|
一、什么是相位滞后指数?
PLI是基于相位滞后的连通性方法,该方法告诉我们(以下是我看到的两种不同解释):
某一时刻(timePoint)不同试验(trial)收集到的两个信号的相角差在复平面的投影是否始终指向同一侧(虚轴的正侧 或 虚轴的负侧)。(这个与PLV的计算有点类似)某一段时间内(timePeriod)收集到的 两个信号的相角差 在复平面的投影是否始终指向同一侧(虚轴的正侧 或 虚轴的负侧)。 PLI可以忽略由体积效应引起的0和pi的相角差。
二、为什么要忽略0和pi的相角差?
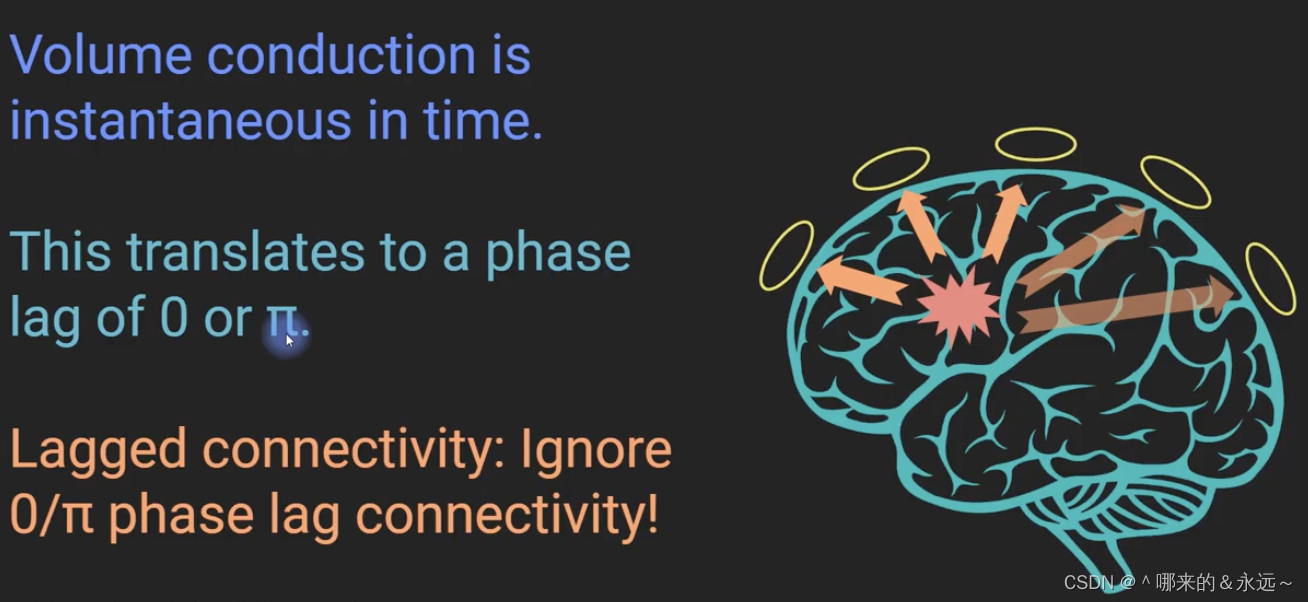

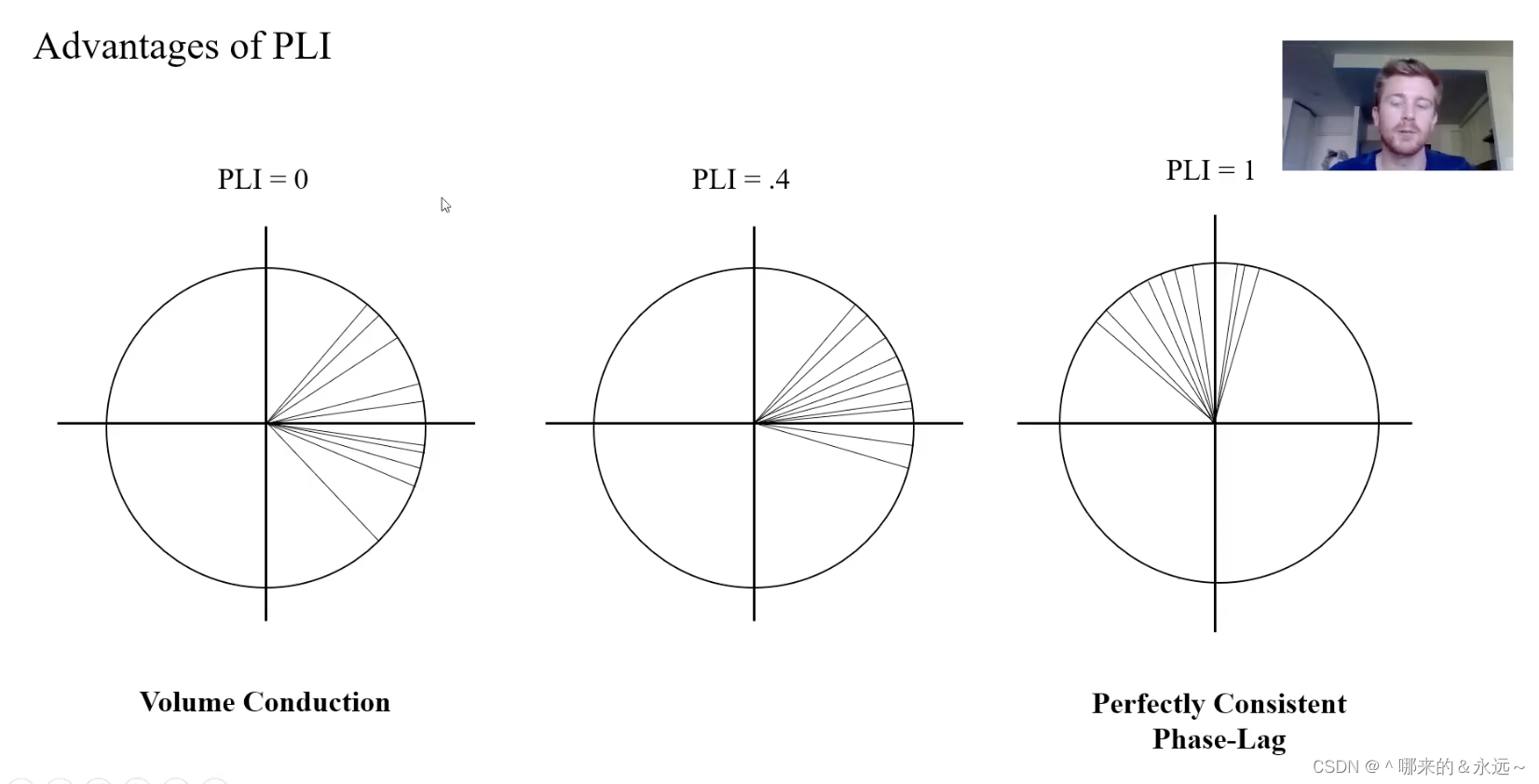
三、复平面上的相位差
 
四、PLI的计算
 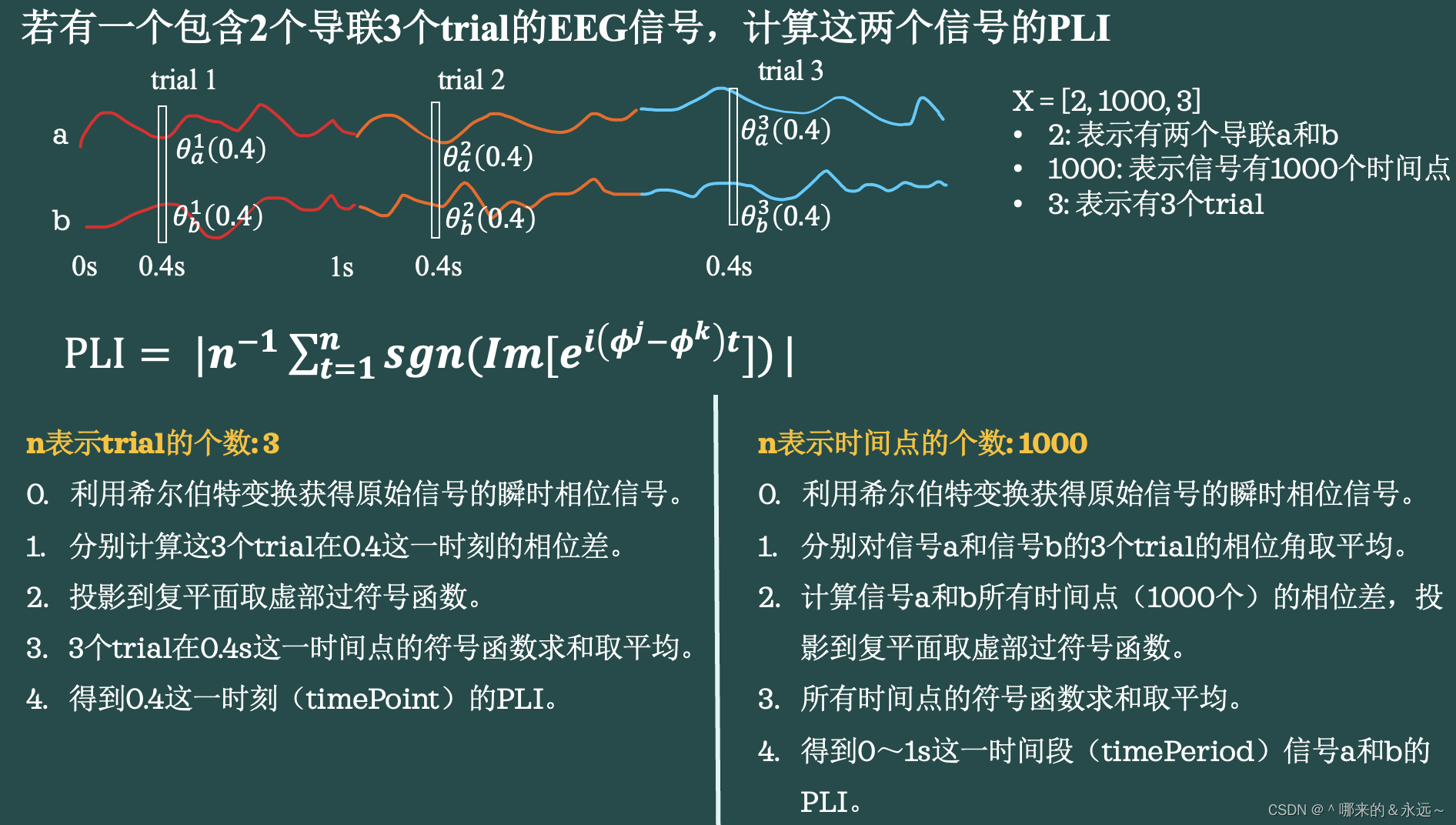
五、MATLAB实现PLI
function PLI = PhaseLagIndex(X, trialTimePoint, timePeriod)
%% Given a multivariate data, returns phase lag index matrix
% trialTimePoint and timePeriod decide which PLI to perform.
% trialTimePoint and timePeriod are both 0 or 1,select timePeriod.
% Modified the mfile of 'phase synchronization'
% X: channel * timePoint * trial
if trialTimePoint==1 && timePeriod==1
trialTimePoint = 0;
end
if trialTimePoint==0 && timePeriod==0
timePeriod = 1;
end
numChannels = size(X, 1);
numtimePoint = size(X, 2);
numTrials = size(X, 3);
%% Obtain the instantaneous phase of each channel by Hilbert transform
dataP = zeros(size(X));
for channelCount = 1:numChannels
dataP(channelCount, :, :) = angle(hilbert(squeeze(X(channelCount, :, :))));
end
% whether the projections of phase angle differences collected from different trials at a given moment always point to the same side in the complex plane
if trialTimePoint == 1
%% Calculation of PLI
PLI = ones(numtimePoint, numChannels, numChannels);
for ch1 = 1:numChannels-1
for ch2 = ch1+1:numChannels
%%%%%% phase lage index
PDiff = squeeze(dataP(ch1,:,:)) - squeeze(dataP(ch2,:,:)); % hase difference at each time point
PLI(:,ch1,ch2) = abs(sum(sign(sin(PDiff)), 2)/numTrials); % only count the asymmetry
PLI(:,ch2,ch1) = PLI(:,ch1,ch2);
end
end
end
% Whether the projections of the phase angle differences collected in a given time period
% always point to the same side of the complex plane
% (positive side of the imaginary axis or negative side of the imaginary axis).
if timePeriod == 1
% Phase averaging between trials
phi1 = mean(dataP, 3);
ch = numChannels;
%% Calculation of PLI
PLI = ones(ch,ch);
for ch1=1:ch-1
for ch2=ch1+1:ch
%%%%%% phase lage index
PDiff=phi1(ch1,:)-phi1(ch2,:); % phase difference
PLI(ch1,ch2)=abs(mean(sign(sin(PDiff)))); % only count the asymmetry
PLI(ch2,ch1)=PLI(ch1,ch2);
end
end
end
end
六、计算结果差异
下面是我用这两种方法计算的某一时间区间的PLI,很明显这两个差别很大,我也不晓得哪个才是对的,但我更倾向于第一个,n表示trial的个数。 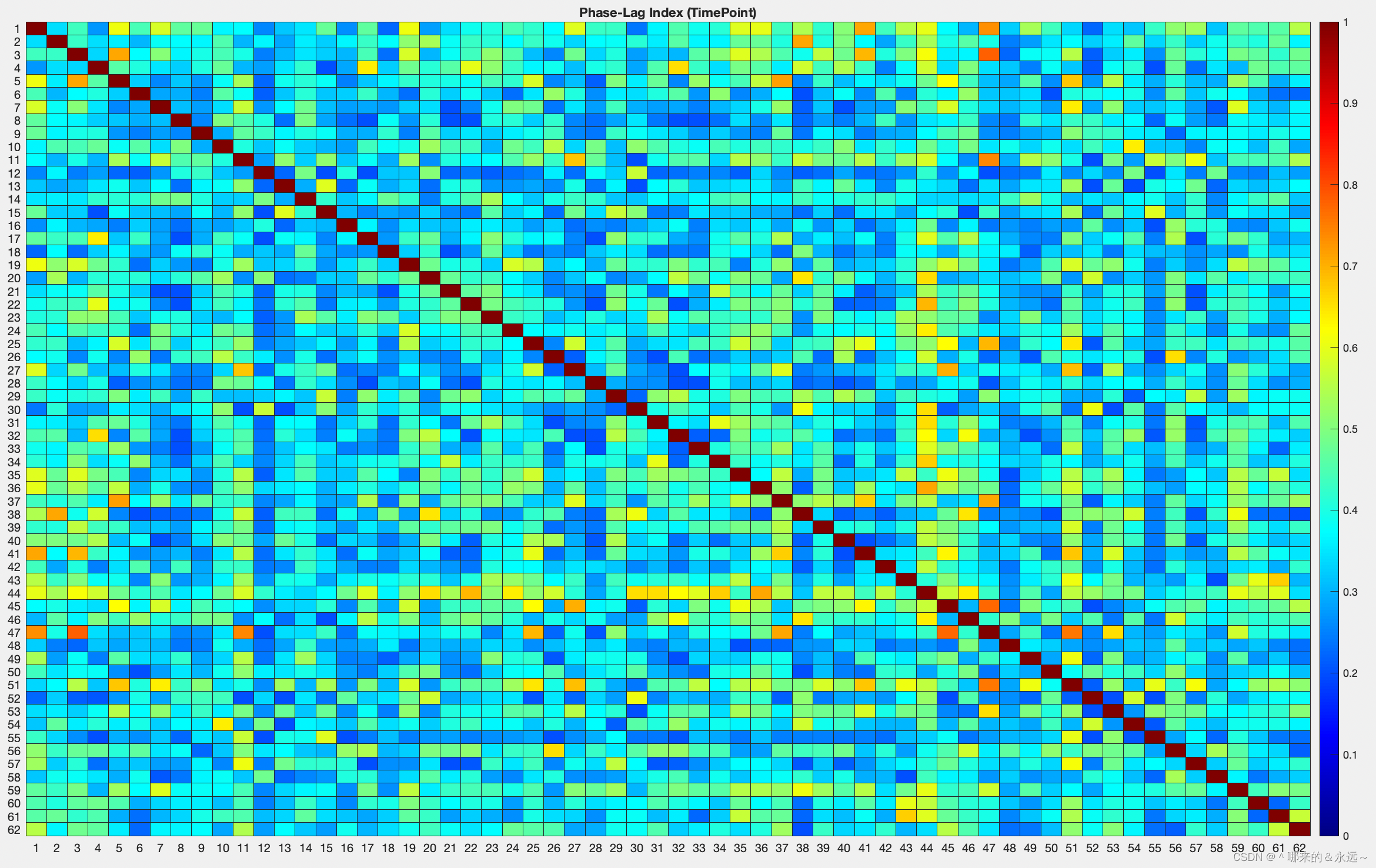 n表示trial时,要计算某区间的PLI:先计算每一个时刻的PLI,得到所有时刻的PLI后,再对所需的时间区间的PLI取平均。 n表示trial时,要计算某区间的PLI:先计算每一个时刻的PLI,得到所有时刻的PLI后,再对所需的时间区间的PLI取平均。 
|







 n表示trial时,要计算某区间的PLI:先计算每一个时刻的PLI,得到所有时刻的PLI后,再对所需的时间区间的PLI取平均。
n表示trial时,要计算某区间的PLI:先计算每一个时刻的PLI,得到所有时刻的PLI后,再对所需的时间区间的PLI取平均。 