J1 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › eth要多少显存 › J1 |
J1
|
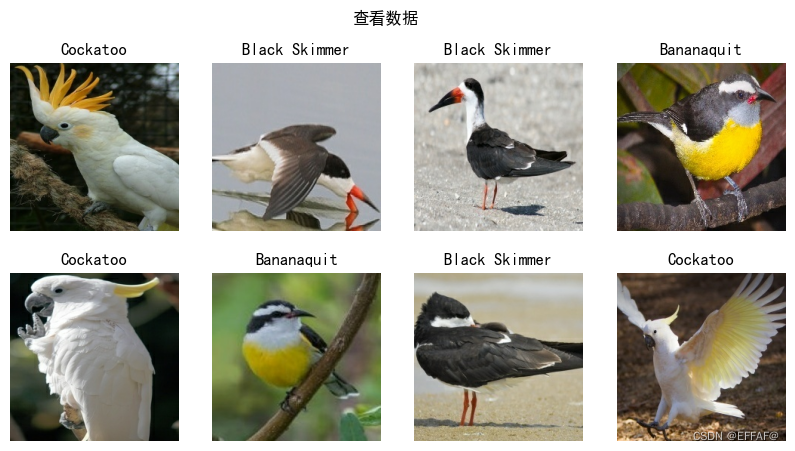
因为之前一直用的Pytorch,这次是TensorFlow ●🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客 ●🍦 参考文章:365天深度学习训练营-第J1周:ResNet-50算法实战与解析 ●🍖 原作者:K同学啊 | 接辅导、项目定制 目录 1.配置GPU ,没有这个就是默认CPU 2. 导入数据 1.配置GPU ,没有这个就是默认CPU具体来说,首先通过 tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU") 获取当前可用的 GPU 设备列表,然后判断是否有可用的 GPU。如果有,则通过 tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus[0], True) 设置第一块 GPU 按需使用显存,即显存会在需要时自动增加,而不是一开始就分配固定显存。接着,通过 tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpus[0],"GPU") 将第一块 GPU 设置为可见设备,即 TensorFlow 只会使用这一块 GPU。这样做可以保证 TensorFlow 在使用 GPU 时不会出现显存占用过高或者多个 CPU、GPU 设备之间的冲突等问题,从而获得更好的性能。 import tensorflow as tf gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU") if gpus: tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus[0], True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用 tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpus[0]],"GPU") 2. 导入数据 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 支持中文 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 import os,PIL,pathlib import numpy as np from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import layers,models data_dir = r"J1\bird_photos" data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir) 3.查看 #查看数据 image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*'))) print("图片总数为:",image_count)配置参数 batch_size = 8 img_height = 224 img_width = 224 二、数据预处理这段代码使用 TensorFlow 中的 image_dataset_from_directory 函数从目录中加载图像数据集,并生成一个 tf.data.Dataset 对象,用于训练模型。 具体来说,代码中的 data_dir 变量表示图像数据集所在的文件夹路径,validation_split 表示将数据集分为训练集和验证集的比例,subset 表示当前生成的是训练集还是验证集(这里是训练集),seed 表示随机数种子,用于保证每次划分数据集时的结果一致。image_size 表示生成的图片大小,即将所有的图片转换为固定尺寸。batch_size 则表示每个 batch 包含的样本数量。 通过调用 image_dataset_from_directory 函数,可以快速创建一个数据集对象,并通过该对象获取到训练集的图片和标签数据,以便后续的训练过程。由于 tf.data.Dataset 对象可以自动进行数据的批处理、预处理等操作,因此使用该对象可以帮助我们更加高效地训练模型。 配置训练集 train_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory( data_dir, validation_split=0.2, subset="training", seed=123, image_size=(img_height, img_width), batch_size=batch_size)配置验证集 val_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory( data_dir, validation_split=0.2, subset="validation", seed=123, image_size=(img_height, img_width), batch_size=batch_size)查看类别 class_names = train_ds.class_names print(class_names)#每个文件夹的名称就是对应的类别名称 2. 可视化数据这段代码中的 plt.imshow(images[i].numpy().astype("uint8")) 用于显示一张图片。 具体来说,images 是一个形状为 (batch_size, image_height, image_width, channels) 的 Tensor 对象,其中 batch_size 是批次大小,image_height 和 image_width 分别是每张图片的高度和宽度,channels 是图片的通道数。在这里,我们通过 images[i] 获取到第 i 张图片,然后使用 numpy() 方法将其转换为 NumPy 数组类型,再使用 astype("uint8") 将像素值转换为 8 位整型(0~255),最后使用 plt.imshow 显示图片。 需要注意的是,plt.imshow 只能显示 RGB 三个通道的图片,如果图片的通道数不是 3,则需要进行转换或选择其中的某个通道来显示。此外,还可以通过 cmap 参数指定显示的颜色映射,以及通过 interpolation 参数指定插值方法来调整图片的显示效果。 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) # 图形的宽为10高为5 plt.suptitle("查看数据") for images, labels in train_ds.take(1):#train_ds.take(1) 从训练集中获取一个 batch 的图片和标签数据 for i in range(8): ax = plt.subplot(2, 4, i + 1) plt.imshow(images[i].numpy().astype("uint8"))#astype("uint8") 将像素值转换为 8 位整型(0~255),最后使用 plt.imshow 显示图片。 plt.title(class_names[labels[i]]) plt.axis("off")#关闭坐标轴,以便更好地展示图片。
(8, 224, 224, 3) (8,) 4. 配置数据集这段代码展示了如何使用 TensorFlow 的 tf.data 模块来构建可用于训练神经网络的数据集。其中 train_ds 和 val_ds 是对训练集和验证集的数据集对象的引用。这两个数据集都使用了缓存和预取机制来提高数据集的读取性能。 具体来说,cache() 方法通过缓存数据集到内存或磁盘中来避免重新读取数据,shuffle() 方法则对数据集进行洗牌,这样可以使得模型在训练时避免过拟合。 而 prefetch() 方法则允许模型在训练时并行地读取数据,从而加快了训练速度。其中 buffer_size 参数代表了要预取的数据的数量,在这里被设置为了 TensorFlow 自动调优的默认值 AUTOTUNE。这个值可以根据具体的运行环境和数据量进行调整,以达到最佳的性能表现。 AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE #tf.data 模块来构建可用于训练神经网络的数据集。其中 train_ds 和 val_ds 是对训练集和验证集的数据集对象的引用。 train_ds = train_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE) #cache() 方法通过缓存数据集到内存或磁盘中来避免重新读取数据,shuffle() 方法则对数据集进行洗牌,这样可以使得模型在训练时避免过拟合 # prefetch() 方法则允许模型在训练时并行地读取数据,从而加快了训练速度。其中 buffer_size 参数代表了要预取的数据的数量,在这里被设置为了 TensorFlow 自动调优的默认值 AUTOTUNE。 val_ds = val_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE) 构建网络模型
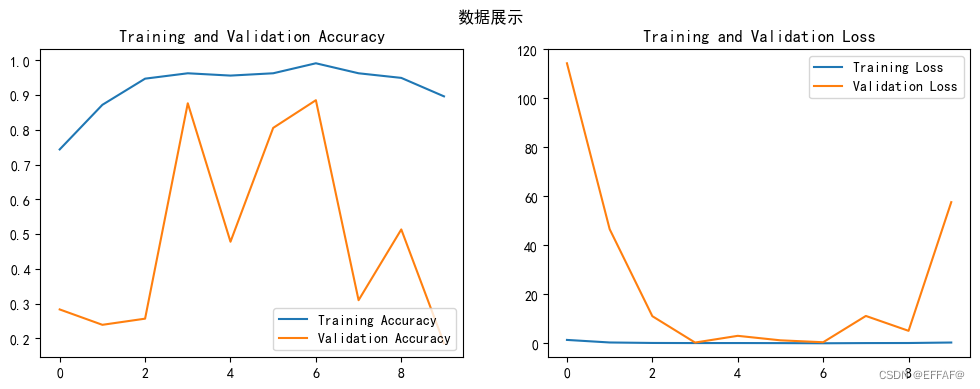
这段代码展示了如何使用 TensorFlow 的 Keras 模块来编译一个神经网络模型。其中,opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-7) 定义了一个优化器对象 opt,该优化器使用了 Adam 算法,并将学习率设置为 1e-7,即 0.0000001。 接着,使用 model.compile() 方法来编译模型。在这里,我们将损失函数(loss function)设为稀疏分类交叉熵(sparse_categorical_crossentropy),这个损失函数通常用于多分类问题中,其中目标类别是整数形式的。而 metrics 参数则定义了训练过程中要监测哪些指标(比如准确率、精确率等),这里我们监测了准确率(accuracy)。 需要注意的是,这里在编译模型时使用了 "adam" 作为 optimizer 参数,而并非前面定义的 opt 对象。这是因为在实际应用中,还可以通过其他方式来设置优化器,例如传递一个优化器名称或自定义的优化器对象,因此在这里我们采用这种更为通用的方式来编译模型。 # 设置优化器,我这里改变了学习率。 opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-7) model.compile(optimizer="adam", loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) 六、训练模型这段代码展示了如何使用 TensorFlow 的 Keras 模块来训练一个神经网络模型。具体来说,model.fit() 方法用于拟合模型,并返回一个 History 对象,包含了训练过程中的一些重要信息。 在这里,train_ds 代表用于训练的数据集对象,validation_data 则代表用于验证的数据集对象。在训练时,模型将依次读取数据集中的每个批次(batch),并根据前面编译时指定的损失函数和优化器来更新模型的参数,从而逐渐减小损失值并提高分类准确率。 epochs 参数表示训练轮数,即遍历整个数据集的次数。在训练过程中,模型会多次读取数据集进行训练,每个轮数会使模型得到更好的学习。最终训练的结果将保存在 History 对象中,可以通过该对象的方法和属性来查看训练过程中的指标、损失值和准确率等信息 epochs = 10 history = model.fit( train_ds, validation_data=val_ds, epochs=epochs ) 查看数据 acc = history.history['accuracy'] val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy'] loss = history.history['loss'] val_loss = history.history['val_loss'] epochs_range = range(epochs) plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4)) plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) plt.suptitle("微信公众号:K同学啊") plt.plot(epochs_range, acc, label='Training Accuracy') plt.plot(epochs_range, val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy') plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy') plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) plt.plot(epochs_range, loss, label='Training Loss') plt.plot(epochs_range, val_loss, label='Validation Loss') plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.title('Training and Validation Loss') plt.show()
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |