python 不同格式的读取效率(pickle/npy/npz/hdf) |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › php读取文件快还是数据库快 › python 不同格式的读取效率(pickle/npy/npz/hdf) |
python 不同格式的读取效率(pickle/npy/npz/hdf)
|
import numpy as np
import time
import pickle as pkl
import os
import tables
a1 = np.random.normal(size=[256, 4096])
label = np.random.normal(size=[256, 1])
all_batch = np.concatenate([a1, label], 1)
# 重新分割
# a1, a2 = np.split(all_batch, [-1], 1)
all_batches = []
for i in range(10):
all_batches.append(all_batch)
all_batches = np.array(all_batches)
print(all_batches.shape)
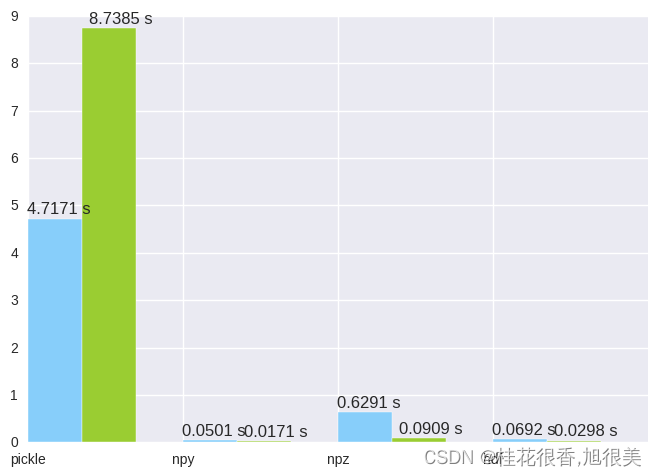
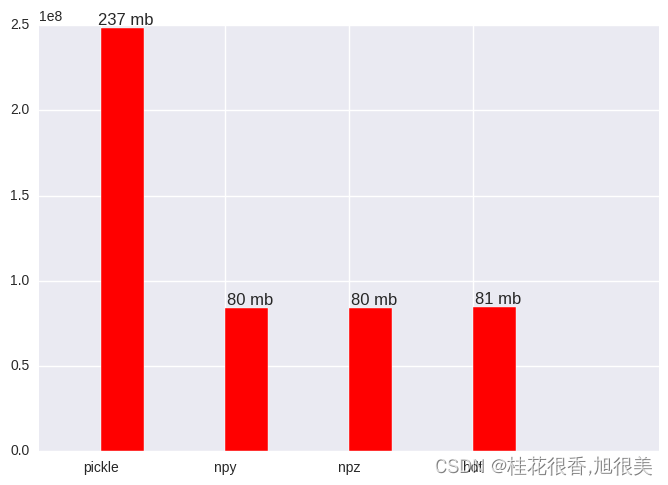
np.random.normal np.concatenate (10, 256, 4097) Pickle s_t = time.time() pkl_name = "a.pkl" with open(pkl_name, "wb") as f: pkl.dump(all_batches, f) pkl_in_time = time.time()-s_t print("pkl dump costs {} sec".format(pkl_in_time)) s_t = time.time() with open(pkl_name) as f: new_a = pkl.load(f) pkl_out_time = time.time() - s_t print("pkl load costs {} sec".format(pkl_out_time)) pkl_size = os.path.getsize(pkl_name) print("pkl file size: {} byte, {} mb".format(pkl_size, float(pkl_size)/(1024*1024))) pkl dump costs 4.71714997292 sec pkl load costs 8.73846507072 sec pkl file size: 248496184 byte, 236.984428406 mb npy s_t = time.time() npy_name = "a.npy" with open(npy_name, "wb") as f: np.save(f, arr=all_batches) npy_in_time = time.time() - s_t print("npy save costs {} sec".format(npy_in_time)) s_t = time.time() with open(npy_name) as f: new_a = np.load(f) npy_out_time = time.time() - s_t print("npy load costs {} sec".format(npy_out_time)) npy_size = os.path.getsize(npy_name) print("npy file size: {} byte, {} mb".format(npy_size, float(npy_size) / (1024 * 1024))) npy save costs 0.0500998497009 sec npy load costs 0.0170629024506 sec npy file size: 83906640 byte, 80.0196075439 mb npz和python自带的zip方法的含义很像,意味着存储多个array,load的时候指定名称,比如data=arr1,label=arr2这样,取的时候,也不能只计算load的时间,因为这个load方法实际上没有把数据加到内存,只不过是返回一个文件io,读取要像使用dict一样指定名称。 s_t = time.time() npz_name = "a.npz" with open(npz_name, "wb") as f: np.savez(f, arr=all_batches) npz_in_time = time.time() - s_t print("npz save costs {} sec".format(npz_in_time)) s_t = time.time() with open(npz_name) as f: npz_f= np.load(f) new_a = npz_f["arr"] npz_out_time = time.time() - s_t print("npz load costs {} sec".format(npz_out_time)) npz_size = os.path.getsize(npz_name) print("npz file size: {} byte, {} mb".format(npz_size, float(npz_size) / (1024 * 1024))) npz save costs 0.629067182541 sec npz load costs 0.0908648967743 sec npz file size: 83906752 byte, 80.0197143555 mb hdfHDF也是一种自描述格式文件,主要用于存储和分发科学数据。气象领域中卫星数据经常使用此格式,比如MODIS,OMI,LIS/OTD等卫星产品。 s_t = time.time() table_name = "a.hdf" f = tables.openFile(table_name, 'w') atom = tables.Atom.from_dtype(all_batches.dtype) ds = f.createCArray(f.root, 'test_a', atom, all_batches.shape) ds[:] = all_batches f.close() table_in_time = time.time() - s_t print("table save costs {} sec".format(table_in_time)) s_t = time.time() f = tables.openFile(table_name, "r") hdf5_data = f.root.test_a[:] f.close() table_out_time = time.time() - s_t print("table load costs {} sec".format(table_out_time)) table_size = os.path.getsize(table_name) print("table file size: {} byte, {} mb".format(table_size, float(table_size) / (1024 * 1024))) table save costs 0.0691781044006 sec table load costs 0.0298302173615 sec table file size: 84613976 byte, 80.6941757202 mb 可视化对比结果 import seaborn from matplotlib import pyplot as plt plt.figure() X = np.array(range(4)) Y_in = [pkl_in_time, npy_in_time, npz_in_time, table_in_time] Y_out = [pkl_out_time, npy_out_time, npz_out_time, table_out_time] print(Y_out) plt.bar(X,Y_in,width = 0.35,facecolor = 'lightskyblue',edgecolor = 'white') plt.bar(X+0.35,Y_out,width = 0.35,facecolor = 'yellowgreen',edgecolor = 'white') #给图加text for x,y in zip(X,Y_in): plt.text(x+0.2, y+0.05, '%.4f s' % y, ha='center', va= 'bottom') for x,y in zip(X,Y_out): plt.text(x+0.6, y+0.05, '%.4f s' % y, ha='center', va= 'bottom') plt.xticks([0,1,2,3],["pickle", "npy", "npz", "hdf"]) plt.figure() Y_size = [pkl_size, npy_size, npz_size, table_size] plt.bar(X+0.5,Y_size,width = 0.35,facecolor = 'red',edgecolor = 'white') for x,y in zip(X,Y_size): plt.text(x+0.7, y+0.05, '%.0f mb' % (float(y)/(1024*1024)), ha='center', va= 'bottom') plt.xticks([0.5,1.5,2.5,3.5],["pickle", "npy", "npz", "hdf"]) plt.xlim(0.0,5) plt.show() [8.738465070724487, 0.017062902450561523, 0.09086489677429199, 0.029830217361450195]
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |