Pandas中使用Merge、Join 、Concat合并数据效率对比 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › dataframe的join › Pandas中使用Merge、Join 、Concat合并数据效率对比 |
Pandas中使用Merge、Join 、Concat合并数据效率对比
|
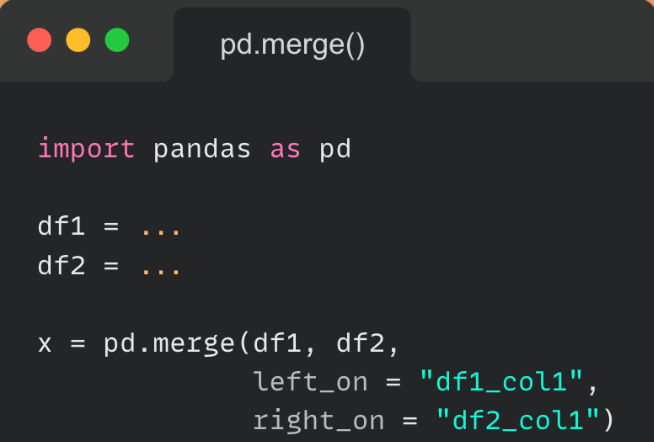
在 Pandas 中有很多种方法可以进行dataframe(数据框)的合并。 本文将研究这些不同的方法,以及如何将它们执行速度的对比。 合并DF Pandas 使用 .merge() 方法来执行合并。 import pandas as pd # a dictionary to convert to a dataframe data1 = {'identification': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'Customer_Name':['King', 'West', 'Adams', 'Mercy'], 'Category':['furniture', 'Office Supplies', 'Technology', 'R_materials'],} # our second dictionary to convert to a dataframe data2 = {'identification': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'Class':['First_Class', 'Second_Class', 'Same_day', 'Standard Class'], 'Age':[60, 30, 40, 50]} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1) df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2)运行我们的代码后,有两个 DataFrame,如下所示。 identification Customer_Name Category 0 a King furniture 1 b West Office Supplies 2 c Adams Technology 3 d Mercy R_materials identification Class Age 0 a First_Class 60 1 b Second_Class 30 2 c Same_day 40 3 d Standard Class 50使用 merge() 函数进一步合并。
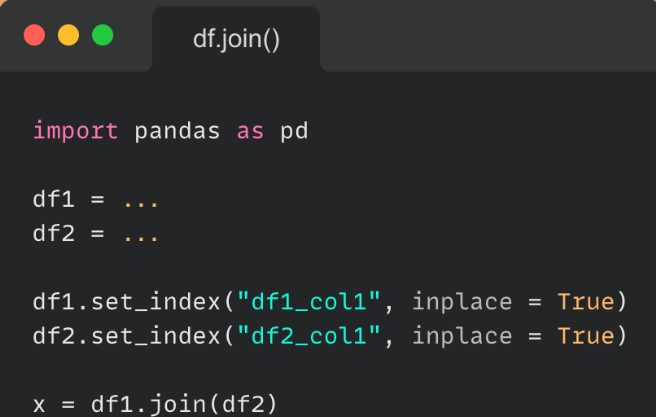
这产生了下面的新数据; identification Customer_Name Category Class Age 0 a King furniture First_Class 60 1 b West Office Supplies Second_Class 30 2 c Adams Technology Same_day 40 3 d Mercy R_materials Standard Class 50.join() 方法也可以将不同索引的 DataFrame 组合成一个新的 DataFrame。我们可以使用参数‘on’参数指定根据哪列进行合并。
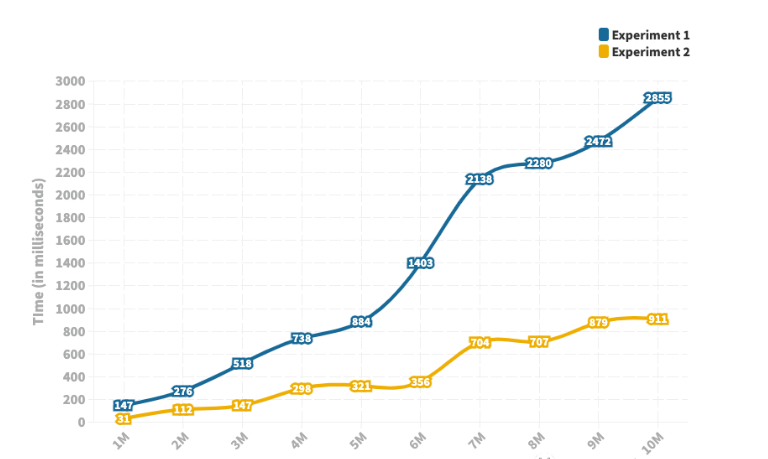
让我们看看下面的例子,我们如何将单索引 DataFrame 与多索引 DataFrame 连接起来; import pandas as pd # a dictionary to convert to a dataframe data1 = { 'Customer_Name':['King', 'West', 'Adams'], 'Category':['furniture', 'Office Supplies', 'Technology'],} 7 # our second dictionary to convert to a dataframe data2 = { 'Class':['First_Class', 'Second_Class', 'Same_day', 'Standard Class'], 'Age':[60, 30, 40, 50]} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame Ndata = pd.DataFrame(data1, index=pd.Index(['a', 'b', 'c'], name='identification')) index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('a', 'x0'), ('b', 'x1'), ('c', 'x2'), ('c', 'x3')], names=['identification', 'x']) 19 # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame Ndata2 = pd.DataFrame(data2, index= index) print(Ndata, "\n\n", Ndata2) # joining singly indexed with # multi indexed result = Ndata.join(Ndata2, how='inner')我们的结果如下所示; Customer_Name Category Class Age identification x 3 a x0 King furniture First_Class 60 b x1 West Office Supplies Second_Class 30 c x2 Adams Technology Same_day 40 x3 Adams Technology Standard Class 50连接DF Pandas 中concat() 方法在可以在垂直方向(axis=0)和水平方向(axis=1)上连接 DataFrame。我们还可以一次连接两个以上的 DataFrame 或 Series。 让我们看一个如何在 Pandas 中执行连接的示例; import pandas as pd # a dictionary to convert to a dataframe data1 = {'identification': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'Customer_Name':['King', 'West', 'Adams', 'Mercy'], 'Category':['furniture', 'Office Supplies', 'Technology', 'R_materials'],} # our second dictionary to convert to a dataframe data2 = {'identification': ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'], 'Class':['First_Class', 'Second_Class', 'Same_day', 'Standard Class'], 'Age':[60, 30, 40, 50]} # Convert the dictionary into DataFrame df1 = pd.DataFrame(data1) df2 = pd.DataFrame(data2) #perform concatenation here based on horizontal axis new_data = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1) print(new_data)这样就获得了新的 DataFrame : identification Customer_Name Category identification \ 0 a King furniture a 3 1 b West Office Supplies b 4 2 c Adams Technology c 5 3 d Mercy R_materials d Class Age 0 First_Class 60 1 Second_Class 30 2 Same_day 40 3 Standard Class 50Merge和Join的效率对比 Pandas 中的Merge Joins操作都可以针对指定的列进行合并操作(SQL中的join)那么他们的执行效率是否相同呢?下面我们来进行一下测。 两个 DataFrame 都有相同数量的行和两列,实验中考虑了从 100 万行到 1000 万行的不同大小的 DataFrame,并在每次实验中将行数增加了 100 万。我对固定数量的行重复了十次实验,以消除任何随机性。下面是这十次试验中合并操作的平均运行时间。
上图描绘了操作所花费的时间(以毫秒为单位)。 正如我们从图中看到的,运行时间存在显着差异——最多相差 5 倍。随着 DataFrame 大小的增加,运行时间之间的差异也会增加。两个 JOIN 操作几乎都随着 DataFrame 的大小线性增加。但是,Join的运行时间增加的速度远低于Merge。 如果需要处理大量数据,还是请使用join()进行操作。 |
【本文地址】