目标检测 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › cg和ca的区别 › 目标检测 |
目标检测
|
系列文章目录
目标检测——map概念、IoU汇总IoU、GIoU、DIoU、CIoU、SIoU、EIoU、Wiou、Focal、alpha 目标检测——YOLOv3、YOLOv4、YOLOv5、YOLOv7正负样本匹配、YOLO3损失函数理解 目标检测——SE、ECA、CA、SA、CBAM、ShuffleAttention、SimAM、CrissCrossAttention、SK、NAM、GAM、SOCA注意力模块、程序 文章目录 系列文章目录1、SE 通道注意力2、ECA 通道注意力3、 CA 通道注意力4、SA 空间注意力5、CBAM(通道注意力和空间注意力)6、ShuffleAttention注意力7、SimAM注意力8、CrissCrossAttention注意力9、SKAttention注意力10、S2-MLPv2注意力11、NAMAttention注意力12、SOCA注意力13、GAMAttention注意力总结 1、SE 通道注意力
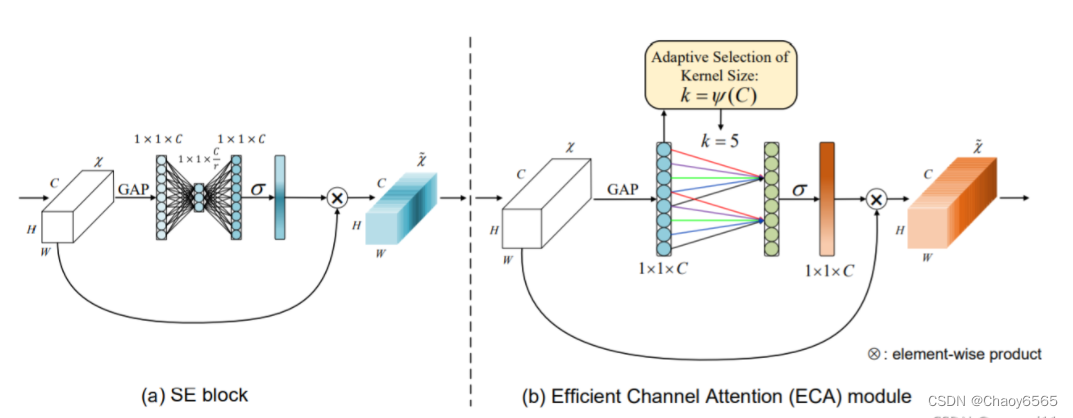
ECANet也是通道注意力机制的一种。ECANet可以看作SENet的改进版。 卷积具有良好的跨通道信息获取能力。ECA把EA的全连接层换成了卷积。
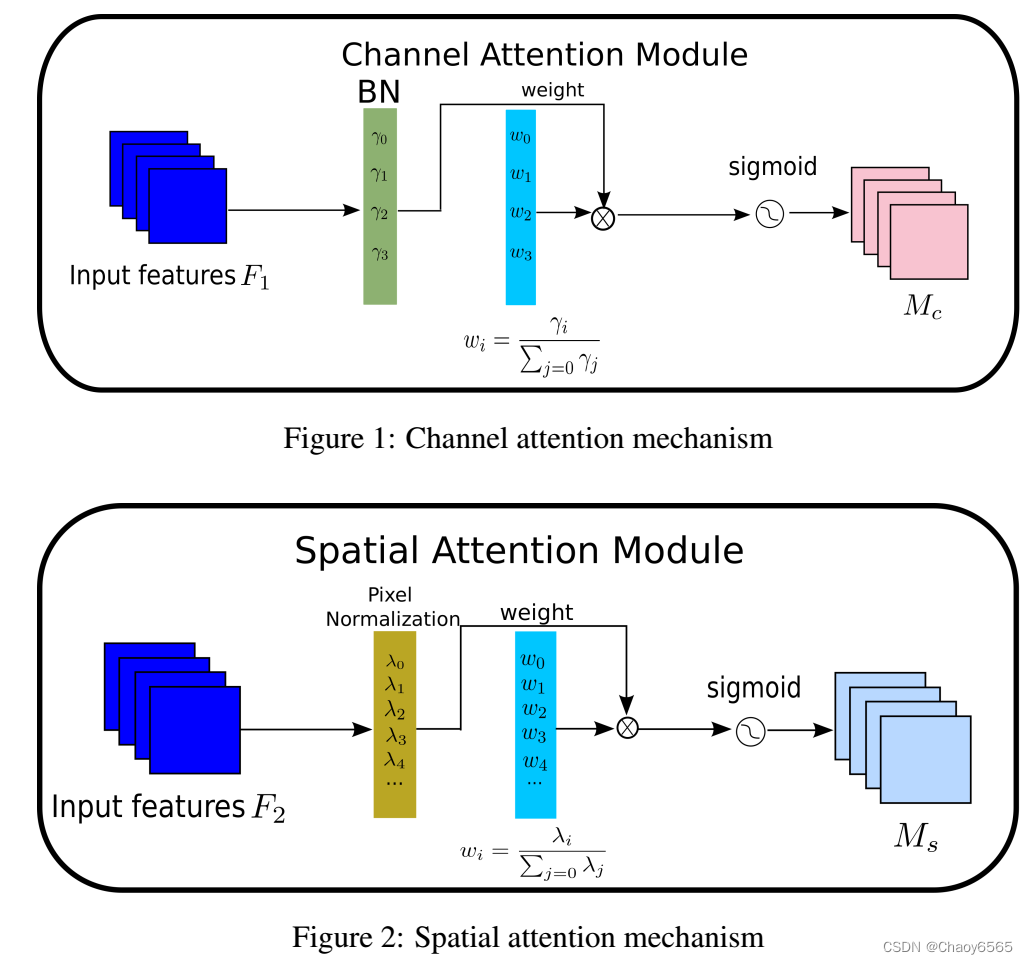
这里只是列出了注意力模块 还需要把最后输出的权值乘上原输入特征层。 例如: x = x * self.ChannelAttention(x),可以参考CBAM那个程序。 4、SA 空间注意力
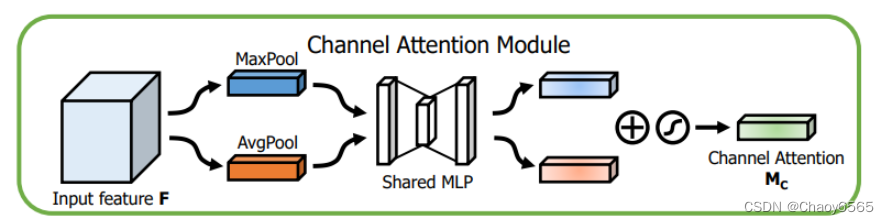
这里只是列出了注意力模块 还需要把最后输出的权值乘上原输入特征层。 例如: x = x * self.SpatialAttention(x),可以参考CBAM那个程序。 5、CBAM(通道注意力和空间注意力)CBAM是通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制的混合。 通道注意力机制:通道注意力机制可以分为两部分,首先对输入进来的单个特征层,分别进行全局平均池化和全局最大池化。之后对平均池化和最大池化的结果,利用共享的全连接层进行处理,对处理后的两个结果进行相加,取Sigmoid将值固定到0-1之间。获得这个权值,将这个权值乘上原输入特征层。 空间注意力机制:对输入进来的特征层,在每一个特征点的通道上取最大值和平均值。之后将这两个结果进行一个堆叠,利用一次通道数为1的卷积调整通道数,取Sigmoid将值固定到0-1之间。获得这个权值,将这个权值乘上原输入特征层。 不足: 1、SE注意力中只关注构建通道之间的相互依赖关系,忽略了空间特征。 2、CBAM中引入了大尺度的卷积核提取空间特征,但忽略了长程依赖问题。 6、ShuffleAttention注意力函数 import numpy as np import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import init from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter # https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.00240.pdf class ShuffleAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel=512,reduction=16,G=8): super().__init__() self.G=G self.channel=channel self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channel // (2 * G), channel // (2 * G)) self.cweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.cbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.sweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.sbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid() def init_weights(self): for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out') if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): init.constant_(m.weight, 1) init.constant_(m.bias, 0) elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001) if m.bias is not None: init.constant_(m.bias, 0) @staticmethod def channel_shuffle(x, groups): b, c, h, w = x.shape x = x.reshape(b, groups, -1, h, w) x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4) # flatten x = x.reshape(b, -1, h, w) return x def forward(self, x): b, c, h, w = x.size() #group into subfeatures x=x.view(b*self.G,-1,h,w) #bs*G,c//G,h,w #channel_split x_0,x_1=x.chunk(2,dim=1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w #channel attention x_channel=self.avg_pool(x_0) #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1 x_channel=self.cweight*x_channel+self.cbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1 x_channel=x_0*self.sigmoid(x_channel) #spatial attention x_spatial=self.gn(x_1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w x_spatial=self.sweight*x_spatial+self.sbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w x_spatial=x_1*self.sigmoid(x_spatial) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w # concatenate along channel axis out=torch.cat([x_channel,x_spatial],dim=1) #bs*G,c//G,h,w out=out.contiguous().view(b,-1,h,w) # channel shuffle out = self.channel_shuffle(out, 2) return out
这里batch_size=8,模型设置batch_size不一样通道数会报错。 可以根据图片改一下这里的通道数也就是(channel // (2 * G),让他等于函数中forward里的x_channel就可以了。 self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channel // (2 * G), channel // (2 * G)) self.cweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.cbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) self.sbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1)) 7、SimAM注意力
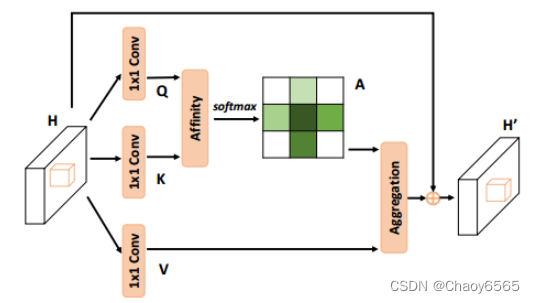
函数 class SimAM(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, channels = None,out_channels = None, e_lambda = 1e-4): super(SimAM, self).__init__() self.activaton = nn.Sigmoid() self.e_lambda = e_lambda def forward(self, x): b, c, h, w = x.size() n = w * h - 1 x_minus_mu_square = (x - x.mean(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True)).pow(2) y = x_minus_mu_square / (4 * (x_minus_mu_square.sum(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True) / n + self.e_lambda)) + 0.5 return x * self.activaton(y)调用 self.SimAM = SimAM(512,512) 8、CrissCrossAttention注意力函数 import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.nn import Softmax def INF(B,H,W): return -torch.diag(torch.tensor(float("inf")).repeat(H),0).unsqueeze(0).repeat(B*W,1,1) class CrissCrossAttention(nn.Module): """ Criss-Cross Attention Module""" def __init__(self, in_dim): super(CrissCrossAttention,self).__init__() self.query_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1) self.key_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1) self.value_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim, kernel_size=1) self.softmax = Softmax(dim=3) self.INF = INF self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1)) def forward(self, x): m_batchsize, _, height, width = x.size() proj_query = self.query_conv(x) proj_query_H = proj_query.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height).permute(0, 2, 1) proj_query_W = proj_query.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width).permute(0, 2, 1) proj_key = self.key_conv(x) proj_key_H = proj_key.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height) proj_key_W = proj_key.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width) proj_value = self.value_conv(x) proj_value_H = proj_value.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height) proj_value_W = proj_value.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width) energy_H = (torch.bmm(proj_query_H, proj_key_H)+self.INF(m_batchsize, height, width)).view(m_batchsize,width,height,height).permute(0,2,1,3) energy_W = torch.bmm(proj_query_W, proj_key_W).view(m_batchsize,height,width,width) concate = self.softmax(torch.cat([energy_H, energy_W], 3)) att_H = concate[:,:,:,0:height].permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,height,height) #print(concate) #print(att_H) att_W = concate[:,:,:,height:height+width].contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,width,width) out_H = torch.bmm(proj_value_H, att_H.permute(0, 2, 1)).view(m_batchsize,width,-1,height).permute(0,2,3,1) out_W = torch.bmm(proj_value_W, att_W.permute(0, 2, 1)).view(m_batchsize,height,-1,width).permute(0,2,1,3) #print(out_H.size(),out_W.size()) return self.gamma*(out_H + out_W) + x
调用 self.CrissCrossAttention = CrissCrossAttention(1024)这里需要注意def init(self, in_dim):函数里 定义的通道数,跟batch_size的大小有关,不一样需要改一下,就是下面这几行。 self.query_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1) self.key_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1) self.value_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim, kernel_size=1) 9、SKAttention注意力
函数 from collections import OrderedDict class SKAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channel=512, kernels=[1, 3, 5, 7], reduction=16, group=1, L=32): super().__init__() self.d = max(L, channel // reduction) self.convs = nn.ModuleList([]) for k in kernels: self.convs.append( nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([ ('conv', nn.Conv2d(channel, channel, kernel_size=k, padding=k // 2, groups=group)), ('bn', nn.BatchNorm2d(channel)), ('relu', nn.ReLU()) ])) ) self.fc = nn.Linear(channel, self.d) self.fcs = nn.ModuleList([]) for i in range(len(kernels)): self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(self.d, channel)) self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=0) def forward(self, x): bs, c, _, _ = x.size() conv_outs = [] ### split for conv in self.convs: conv_outs.append(conv(x)) feats = torch.stack(conv_outs, 0) # k,bs,channel,h,w ### fuse U = sum(conv_outs) # bs,c,h,w ### reduction channel S = U.mean(-1).mean(-1) # bs,c Z = self.fc(S) # bs,d ### calculate attention weight weights = [] for fc in self.fcs: weight = fc(Z) weights.append(weight.view(bs, c, 1, 1)) # bs,channel attention_weughts = torch.stack(weights, 0) # k,bs,channel,1,1 attention_weughts = self.softmax(attention_weughts) # k,bs,channel,1,1 ### fuse V = (attention_weughts * feats).sum(0) return V调用 self.SKAttention = SKAttention(1024) 10、S2-MLPv2注意力
函数 def spatial_shift1(x): b,w,h,c = x.size() x[:,1:,:,:c//4] = x[:,:w-1,:,:c//4] x[:,:w-1,:,c//4:c//2] = x[:,1:,:,c//4:c//2] x[:,:,1:,c//2:c*3//4] = x[:,:,:h-1,c//2:c*3//4] x[:,:,:h-1,3*c//4:] = x[:,:,1:,3*c//4:] return x def spatial_shift2(x): b,w,h,c = x.size() x[:,:,1:,:c//4] = x[:,:,:h-1,:c//4] x[:,:,:h-1,c//4:c//2] = x[:,:,1:,c//4:c//2] x[:,1:,:,c//2:c*3//4] = x[:,:w-1,:,c//2:c*3//4] x[:,:w-1,:,3*c//4:] = x[:,1:,:,3*c//4:] return x class SplitAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self,channel=512,k=3): super().__init__() self.channel=channel self.k=k self.mlp1=nn.Linear(channel,channel,bias=False) self.gelu=nn.GELU() self.mlp2=nn.Linear(channel,channel*k,bias=False) self.softmax=nn.Softmax(1) def forward(self,x_all): b,k,h,w,c=x_all.shape x_all=x_all.reshape(b,k,-1,c) a=torch.sum(torch.sum(x_all,1),1) hat_a=self.mlp2(self.gelu(self.mlp1(a))) hat_a=hat_a.reshape(b,self.k,c) bar_a=self.softmax(hat_a) attention=bar_a.unsqueeze(-2) out=attention*x_all out=torch.sum(out,1).reshape(b,h,w,c) return out class S2Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channels=512 ): super().__init__() self.mlp1 = nn.Linear(channels,channels*3) self.mlp2 = nn.Linear(channels,channels) self.split_attention = SplitAttention() def forward(self, x): b,c,w,h = x.size() x=x.permute(0,2,3,1) x = self.mlp1(x) x1 = spatial_shift1(x[:,:,:,:c]) x2 = spatial_shift2(x[:,:,:,c:c*2]) x3 = x[:,:,:,c*2:] x_all=torch.stack([x1,x2,x3],1) a = self.split_attention(x_all) x = self.mlp2(a) x=x.permute(0,3,1,2) return x调用 self.S2Attention = S2Attention(512) 11、NAMAttention注意力
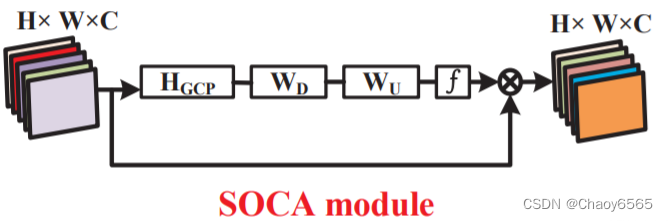
函数 class Channel_Att(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channels, t=16): super(Channel_Att, self).__init__() self.channels = channels self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.channels, affine=True) def forward(self, x): residual = x x = self.bn2(x) weight_bn = self.bn2.weight.data.abs() / torch.sum(self.bn2.weight.data.abs()) x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous() x = torch.mul(weight_bn, x) x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous() x = torch.sigmoid(x) * residual # return x class NAMAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channels, out_channels=None, no_spatial=True): super(NAMAttention, self).__init__() self.Channel_Att = Channel_Att(channels) def forward(self, x): x_out1 = self.Channel_Att(x) return x_out1调用 self.NAMAttention = NAMAttention(512) 12、SOCA注意力
|
【本文地址】
今日新闻 |
推荐新闻 |
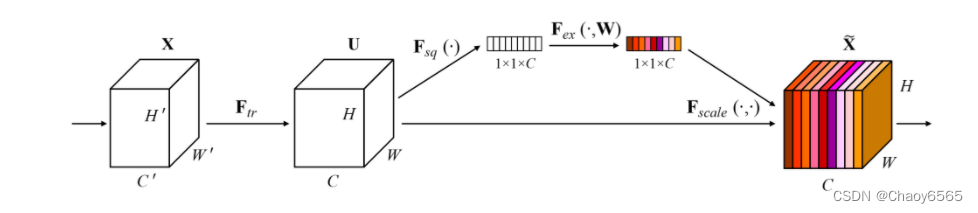 SENet: 1、对输入进来的特征层进行全局平均池化。 2、然后进行两次全连接。 3、取Sigmoid将值固定到0-1之间。 4、将这个权值乘上原输入特征层。
SENet: 1、对输入进来的特征层进行全局平均池化。 2、然后进行两次全连接。 3、取Sigmoid将值固定到0-1之间。 4、将这个权值乘上原输入特征层。 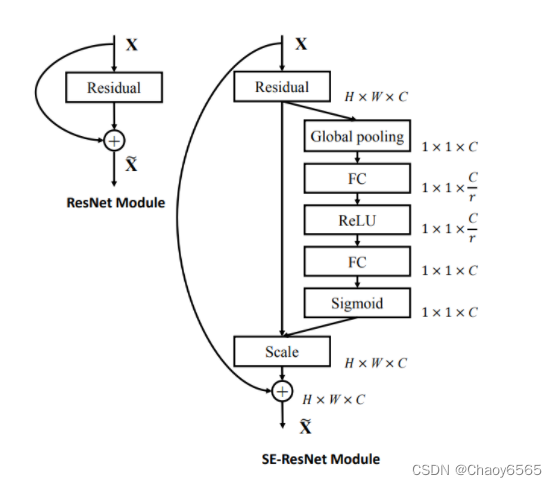
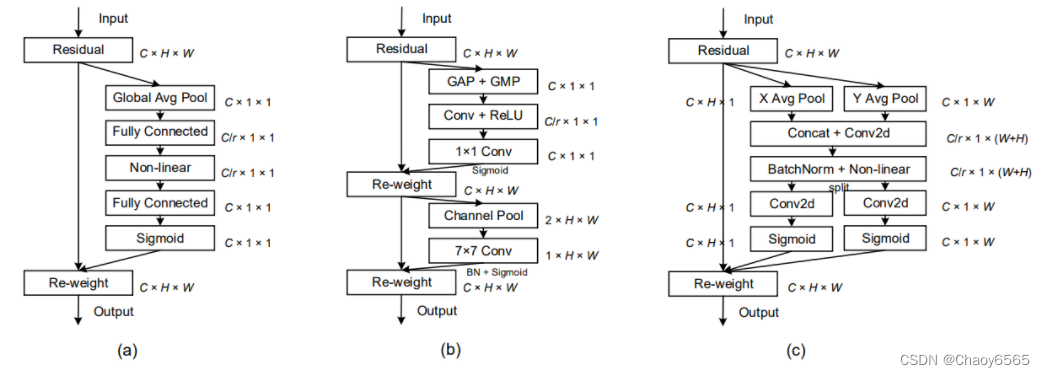
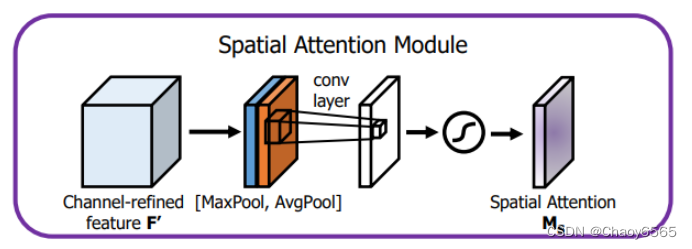
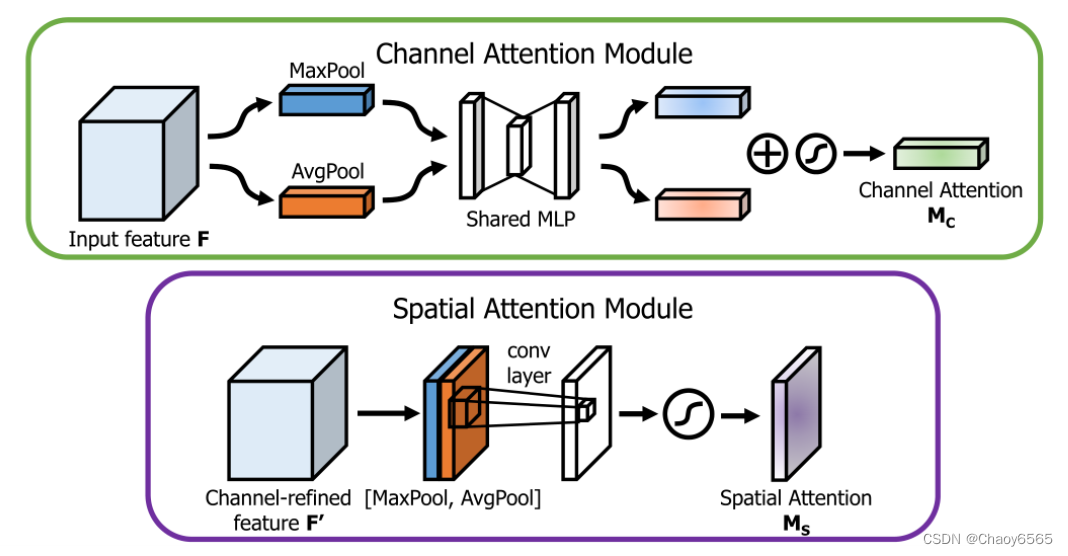
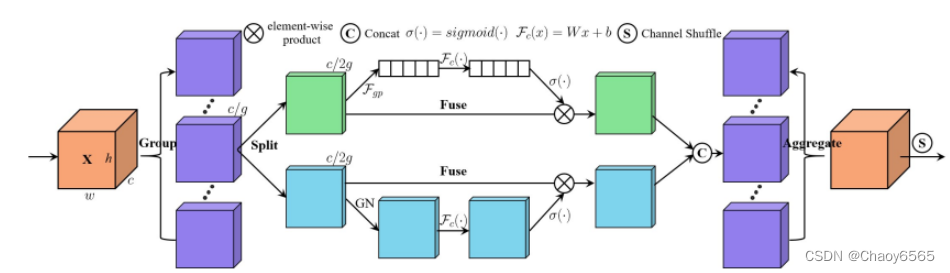 调用
调用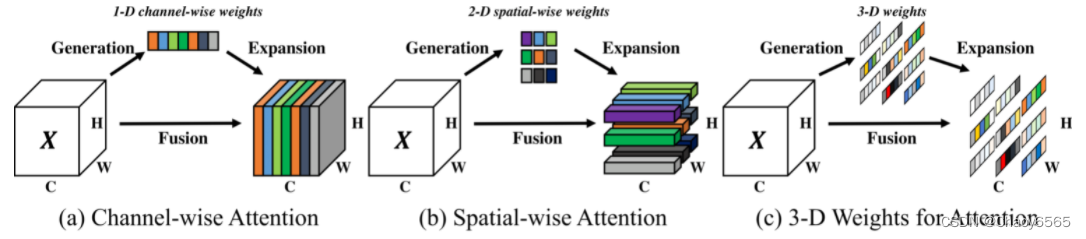
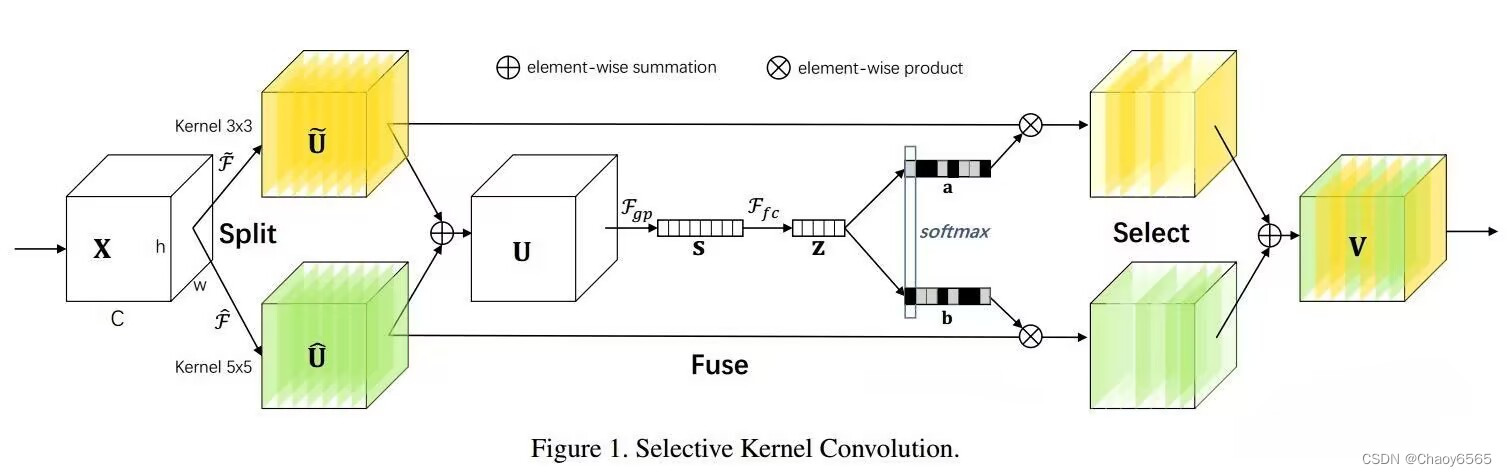
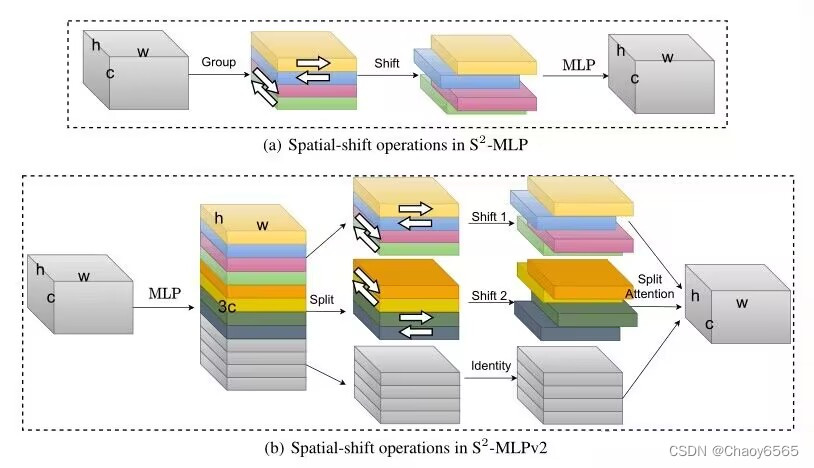
 函数
函数