常用基本初等函数的求导公式推导 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › lnx的反函数求导法 › 常用基本初等函数的求导公式推导 |
常用基本初等函数的求导公式推导
|
文章目录
0、常用基本初等函数的求导公式1、
a
x
a^x
ax和
e
x
e^x
ex的导数2、
l
o
g
a
x
log_ax
logax和
l
n
x
lnx
lnx的导数2.1
l
n
x
lnx
lnx的导数2.2
l
o
g
a
x
log_ax
logax的导数
3、
x
x
x^x
xx的导数4、
x
r
x^r
xr的导数(r为实数)5、三角函数的导数5.1
sin
x
\sin x
sinx的导数方法一方法二
5.2
cos
x
\cos x
cosx的导数5.3
tan
x
\tan x
tanx的导数5.4
csc
x
\csc x
cscx的导数5.5
sec
x
\sec x
secx的导数5.6
cot
x
\cot x
cotx的导数
6、反三角函数的导数6.1
arcsin
x
\arcsin x
arcsinx的导数6.2
arccos
x
\arccos x
arccosx的导数6.3
arctan
x
\arctan x
arctanx的导数
7、双曲函数的导数7.1
sinh
x
\sinh x
sinhx的导数7.2
cosh
x
\cosh x
coshx的导数7.3
tanh
x
\tanh x
tanhx的导数
0、常用基本初等函数的求导公式
根据导数的定义
d
d
x
a
x
=
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
x
+
Δ
x
−
a
x
Δ
x
=
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
x
⋅
a
Δ
x
−
a
x
Δ
x
=
a
x
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
Δ
x
−
1
Δ
x
\frac{d}{dx}a^x=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^{x+\Delta x}-a^x}{\Delta x}=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^x\cdot a^{\Delta x}-a^x}{\Delta x}=a^x\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^{\Delta x}-1}{\Delta x}
dxdax=Δx→0limΔxax+Δx−ax=Δx→0limΔxax⋅aΔx−ax=axΔx→0limΔxaΔx−1
令
M
(
a
)
=
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
Δ
x
−
1
Δ
x
\text{令}M\left( a \right) =\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^{\Delta x}-1}{\Delta x}
令M(a)=Δx→0limΔxaΔx−1
则
d
d
x
a
x
=
a
x
M
(
a
)
\text{则}\frac{d}{dx}a^x=a^xM\left( a \right)
则dxdax=axM(a) 由于
M
(
a
)
=
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
Δ
x
−
1
Δ
x
=
lim
Δ
x
→
0
a
0
+
Δ
x
−
a
0
Δ
x
=
d
d
x
a
x
∣
x
=
0
M\left( a \right) =\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^{\Delta x}-1}{\Delta x}=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{a^{0+\Delta x}-a^0}{\Delta x}=\left. \frac{d}{dx}a^x \right|_{x=0}
M(a)=Δx→0limΔxaΔx−1=Δx→0limΔxa0+Δx−a0=dxdax∣∣∣∣x=0 得
M
(
a
)
M(a)
M(a)为函数图像
y
=
a
x
y=a^x
y=ax在
x
=
0
x=0
x=0处切线的斜率,如图所示 现在我们有 M ( e ) = 1 M(e)=1 M(e)=1,即可得 M ( e ) = lim Δ x → 0 e Δ x − 1 Δ x = 1 ( 实 际 上 此 极 限 也 可 从 e 的 定 义 推 导 可 得 , 从 而 通 过 导 数 的 定 义 计 算 e x 的 导 数 ) M\left( e \right) =\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{e^{\Delta x}-1}{\Delta x}=1 (实际上此极限也可从e的定义推导可得,从而通过导数的定义计算e^x的导数) M(e)=Δx→0limΔxeΔx−1=1(实际上此极限也可从e的定义推导可得,从而通过导数的定义计算ex的导数) 可计算出导数 d d x e x = e x \frac{d}{dx}e^x=e^x dxdex=ex 回到计算 a x a^x ax,通过将 a x a^x ax化为以 e e e为底的指数,来计算其导数 d d x a x = d d x e x ln a = ( ln a ) e x ln a = a x ln a \frac{d}{dx}a^x=\frac{d}{dx}e^{x\ln a}=\left( \ln a \right) e^{x\ln a}=a^x\ln a dxdax=dxdexlna=(lna)exlna=axlna 2、 l o g a x log_ax logax和 l n x lnx lnx的导数 2.1 l n x lnx lnx的导数令 y = ln x 则 e y = x \text{令\,\,}y=\ln x\ \text{则\,\,}e^y=x 令y=lnx 则ey=x d d x ( e y = x ) ⇒ e y ⋅ d y d x = 1 \frac{d}{dx}\left( e^y=x \right) \ \Rightarrow e^y\cdot \frac{dy}{dx}=1 dxd(ey=x) ⇒ey⋅dxdy=1 d y d x = 1 e y = 1 x \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{e^y}=\frac{1}{x} dxdy=ey1=x1 2.2 l o g a x log_ax logax的导数令 y = log a x 则 a y = x \text{令\,\,}y=\log _ax\ \text{则\,\,}a^y=x 令y=logax 则ay=x d d x ( a y = x ) ⇒ a y ⋅ ln a ⋅ d y d x = 1 \frac{d}{dx}\left( a^y=x \right) \Rightarrow a^y\cdot \ln a\cdot \frac{dy}{dx}=1 dxd(ay=x)⇒ay⋅lna⋅dxdy=1 d y d x = 1 a y ⋅ ln a = 1 x ln a \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{a^y\cdot \ln a}=\frac{1}{x\ln a} dxdy=ay⋅lna1=xlna1 3、 x x x^x xx的导数x x = ( e ln x ) x = e x ln x x^x=\left( e^{\ln x} \right) ^x=e^{x\ln x} xx=(elnx)x=exlnx d d x x x = d d x e x ln x = e x ln x ( ln x + x ⋅ 1 x ) = x x ( ln x + 1 ) \frac{d}{dx}x^x=\frac{d}{dx}e^{x\ln x}=e^{x\ln x}\left( \ln x+x\cdot \frac{1}{x} \right) =x^x\left( \ln x+1 \right) dxdxx=dxdexlnx=exlnx(lnx+x⋅x1)=xx(lnx+1) 4、 x r x^r xr的导数(r为实数)x r = ( e ln x ) r = e r ln x x^r=\left( e^{\ln x} \right) ^r=e^{r\ln x} xr=(elnx)r=erlnx d d x x r = d d x e r ln x = e r ln x ⋅ r x = x r ⋅ r x = r ⋅ x r − 1 \frac{d}{dx}x^r=\frac{d}{dx}e^{r\ln x}=e^{r\ln x}\cdot \frac{r}{x}=x^r\cdot \frac{r}{x}=r\cdot x^{r-1} dxdxr=dxderlnx=erlnx⋅xr=xr⋅xr=r⋅xr−1 5、三角函数的导数 5.1 sin x \sin x sinx的导数 方法一d d x sin x = lim Δ x → 0 sin ( x + Δ x ) − sin x Δ x = lim Δ x → 0 sin x ⋅ cos Δ x + cos x ⋅ sin Δ x − sin x Δ x ( 两 角 和 公 式 sin ( a + b ) = sin a ⋅ cos b + cos a ⋅ sin b ) = lim Δ x → 0 sin x ⋅ ( cos Δ x − 1 ) Δ x + lim Δ x → 0 cos x ⋅ sin Δ x Δ x \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx}\sin x&=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin \left( x+\Delta x \right) -\sin x}{\Delta x} \\ &=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin x\cdot \cos \Delta x+\cos x\cdot \sin \Delta x-\sin x}{\Delta x}\ \left(两角和公式 \sin \left( a+b \right) =\sin a\cdot \cos b+\cos a\cdot \sin b \right) \\ &=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin x\cdot \left( \cos \Delta x-1 \right)}{\Delta x}+ \underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos x\cdot \sin \Delta x}{\Delta x} \end{aligned} dxdsinx=Δx→0limΔxsin(x+Δx)−sinx=Δx→0limΔxsinx⋅cosΔx+cosx⋅sinΔx−sinx (两角和公式sin(a+b)=sina⋅cosb+cosa⋅sinb)=Δx→0limΔxsinx⋅(cosΔx−1)+Δx→0limΔxcosx⋅sinΔx 由于 lim x → 0 cos x − 1 x = lim x → 0 1 − 2 sin 2 x 2 − 1 x ( 倍 角 公 式 cos 2 x = 1 − 2 sin 2 x ) = − lim x → 0 ( sin x 2 x 2 ⋅ sin x 2 ) = − lim x → 0 sin x 2 ( 重要极限 lim x → 0 sin x x = 1 ) = 0 \begin{aligned} \underset{x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos x-1}{x}&=\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{1-2\sin ^2\frac{x}{2}-1}{x}\ \left(倍角公式 \cos 2x=1-2\sin ^2x \right)\\ &=-\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\left( \frac{\sin \frac{x}{2}}{\frac{x}{2}}\cdot \sin \frac{x}{2} \right) \\ &=-\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\sin \frac{x}{2}\ \left( \text{重要极限}\underset{x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin x}{x}=1 \right) \\ &=0 \end{aligned} x→0limxcosx−1=x→0limx1−2sin22x−1 (倍角公式cos2x=1−2sin2x)=−x→0lim(2xsin2x⋅sin2x)=−x→0limsin2x (重要极限x→0limxsinx=1)=0 得 d d x sin x = lim Δ x → 0 sin x ⋅ ( cos Δ x − 1 ) Δ x + lim Δ x → 0 cos x ⋅ sin Δ x Δ x = cos x \frac{d}{dx}\sin x=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin x\cdot \left( \cos \Delta x-1 \right)}{\Delta x}+ \underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos x\cdot \sin \Delta x}{\Delta x}=\cos x dxdsinx=Δx→0limΔxsinx⋅(cosΔx−1)+Δx→0limΔxcosx⋅sinΔx=cosx 方法二
d d x cos x = lim Δ x → 0 cos ( x + Δ x ) − cos x Δ x = lim Δ x → 0 cos x ⋅ cos Δ x − sin x ⋅ sin Δ x − cos x Δ x ( 两 角 和 公 式 cos ( a + b ) = cos a ⋅ cos b − sin a ⋅ sin b ) = lim Δ x → 0 cos x ⋅ ( cos Δ x − 1 ) Δ x − lim Δ x → 0 sin x ⋅ sin Δ x Δ x = − sin x \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx}\cos x&=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos \left( x+\Delta x \right) -\cos x}{\Delta x}\\ &=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos x\cdot \cos \Delta x-\sin x\cdot \sin \Delta x-\cos x}{\Delta x}\ \left(两角和公式 \cos \left( a+b \right) =\cos a\cdot \cos b-\sin a\cdot \sin b \right) \\ &=\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\cos x\cdot \left( \cos \Delta x-1 \right)}{\Delta x}-\underset{\Delta x\rightarrow 0}{\lim}\frac{\sin x\cdot \sin \Delta x}{\Delta x}\\ &=-\sin x \end{aligned} dxdcosx=Δx→0limΔxcos(x+Δx)−cosx=Δx→0limΔxcosx⋅cosΔx−sinx⋅sinΔx−cosx (两角和公式cos(a+b)=cosa⋅cosb−sina⋅sinb)=Δx→0limΔxcosx⋅(cosΔx−1)−Δx→0limΔxsinx⋅sinΔx=−sinx 5.3 tan x \tan x tanx的导数d d x tan x = d d x sin x cos x = cos 2 x + sin 2 x cos 2 x ( 商的求导法则 ) = 1 cos 2 x = sec 2 x \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx}\tan x&=\frac{d}{dx}\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}\\ &=\frac{\cos ^2x+\sin ^2x}{\cos ^2x}\ \left( \text{商的求导法则} \right) \\ &=\frac{1}{\cos ^2x}\\ &=\sec ^2x \end{aligned} dxdtanx=dxdcosxsinx=cos2xcos2x+sin2x (商的求导法则)=cos2x1=sec2x 5.4 csc x \csc x cscx的导数d d x csc x = d d x ( sin x ) − 1 = − ( sin x ) − 2 cos x = − cos x sin 2 x = − csc x ⋅ cot x \frac{d}{dx}\csc x=\frac{d}{dx}\left( \sin x \right) ^{-1}=-\left( \sin x \right) ^{-2}\cos x=-\frac{\cos x}{\sin ^2x}=-\csc x\cdot \cot x dxdcscx=dxd(sinx)−1=−(sinx)−2cosx=−sin2xcosx=−cscx⋅cotx 5.5 sec x \sec x secx的导数d d x sec x = d d x ( cos x ) − 1 = − ( cos x ) − 2 ( − sin x ) = sin x cos 2 x = sec x ⋅ tan x \frac{d}{dx}\sec x=\frac{d}{dx}\left( \cos x \right) ^{-1}=-\left( \cos x \right) ^{-2}\left( -\sin x \right) =\frac{\sin x}{\cos ^2x}=\sec x\cdot \tan x dxdsecx=dxd(cosx)−1=−(cosx)−2(−sinx)=cos2xsinx=secx⋅tanx 5.6 cot x \cot x cotx的导数d d x cot x = d d x cos x sin x = − sin 2 x − cos 2 x sin 2 x ( 商的求导法则 ) = − 1 sin 2 x = − csc 2 x \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx}\cot x&=\frac{d}{dx}\frac{\cos x}{\sin x}\\ &=\frac{-\sin ^2x-\cos ^2x}{\sin ^2x}\,\,\left( \text{商的求导法则} \right)\\ &=-\frac{1}{\sin ^2x}\\ &=-\csc ^2x\\ \end{aligned} dxdcotx=dxdsinxcosx=sin2x−sin2x−cos2x(商的求导法则)=−sin2x1=−csc2x 6、反三角函数的导数 6.1 arcsin x \arcsin x arcsinx的导数令 y = arcsin x 则 sin y = x \text{令\ }y=\arcsin x\ \text{则\ }\sin y=x 令 y=arcsinx 则 siny=x d d x ( sin y = x ) ⇒ cos y ⋅ d y d x = 1 \frac{d}{dx}\left( \sin y=x \right) \Rightarrow \cos y\cdot \frac{dy}{dx}=1\ dxd(siny=x)⇒cosy⋅dxdy=1 d y d x = 1 cos y = 1 1 − sin 2 y = 1 1 − x 2 \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{\cos y}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\sin ^2y}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} dxdy=cosy1=1−sin2y 1=1−x2 1 6.2 arccos x \arccos x arccosx的导数令 y = arccos x 则 cos y = x \text{令\ }y=\arccos x\ \text{则\ }\cos y=x 令 y=arccosx 则 cosy=x d d x ( cos y = x ) ⇒ − sin y ⋅ d y d x = 1 \frac{d}{dx}\left( \cos y=x \right) \Rightarrow -\sin y\cdot \frac{dy}{dx}=1\ dxd(cosy=x)⇒−siny⋅dxdy=1 d y d x = − 1 sin y = − 1 1 − cos 2 y = − 1 1 − x 2 \frac{dy}{dx}=-\frac{1}{\sin y}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\cos ^2y}}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x^2}} dxdy=−siny1=−1−cos2y 1=−1−x2 1 6.3 arctan x \arctan x arctanx的导数
令
y
=
arctan
x
则
tan
y
=
x
\text{令\ }y=\arctan x\ \text{则\ }\tan y=x
令 y=arctanx 则 tany=x
d
d
x
(
tan
y
=
x
)
⇒
sec
2
y
⋅
d
y
d
x
=
1
\frac{d}{dx}\left( \tan y=x \right) \Rightarrow \sec ^2y\cdot \frac{dy}{dx}=1\
dxd(tany=x)⇒sec2y⋅dxdy=1
d
y
d
x
=
cos
2
y
\frac{dy}{dx}=\cos ^2y
dxdy=cos2y sinh ( x ) = e x − e − x 2 , cosh ( x ) = e x + e − x 2 , tanh ( x ) = sinh ( x ) cosh ( x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x \sinh\left( x \right) =\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{2}\ ,\ \cosh\left( x \right) =\frac{e^x+e^{-x}}{2}\ ,\ \tanh\left( x \right) =\frac{\sinh\left( x \right)}{\cosh\left( x \right)}=\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{e^x+e^{-x}} sinh(x)=2ex−e−x , cosh(x)=2ex+e−x , tanh(x)=cosh(x)sinh(x)=ex+e−xex−e−x 7.1 sinh x \sinh x sinhx的导数d d x sinh x = d d x ( e x − e − x 2 ) = e x + e − x 2 = cosh x \frac{d}{dx}\sinh x=\frac{d}{dx}\left( \frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{2} \right) =\frac{e^x+e^{-x}}{2}=\cosh x dxdsinhx=dxd(2ex−e−x)=2ex+e−x=coshx 7.2 cosh x \cosh x coshx的导数d d x cosh x = d d x ( e x + e − x 2 ) = e x − e − x 2 = sinh x \frac{d}{dx}\cosh x=\frac{d}{dx}\left( \frac{e^x+e^{-x}}{2} \right) =\frac{e^x-e^{-x}}{2}=\sinh x dxdcoshx=dxd(2ex+e−x)=2ex−e−x=sinhx 7.3 tanh x \tanh x tanhx的导数d d x tanh x = d d x sinh x cosh x = cosh 2 x − sinh 2 x cosh 2 x ( 商的求导法则 ) = 1 cosh 2 x ( 由 cosh 2 x − sinh 2 x = 1 可 得 ) \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx}\tanh x&=\frac{d}{dx}\frac{\sinh x}{\cosh x}\\ &=\frac{\cosh ^2x-\sinh ^2x}{\cosh ^2x}\,\,\left( \text{商的求导法则} \right)\\ &=\frac{1}{\cosh^2x}\ \left( 由\cosh^2x-\sinh^2x=1 可得\right)\\ \end{aligned} dxdtanhx=dxdcoshxsinhx=cosh2xcosh2x−sinh2x(商的求导法则)=cosh2x1 (由cosh2x−sinh2x=1可得) |
【本文地址】
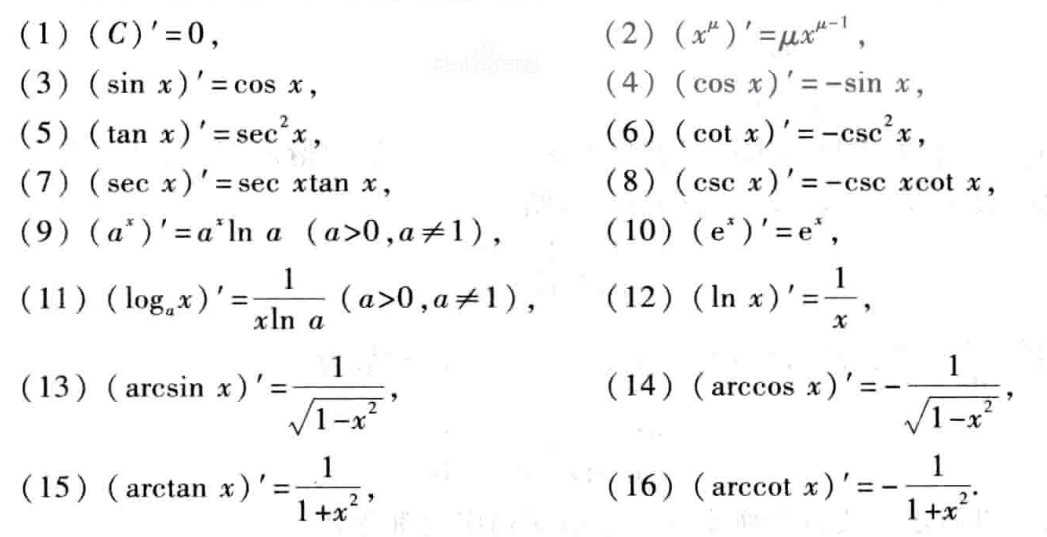
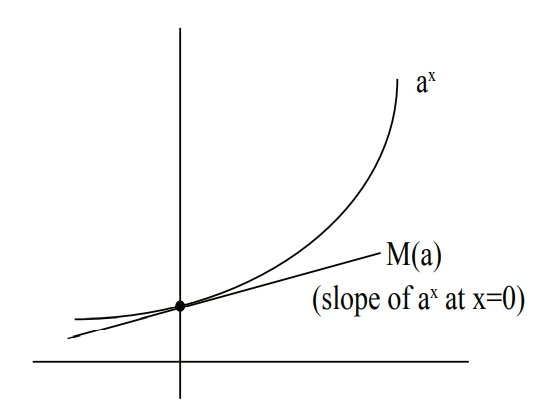 考虑是否存在
b
b
b使
M
(
b
)
=
1
M(b)=1
M(b)=1 令
a
=
2
a=2
a=2,函数图像如图所示,割线(secant line)经过点
(
0
,
1
)
(0,1)
(0,1)和
(
1
,
2
)
(1,2)
(1,2),其斜率为1,所以可得
M
(
2
)
<
1
M(2)1
M(4)>1
考虑是否存在
b
b
b使
M
(
b
)
=
1
M(b)=1
M(b)=1 令
a
=
2
a=2
a=2,函数图像如图所示,割线(secant line)经过点
(
0
,
1
)
(0,1)
(0,1)和
(
1
,
2
)
(1,2)
(1,2),其斜率为1,所以可得
M
(
2
)
<
1
M(2)1
M(4)>1  所以存在
b
∈
(
2
,
4
)
b\in(2,4)
b∈(2,4)使
M
(
b
)
=
1
M(b)=1
M(b)=1 实际上
M
(
e
)
=
1
(
e
为
自
然
常
数
)
M(e)=1 (e为自然常数)
M(e)=1(e为自然常数) 详见: 谈谈高等数学中自然常数e的来历 The Enigmatic Number e: A History in Verse and Its Uses in the Mathematics Classroom
所以存在
b
∈
(
2
,
4
)
b\in(2,4)
b∈(2,4)使
M
(
b
)
=
1
M(b)=1
M(b)=1 实际上
M
(
e
)
=
1
(
e
为
自
然
常
数
)
M(e)=1 (e为自然常数)
M(e)=1(e为自然常数) 详见: 谈谈高等数学中自然常数e的来历 The Enigmatic Number e: A History in Verse and Its Uses in the Mathematics Classroom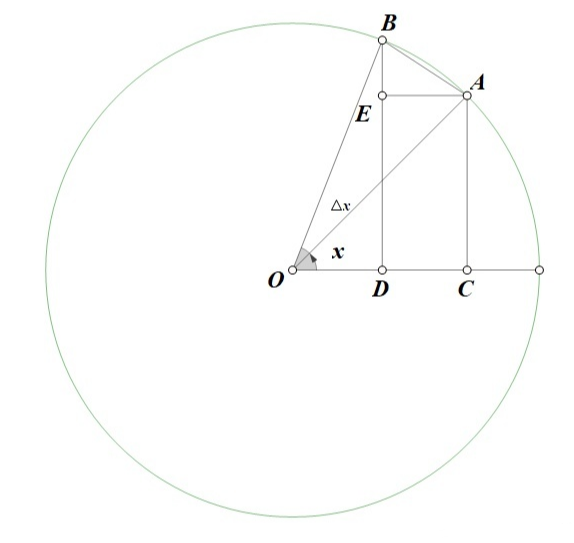 由于
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx很小,所以可以认为
O
A
⊥
A
B
OA \bot AB
OA⊥AB和
A
B
=
Δ
x
(
Δ
x
为
弧
度
)
AB=\Delta x (\Delta x 为弧度)
AB=Δx(Δx为弧度),易证
∠
A
B
E
=
x
\angle ABE=x
∠ABE=x(OA逆时针旋转90°和AB平行,OD逆时针旋转90°和BE平行,OA与OD的夹角为
x
x
x,则AB与BE的夹角也为
x
x
x)
可
得
Δ
y
Δ
x
=
B
E
A
B
=
cos
x
,
即
d
d
x
sin
x
=
cos
x
可得\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\frac{BE}{AB}=\cos x,即\frac{d}{dx}\sin x=\cos x
可得ΔxΔy=ABBE=cosx,即dxdsinx=cosx
由于
Δ
x
\Delta x
Δx很小,所以可以认为
O
A
⊥
A
B
OA \bot AB
OA⊥AB和
A
B
=
Δ
x
(
Δ
x
为
弧
度
)
AB=\Delta x (\Delta x 为弧度)
AB=Δx(Δx为弧度),易证
∠
A
B
E
=
x
\angle ABE=x
∠ABE=x(OA逆时针旋转90°和AB平行,OD逆时针旋转90°和BE平行,OA与OD的夹角为
x
x
x,则AB与BE的夹角也为
x
x
x)
可
得
Δ
y
Δ
x
=
B
E
A
B
=
cos
x
,
即
d
d
x
sin
x
=
cos
x
可得\frac{\Delta y}{\Delta x}=\frac{BE}{AB}=\cos x,即\frac{d}{dx}\sin x=\cos x
可得ΔxΔy=ABBE=cosx,即dxdsinx=cosx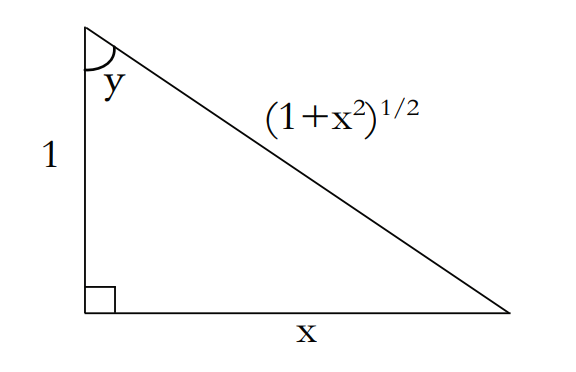 由图可得
cos
y
=
1
1
+
x
2
则
d
y
d
x
=
cos
2
y
=
1
1
+
x
2
\text{由图可得\ }\cos y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^2}}\ \text{则\ }\frac{dy}{dx}=\cos ^2y=\frac{1}{1+x^2}
由图可得 cosy=1+x2
1 则 dxdy=cos2y=1+x21
由图可得
cos
y
=
1
1
+
x
2
则
d
y
d
x
=
cos
2
y
=
1
1
+
x
2
\text{由图可得\ }\cos y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^2}}\ \text{则\ }\frac{dy}{dx}=\cos ^2y=\frac{1}{1+x^2}
由图可得 cosy=1+x2
1 则 dxdy=cos2y=1+x21