Python实现直方图的绘制 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › jupyternotebook画饼图 › Python实现直方图的绘制 |
Python实现直方图的绘制
|
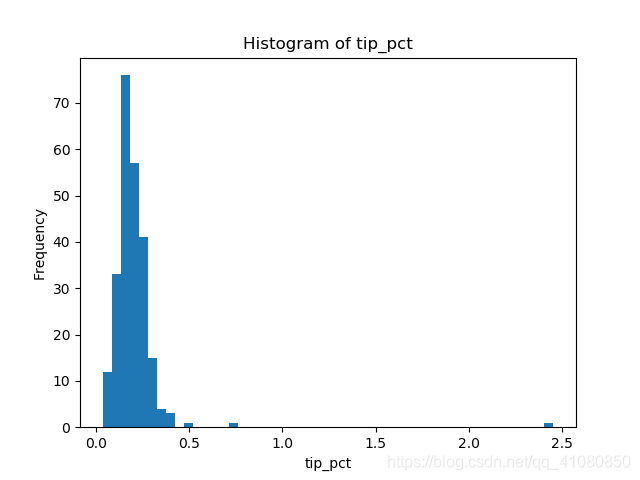
说明:代码运行环境为 Win10+Python3+jupyter notebook 直方图简介:直方图是一种常用的数量型数据的图形描述方法。它的一个最重要应用是提供了数据的分布形态的信息。 直方图主要的绘制方法:方法1:通过pandas包中的调用Series对象或DataFrame对象的plot()、plot.hist()或hist()方法 方法2:通过matplotlib包中的Axes对象调用hist()方法创建直方图: 首先导出需要的各种包,并准备好数据: %matplotlib notebook import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plot import numpy as np tips = pd.read_csv('examples/tips.csv') tips['tip_pct']=tips['tip']/(tips['total_bill']-tips['tip']) # 向tips 中添加'tip_pct'列加入'tip_pct'列后的tips表的结构如下图所示: Series.plot.hist()示例: fig,axes = plt.subplots() tips['tip_pct'].plot.hist(bins=50,ax=axes) axes.set_title('Histogram of tip_pct') #设置直方图的标题 axes.set_xlabel('tip_pct') # 设置直方图横坐标轴的标签 fig.savefig('p1.png') # 保存图片上述代码绘制的图形为:
Series.plot.hist()的用法具体参考: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.Series.plot.hist.html Series.plot(kind='hist')的用法与Series.plot.hist()类似,具体参考: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.Series.plot.html#pandas.Series.plot DataFrame.plot.hist()示例: fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2) tips.plot.hist(bins=50,subplots=True,ax=axes,legend=False) axes[0,0].set_title('Histogram og total bill') axes[0,0].set_xlabel('total_bill') axes[0,1].set_title('Histogram of tip') axes[0,1].set_xlabel('tip') axes[1,0].set_title('Histogram of size') axes[1,0].set_xlabel('size') axes[1,1].set_title('Histogram of tip_pct') axes[1,1].set_xlabel('tip_pct') fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5,hspace=0.5) # 调整axes中各个子图之间的间距 fig.savefig('p2.png')上述代码绘制的图形为:
可以看到,上图中四个子图的横坐标范围是完全相同的,DataFrame.plot.hist不会根据各个子图中的数据自动调整横坐标轴上数值的范围。与DataFrame.plot.hist()方法相比,DataFrame.hist()会根据不同数据自动调整横坐标轴上的的数值范围,使用起来更加的方便。 DataFrame.plot.hist()的用法具体参考: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.plot.hist.html DataFrame.plot(kind='hist')的用法与DataFrame.plot.hist()类似,具体参考: ttps://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.plot.html DataFrame.hist()示例: fig,axes = plt.subplots(2,2) tips.hist(column='total_bill',ax=axes[0,0],bins=50) axes[0,0].set_title('Histogram of total_bill') axes[0,0].set_xlabel('total_bill') tips.hist(column='tip',ax=axes[0,1],bins=50) axes[0,1].set_title('Histogram of tip') axes[0,1].set_xlabel('tip') tips.hist(column='size',ax=axes[1,0],bins=50) axes[1,0].set_title('Histogram of size') axes[1,0].set_xlabel('size') tips.hist(column='tip_pct',ax=axes[1,1],bins=50) axes[1,1].set_title('Histogram of tip_pct') axes[1,1].set_xlabel('tip_pct') fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.42,hspace=0.42) fig.savefig('p3.png')上述代码绘制的图形为:
DataFrame.hist()的用法具体参考: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.DataFrame.hist.html#pandas.DataFrame.hist Series.hist()示例: fig,axes = plt.subplots(1,2) # xrot表示x轴上数据标签的偏转角度 tips['tip_pct'].hist(by=tips['smoker'],ax=axes,bins=50,xrot=0.1) axes[0].set_title('tip_pct of non-smoker ') axes[0].set_xlabel('tip_pct') axes[1].set_title('tip_pct of smoker ') axes[1].set_xlabel('tip_pct') fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.4,hspace=0.4) fig.savefig('p4.png')上述代码绘制的图形为:
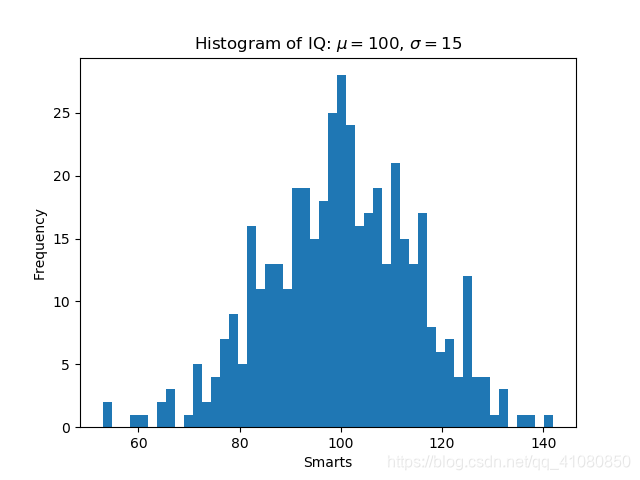
Series.hist()的用法具体参考: https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/generated/pandas.Series.hist.html#pandas.Series.hist 方法2具体示例:Axes.hist()的用法具体参考: https://matplotlib.org/api/_as_gen/matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist.html#matplotlib.axes.Axes.hist 频数分布直方图示例: import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(19680801) # 让每次生成的随机数相同 # 示例数据 mu = 100 # 数据均值 sigma = 15 # 数据标准差 x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(437) num_bins = 50 fig, ax = plt.subplots() # 等价于fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1) # 数据的频数分布直方图 n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, num_bins,density=False) # n是一个数组或者由数组组成的列表,表示落在每个分组中的数据的频数 # bins是一个数组,表示每个分组的边界,一共有50个组,所以bins的长度就是51 # patches是一个列表或者嵌套列表,长度是50,,列表里的元素可以理解成直方图中的小长方条 ax.set_xlabel('Smarts') ax.set_ylabel('Frequency') ax.set_title(r'Histogram of IQ: $\mu=100$, $\sigma=15$') fig.savefig('p5.png')上述代码绘制的图形为:
频率分布直方图示例: np.random.seed(19680801) # 让每次生成的随机数相同 # 示例数据 mu = 100 # 数据均值 sigma = 15 # 数据标准差 x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(437) num_bins = 50 fig, ax = plt.subplots() # 等价于fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1) # 数据的频率分布直方图 n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, num_bins,density=True) # n是一个数组或者由数组组成的列表,表示落在每个分组中的数据的频数 # bins是一个数组,表示每个分组的边界,一共有50个组,所以bins的长度就是51 # patches是一个列表或者嵌套列表,长度是50,,列表里的元素可以理解成直方图中的小长方条 ax.set_xlabel('Smarts') ax.set_ylabel('Probability density') # 频率分布直方图的纵轴表示的是频率/组距 ax.set_title(r'Histogram of IQ: $\mu=100$, $\sigma=15$') fig.savefig('p6.png')上述代码绘制的图形为:
如何给直方图中的长条添加数据标记? np.random.seed(19680801) # 让每次生成的随机数相同 # 示例数据 mu = 100 # 数据均值 sigma = 15 # 数据标准差 x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(437) num_bins = 5 # 为了便于给直方图中的长条添加数据标签,将数据分成五组 fig, ax = plt.subplots() # 等价于fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1) # 数据的频率分布直方图(带数据标签) n, bins, patches = ax.hist(x, num_bins,density=True) # n是一个数组或者由数组组成的列表,表示落在每个分组中的数据的频数 # bins是一个数组,表示每个分组的边界,一共有50个组,所以bins的长度就是51 # patches是一个列表或者嵌套列表,长度是50,,列表里的元素可以理解成直方图中的小长方条 # 写一个给直方图中的长条添加数据标签的函数 def data_marker(patches): for patch in patches: height = patch.get_height() if height != 0: ax.text(patch.get_x() + patch.get_width()/4, height + 0.0002,'{:.5f}'.format(height)) data_marker(patches) # 调用data_marker函数 ax.set_xlabel('Smarts') ax.set_ylabel('Probability density') # 频率分布直方图的纵轴表示的是频率/组距 ax.set_title(r'Histogram of IQ: $\mu=100$, $\sigma=15$') fig.savefig('p7.png') # 保存生成的图片上述代码绘制的图形为:
参考资料: 《Python for Data Analysis》第二版 https://blog.csdn.net/a821235837/article/details/52839050 https://wenku.baidu.com/view/036fea38aef8941ea66e052f.html https://blog.csdn.net/yywan1314520/article/details/50818471 matplotlib、pandas官方文档 PS:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处。
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |