YOLO训练自己的数据集 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › json数据集怎么转xml › YOLO训练自己的数据集 |
YOLO训练自己的数据集
|
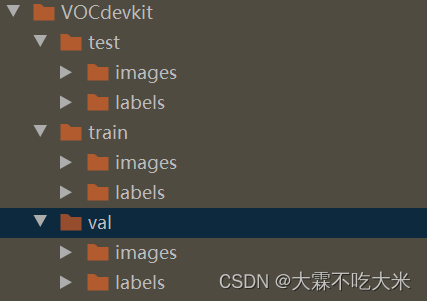
当我们在使用了Labelme等一系列数据标注软件后,便会得到与图片对应的JSON文件,但我们在训练YOLO模型之前,通常需要将标注数据转换为YOLO能识别的格式,也即TXT文件格式。再用于训练模型。而TXT格式是一种简单易读的文本格式,可以方便地手动修改标签中的信息,例如类别名称、边界框坐标等。将标签转换为TXT格式是为了方便后续的YOLO训练和测试,并提高工作效率。 转换步骤🌙 step 1.将JSON文件转换为XML文件创建create_xml_anno.py文件 from xml.dom.minidom import Document class CreateAnno: def __init__(self, ): self.doc = Document() # 创建DOM文档对象 self.anno = self.doc.createElement('annotation') # 创建根元素 self.doc.appendChild(self.anno) self.add_folder() self.add_path() self.add_source() self.add_segmented() # self.add_filename() # self.add_pic_size(width_text_str=str(width), height_text_str=str(height), depth_text_str=str(depth)) def add_folder(self, floder_text_str='JPEGImages'): floder = self.doc.createElement('floder') ##建立自己的开头 floder_text = self.doc.createTextNode(floder_text_str) ##建立自己的文本信息 floder.appendChild(floder_text) ##自己的内容 self.anno.appendChild(floder) def add_filename(self, filename_text_str='00000.jpg'): filename = self.doc.createElement('filename') filename_text = self.doc.createTextNode(filename_text_str) filename.appendChild(filename_text) self.anno.appendChild(filename) def add_path(self, path_text_str="None"): path = self.doc.createElement('path') path_text = self.doc.createTextNode(path_text_str) path.appendChild(path_text) self.anno.appendChild(path) def add_source(self, database_text_str="Unknow"): source = self.doc.createElement('source') database = self.doc.createElement('database') database_text = self.doc.createTextNode(database_text_str) # 元素内容写入 database.appendChild(database_text) source.appendChild(database) self.anno.appendChild(source) def add_pic_size(self, width_text_str="0", height_text_str="0", depth_text_str="3"): size = self.doc.createElement('size') width = self.doc.createElement('width') width_text = self.doc.createTextNode(width_text_str) # 元素内容写入 width.appendChild(width_text) size.appendChild(width) height = self.doc.createElement('height') height_text = self.doc.createTextNode(height_text_str) height.appendChild(height_text) size.appendChild(height) depth = self.doc.createElement('depth') depth_text = self.doc.createTextNode(depth_text_str) depth.appendChild(depth_text) size.appendChild(depth) self.anno.appendChild(size) def add_segmented(self, segmented_text_str="0"): segmented = self.doc.createElement('segmented') segmented_text = self.doc.createTextNode(segmented_text_str) segmented.appendChild(segmented_text) self.anno.appendChild(segmented) def add_object(self, name_text_str="None", xmin_text_str="0", ymin_text_str="0", xmax_text_str="0", ymax_text_str="0", pose_text_str="Unspecified", truncated_text_str="0", difficult_text_str="0"): object = self.doc.createElement('object') name = self.doc.createElement('name') name_text = self.doc.createTextNode(name_text_str) name.appendChild(name_text) object.appendChild(name) pose = self.doc.createElement('pose') pose_text = self.doc.createTextNode(pose_text_str) pose.appendChild(pose_text) object.appendChild(pose) truncated = self.doc.createElement('truncated') truncated_text = self.doc.createTextNode(truncated_text_str) truncated.appendChild(truncated_text) object.appendChild(truncated) difficult = self.doc.createElement('difficult') difficult_text = self.doc.createTextNode(difficult_text_str) difficult.appendChild(difficult_text) object.appendChild(difficult) bndbox = self.doc.createElement('bndbox') xmin = self.doc.createElement('xmin') xmin_text = self.doc.createTextNode(xmin_text_str) xmin.appendChild(xmin_text) bndbox.appendChild(xmin) ymin = self.doc.createElement('ymin') ymin_text = self.doc.createTextNode(ymin_text_str) ymin.appendChild(ymin_text) bndbox.appendChild(ymin) xmax = self.doc.createElement('xmax') xmax_text = self.doc.createTextNode(xmax_text_str) xmax.appendChild(xmax_text) bndbox.appendChild(xmax) ymax = self.doc.createElement('ymax') ymax_text = self.doc.createTextNode(ymax_text_str) ymax.appendChild(ymax_text) bndbox.appendChild(ymax) object.appendChild(bndbox) self.anno.appendChild(object) def get_anno(self): return self.anno def get_doc(self): return self.doc def save_doc(self, save_path): with open(save_path, "w") as f: self.doc.writexml(f, indent='\t', newl='\n', addindent='\t', encoding='utf-8')再创建read_json_anno.py文件 import numpy as np import json class ReadAnno: def __init__(self, json_path, process_mode="rectangle"): self.json_data = json.load(open(json_path)) self.filename = self.json_data['imagePath'] self.width = self.json_data['imageWidth'] self.height = self.json_data['imageHeight'] self.coordis = [] assert process_mode in ["rectangle", "polygon"] if process_mode == "rectangle": self.process_polygon_shapes() elif process_mode == "polygon": self.process_polygon_shapes() def process_rectangle_shapes(self): for single_shape in self.json_data['shapes']: bbox_class = single_shape['label'] xmin = single_shape['points'][0][0] ymin = single_shape['points'][0][1] xmax = single_shape['points'][1][0] ymax = single_shape['points'][1][1] self.coordis.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, bbox_class]) def process_polygon_shapes(self): for single_shape in self.json_data['shapes']: bbox_class = single_shape['label'] temp_points = [] for couple_point in single_shape['points']: x = float(couple_point[0]) y = float(couple_point[1]) temp_points.append([x, y]) temp_points = np.array(temp_points) xmin, ymin = temp_points.min(axis=0) xmax, ymax = temp_points.max(axis=0) self.coordis.append([xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, bbox_class]) def get_width_height(self): return self.width, self.height def get_filename(self): return self.filename def get_coordis(self): return self.coordis最后创建main.py文件,需要修改root_json_dir、root_save_xml_dir import os from tqdm import tqdm from read_json_anno import ReadAnno from create_xml_anno import CreateAnno def json_transform_xml(json_path, xml_path, process_mode="rectangle"): json_path = json_path json_anno = ReadAnno(json_path, process_mode=process_mode) width, height = json_anno.get_width_height() filename = json_anno.get_filename() coordis = json_anno.get_coordis() xml_anno = CreateAnno() xml_anno.add_filename(filename) xml_anno.add_pic_size(width_text_str=str(width), height_text_str=str(height), depth_text_str=str(3)) for xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, label in coordis: xml_anno.add_object(name_text_str=str(label), xmin_text_str=str(int(xmin)), ymin_text_str=str(int(ymin)), xmax_text_str=str(int(xmax)), ymax_text_str=str(int(ymax))) xml_anno.save_doc(xml_path) if __name__ == "__main__": root_json_dir = r"放存放JSON文件的路径" root_save_xml_dir = r"放即将生成的XML文件的保存路径" for json_filename in tqdm(os.listdir(root_json_dir)): if json_filename.split('.')[-1]=='json': json_path = os.path.join(root_json_dir, json_filename) save_xml_path = os.path.join(root_save_xml_dir, json_filename.replace(".json", ".xml")) json_transform_xml(json_path, save_xml_path, process_mode="polygon") # labelme原数据的标注方式(矩形rectangle和多边形polygon) step 2.将XML文件转换为TXT文件,并按照比例划分训练集、测试集、验证集创建xml_to_txt.py文件 import os import shutil import random # 保证随机可复现 random.seed(0) def split_data(file_path, new_file_path, train_rate, val_rate, test_rate): eachclass_image = [] for image in os.listdir(file_path): eachclass_image.append(image) total = len(eachclass_image) random.shuffle(eachclass_image) train_images = eachclass_image[0:int(train_rate * total)] # 注意左闭右开 val_images = eachclass_image[int(train_rate * total):int((train_rate + val_rate) * total)] # 注意左闭右开 test_images = eachclass_image[int((train_rate + val_rate) * total):] # 训练集 for image in train_images: print(image) old_path = file_path + '/' + image new_path1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'train' + '/' + 'images' if not os.path.exists(new_path1): os.makedirs(new_path1) new_path = new_path1 + '/' + image # print(new_path) shutil.copy(old_path, new_path) new_name = os.listdir(new_file_path + '/' + 'train' + '/' + 'images') # print(new_name[1][:-4]) for im in new_name: old_xmlpath = xmlpath + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' print('old',old_xmlpath) new_xmlpath1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'train' + '/' + 'labels' if not os.path.exists(new_xmlpath1): os.makedirs(new_xmlpath1) new_xmlpath = new_xmlpath1 + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' print('xml name',new_xmlpath) if not os.path.exists(f'{old_xmlpath}'): open(f'{old_xmlpath}', 'w') shutil.copy(old_xmlpath, new_xmlpath) # 验证集 for image in val_images: old_path = file_path + '/' + image new_path1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'val' + '/' + 'images' if not os.path.exists(new_path1): os.makedirs(new_path1) new_path = new_path1 + '/' + image shutil.copy(old_path, new_path) new_name = os.listdir(new_file_path + '/' + 'val' + '/' + 'images') for im in new_name: old_xmlpath = xmlpath + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' new_xmlpath1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'val' + '/' + 'labels' if not os.path.exists(new_xmlpath1): os.makedirs(new_xmlpath1) new_xmlpath = new_xmlpath1 + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' if not os.path.exists(f'{old_xmlpath}'): open(f'{old_xmlpath}', 'w') shutil.copy(old_xmlpath, new_xmlpath) #测试集 for image in test_images: old_path = file_path + '/' + image new_path1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'test' + '/' + 'images' if not os.path.exists(new_path1): os.makedirs(new_path1) new_path = new_path1 + '/' + image shutil.copy(old_path, new_path) new_name = os.listdir(new_file_path + '/' + 'test' + '/' + 'images') for im in new_name: old_xmlpath = xmlpath + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' new_xmlpath1 = new_file_path + '/' + 'test' + '/' + 'labels' if not os.path.exists(new_xmlpath1): os.makedirs(new_xmlpath1) new_xmlpath = new_xmlpath1 + '/' + im[:-3] + 'txt' if not os.path.exists(f'{old_xmlpath}'): open(f'{old_xmlpath}', 'w') shutil.copy(old_xmlpath, new_xmlpath) print('ok') if __name__ == '__main__': file_path = "存放图片的文件夹路径//" xmlpath = '存放xml文件的路径//' new_file_path = "存放生成数据集的路径//" split_data(file_path, new_file_path, train_rate=0.8, val_rate=0.1, test_rate=0.1)#这里是划分比例,可自己调节,一般是8:1:1,也有7:2:1的划分比例情况没具体划分情况看数据集的大小运行xml_to_txt.py文件后看到这样的格式,也就代表成功啦 有的小伙伴再使用了Labelme这种标注软件之后,想直接把JSON文件转换为TXT文件,当然这也是可以的,废话不多说,直接上代码 转换步骤🌙创建json_to_txt.py文件,需要修改txt_name、json_floder_path import json import os import pandas as pd def convert(img_size, box): x1 = box[0] y1 = box[1] x2 = box[2] y2 = box[3] return (x1, y1, x2, y2) def decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name,label): txt_name = r'这里存放即将生成txt文件的路径/' + json_name[0:-5] + '.txt' txt_file = open(txt_name, 'w') json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name) data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r')) img_w = data['imageWidth'] img_h = data['imageHeight'] for i in data['shapes']: if i['shape_type'] == 'rectangle': if (label['label'] != i['label']).all(): new_label=pd.DataFrame(columns=['label'], data=[i['label']]) label=label.append(new_label,ignore_index=True) try: x1 = float((i['points'][0][0])) / img_w y1 = float((i['points'][0][1])) / img_h x2 = float((i['points'][1][0])) / img_w y2 = float((i['points'][1][1])) / img_h n = label[label['label']==i['label']].index[0] bb = (x1, y1, x2, y2) bbox = convert((img_w, img_h), bb) txt_file.write(str(n) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox]) + '\n') except IndexError: print(json_name[0:-5]+'的'+i['label']+"标签坐标缺失") return label if __name__ == "__main__": json_floder_path = r'这里存放你存json文件的路径/' json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path) label= pd.DataFrame(columns = ['label']) for json_name in json_names: if json_name[-4:]=='json': print(json_name) label=decode_json(json_floder_path, json_name,label) label.to_csv('label.txt', sep='\t', index=True) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 场景3.将TXT文件直接转换成JSON文件☀ 需求分析🌙有的小伙伴在将JSON文件转换为TXT文件后,就把JSON文件给删除了,但是后续想要对图像进行再次标注的时候,无法找到原始的JSON数据,产生了想要重新标注的危险想法,以下代码可实现对TXT文件直接转换为JSON文件的需求,废话不多说,直接上代码 转换步骤🌙创建txt_to_json.py文件,这里假设需要数据集有两类,分别为dog和cat,如果你的标签名是别的,那么就需要修改class_name,你将修改的是txt_folder、output_folder,img_folder。 import os import json import base64 import cv2 def read_txt_file(txt_file): with open(txt_file, 'r') as f: lines = f.readlines() data = [] for line in lines: line = line.strip().split() class_name = line[0] bbox = [coord for coord in line[1:]] data.append({'class_name': class_name, 'bbox': bbox}) return data def convert_to_labelme(data, image_path, image_size): labelme_data = { 'version': '4.5.6', 'flags': {}, 'shapes': [], 'imagePath': json_image_path, 'imageData': None, 'imageHeight': image_size[0], 'imageWidth': image_size[1] } for obj in data: dx = obj['bbox'][0] dy = obj['bbox'][1] dw = obj['bbox'][2] dh = obj['bbox'][3] w = eval(dw) * image_size[1] h = eval(dh) * image_size[0] center_x = eval(dx) * image_size[1] center_y = eval(dy) * image_size[0] x1 = center_x - w/2 y1 = center_y - h/2 x2 = center_x + w/2 y2 = center_y + h/2 if obj['dog'] == '0': #判断对应的标签名称,写入json文件中 label = str('grape') else: label = obj['cat'] shape_data = { 'label': label, 'points': [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]], 'group_id': None, 'shape_type': 'rectangle', 'flags': {} } labelme_data['shapes'].append(shape_data) return labelme_data def save_labelme_json(labelme_data, image_path, output_file): with open(image_path, 'rb') as f: image_data = f.read() labelme_data['imageData'] = base64.b64encode(image_data).decode('utf-8') with open(output_file, 'w') as f: json.dump(labelme_data, f, indent=4) # 设置文件夹路径和输出文件夹路径 txt_folder = r"存放txt文件的文件夹路径//" output_folder = r"输出json文件的文件夹路径//" img_folder = r"存放对应标签的图片文件夹路径//" # 创建输出文件夹 if not os.path.exists(output_folder): os.makedirs(output_folder) # 遍历txt文件夹中的所有文件 for filename in os.listdir(txt_folder): if filename.endswith('.txt'): # 生成对应的输出文件名 output_filename = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.json' # 读取txt文件 txt_file = os.path.join(txt_folder, filename) data = read_txt_file(txt_file) # 设置图片路径和尺寸 image_filename = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] + '.jpg' # 图片文件名与txt文件名相同,后缀为.jpg image_path = os.path.join(img_folder, image_filename) # image_size = (1280, 720) # 根据实际情况修改 json_image_path = image_path.split('\\')[-1] print("image_path:", image_path) image_size = cv2.imread(image_path).shape # 转化为LabelMe格式 labelme_data = convert_to_labelme(data, image_path, image_size) # 保存为LabelMe JSON文件 output_file = os.path.join(output_folder, output_filename) save_labelme_json(labelme_data, image_path, output_file) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 场景4.将TXT文件直接转换成XML文件☀ 需求分析🌙当我们需要对数据集利用imgaug库进行数据增强时,或者需要对锚框重聚类分析,包括但不限于kmeans聚类、kmeans++聚类、kmeans聚类融合遗传算法等聚类方法时,这个时候就需要使用到我们XML格式的文件了,但是有的小伙伴没有保存此类文件,仅有TXT文件时,我们可以利用TXT文件转为XML文件。 转换步骤🌙 待更新... |
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |