = fig.add_gridspec(3, 3) ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 0]) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1:]) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1:, 0:2]) ax4 = fig.add_subplot(gs[1:, -1]) example_plot(ax1) example_plot(ax2) example_plot(ax3) example_plot(ax4)
注意constrained_layout只能管ticklabels, axis labels, titles,和legends,其他的Artist没法管。 函数链接matplotlib.rcParams-基本参数设置 suptitle-整个图片的标题 set_constrained_layout_pads-设置paddings set_position-设置axes的位置 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |