js数组遍历十种方法 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › js数组原型 › js数组遍历十种方法 |
js数组遍历十种方法
|
1. some()
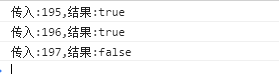
遍历数组,只要有一个以上的元素满足条件就返回 true,否则返回 false ,退出循环 对数组中每个元素执行一次ok函数,知道某个元素返回true,则直接返回true。如果都返回false,则返回false 检查整个数组中是否有满足元素。 private some(id: number) { const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 198, cityName: '上海'} ] let result = arr.some((item: any) => { return item.cityId === id }) console.log(`传入:${id},结果:${result}`) }
2. every() 遍历数组,每一个元素都满足条件 则返回 true,否则返回 false private every() { const arr = [1,2,3,4,5] let result = arr.every((item: any) => { return item > 0 }) console.log(`结果:${result}`) }
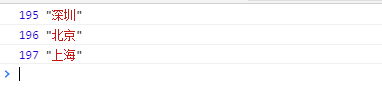
5. filter() 方法创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素。不会改变原始数组。 private filter(id: number): string { const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] let name: string = '' arr.filter((item: any) => { if(item.cityId === id) { name = item.cityName } }) console.log(`传入:${id},结果:${name}`) return name }
6. find() 遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 undefined let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.find((item:any) => { return item === 3 }) console.log(num)
遍历数组,返回符合条件的第一个元素的索引,如果没有符合条件的元素则返回 -1 let arr = [1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,5,6] let num = arr.findIndex((item:any) => { return item === 2 }) console.log(num)
8. for…of…(ES6) 自动解构 for of不能对象用 const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] for(const {cityId, cityName} of arr) { console.log(cityId, cityName) }
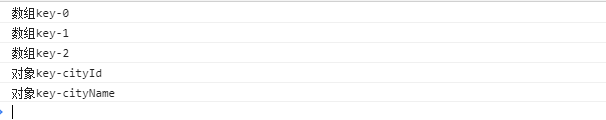
9. for…in… for...in 语句用于遍历数组或者对象的属性(对数组或者对象的属性进行循环操作)。 for in得到对对象的key或数组,字符串的下标 const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] const obj = { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'} for(const key in arr) { console.log(`数组key-${key}`) } for(const key in obj) { console.log(`对象key-${key}`) }
10. for 最简单的一种循环遍历方法,也是使用频率最高的一种,可优化 const arr = [ { cityId: 195, cityName: '深圳'}, { cityId: 196, cityName: '北京'}, { cityId: 197, cityName: '上海'} ] for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { console.log(arr[i]) }
四种遍历方法对于100万的循环时间
for最快,但可读性比较差 forEach比较快,能够控制内容 for....of比较慢,香 for...in比较慢,不方便 |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |