自己动手写编译器:DFA状态机最小化算法 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › nfa转变为dfa › 自己动手写编译器:DFA状态机最小化算法 |
自己动手写编译器:DFA状态机最小化算法
|
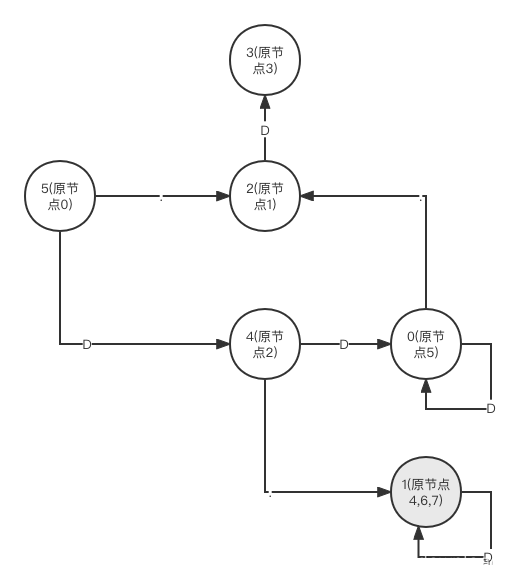
上一节我们完成了从NFA到DFA的状态机转换,有个问题是状态机并非处于最有状态: 首先我们把所有节点罗列成下表: 所有节点输入字符D后跳转输入字符.后跳转是否是接收状态021no13_no254no3__yes46_yes551no67_yes77_yes第一步我们先把节点根据是否为终结点分成两组,非终结点为一组,终结点为一组,并给每组设置编号,第一组编号0,第二组编号1: [0,1,2,5]->(0), [3,4,6,7]->(1) 接下来我们分别进入每个分区,分别取出其中两个节点,如果他们接收相同输入,如果跳转的节点在不同分区,那么我们就认为这两个节点不能合成一个点,首先我们看分区0中的点0,它接收D后跳转到2,而节点2位于分区0;分区0中的点1接收D后跳转到节点3,它位于分区1;分区0中节点2接收D后跳转到节点5,后者位于分区0;分区0中节点5接收D后跳转5,后者同样位于分区0,于是我们把分区0中的节点1单独隔离出来形成一个分区: [0,2,5]->(0), [1]->(2), [3,4,6,7]->(1) 接着我们看分区1,分区1中的节点3接收D后没有跳转,节点4接收D后跳转6,后者位于分区1;节点6,7接收D后跳转分区1,因此节点3要从分区1中隔离出来自己形成一个分区: [0,2,5]->(0), [1]->(2), [3]->(3), [4,6,7]->(1) 接下来我们以输入’.‘来看每个分区,在分区0中节点0接收’.‘后跳转1,后者位于分区2;节点2接收’.‘,跳转到节点4,后者位于分区1,节点5接收’.'后跳转到节点1,后者为于分区2,因此我们把节点2从分区0中区分开成为一个新分区: [0,5]->(0), [1]->(2), [3]->(3), [2]->(4), [4,6,7]->(1) 对于只有1个节点的分区我们可以忽略,现在我们看分区1,节点4接收’.‘后没有跳转,节点6接收’.'后没有跳转,节点7接收’.'后也是没有跳转,因此这三个点依然可以属于同一个分区。接下来我们继续返回到分区0,节点0接收D后跳转节点2,后者位于分区4,节点5接收D后跳转到节点5,后者位于分区0,因此我们把点0从分区0拿出来形成一个新分区: [5]->(0), [1]->(2), [3]->(3), [2]->(4),[4,6,7]->(1), [0]->(5) 由此我们把节点4,6,7合并成一个节点,其他分区都只有一个节点,现在我们用分区编号替代每个分区集合中的点,由此得到DFA状态机如下:
下面我们给出算法的步骤描述,首先给出变量声明: c: 当前输入字符 group: 一个分区中节点的集合,它也对应一个分区 groups: 当前分区集合 new: 当前分区中被拿出来的节点集合 first: 当前分区中第一个节点 next: 分区中不同于first的另一个节点,如果当前分区除了first对应节点外没有其他未访问过的节点,那么它取值nil go_first: first对应节点在接收c表示的输入后跳转的节点 go_next: next对应节点接收c表示输入后跳转的节点。 初始化: 先将所有非终结节点放入分区0,将所有终结节点放入分区1,于是groups中包含两个group对象 重复如下步骤,直到groups为空 for(从groups中取出一个group) { new = [] first = group中第一个节点 next = group中不同于first的节点,如果没有新节点那么设置为nil for next { for (当前输入字符c) { go_first = first 对应节点接收字符c后跳转的节点 go_next = next对应节点接收字符c后跳转的节点 if go_first 和 go_next不属于同一个分区,把next对应节点加入到集合new } next 指向当前集合中下一个节点 } if new != nil { groups = append(groups, new } } 下面我们看看具体代码实现,在nfa_to_dfa.go中继续添加以下代码: func (n *NfaDfaConverter) initGroups() { //先把节点根据接收状态分为两个分区 for i := 0; i n.groups[1] = append(n.groups[1], n.dstates[i].state) //记录状态点对应的分区 n.inGroups[n.dstates[i].state] = 1 } else { n.groups[0] = append(n.groups[0], n.dstates[i].state) n.inGroups[n.dstates[i].state] = 0 } } n.numGroups = 2 } func (n *NfaDfaConverter) printGroups() { //打印当前分区的信息 for i := 0; i fmt.Printf("%d ", group[j]) } fmt.Printf("\n") } } func (n *NfaDfaConverter) minimizeGroups() { for { oldNumGroups := n.numGroups for current := 0; current //对于只有1个元素的分区不做处理 continue } idx := 0 //获取分区第一个元素 first := n.groups[current][idx] newPartition := false for idx+1 gotoFirst := n.dtrans[first][c] gotoNext := n.dtrans[next][c] if gotoFirst != gotoNext && (gotoFirst == F || gotoNext == F || n.inGroups[gotoFirst] != n.inGroups[gotoNext]) { //如果first和next对应的两个节点在接收相同输入后跳转的节点不在同一分区,那么需要将next对应节点加入新分区 //先将next对应节点从当前分区拿走 n.groups[current] = append(n.groups[current][:idx+1], n.groups[current][idx+2:]...) n.groups[n.numGroups] = append(n.groups[n.numGroups], next) n.inGroups[next] = n.numGroups newPartition = true break } } if !newPartition { //如果next没有被拿出当前分区,那么idx要增加去指向下一个元素 idx += 1 } else { //如果next被挪出当前分区,那么idx不用变就能指向下一个元素♀️ newPartition = false } } if len(n.groups[n.numGroups]) > 0 { //有新的分区生成,因此分区计数要加1 n.numGroups += 1 } } if oldNumGroups == n.numGroups { //如果没有新分区生成,算法结束 break } } n.printGroups() } func (n *NfaDfaConverter) fixTran() { newDTran := make([][]int, DFA_MAX) //新建一个跳转表 for i := 0; i //从当前分区取出一个节点即可 state := n.groups[i][0] for c := MAX_CHARS - 1; c >= 0; c-- { if n.dtrans[state][c] == F { newDTran[state][c] = F } else { destState := n.dtrans[state][c] destPartition := n.inGroups[destState] newDTran[state][c] = destPartition } } } n.dtrans = newDTran } func (n *NfaDfaConverter) MinimizeDFA() { n.initGroups() n.minimizeGroups() n.fixTran() } func (n *NfaDfaConverter) PrintMinimizeDFATran() { for i := 0; i if n.dtrans[i][j] != F { fmt.Printf("from state %d jump to state %d with input: %s\n", i, n.dtrans[i][j], string(j)) } } } }完成上面代码后,我们在main.go调用一下上面的实现: func main() { lexReader, _ := nfa.NewLexReader("input.lex", "output.py") lexReader.Head() parser, _ := nfa.NewRegParser(lexReader) start := parser.Parse() parser.PrintNFA(start) //str := "3.14" //if nfa.NfaMatchString(start, str) { // fmt.Printf("string %s is accepted by given regular expression\n", str) //} nfaConverter := nfa.NewNfaDfaConverter() nfaConverter.MakeDTran(start) nfaConverter.PrintDfaTransition() nfaConverter.MinimizeDFA() fmt.Println("---------new DFA transition table ----") nfaConverter.PrintMinimizeDFATran() }上面代码运行后输出结果如下: 分区号: 0分区节点如下: 0 分区号: 1分区节点如下: 3 分区号: 2分区节点如下: 1 分区号: 3分区节点如下: 4 6 7 分区号: 4分区节点如下: 2 分区号: 5分区节点如下: 5 ---------new DFA transition table ---- from state 0 jump to state 2 with input: . from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 0 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 1 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 2 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 3 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 4 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 5 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 6 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 7 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 8 from state 0 jump to state 4 with input: 9 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 0 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 1 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 2 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 3 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 4 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 5 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 6 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 7 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 8 from state 1 jump to state 1 with input: 9 from state 2 jump to state 3 with input: . from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 0 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 1 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 2 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 3 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 4 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 5 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 6 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 7 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 8 from state 2 jump to state 5 with input: 9 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 0 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 1 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 2 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 3 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 4 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 5 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 6 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 7 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 8 from state 4 jump to state 3 with input: 9 from state 5 jump to state 2 with input: . from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 0 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 1 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 2 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 3 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 4 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 5 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 6 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 7 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 8 from state 5 jump to state 5 with input: 9上面输出的跳转表画出来时可能跟我们上面不太一样,不一样的主要是节点的编号,但是节点的跳转结构跟我们在前面的分析完全相符,更详细的讲解和调试演示,请在B站搜索coding迪斯尼。 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |
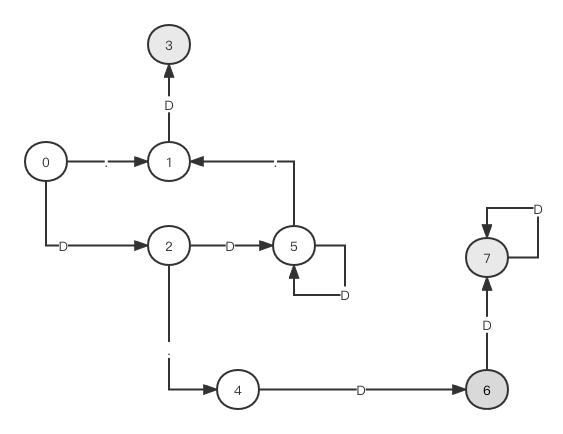 在上图的状态机中,状态6和7其实可以合成一个状态点,本节我们看看如何将这类节点进行合并,使得状态机处于最精简状态(状态4也是终结点,图中有误)。
在上图的状态机中,状态6和7其实可以合成一个状态点,本节我们看看如何将这类节点进行合并,使得状态机处于最精简状态(状态4也是终结点,图中有误)。