如何使用Python3.5并行执行多个web请求(不适用aiohttp |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › python怎么执行多行 › 如何使用Python3.5并行执行多个web请求(不适用aiohttp |
如何使用Python3.5并行执行多个web请求(不适用aiohttp
腾讯云实验平台开春福利,100+门实验限免体验,精品实验享8折优惠! >>>
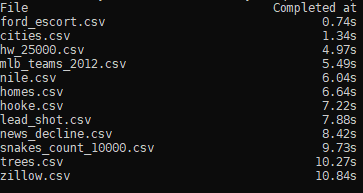
阅读时间 8 分钟 > 作者的生产环境刚从2.6升级到3.5.0,但满足不了aiohttp的最低版本需求。所以在有了这篇文章,如何改造代码,充分利用python3.5 asyncio提供的异步功能。原文链接 近日IT部门最终将我们工作环境的分布式Python版本升级到了3.5.0。这对从2.6版本来说是一次巨大的升级,但依然有些遗憾。3.5.0 不能满足一些库的最小版本需求,这其中就包括aiohttp。 尽管有这些限制,我依然需要写脚本从我们的API获取数以百计的csv文件,然后处理数据。Python本身并不想NodeJS那样基于事件驱动和原生异步,但这并不妨碍Python 也能实现一样的功能。这篇文档将详细介绍我如何学习异步操作,并列出它的优势。 声明: 如果你有更高的版本(3.5.2+),强烈推荐你使用aiohttp。这是个非常健壮的库, 特别适合解决这类问题。网上也有很多关于她的教程。 假设作如下假设: > * 熟悉Python和它的语法 > * 熟悉基础的网络请求 > * 知道异步执行的概念 开始安装requests $ python -m pip install requests没有权限可以做如下安装 $ python -m pip install requests --user 错误的做法:同步请求为了体现并行的好处,先看看同步的做法。我大概描述一下代码将要做什么。我们要执行一个能获取csv文件的GET请求,测量读取其中文本的时间。 我们将从这个网址(https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/)下载多个csv文件, 里面有很多实例数据。 在说明一下,我们将用requests 库里 Session对象,执行GET请求。 首先,需要一个方法执行web请求: def fetch(session, csv): base_url = "https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/" with session.get(base_url + csv) as response: data = response.text if response.status_code != 200: print("FAILURE::{0}".format(url)) # Return .csv data for future consumption return data这个函数使用Session对象和csv名字,执行网络请求,然后返回response里的文本内容。 下面,我们需要一个函数遍历文件列表,然后去请求,统计执行请求的时间。 from timeit import default_timer() def get_data_synchronous(): csvs_to_fetch = [ "ford_escort.csv", "cities.csv", "hw_25000.csv", "mlb_teams_2012.csv", "nile.csv", "homes.csv", "hooke.csv", "lead_shot.csv", "news_decline.csv", "snakes_count_10000.csv", "trees.csv", "zillow.csv" ] with requests.Session() as session: print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format("File", "Completed at")) # Set any session parameters here before calling `fetch` # For instance, if you needed to set Headers or Authentication # this can be done before starting the loop total_start_time = default_timer() for csv in csvs_to_fetch: fetch(session, csv) elapsed = default_timer() - total_start_time time_completed_at = "{:5.2f}s".format(elapsed) print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format(csv, time_completed_at))这个函数创建了一个Session对象,然后遍历csvs_to_fetch里的每个文件。一旦fetch操作结束, 就将计算下载时间,并以易读的格式展示。 最后main函数调用: def main(): # Simple for now get_data_synchronous() main()同步执行的完整代码 import requests from timeit import default_timer def fetch(session, csv): base_url = "https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/" with session.get(base_url + csv) as response: data = response.text if response.status_code != 200: print("FAILURE::{0}".format(url)) # Return .csv data for future consumption return data def get_data_synchronous(): csvs_to_fetch = [ "ford_escort.csv", "cities.csv", "hw_25000.csv", "mlb_teams_2012.csv", "nile.csv", "homes.csv", "hooke.csv", "lead_shot.csv", "news_decline.csv", "snakes_count_10000.csv", "trees.csv", "zillow.csv" ] with requests.Session() as session: print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format("File", "Completed at")) # Set any session parameters here before calling `fetch` # For instance, if you needed to set Headers or Authentication # this can be done before starting the loop total_start_time = default_timer() for csv in csvs_to_fetch: fetch(session, csv) elapsed = default_timer() - total_start_time time_completed_at = "{:5.2f}s".format(elapsed) print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format(csv, time_completed_at)) def main(): # Simple for now get_data_synchronous() main()结果:
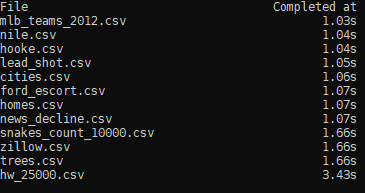
多亏了Python3 asyncio, 通过它我们可以大幅度提高性能。 正确的解决办法: 一次执行多个异步请求为了能起作用,我们要先重做现有的代码。从fetch开始: import requests from timeit import default_timer # We'll need access to this variable later START_TIME = default_timer() def fetch(session, csv): base_url = "https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/" with session.get(base_url + csv) as response: data = response.text if response.status_code != 200: print("FAILURE::{0}".format(url)) # Now we will print how long it took to complete the operation from the # `fetch` function itself elapsed = default_timer() - START_TIME time_completed_at = "{:5.2f}s".format(elapsed) print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format(csv, time_completed_at)) return data下一步, 改造get_data为异步函数 import asyncio from timeit import default_timer from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor async def get_data_asynchronous(): csvs_to_fetch = [ "ford_escort.csv", "cities.csv", "hw_25000.csv", "mlb_teams_2012.csv", "nile.csv", "homes.csv", "hooke.csv", "lead_shot.csv", "news_decline.csv", "snakes_count_10000.csv", "trees.csv", "zillow.csv" ] print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format("File", "Completed at")) # Note: max_workers is set to 10 simply for this example, # you'll have to tweak with this number for your own projects # as you see fit with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as executor: with requests.Session() as session: # Set any session parameters here before calling `fetch` # Initialize the event loop loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() # Set the START_TIME for the `fetch` function START_TIME = default_timer() # Use list comprehension to create a list of # tasks to complete. The executor will run the `fetch` # function for each csv in the csvs_to_fetch list tasks = [ loop.run_in_executor( executor, fetch, *(session, csv) # Allows us to pass in multiple arguments to `fetch` ) for csv in csvs_to_fetch ] # Initializes the tasks to run and awaits their results for response in await asyncio.gather(*tasks): pass现在的代码创建了多个线程,为每个csv文件执行fetch函数进行下载。 最后,我们的mian函数为了正确的初始化异步函数,也需要稍微做些修改。 def main(): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() future = asyncio.ensure_future(get_data_asynchronous()) loop.run_until_complete(future) main()再执行下,看看结果:
略微修改后,12个文件的下载时间3.43s vs 10.84s。下载时间减少了近70%。 import requests import asyncio from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor from timeit import default_timer START_TIME = default_timer() def fetch(session, csv): base_url = "https://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/data/csv/" with session.get(base_url + csv) as response: data = response.text if response.status_code != 200: print("FAILURE::{0}".format(url)) elapsed = default_timer() - START_TIME time_completed_at = "{:5.2f}s".format(elapsed) print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format(csv, time_completed_at)) return data async def get_data_asynchronous(): csvs_to_fetch = [ "ford_escort.csv", "cities.csv", "hw_25000.csv", "mlb_teams_2012.csv", "nile.csv", "homes.csv", "hooke.csv", "lead_shot.csv", "news_decline.csv", "snakes_count_10000.csv", "trees.csv", "zillow.csv" ] print("{0:;30} {1:;20}".format("File", "Completed at")) with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as executor: with requests.Session() as session: # Set any session parameters here before calling `fetch` loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() START_TIME = default_timer() tasks = [ loop.run_in_executor( executor, fetch, *(session, csv) # Allows us to pass in multiple arguments to `fetch` ) for csv in csvs_to_fetch ] for response in await asyncio.gather(*tasks): pass def main(): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() future = asyncio.ensure_future(get_data_asynchronous()) loop.run_until_complete(future) main()希望你喜欢这篇文章,并将这些技术应用到必须使用旧版本Python的项目。 尽管Python没有简单的async / await 模式,但要取得类似的结果,也并不难。 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |