UE4 面试题整理 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › new和malloc有什么区别 › UE4 面试题整理 |
UE4 面试题整理
|
1、new与malloc的区别 new:
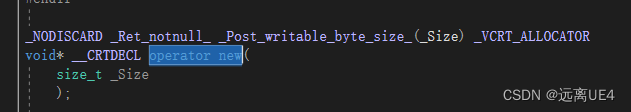
new首先会去调用operator new函数,申请足够的内存(大多数底层用malloc实现),然后调用类型的构造函数来初始化变量,最后返回自定义类型的指针,delete先调用析构函数,然后调用operator delete函数释放内存(大多数底层用free实现) __cdecl 是C Declaration的缩写(declaration,声明) malloc:
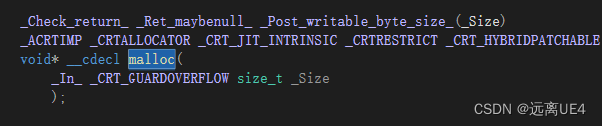
malloc是库函数,只能申请内存,没有初始化功能 所以new与malloc最大的区别就是new能进行构造函数初始化 2、strcpy、sprintf、memcpy的区别 strcpy:用于将一个字符串复制到另一个字符串中 sprintf:sprintf函数用于将格式化的字符串输出到一个字符数组中 char str[10]; int num = 4; sprintf(str, "number is %d", num); printf("%s\n", str); // 输出 number is 4memcpy:用于将一个内存地址的数据复制到另一个内存地址中 3、子弹穿墙问题
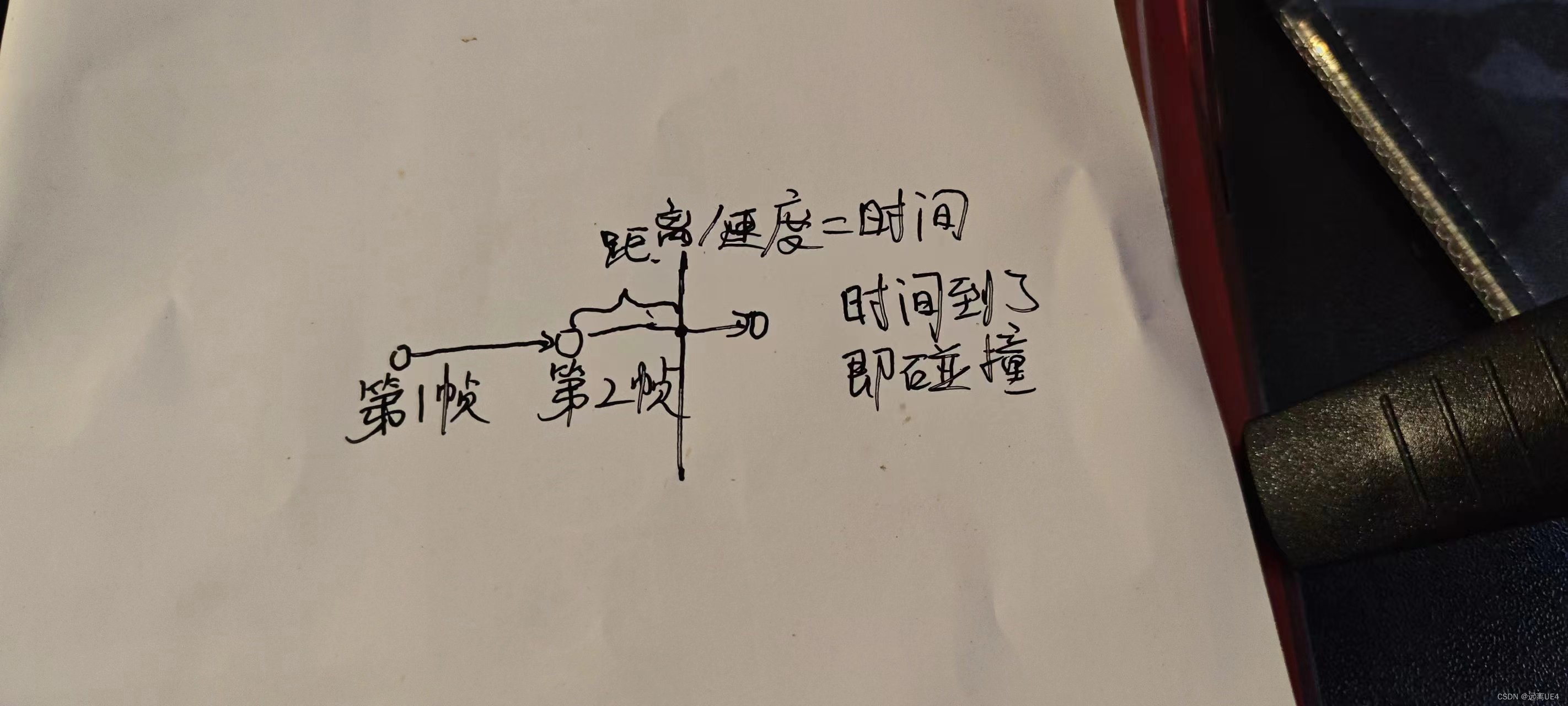
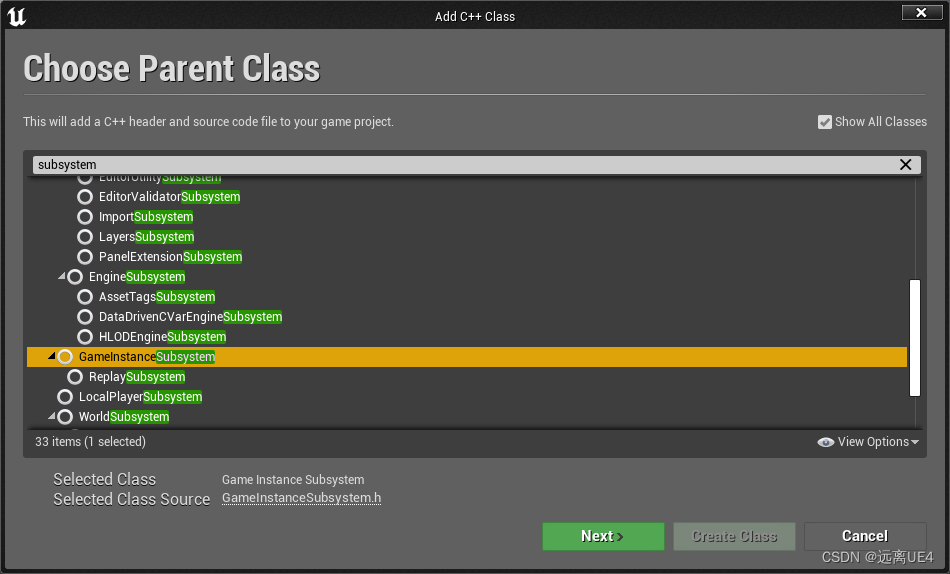
子弹向前打出一个身位长的射线,若打到了墙面则开始计算子弹与墙的距离,在通过距离除以速度算出时间,时间过后则进行碰撞 4、UE4如何切关卡后保留数据 存放在GameInstancesubsystem中,不要存在gameinstance内,这样会导致项目臃肿
5、UE4客户端能否使用AIController 不可以,在DS(dedicated server)模型下,AIController只存在于服务端,其主要是通过在服务端对Pawn进行操控, 然后再同步到客户端。 6、Blueprintable与NotBlueprintable
将C++类加入蓝图类 如果为NotBlueprintable则不能被蓝图化 7、BlueprintImplementEvent与BlueprintNativeEvent的区别
如果实现了蓝图,那么C++的Implement接口则不调用
如果没写蓝图接口则调用C++接口
而BlueprintImplementEvent只是做接口给蓝图,不拓展C++接口。 8、C++类中默认有什么函数 1、构造函数 2、拷贝构造函数 3、析构函数 4、重载赋值运算符函数 9、UE4生命周期 从先到后:UGameEngine->GameInstance->World和WorldContext->PersistentLevel->GameMode->GameState->PlayerController->PlayerState->HUD->Character 在UGameEngine(继承自UEngine)
UGameInstance继承自FExec,Exec就是UE4的命令行 void UGameInstance::InitializeStandalone(const FName InPackageName, UPackage* InWorldPackage) { // Creates the world context. This should be the only WorldContext that ever gets created for this GameInstance. WorldContext = &GetEngine()->CreateNewWorldContext(EWorldType::Game); WorldContext->OwningGameInstance = this; // In standalone create a dummy world from the beginning to avoid issues of not having a world until LoadMap gets us our real world UWorld* DummyWorld = UWorld::CreateWorld(EWorldType::Game, false, InPackageName, InWorldPackage); DummyWorld->SetGameInstance(this); WorldContext->SetCurrentWorld(DummyWorld); Init(); }然后在GameInstance的初始化单例中生成对应的World和一个WorldContext
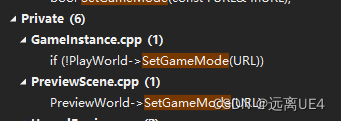
同时GameInstance内对GameMode进行绑定生成,但这个动作不是在初始化函数中进行的,而是在
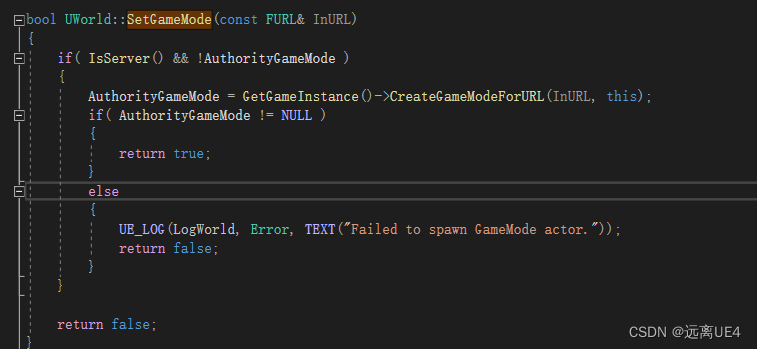
在PreviewScene中在构造函数中调用了SetGameMode
World中在FSeamlessTravelHandler类中进行Tick设置 去调用的
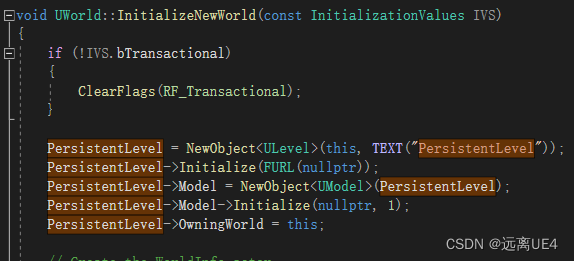
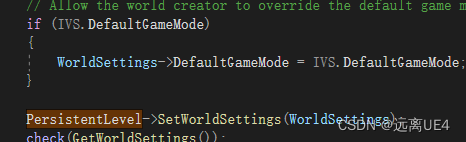
然后在GameMode里面对所有的GameState,PlayerController,PlayerState,HUD和Default Panw,Spectator进行绑定 void UWorld::InitializeNewWorld(const InitializationValues IVS) { if (!IVS.bTransactional) { ClearFlags(RF_Transactional); } PersistentLevel = NewObject(this, TEXT("PersistentLevel")); PersistentLevel->Initialize(FURL(nullptr)); PersistentLevel->Model = NewObject(PersistentLevel); PersistentLevel->Model->Initialize(nullptr, 1); PersistentLevel->OwningWorld = this; // Create the WorldInfo actor. FActorSpawnParameters SpawnInfo; // Mark objects are transactional for undo/ redo. if (IVS.bTransactional) { SpawnInfo.ObjectFlags |= RF_Transactional; PersistentLevel->SetFlags( RF_Transactional ); PersistentLevel->Model->SetFlags( RF_Transactional ); } else { SpawnInfo.ObjectFlags &= ~RF_Transactional; PersistentLevel->ClearFlags( RF_Transactional ); PersistentLevel->Model->ClearFlags( RF_Transactional ); } #if WITH_EDITORONLY_DATA // Need to associate current level so SpawnActor doesn't complain. CurrentLevel = PersistentLevel; #endif SpawnInfo.SpawnCollisionHandlingOverride = ESpawnActorCollisionHandlingMethod::AlwaysSpawn; // Set constant name for WorldSettings to make a network replication work between new worlds on host and client SpawnInfo.Name = GEngine->WorldSettingsClass->GetFName(); AWorldSettings* WorldSettings = SpawnActor(GEngine->WorldSettingsClass, SpawnInfo ); // Allow the world creator to override the default game mode in case they do not plan to load a level. if (IVS.DefaultGameMode) { WorldSettings->DefaultGameMode = IVS.DefaultGameMode; } PersistentLevel->SetWorldSettings(WorldSettings); check(GetWorldSettings()); #if WITH_EDITOR WorldSettings->SetIsTemporarilyHiddenInEditor(true); #endif #if INCLUDE_CHAOS /*FChaosSolversModule* ChaosModule = FModuleManager::Get().GetModulePtr("ChaosSolvers"); check(ChaosModule); FActorSpawnParameters ChaosSpawnInfo; ChaosSpawnInfo.SpawnCollisionHandlingOverride = ESpawnActorCollisionHandlingMethod::AlwaysSpawn; ChaosSpawnInfo.Name = TEXT("DefaultChaosActor"); SpawnActor(ChaosModule->GetSolverActorClass(), nullptr, nullptr, ChaosSpawnInfo); check(PhysicsScene_Chaos);*/ #endif // Initialize the world InitWorld(IVS); // Update components. UpdateWorldComponents( true, false ); }在World内对PersistentLevel进行初始化,再对PersistentLevel中的WorldSetting进行设置,这里的WorldSetting设置只是Level与WorldSetting进行绑定,WorldSetting初始化还是在GameInstance里面
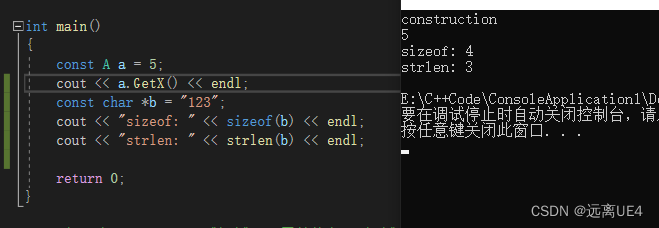
10、sizeof与strlen的区别
sizeof包括最后的'\0',所以为4,strlen不包括最后的'\0',所以为3 sizeof是字节个数,不止用在字符串上,而strlen只能用在字符串上,输出字符串个数 11、重写与重载的区别 1、重写是子类覆盖父类名字相同的方法,对其进行重新实现 2、重载有两种情况,在同一个类中,同一个方法名拥有不同的参数个数,或者同一个方法名拥有参数个数相同的不同类型参数 12、构造函数和析构函数都能加Virtual吗?
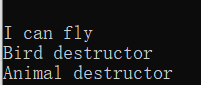
虚函数 虚函数跟着对象走 函数名后面加override没有任何功能性作用,只是开发规范要求写上。 override作用或C++语言哲学:将大多数错误暴露在编译阶段 普通函数属于编译期状态,虚函数属于运行期状态。 编译器是看代码人就知道答案,运行期是看代码也不能清楚答案。 基类析构函数都要加virtual
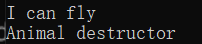
如果析构函数不加virtual,普通成员函数跟类走,那么delete p;就会去调用p的类型的析构函数即Animal的析构函数
加了情况就一不一样:
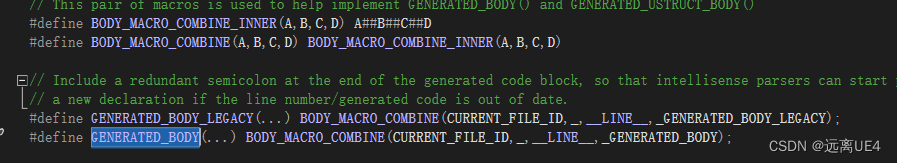
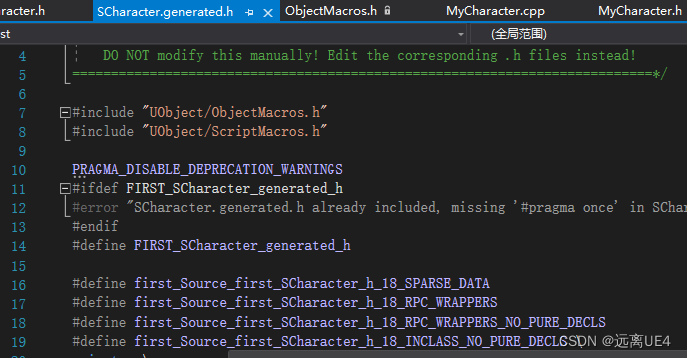
构造函数是用来创建一个新的对象,而虚函数的运行是建立在对象的基础上,在构造函数执行时,对象尚未形成(普通函数属于编译期状态,虚函数属于运行期状态),所以不能将构造函数定义为虚函数,通常析构函数才会用virtual修饰(虚函数实际存放在对象的头部的虚函数表中的) 所以构造函数不能加virtual,析构函数子类必须加virtual 13、UCLASS、GENERATED_BODY以及为何要加 文件名.generated.h 1、GENERATED_BODY
通过当前文件ID以及行号来建立一个唯一的键值名称 2、UCLASS
与GENERATED_BODY是一样的 3、xxx.generated.h
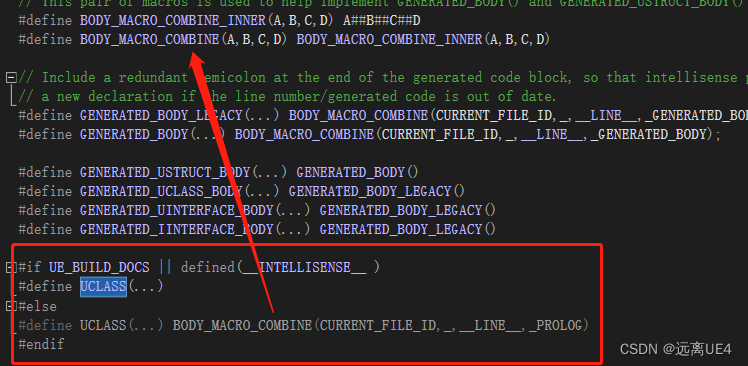
在Intermediate(中间生成文件)中生成,这个生成是在项目文件编译成功后它会自动生成xxx.generated.h以及xxx.gen.cpp 结合之前的UCLASS和GENERATED_BODY
.generated.h里面生成了这些文件,是通过UCLASS和GENERATED_BODY来生成的
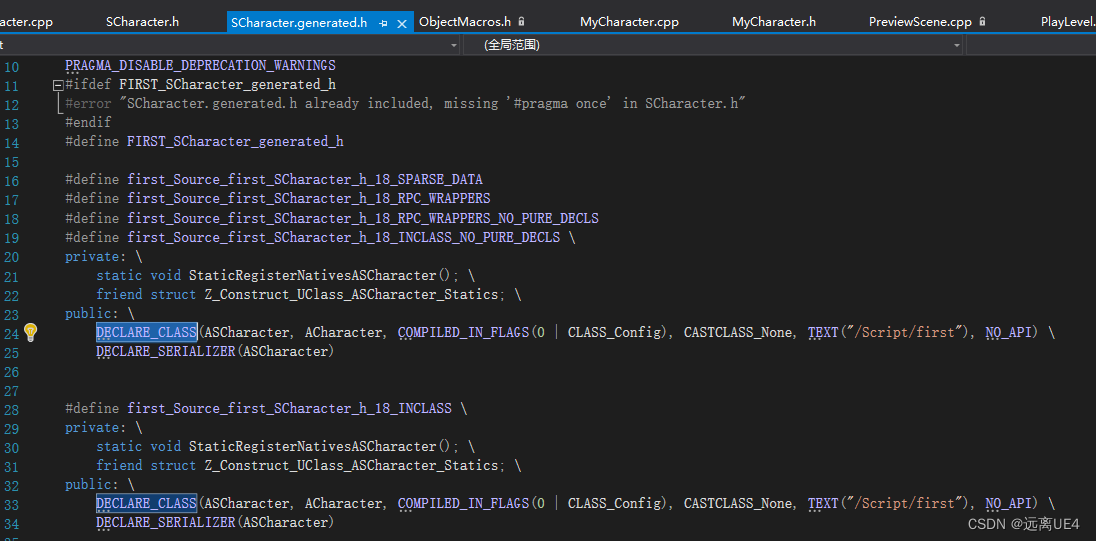
例如GENRATED_BODY在18行,CURRENT_FILE_ID为first_Source_first_SCharacter_h
注意这个DECLARE_CLASS
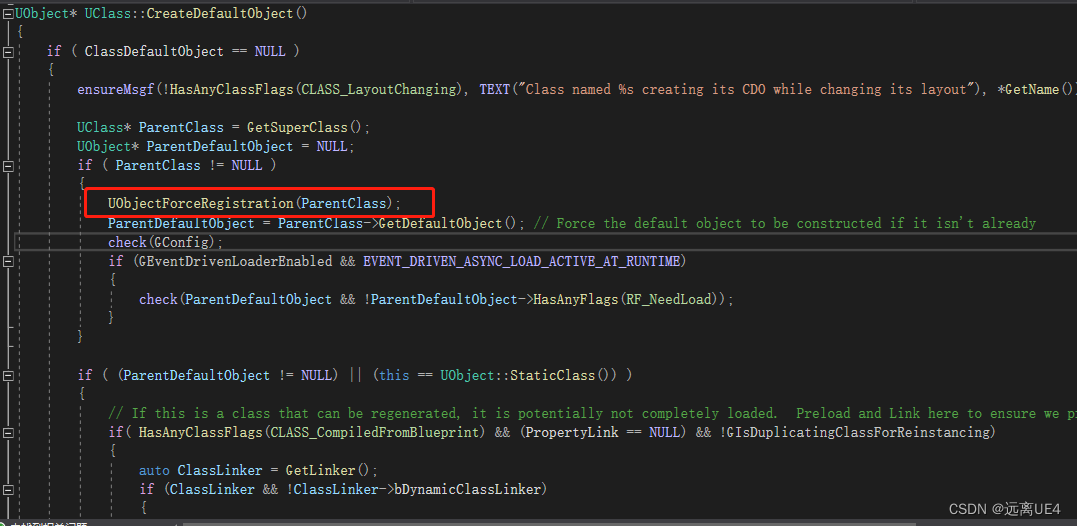
这里完成了对反射类型做了操作
同时还在里面对new进行了重载 最后new出来的对象在UClass内对类进行注册,构建了基础的反射系统
14、UE4内存管理 内存管理机制的三种形式 1、垃圾回收 2、智能指针 3、C++内存管理(malloc realloc calloc new) 一、对非UObject类型进行TSharedPtr管理,不能用于UObject对象,不然等TSharedPtr释放后,UObject自带的GC机制再去进行垃圾回收就会引起两次free的异常 二、以及对UObject类型进行GC机制的回收 三、UE4中的C++内存管理通常通过FMalloc以及GMalloc进行管理 class CORE_API FMalloc : public FUseSystemMallocForNew, public FExec { public: virtual void* Malloc( SIZE_T Count, uint32 Alignment=DEFAULT_ALIGNMENT ) = 0; virtual void* TryMalloc( SIZE_T Count, uint32 Alignment=DEFAULT_ALIGNMENT ); virtual void* Realloc( void* Original, SIZE_T Count, uint32 Alignment=DEFAULT_ALIGNMENT ) = 0; virtual void* TryRealloc(void* Original, SIZE_T Count, uint32 Alignment=DEFAULT_ALIGNMENT); virtual void Free( void* Original ) = 0为了在调用new/delete能够调用ue4的自定义函数,ue4内部替换了operator new。这一替换是通过IMPLEMENT_MODULE宏引入的 FMallocBinned使用freelist机制管理空闲内存。每个空闲块的信息记录在FFreeMem结构中,显式存储。 FMallocBinned使用内存池机制,内部包含POOL_COUNT(42)个内存池和2个扩展的页内存池;其中每个内存池的信息由FPoolInfo结构体维护,记录了当前FreeMem内存块指针等,而特定大小的所有内存池由FPoolTable维护;内存池内包含了内存块的双向链表。 15、有一个UObject子类中声明了另外一个UObject子类,如何当前者UObject子类垃圾回收时不回收类中的UObject子类 1、被另一个对象引用,通过调用 UObject::AddReferencedObjects 2、是GC root对象,通过调用 UObject::AddToRoot |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |